Chapter 2 Concepts and Biomes Review
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A study set of flashcards covering climate processes, soil science, pedogenesis, climate diagrams, and major terrestrial biomes based on the provided notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What drives climate?
The sun.
What is the global energy balance equation?
Ein = Eout.
What percentages of sunlight are reflected and absorbed by Earth?
About 30% reflected; about 70% absorbed in the biosphere.
What happens to absorbed solar energy?
It is absorbed primarily as heat; photosynthesis is insignificant.
hemispheres and seasons
the two hemispheres have opposite seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis. As the Earth orbits the Sun, one hemisphere is tilted toward it, experiencing summer, while the opposite hemisphere is tilted away, experiencing winter.
constant tilt is 23.5 degrees
How is heat dissipated to balance energy input?
By reradiation as longwave heat, plus conversion to wind and evaporation.
What effect does the Coriolis force have on atmospheric circulation?
It breaks up air circulation into Trade Winds, Westerlies, and Polar Easterlies.
polar westerlies at the north and south pole
westerlies between the trade winds and polar easterlies
northeast and southeast trade winds are near the equator
the coriolis effect causes the winds in the northern hemisphere to be deflected to the right of their direction of travel and winds in the southern hemisphere to be deflected to the left.
ocean currents
due to
air currents
also due to absorbed solar energy by water
strongly influenced by continental positions
Which factors influence regional climate and biomes?
Atmospheric circulation
ocean currents
topography
vegetation
What causes a rain shadow and windward–leeward moisture differences?
The Orographic effect; air rises on the windward side causing rain and leaves the leeward side drier.
Name the five crucial ecological roles of soil.
Medium for plant growth
recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes
water supply and purification
engineering medium
habitat for soil organisms
What are the major soil horizons in a typical profile?
O organic horizon (litter in various stages of decay)
A first mineral horizon (accumulation of organic matter)
E eluviation (loss of clay)
B illuviation (accumulation of clay)
C weathered parent material (chemical weathering)
What does CLORPT stand for in pedogenesis?
Climate, Organisms, Relief, Parent material, Time.
What is pedogenesis?
The process of soil formation influenced by climate, organisms, relief, parent material, and time.
What is the purpose of the soil texture triangle?
To classify soils by proportions of sand, silt, and clay
What are soil drainage classes?
Range from well-drained to very poorly drained; drainage varies with landscape position (uplands to wetlands).
What is a hydric soil?
A soil that is saturated with water long enough to develop hydric properties and support hydrophytic vegetation.
What composition corresponds to 55% clay, 32% silt, and 13% sand on the texture triangle?
Clay 55%; Silt 32%; Sand 13%.
Name the major terrestrial biomes discussed.
Tropical rainforest; Tropical dry forest; Tropical Savanna; Desert; Mediterranean woodland/shrubland; Temperate grassland; Temperate forest; Boreal forest (Taiga); Tundra.
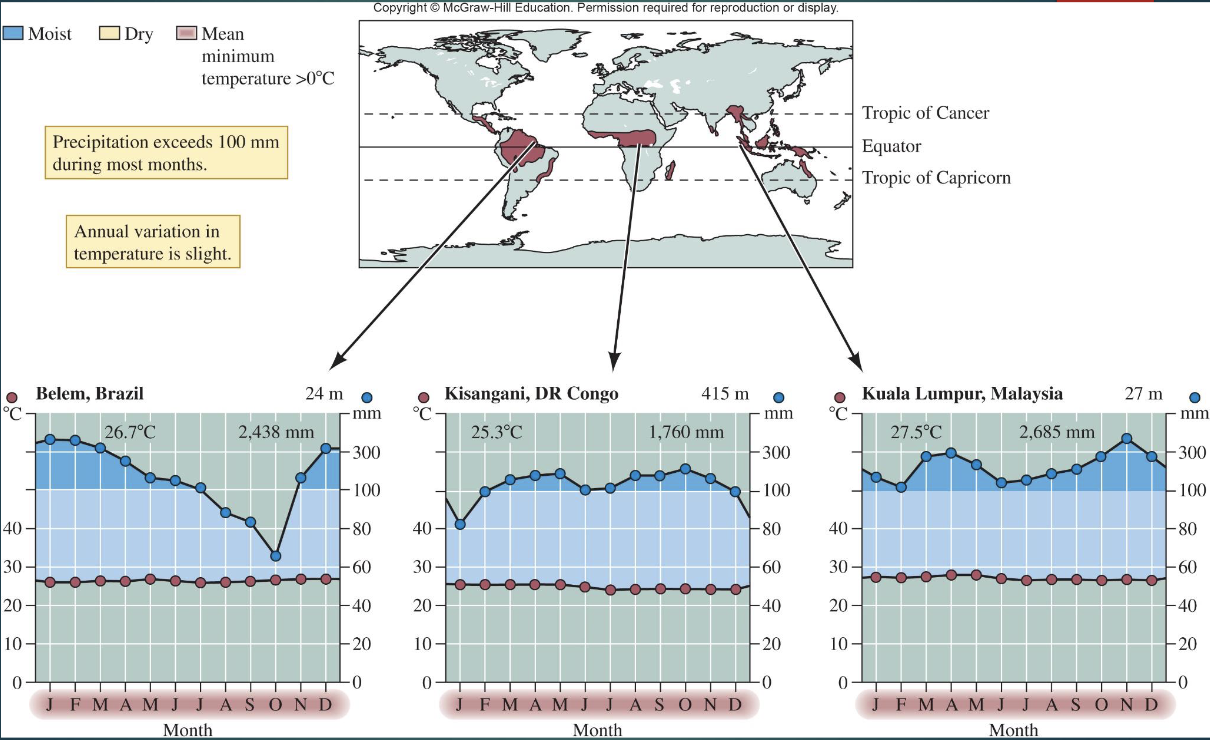
What are the climatic and soil features of Tropical Rainforests?
Near the equator (within ~10°)
little monthly temperature variation
high, evenly distributed rainfall (2000–4000 mm/yr)
leached soils
mycorrhizae aid nutrient uptake
high biodiversity and vertical layering
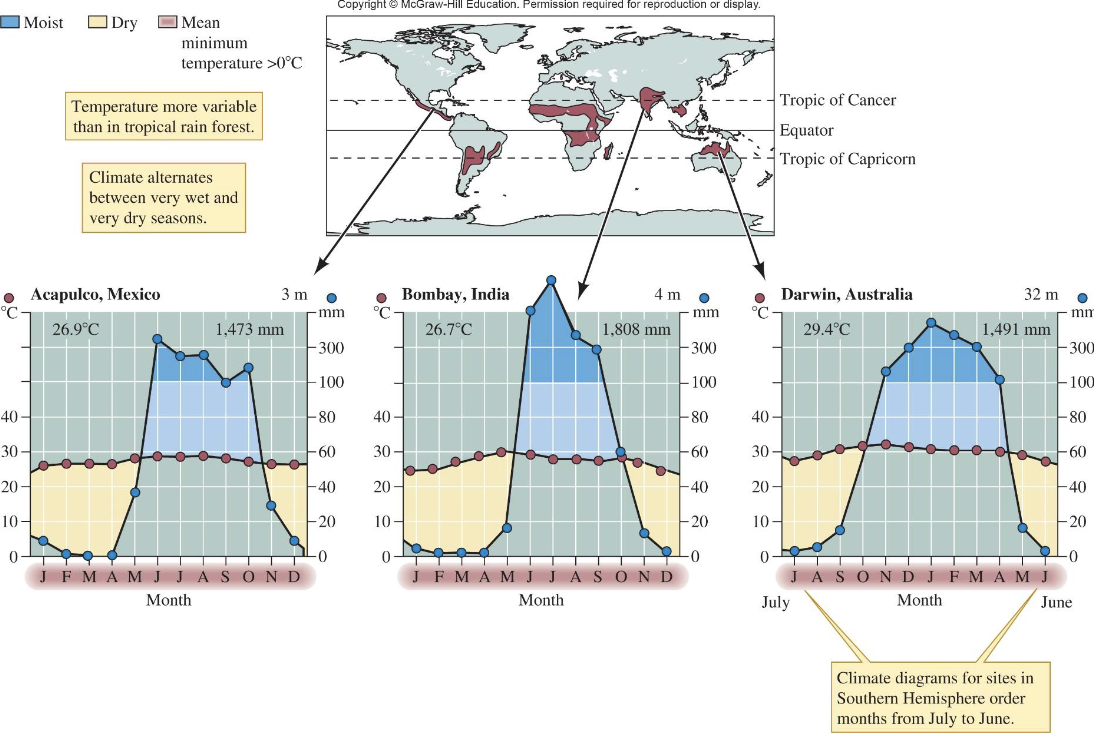
How do Tropical Dry Forests differ from Tropical Rainforests?
Dry forests have more seasonal rainfall and soils richer but more erosion-prone
extensive human clearing; share many species with rainforests
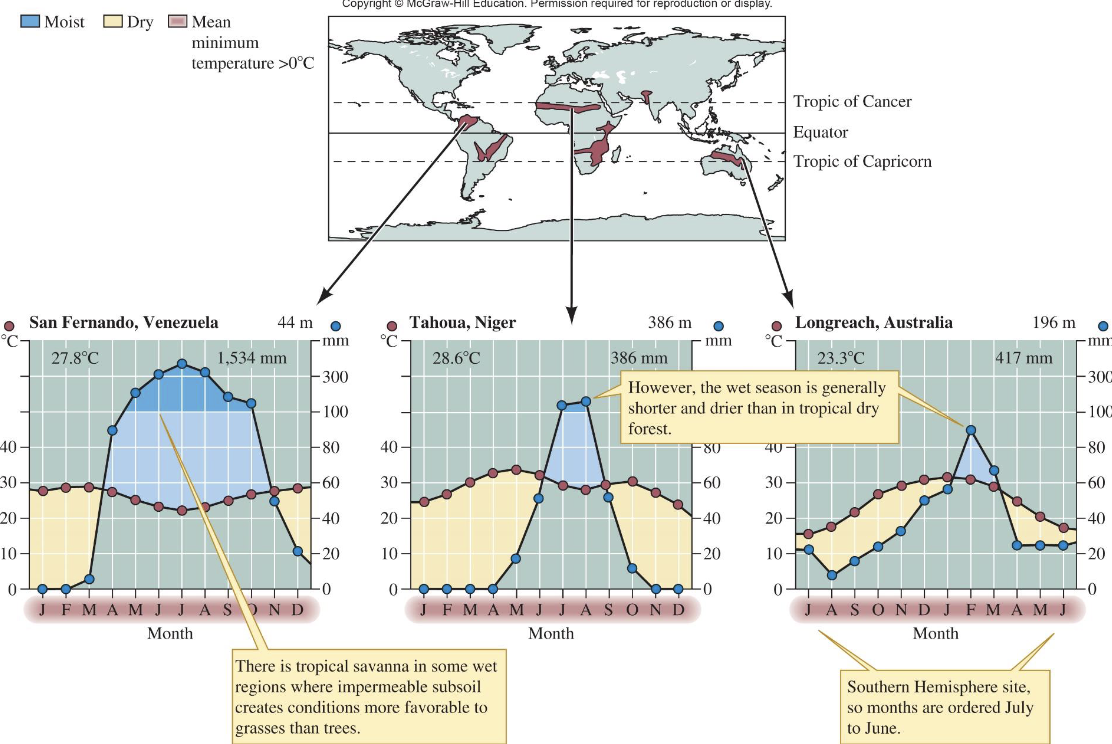
What are the key features of Tropical Savanna?
Located roughly between 10°–20° latitude
wet and dry seasons
droughts can cause wildfires
soils with low water permeability
grasses favored
livestock production common
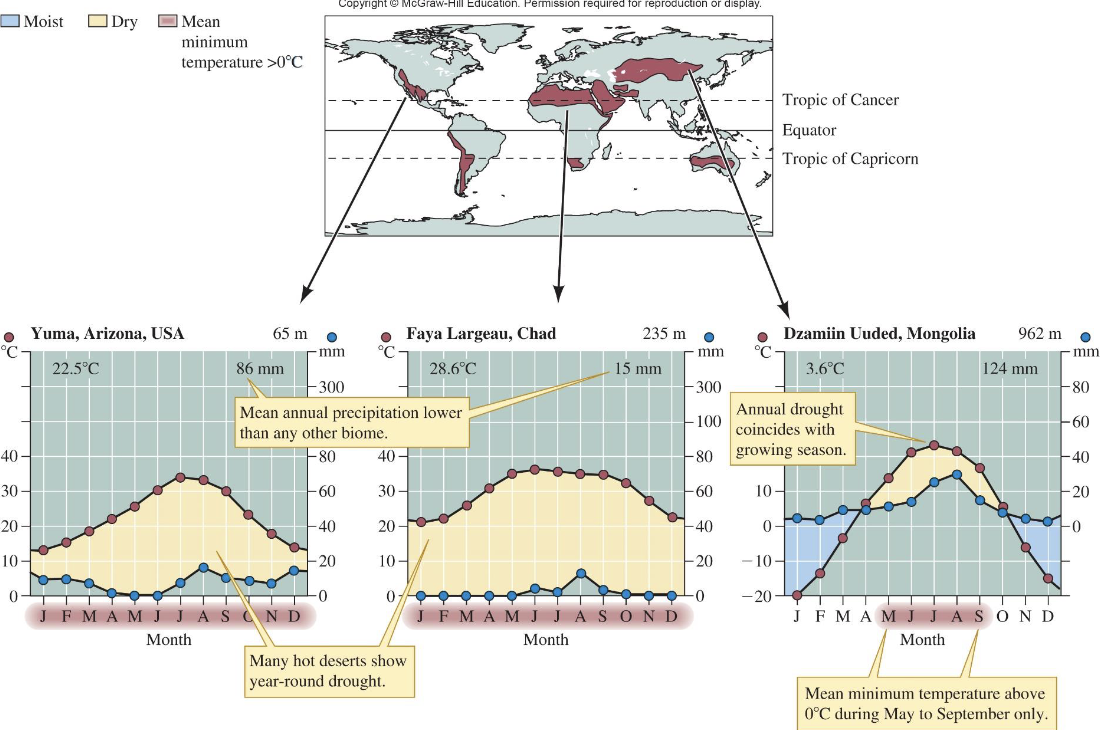
Desert biome features?
Major bands at ~30° N/S; about 20% of Earth's land
water loss exceeds precipitation
soils low in organic matter
sparse to absent vegetation
animals adapted
high biodiversity in some deserts
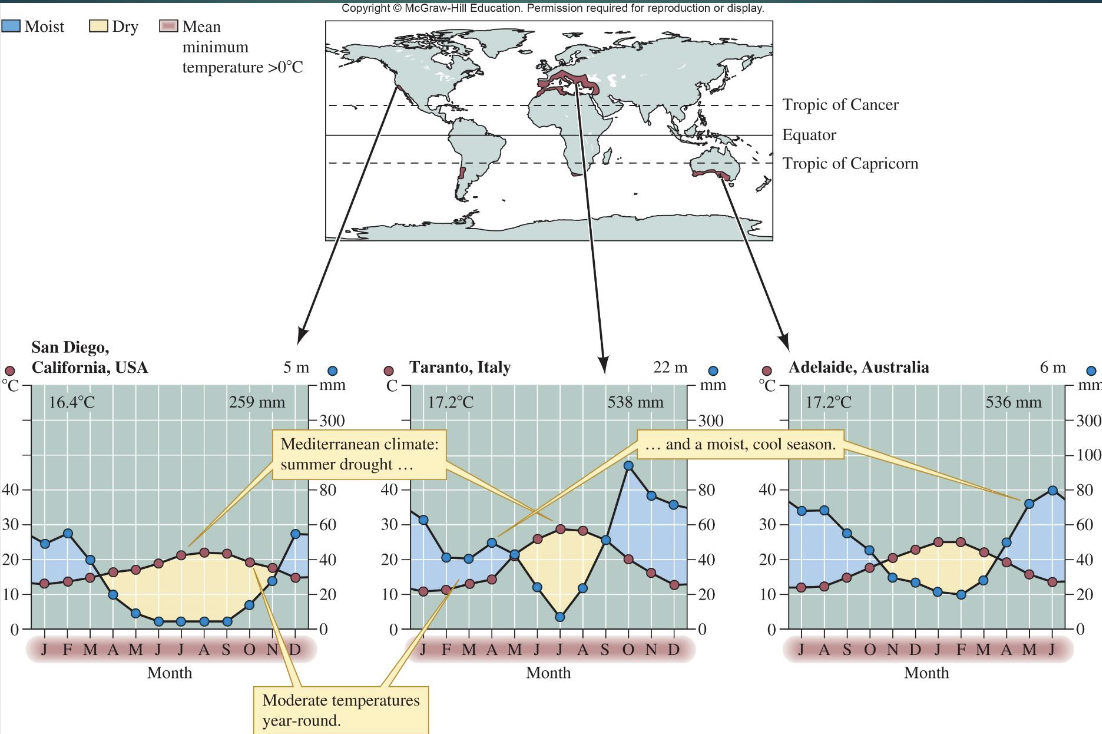
What defines Mediterranean Woodland and Shrubland?
Found on most continents except Antarctica
cool, moist fall-winter-spring
hot, dry summers
moderately fertile soils
evergreen, fire-tolerant vegetation
history of human intrusion
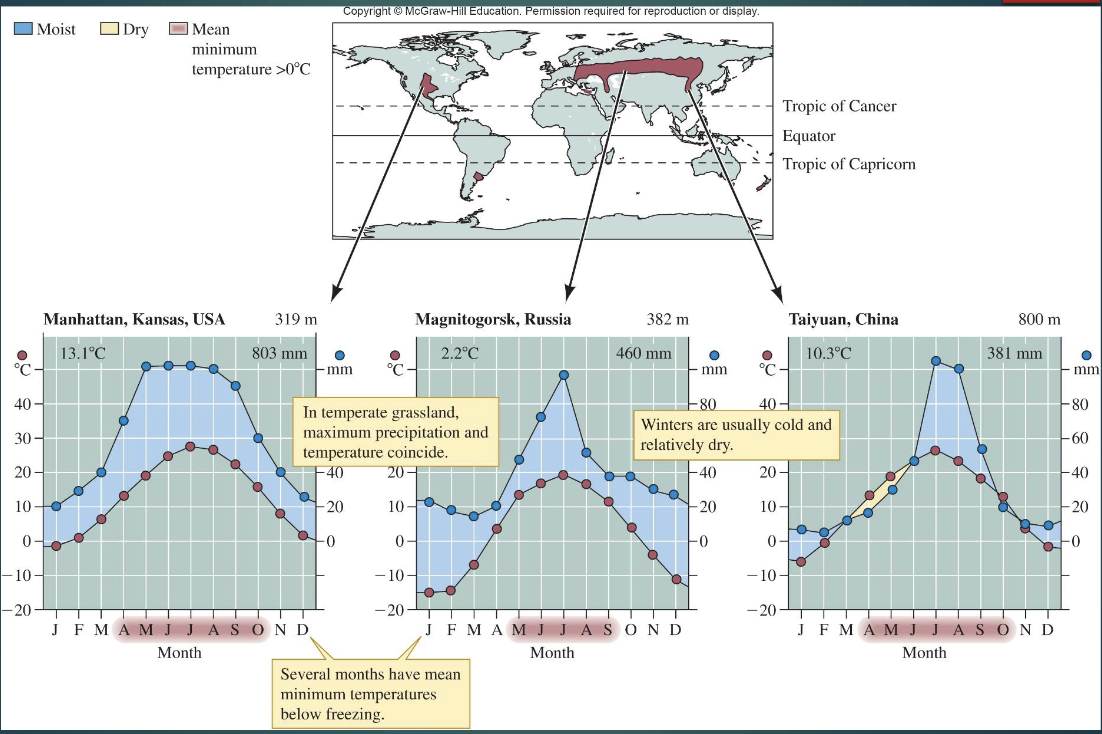
Temperate Grassland features?
Widespread
annual rainfall 300–1000 mm
periodic droughts
nutrient-rich deep soils
dominated by herbaceous vegetation
large roaming ungulates
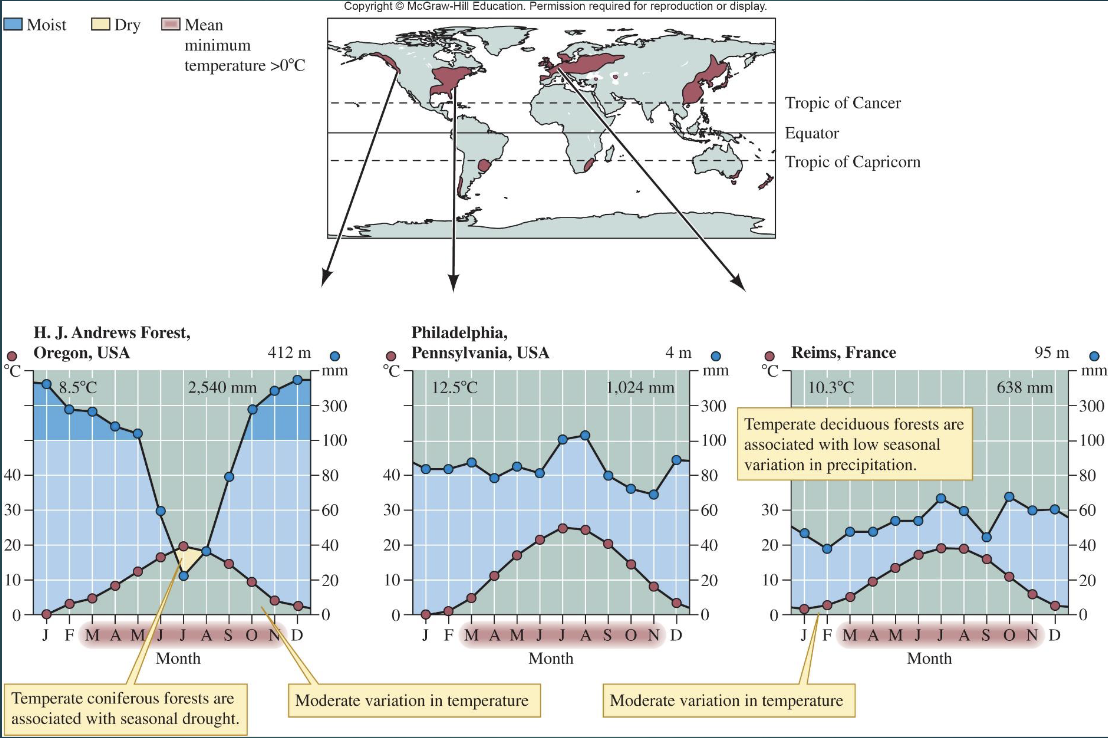
Temperate Forest features?
Mostly between 40° and 50° latitude
rainfall 650–3000 mm
fertile soils
long growing seasons with deciduous plants
short seasons with conifers
high biomass
many human population centers
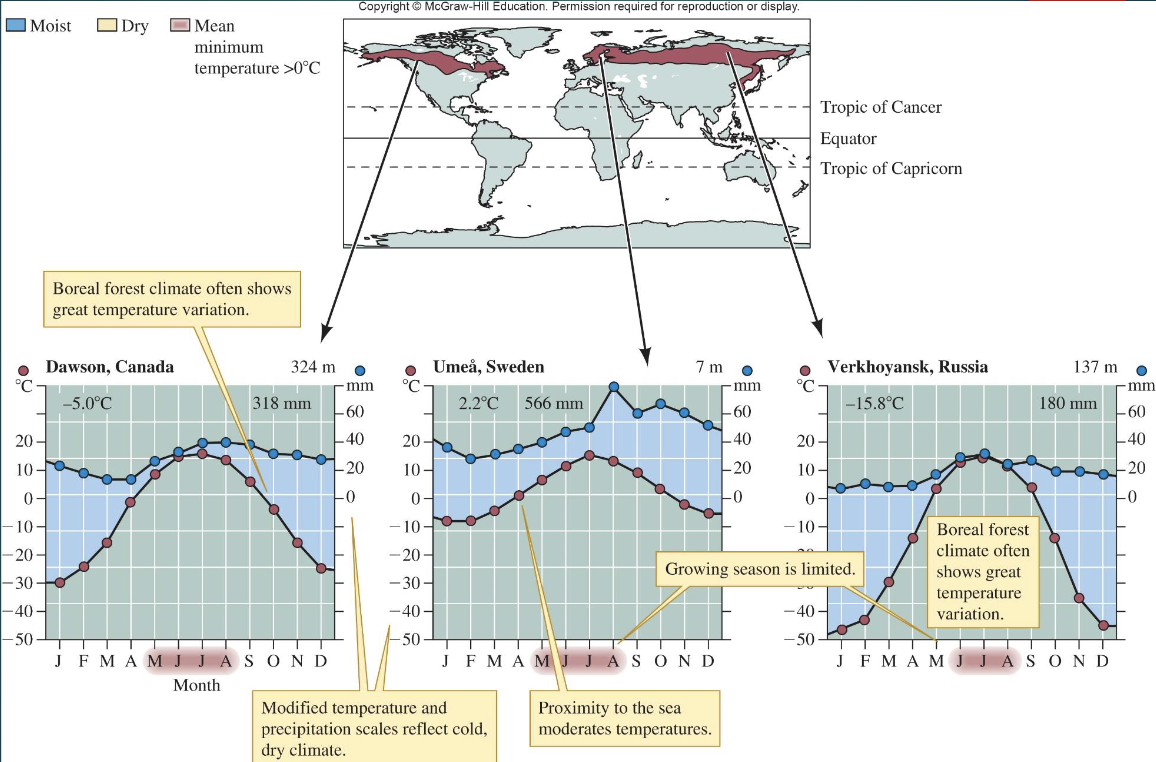
Boreal Forest (Taiga) climate and features?
Northern Hemisphere
~11% of land
thin acidic soils
evergreen conifers
relatively high animal density
historically low human intrusion
short growing season
great temperature variation
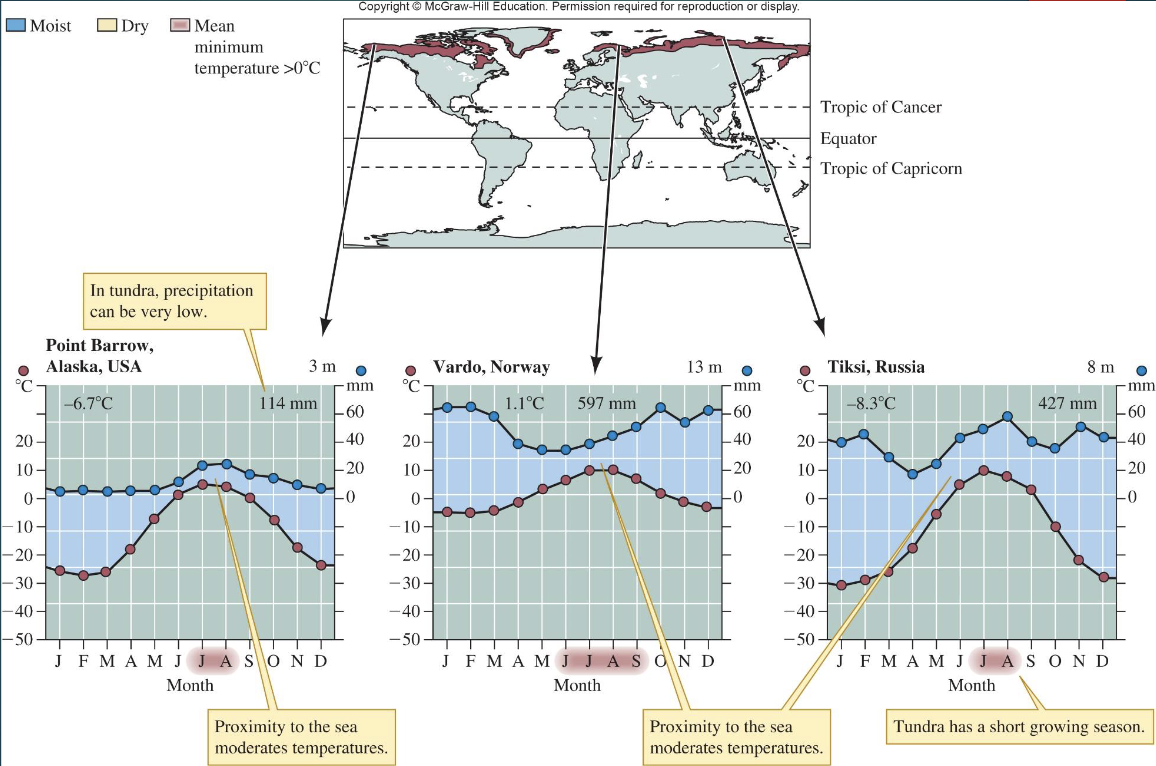
Tundra climate and features?
Covers lands north of the Arctic Circle
cool and dry with short summers
200–600 mm precipitation
low decomposition
supports many native mammals
limited historical human intrusion
Mountains: 'Islands in the Sky' concept?
Mountains act like islands
climate changes with elevation
soils are thin and well-drained
flora and fauna shift with elevation
altitude mimics latitude
mountain ranges in north and south america run north to south
mountain ranges in europe and asia run east to west
North-facing vs. South-facing slopes climate differences?
South-facing slopes are sunnier, warmer, drier with greater temperature fluctuations
north-facing slopes are cooler and moister
different affects plant/animal distributions and deer behavior
deer use N facing slopes in the summer
use S facing slopes in the winter and spring bc less snow, earlier spring, and warmer
Macroclimate vs. Microclimate?
Macroclimate is the general regional climate
microclimate is the local climate around organisms (within about 1 m of the ground)
climate surrounding organism parts such as
a single leaf
insect parasite on an animal
organ of the body
How are climate diagrams structured?
Temperature on the left axis; precipitation on the right axis; 10°C equals 20 mm; lines show water availability; adequate moisture when precipitation exceeds temperature.
What does The Whittaker Biome Classification relate?
Relates mean temperature and precipitation to plant distributions and biomes (The Whittaker Graph).
How does elevation affect climate in mountains?
Altitude mimics latitude
climate changes with elevation
soils are thin and well-drained
flora and fauna shift with elevation
What is eluviation (E) and illuviation (B) in soils?
Eluviation (E) is the loss of clay and other materials from a horizon; illuviation (B) is the deposition of those materials in a lower horizon.
What do soil horizon letters O, A, E, B, C represent?
O organic horizon
A mineral horizon with organic matter accretion
E eluviation
B illuviation
C weathered parent material
water vapor and temperature
low temp air is saturated by low water vapor and water vapor pressure is low
high temp amount of water air holds at saturation and saturation water vapor pressure increases
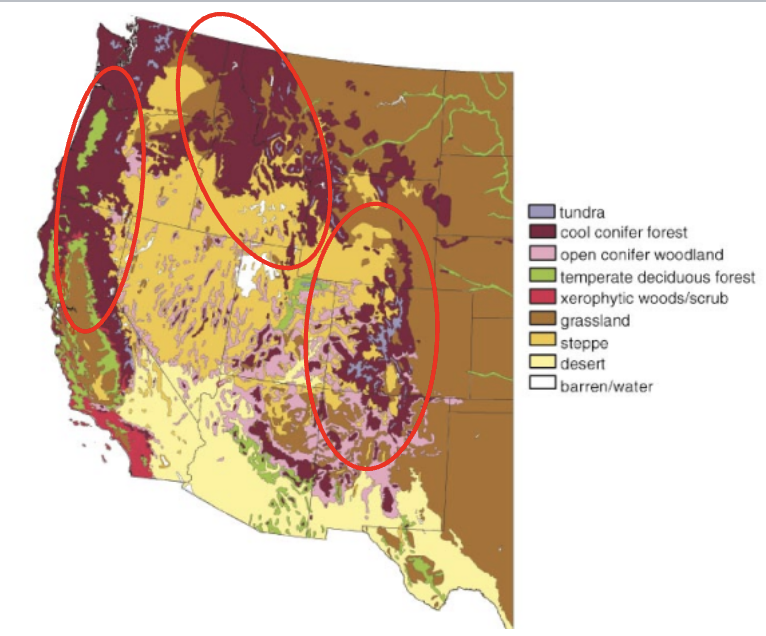
vegetation biomes of the western US
mountain ranges: rockies, cascades, coastal, and serra nevada
cool conifer forest!
rapid change in vegetation based on altitude/elevation
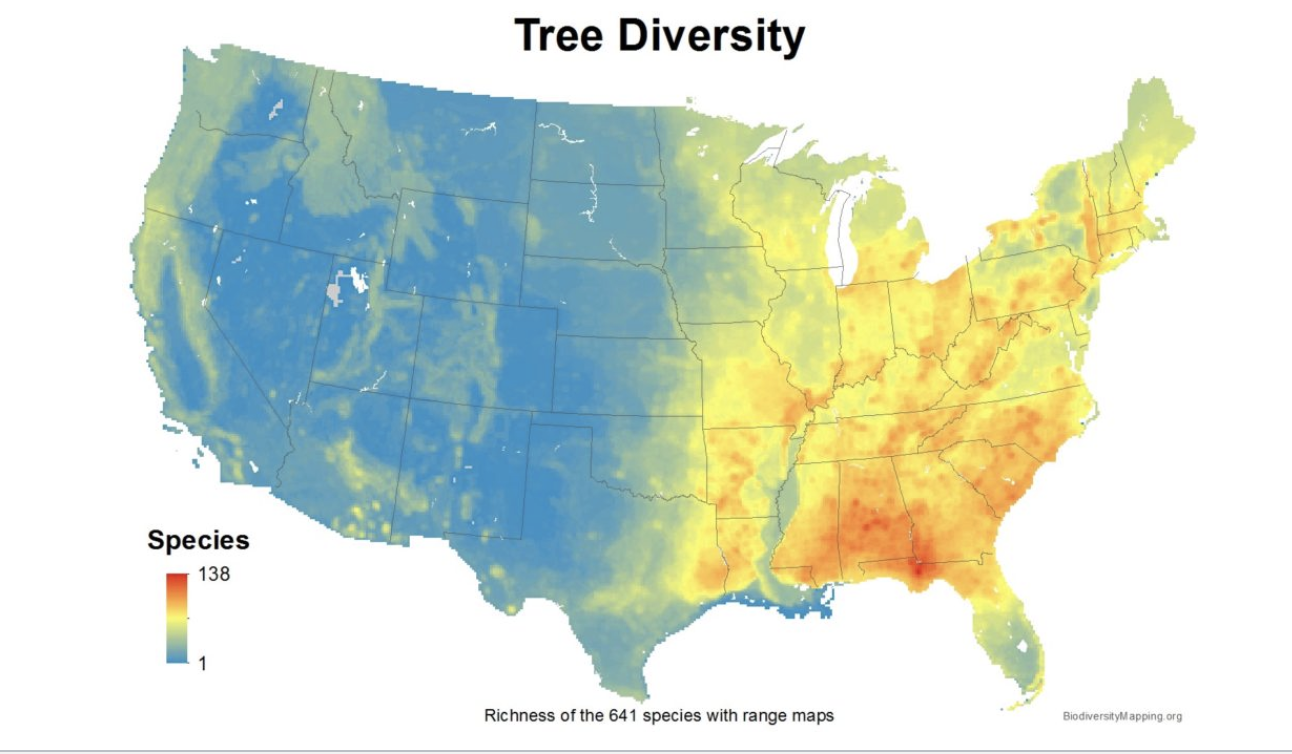
tree diversity
south east has the most tree diversity while the west has barely any tree diversity
similar trend for tree endemics