2nd practical
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
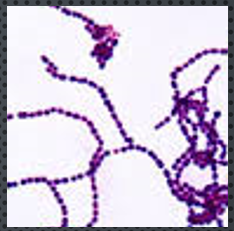
genus streptococcus
coccus - in chains
gram positive
no enzyme catalase
fastidious microaerophilic organisms
Need extra nutrients for growth
More CO2 and less O2 than atmospheric level
streptococcus pathogenic
normal throat flora and beneficial active cultures
Strep Throat, Pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis, pharyngitis
streptococci species identification methods
hemolytic activity
lancefield classification system - cell surface antigens
hemolytic patterns
beta
alpha
gamma
hemolysis
Ability of bacterial enzymes to cause lysis of the red blood cells when grown on blood agar

beta - hemolysis S. pyogenes
complete destruction of red blood cells (and digestion)
Results in a clear area around the bacterial colony

alpha - hemolysis S. pneumoniae
partial hemolysis (no digestion)
Hemoglobin is modified to form hemoverdin
Produce greenish/brownish zone around the colonies

gamma - hmolysis non pathogenic Enterococcus faecalis
absence of hemolysis - no reaction surrounding the colony
No bacterial enzymes to lyse red blood cells
lancefield classification
based on unique proteins (antigens) on cell surface of streptococcus species
pioneered by rebecca lancefield
separates streptococcus into 13 groups (A,B,C,D….)
A-D cause most human disease
Group A Streptococcus
Sensitive to Bacitracin (ZOI around antibiotic disk using KB method)
Beta hemolytic/complete clearing
Only 1 species - Streptococcus pyogenes
Causes Strep throat > Untreated > secondary infections
Group A can be ‘flesh-eating’ or ‘pus generating’
Group B Streptococcus
agglutination Test
Beta hemolytic/complete clearing
Only 1 species – Streptococcus agalactiae
normal flora of the vaginal mucosa but can be severely harmful to babies when they are born
Causes neonatal meningitis and septicemia
Group D Streptococcus
may be alpha, beta, or gamma hemolytic
Includes many different species
Enterococci >> E. faecalis endocarditis, biliary infections, UTIs = VRE
Streptocard Acid Latex Test
Rapid test for Lancefield grouping
Does NOT work for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Antibody-Antigen reaction - agglutination
A reagent with latex beads coated with a specific Lancefield
antibody.
Presumably only one antibody would recognize the antigen of
Streptococcus.
Agglutination occurs when the antibody coated latex beads
specifically bind to the specific antigen and crosslinks with
multiple latex beads.
Result is visual clumping of the latex beads
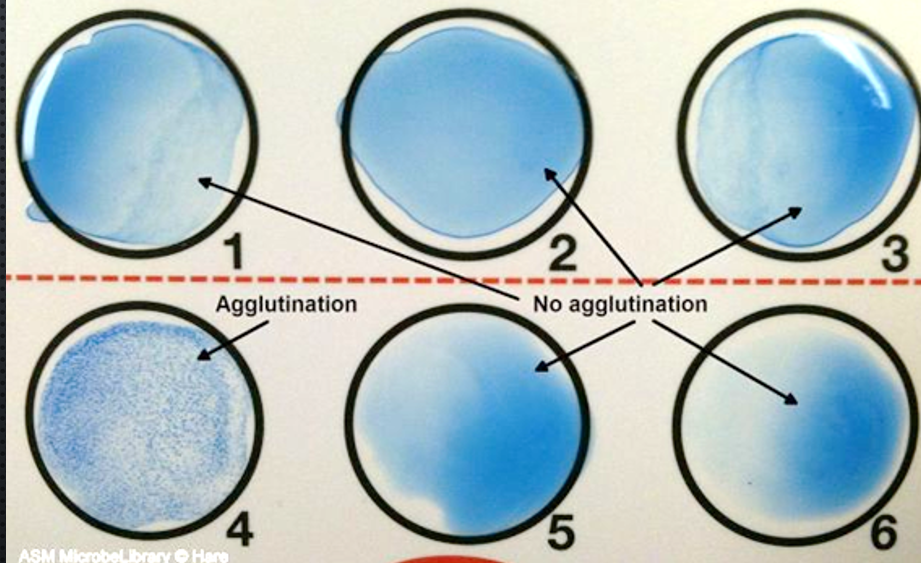
Lancefield Strep Typing
Latex beads coated with a specific Lancefield antibody
Agglutination occurs when the antibody coated latex beads bind to the specific antigen resulting in crosslinks of multiple latex beads (visible clumping occurs)
Agglutination
Rapid Antibody-Antigen reaction test for Lancefield grouping
Staphylococcus vs Streptococcus
Staphylococcus - occurs in clusters, Catalase positive, Coagulase positive, Protein A - surface protein, Tests: Staphyloslide (quick), Coagulase test (incubate)
Streptococcus - occurs in chains, Catalase negative, lancefield classification system, tests: lancefield strep typing (quick), hemolysis typing (incubate)
biochemical testing and identifying bacteria
reals information necessary to help identify bacteria within a sample
metabolism
used as an additional factor to identify bacteria because many of them share colony and cell morphology. bacteria produce enzymes that play a role in metabolic processes. the enzymes allow for identification through biochemical testing
biochemical testing agar
Simmons citrate agar and urea agar

Simmons citrate
differential
enzyme citrate lyase are able to use citrate as a carbon source
when citrate is used it becomes more alkaline
turns green to blue

Bromothymol Blue
the pH indictor in the medium for a Simmons citrate agar, changes medium from a green to blue color.
Uninoculated Simmons Citrate slant
pH 6.9 – 7.6, green agar slant, negative reaction
Inoculated Simmons Citrate slant
pH > 7.6, blue agar slant, positive reaction

urea agar
differential - only organisms with enzyme urease can break down urea
when ammonia (NH4) is freed from the agar it causes a pH change and the environment becomes more alkaline
urea
a waste product of protein digestion in most vertebrates and is excretes in the urine
pH indicator in urea agar
phenol red, changes color yellow to hot pink (fuchsia)
Uninoculated Urea agar slant
pH 6.8 – 8.0, yellow agar slant, negative reaction
Inoculated Urea agar slant
pH > 8.0, fuchsia agar slant, positive reaction
2 differential media
contains various nutrients that allow one to distinguish one bacterium from another by how they metabolize or change media with a waste product
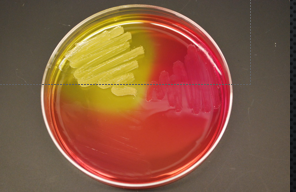
mannitol salt agar
selective = contains a high salt concentration (only organism that are halophiles or halotolerant will grow)
differential = contains the sugar mannitol (looking for mannitol fermentation)
also contains pH indicator called phenol red
fermentation of mannitol
the medium will change from red to yellow due to the pH
pH color change for mannitol
pH >8.4 = pink
pH 6.9-8.4 = red
pH < 6.9 =
Microbiological Culture
method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in a predetermined culture media under controlled laboratory conditions
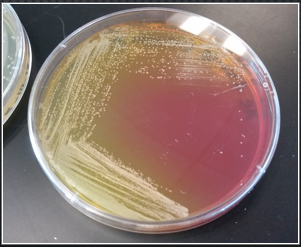
mixed culture
yellow, more than one type of organism
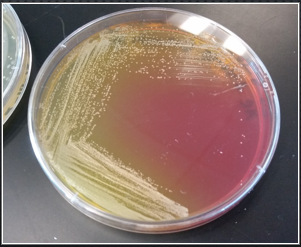
pure culture
pink, single type of organism, main idea is to dilute the original sample until the organism of interest is isolated and pure
ways to obtain pure culture
spread, pour, streak plate
details of methods of getting pure culture
they dilute or thin out a heavy population of bacteria across an agar surface. Once a pure culture is obtained it can be used to identify if the bacteria is sensitive or resistant to an antibiotic
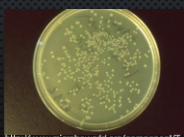
spread plate
original culture is serially diluted then the final dilution is spread on the surface of the plate. surface colonies grow

pour plate
serial dilution than final dilution added to molten agar which is poured over an agar plate. surface and subsurface colonies grow
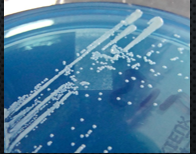
streak plate
original culture directly diluted across (agar) new plate with inoculating loop. 3 sections in a T pattern, in each section start with a line from the previous section
types of media
broth, agar
broth
liquid media; nutrients (used in motility experiment)
agar
jellylike substance derived from seaweed: thickening agent
why do we use agar
because microorganisms cannot digest agar. it’s a solid surface for microorganisms to grow and we can pick out individual colonies
all purpose/supportive media
contains nutrients that will support the growth of a large variety microorganisms
selective media
promote growth of some bacteria and/or limits growth of other bacteria
differential media
distinguish between different bacteria based on changes in colonies or changes in media
types of agar
tryptic soy agar, Eosin methylene blue agar

tryptic soy agar (TSA)
all-purpose/supportive medium used to grow most microorganisms
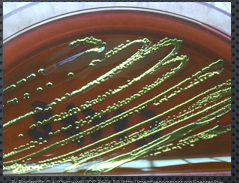
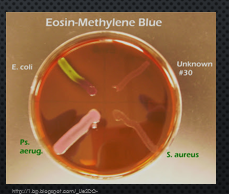
Eosin methylene blue agar (EMB)
selective media for gram negative organisms. inhibits the growth of gram-positive organisms due to the dye’s eosin Y and methylene Blue
lactose fermentation makes it a differential media. it causes precipitation of the dyes on the surface of the colonies resulting in different colors.
Lots of acid = green metallic sheen
small amount of acid = pink or blue center (fish eye)
no fermentation = colorless
aseptic transfer
conducting your work in a way that will not contaminate the culture itself, and also without contaminating your workspace to yourself with the specimen
keep the lid on the plate at all times, can come off to pick a colony and then immediately
how to achieve aseptic technique
disinfect work area
all tools that handle bacteria need to be sterile
loops/needles: flamed in the incinerator or Bunsen burner to sterilize
tubes, plates, etc: autoclaved
keep all cultures covered unless you are using it that second
if unaware if tools are sterile start over