Lecture #3 - Record Base and Occlusal Rim Fabrication Lecture
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
When would you mount your master casts to the articulator in a real world appointment
after the jaw relations have been taken in the patient's mouth; no jig in the real world
why might you save the final impression
in case your master cast breaks!
recall, the final impressions are made by using what?
custom trays!
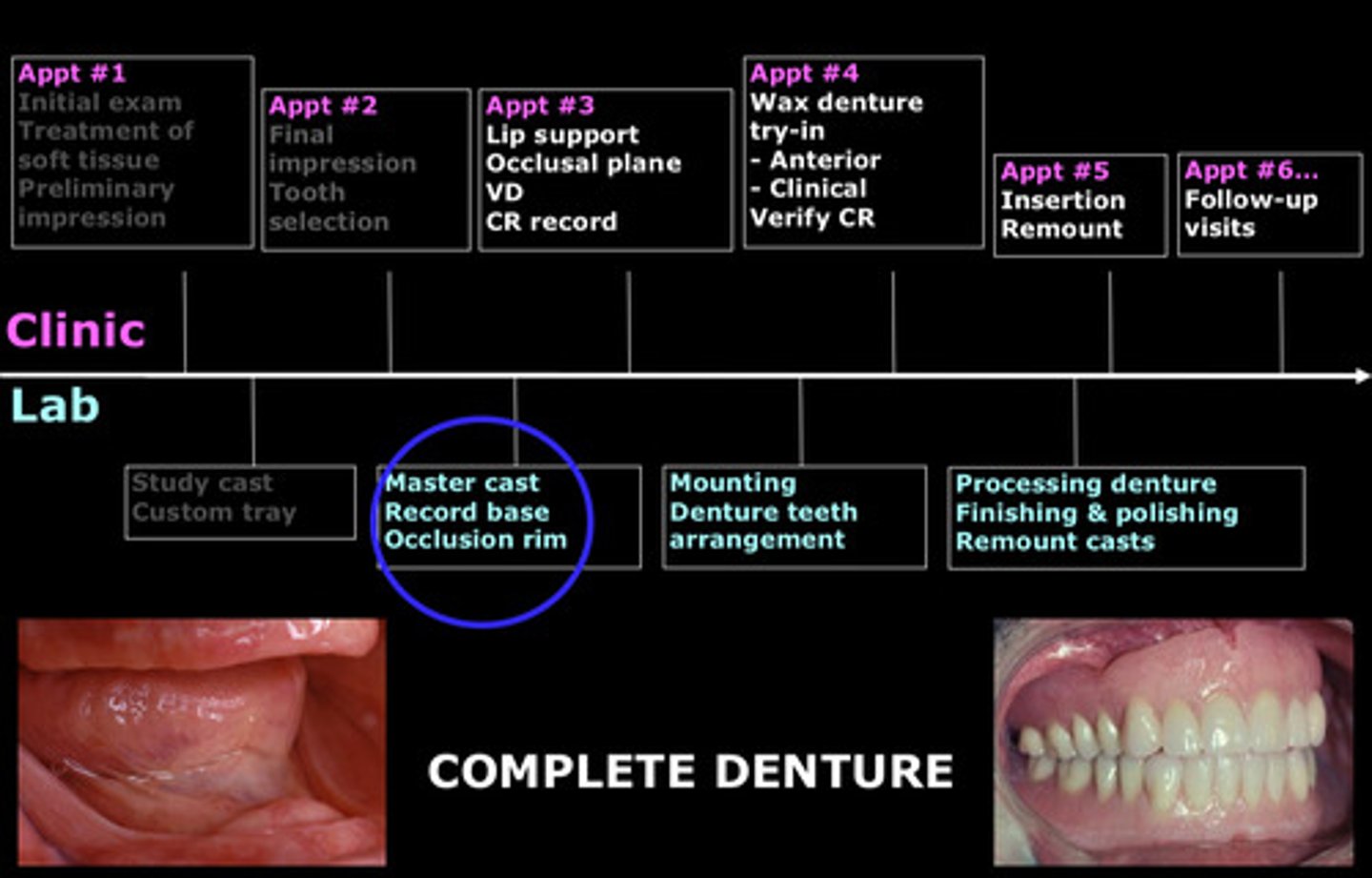
describe the procedures that have been completed leading up to occlusion rim fabrication
1) preliminary impression already made
2) study cast made from preliminary impressions
3) custom trays made from study casts
4) final impression using custom trays
5) master cast made from final impressions
6) record base and occlusion rim using the master cast (which are not mounted until after jaw relations are done)
what is the occlusion rim typically made of
wax
what is the record base or baseplate typically made of
resin: nobiltray, triad, orthoresin
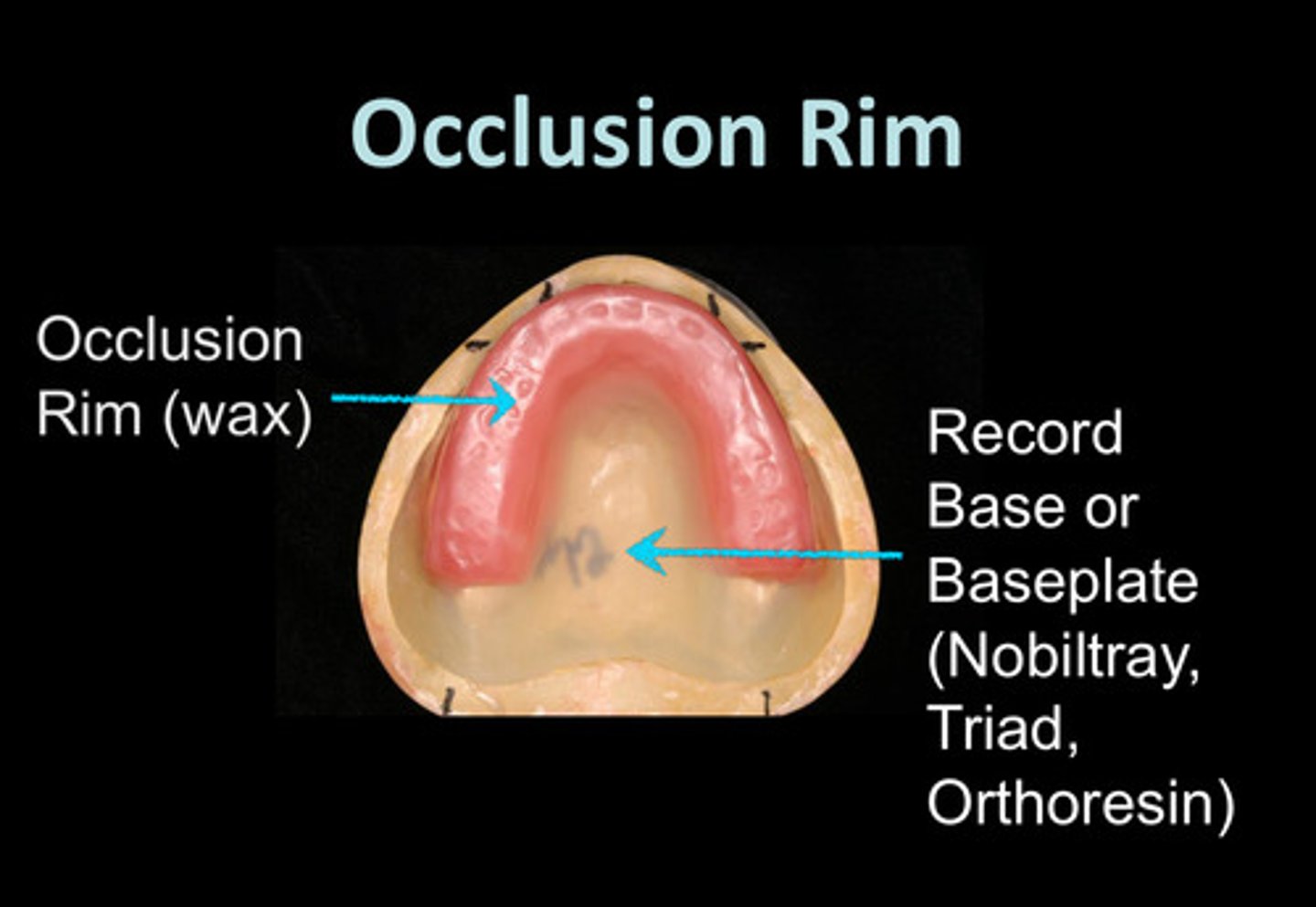
what are the 3 uses/purposes of the occlusion rims (record base + wax rim)
1) to place master casts in articulator in the same relation as maxilla and mandible have in the mouth
2) for the denture teeth try-in to verify esthetics, speech, and jaw relation records
3) to help form a portion of the mold in which the denture is processed
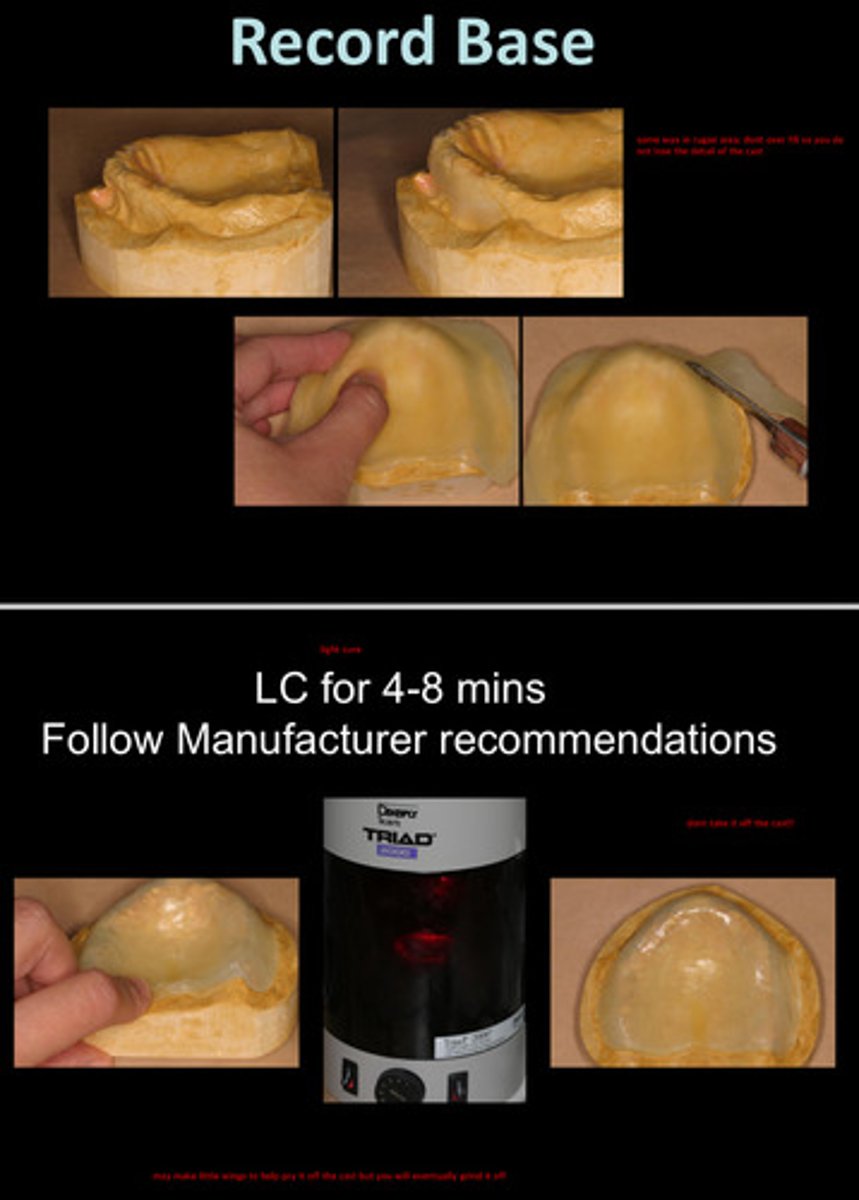
how to make a record base
1) flow pink wax into rough surfaces (such as rugae, but not so much that you lose the detail of the cast)
2) block out undercut with wax to preserve integrity of master cast
3) apply separator (vaseline)
4) adapt recordbase sheet over the cast
what is the purpose of blocking out areas on the master cast
1) to be able to remove the record base from the cast without fracture of the resin/triad material
2) to prevent damage to the master casts
how long might you light cure the record base for
4-8 minutes; but follow manufacturer recommendations
note: do not take the record base off the cast while curing as it may warp
how thick should the record base be over the ridge & to the labial/buccal aspect of the ridge
~1 mm
how thick should the record base be in the palate
no greater than 2-3 mm
when adjusting the thickness of your record base, which areas should also be relieved?
frenal areas
if your master cast breaks when trying to remove the record base, and you didn't save your final impression, what do you need to do
repeat the final impression
image of how to make occlusion rims
we want the wax rim to conform to the contour of the ridge —> contour of wax rim should approximate shape and B-L position of final denture teeth

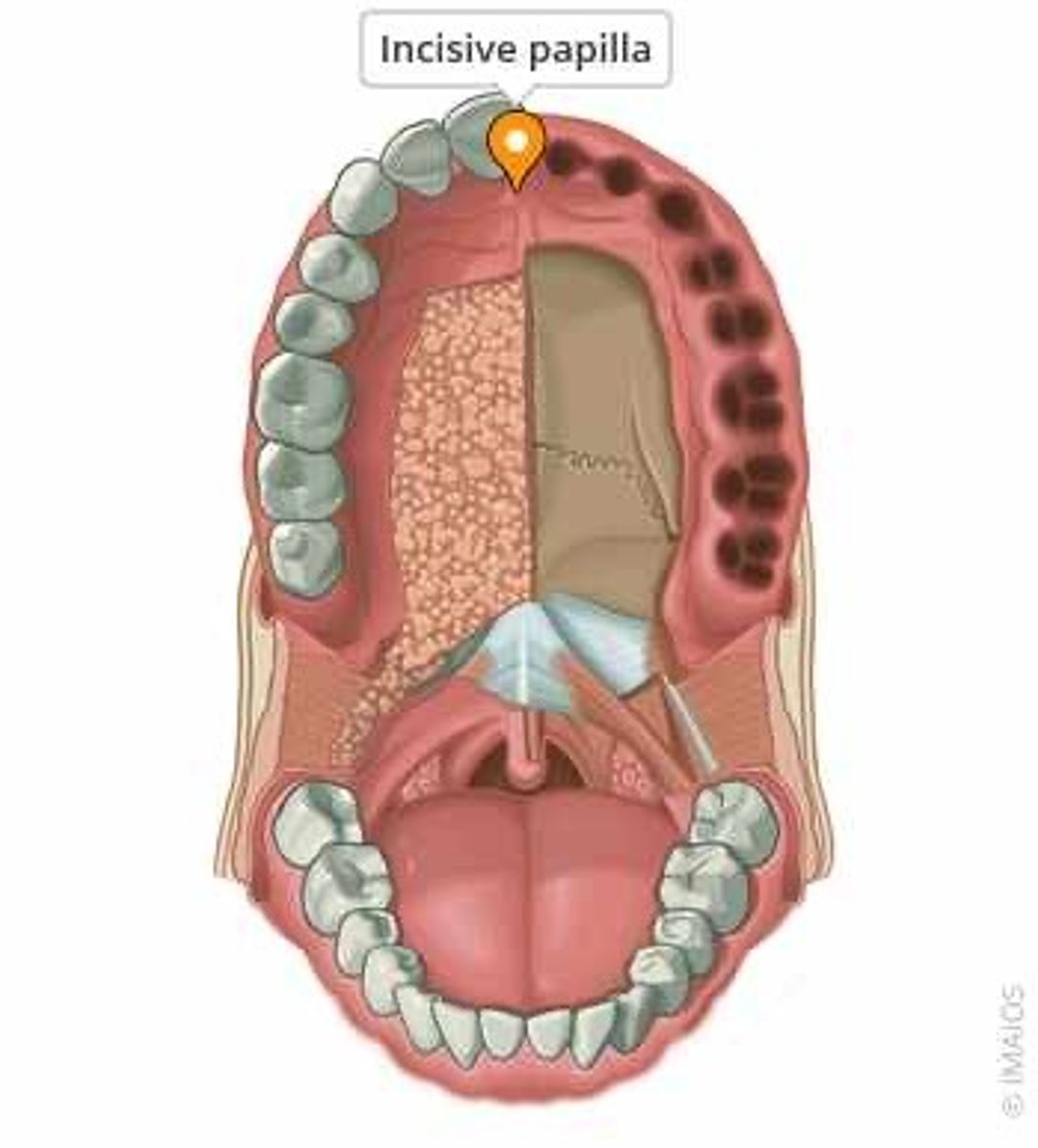
the labial portion of the maxillary occlusion rim should be approximately how many mm anterior to center of incisive papilla
7 mm
the maxillary occlusion rim occlusal plane should be _______ with the base of the cast
parallel with the base of the cast (which should be parallel w ridge crest)
how much OJ (horizontal overlap) should be present between the max and mand occlusion rims
~2 mm; we eventually want 1-2 mm of space between labial of lower to incisal edge of upper
how wide should the occlusion rim be in the anterior and posterior dimensions
anterior: 8 mm
posterior: 10 mm
what are the requirements of an acceptable baseplate and occlusion rim
1) good surface detail
2) border areas must fill the vestibule
3) accurate fit on master cast without rocking
4) minimal wax block out undercut with labial flange
the occlusal plane of the mandibular occlusion rim should intersect where?
the middle of the retromolar pad
what are the arbitrary heights used for the max and mand occlusion rims, respectively
22 and 18 mm from the edentulous ridge crest to incisal edge plane (final height is determined chairside)
what width do we want for the occlusion rims
8-10 mm (anterior 8 mm, posterior 10 mm)
how should the contours of the wax occlusion rims look like
slight proclination (flare) in the max anterior and straight in the posterior