Unit 4: Political Processes and Patterns
Political Entities:
States:
the primary building blocks of the world political map
Must have:
clear boundaries
Permanent population
Sovereignty: recognized government authority that can control and defend its land area
Nation: A group of people tied together by common culture, ethnicity, history, and attachment to homeland
Nation-State: The cultural borders of a nation correspond with the state borders of a country
Japan, Denmark
75% of pop. is ethnic or higher
Multinational State: A state that contains more than one nation/ without a dominant ethnic group
USA, Canada, South Africa
Multi-State Nation: An ethnic group across borders and living in more than one state
South & North Korea, Austria-Hungary
Autonomous region: An area that has a high degree of self-governing within a larger political entity
Svalbard, Norway; Greenland, Denmark
Semi-Autonomous Region: An area of a country that has some degree of governing within a larger political entity.
Hong Kong, Catalonia, Indigenous reservations
Political Processes:
Sovereignty: recognized government authority that can control and defend its land area
Self- determination: a group of people believe they have the right to form their own state and self govern.
Colonialism & Imperialism:
Colonizers and Imperialists took over the land and changed/placed borders in the area, resulting in current state borders today.
Independence Movements:
When a group of people due self-determination to try to separate from a state and make a new one
Devolution: the transfer of power to a lower level
USA, UK
Political Power expressed geographically:
Shatterbelt: a region with conflict that involves outside powers
Korean War, Vietnam War
Choke point: a narrow passage where trade & travel can be restricted
Panama Canal, Strait of Malaca
Territoriality: connection of people’s culture and economy to the land
Neocolonialism: use of economic, political, or cultural pressures to influence other countries
former dependencies (African countries to European ones)
Boundaries:
Relic: a former boundary that is still marked by cultural landscape feature
Great Wall of China
Superimposed: placed over and ignores cultural pattern
Colonization, Scramble for Africa
Subsequent: established after settled and reflects culture of bounded area
North Vietnam & China
Consequent: coincide with cultural divide
religion, language, ethnicity
India & Pakistan
Pakistan was split for Muslims (Muslims move to Pakistan from India)
Geometric boundary: created by a straight line or arc “Artificial boundary”
line of latitude for USA & Canada (49th parallel)
Many African borders today:
Egypt, Libya, Algeria
Boundaries II:
Defined: written, legal description
through a treaty or document
Delimited: drawn on a map
cartography
Demarcated: placing of political boundary on a landscape
physical boundary
wall, fence, barrier
Demilitarized Zone: area that forbids military activity based on an agreement or treaty
Korea DMZ, Kuwait & Iraq
Berlin Conference (1884-1885): Boundaries in Africa were negotiated by Europeans to control resources
Created superimposed, geometric boundaries.
Boundary disputes:
Definitional: disagree over description of how a boundary was written in a treaty.
Chile & Argentina
Locational: Disagree over the delimitation or demarcation of a boundary
Morocco & Western Sahara
Operational: Disagree over the actual function of a boundary
Often migration control
USA & Mexico, EU
Allocational: disagreement over control and/or location of economic resources near boundary
Iraq & Kuwait
Law of the Sea (UNCLOS):
UNCLOS: The code of maritime law approved by the UN in 1982 that authorizes territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200 nautical-mile-wide exclusive economic zones
International Waters/ High Sea:
Regulated by the International Seabed Authority
Exclusive Economic Zone: the state has economic control over resources in zone
Territorial Waters: The state has sovereignty over waters
Median Line: If the EEZ or territorial waters between two states overlap, a middle line is placed between the two zones.
Voting Boundaries:
Voting district: Subnational regions used by governments to organize elections with clear boundaries
Redistricting: Each state redraws boundaries of voting districts to reflect population changes
Districts must be equally populated
Gerrymandering: the process of manipulating boundaries of voting districts to favor one political party
US Census:
Every 10 years
Used for Reapportionment: Redistribution of the 435 seats for local rep. in national legislature
Used for Redistricting
Forms of Governance:
Unitary State: a top-down, centralized form of government
power is help primarily by central government
not much power given to sub-national governments
France, UK, China, North Korea, Japan
Pros:
Decisions are made quicker
Lower cost of government
Standardization of laws & taxes
good for compact states
Cons:
Ignores local needs
Can lack infrastructure
Can lead to abuse of power
Marginalization of local cultures
Federal State: power is shared between the central government and subnational governments (more locally based, dispersed power centers)
USA, Germany, Brazil, Australia
Pros:
Can prevent tyranny or corruption
Better addresses multiculturalism
More effectively address local issues
Better for larger or fragmented states
Cons:
more costly government spending
Regional inequalities
overlapping roles and powers
Regionalism over Patriotism
Devolutionary Factors:
Ethnic Separatism:
minority ethnic groups advocated for autonomy or sovereignty
Ethnic cleansing:
ethnic group is targeted to eliminate them through expulsion or mass murder
Terrorism:
organized violence aimed at government or civilians intended to create fear and chaos to accomplish political aims
Irredentism:
an ethnic group claims territory from neighboring state due to shared culture or history with people residing across the border
Russia & Ukraine/Crimea
Physical Geography:
separation by physical features
fragmented states
Supranationalism: an organization of 3 or more states with common goals and/or represents interests on the global level
Advantages:
More military or political strength
More access to resources
More economic growth
trade, open borders, common currency
More global representation
Easier travel
Open borders
Disadvantages:
Less sovereignty
must follow policies & laws internally
Financial costs can spill to other members
Unequal costs/benefits to member states
Interdependency or overreliance can occur
Security/border issues
Protests within pop. against membership
United Nations:
Goals: safeguard peace, protect human rights, promote economic and social progress
Founded in 1945
HQ: New York City
5 permanent security council members: USA, France, UK, Russia, China
NATO:
Holds immense power
Article 5: collective defense
an attack against one is considered an attack against all
members must contribute to defense
Article 5 was invoked after 9/11
European Union:
Euro-zone
common currency: Euro
Promote peace, improve environment, promote human rights
Greek debt crisis affects everyone else
ASEAN:
Is argued that it is not collectively responding to:
Chinese-US tensions
South China sea territorial claims
Myanmar: civil war
Accelerates economic growth of countries
Leads to increased employment rates
Arctic Council:
fights pollution
fights to protect the Arctic
protects environment
protects indigenous people
African Union:
Helps people of Africa
Promote cooperation
Eradicates colonialism
Centripetal and Centrifugal forces:
Centrifugal forces can lead to:
Ethnic Nationalist Movements:
Catalonia, Quebec
Stateless Nations:
Kurdistan, Palestine
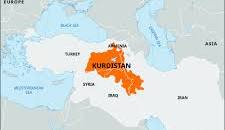
Centripetal forces can lead to:
Ethnonationalism:
Semi-autonomous region Nunavut, Canada
Allows indigenous group to maintain their own culture and local government
Increased cultural cohesion