PSYCHOLOGY - biopsychology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
the key assumptions made by biopsychologists
behaviour and experiences are caused by activity in the nervous system
the nervous system transmits signals for communication via billions of neurons
what is a neuron
nerve cells in the human nervous system,
80% in the brain
send signals electrically and chemically
used for communication
what are the three types of neurons
sensory
relay
motor
what do these neurons look like
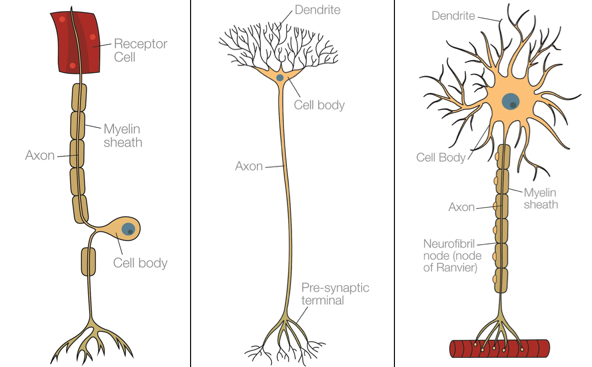
what is the dendrite
branch-like structures that receive the nerve impulses from adjacent neurons.
what is the axon
where the impulses travel along
what is the myelin sheath
protects the axon from external influences - so transmission is not affected.
what are the nodes of ranvier
these speed up the transmission of nerve impulses by forcing them to jump between myelin sheath segments.
what are terminal buttons
send signals to the adjacent cell/neuron
function and structure of motor neuron
carries messages from the CNS to effectors like muscles or glands
short dendrites
long axons
function and structure of relay neuron
transfers messages from sensory neurons to other relay or motor neurons
short dendrites
short axons
function and structure of sensory neuron
carries messages from the PNS to the brain and spinal chord
long dendrites
short axons
what is a knee jerk reaction, as a reflex arc
stimulus is detected by sense organs in the peripheral nervous system
this conveys a message along a sensory neuron
when the message reaches the central nervous system it connects with a relay neuron
this then transfers the message to a motor neuron
which triggers a response in the effector muscle, resulting in a quick, involuntary movement.
excitation vs inhibition
excitatory - make neurons more likely to fire
inhibitory - make it less likely that the neuron will fire
what is summation
The process by which multiple signals combine to influence a neuron's likelihood of firing. Summation can be either
spatial, where signals from different neurons are received at the same time
temporal, where signals from the same neuron are received in quick succession.
what are the two different nervous systems
central nervous system (CNS), the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS), CNS to the rest of the body.
how can the PNS be subdivided
somatic nervous system - controls muscle movement and receives information from sensory receptors
autonomic nervous system - regulates involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, sexual arousal and stress responses.
how can the ANS be divided
into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
what makes up the endocrine system
glands and hormones that regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. In addition to the glands, such as the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, hormones are released into the bloodstream to target organs.
how does the flight or fight reaction occur
the stressor is perceived
the hypothalamus activates the pituitary gland and triggers activity in the sympathetic branch of the ANS
the ANS transfers from the resting state (parasympathetic) to its aroused state (sympathetic)
the stress hormone adrenaline is released into the blood stream
this stimulates reactions in the body such as an elevated heart rate
this response is immediate and automatic
once the threat has passed, the body returns to the parasympathetic state.
what did Broca and Wernicke cause
a paradigm shift from supporting a holistic approach to the mind, to the localisation of function
what is the holistic approach
looking at the body as a whole picture
what is the localisation of function
the idea that specific parts of the brain are responsible for specific functions
what is lateralisation
that body functions are more dominantly controlled by one hemisphere of the brain.
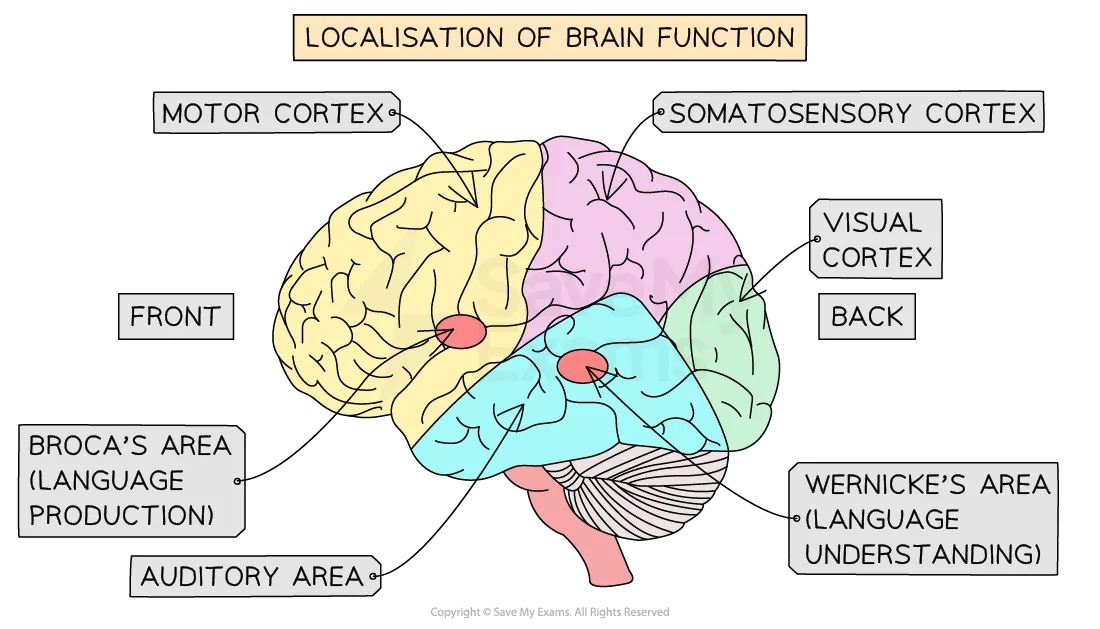
what are the four centres of function in the brain
motor
somatosensory
visual
auditory
what/where is the motor centre
The area of the brain responsible for the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
found at the back of the frontal lobe
what/where is the somatosensory centre
The part of the brain that processes sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
It is located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe.
what/where is the visual centre
The region of the brain responsible for processing visual information, including shapes, colours, and motion.
It is primarily located in the occipital lobe.
what/where is the auditory centre
The area of the brain that processes auditory information, including sound frequency and rhythm.
It is mainly located in the temporal lobe.
what/where is the Broca area
The region of the brain responsible for speech production and language processing, crucial for forming coherent sentences.
it is primarily located in the left frontal lobe.
what are the symptoms of Broca’s aphasia
Broca's aphasia is characterized by difficulty in speech production, including halting speech, poor grammar, and trouble forming complete sentences while comprehension remains relatively intact.
what/where is the Wernicke area
The area of the brain involved in understanding and processing spoken and written language.
It is primarily located in the left temporal lobe.
what are the symptoms of Wernicke’s aphasia
Wernicke's aphasia is characterized by fluent but nonsensical speech, lack of meaningful content, and difficulty comprehending language, while speech production is typically preserved.
what are the 4 lobes of each hemisphere
evaluate localisation of function
+ evidence from neurosurgery
+ case study evidence
+ evidence from brain scans -
COUNTERPOINT - karl lashely (1950)
- language localisation questioned
strengths of localisation of function
P - neurosurgery evidence
E - damage to specific areas of the brain have been linked to mental disorders. Dougherty et al (2002) found that in 44 OCD patients who underwent cingulotomy, 30% met the criteria for successful response to the procedure.
E - so shows that OCD is linked to the cingulate gyrus, and that separate parts of the brain are used for different functions
P - brain scan evidence
E - Petersen et al (1988) used scans to demonstrate how Wernicke’s area was active during a listening task
E - So showing the specific functions and supporting the localisation of function theory. - COUNTERPOINT
P - case study evidence
E - Phineas Gage (1848) blasting rock for railway, tamping iron used to pack explosives went through his left cheek, passing behind his left eye and exiting from the top of his head - removing a large portion of his temporal lobe. survived, but his personality changed dramatically from calm to quick tempered.
E - this supports localised function as damage/loss of the frontal lobe changed his mood and ability to regulate mood, suggesting that that function is specific to that area.
limitations of localisation of function
COUNTERPOINT -
P - research
E - Lashley (1950) - removed 10% - 50% of rats cortexes that were learning the way through a maze. No area seemed more useful
E- suggesting a more holistic process
P - language may not be localised
E - Dick and Tremblay (2016) found only 2% of modern researchers think that language is exclusive to Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas. fMRI means that now we can see a holistic representation of brain function when language functions take place. areas such as subcortical regions and the thalamus have been noted.
E - this is a representation of holistic functioning in humans as well, so rejects the idea of purely localised functions in the brain
how are the two hemispheres wired
in a contralateral way - left controls right of the body and vice versa
what connects the two hemispheres
The corpus callosumis a wide band of neural fibers
what are the left brain functions
reasoning
number skills
written language
spoken language
scientific skills
right-hand controls
what are the right brain functions
insight
3D forms
art awareness
imagination
left-hand control
music awareness
which hemisphere does the LVF send info to
left visual field goes to the RH and vice versa
who pioneered split brain research
Roger Sperry
outline Sperry’s procedure
(1968)
11 Ps who had undergone a split brain procedure - had their corpus callosum severed
focused on a point and stimuli were shown on either side, sending information to each hemisphere separately
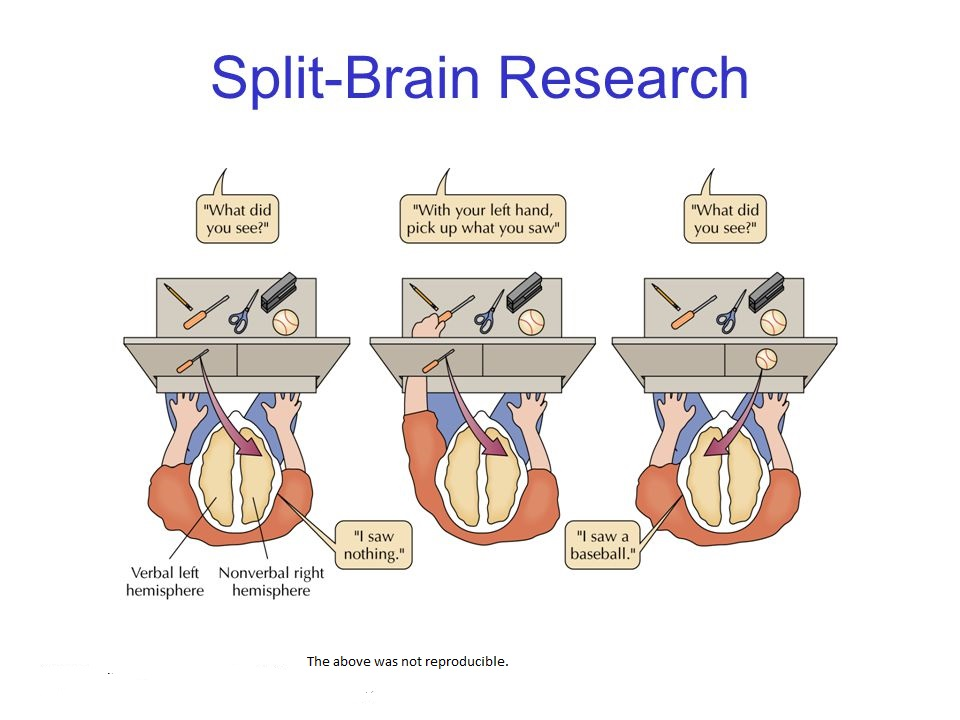
outline Sperry’s findings
when LVF shown stimuli, RH couldn’t verbalise the information , but with the left hand (controlled by the RH) they could identify associated or matching stimuli.
also found that Ps would say they didn’t see anything, but sometimes the stimuli would elicit an emotional response
when RVF shown stimuli, the LH (where the speech an d language centre is focused) allowed the Ps to verbalise the stimuli they saw.
conclusions from Sperry’s research
supports hemispheric lateralisation
LH - speech centre focused
RH - emotional processes focused
evaluate Sperry’s research
+ research support - Luck et al (1989)
+ high internal validity
- issues with generalisation
- ethics
strengths of Sperry’s research
P - research support
E - luck et al (1989) found that split brain patients perform better in some tasks - as left brain is not watering down the right brain
E - so supports theory that two have separate functions
P - high internal validity
E - as controlled lab setting, and clearly testing what it intended to test
E - so little to confound results
limitations of Sperry’s research
P - generalisation issues
E - the control group used were neurotypical, as all of the split brain patients all have the procedure to cure severe epilepsy this means that the data is difficult to apply to the population as epilepsy is an extraneous variable
E - as it may not represent the general population's brain functionality.
P- ethics
E - trauma from major brain surgery may have influenced their ability to give informed consent, and testing is over many years, so could cause stress or inconvenience.
what is brain plasticity
the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
what is the term for strengthening frequently used connections, and deleting rarely-used connections
synaptic pruning
how does brain plasticity change
more synaptic connections in infancy - peaks at 2-3 with double an adult (15,000)
what studies were done into brain plasticity
Maguire et al (2000)
conducted a study on London taxi drivers, showing larger hippocampi due to spatial navigation experience. she believed that taking the knowledge changed the structure of their brains - and the longer they’d been a taxi driver the more extreme the structural difference
Draganski et al (2006) - imaged students brains 3 months before and after a test. changes were seen in the hippocampus and parietal cortex
what is functional recovery
an example of plasticity
when healthy brain areas take over the functions that the damaged areas were in control of. This can happen very quickly after injury (spontaneous recovery) which eventually slows down and therapies are used to further recovery after a few weeks-months.
what happens to the brain during functional recovery
brain rewires itself by forming new synaptic connections, and secondary neural pathways are activated to take over the damaged function. this happens by three processes
axonal sprouting - growth of new nerve endings which connect with other undamaged nerve cells - creating new neural pathways
denervation supersensitivity - when axons the perform similar functions become aroused to a higher level to compensate for the nerves lost- can sometimes lead too pain if aroused too high
recruitment of homologous areas - areas on the opposite hemisphere of the brain taking over the function of the damaged area, aiding in recovery. - after time this can shift back
evaluate brain plasticity
P - negative plasticity
E - Medina et al (2007) - brains adaptation to prolonged drug use leads to poorer cognitive functioning in later life, and increases the risk of dementia
E - so can also harm the brain
P - age and plasticity
E - Bezzola et al (2012) - how 40 hours of golf training caused changes in neural representations of movement in Ps aged 40-60 (reduced motor cortex activity - more efficient)
E- so shows that can occur at any age
P - seasonal brain changes
E - animals brains structures shrink during spring and expand in autumn - most experiments on songbirds so not super generalisable
evaluate functional recovery
P - real world application
E - understanding has contributed to neurorehabilitation. new therapies were developed based on axon growth. e.g constraint-induced movement therapy
P - cognitive reserve
E - Shneider et al (2014) says that the higher a persons cognitive reserve (or level of education) the higher their chance of disability free recovery.
40% with DFR had more than 16 years of education
10% with DFR had less than 12 years of education
E - so recovery is more likely for people with higher levels of education
what are the techniques for investigating the brain
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
electroencephalography (EEG)
event related potential
post-mortem examinations
what is functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
detects change in the O2 conc. of blood that occur as a result of brain activity.
more active areas require more O2 so blood flow is directed there - called the haemodynamic response
what is electroencephalography (EEG)
measures the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
the scan recording represents the pattern of brainwaves generated by the action of thousands of neurons to give an overall measure of brain activity
disorders can be diagnosed by recording unusual arrhythmic patterns (Alzhimers, epilepsy, sleep disorders)
used for ; sleep studies, determining death, measuring the depth of amnesia=
what does DARE stand for (EEG)
D - detects
A - amplifies
R - records
E - electrical activity
what is event related potential
(ERP) is a measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event, typically obtained through EEG. ERPs are used to assess cognitive processes and brain function related to specific tasks.
what are post-mortem examinations
Post-mortem examinations are procedures performed on the deceased to investigate the cause of death or study disease processes and brain structure.
evaluate functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
P - does not rely on radiation
E - non invasive and risk free if done correctly.
P - high spatial resolution
E - can depict details up to 1mm so localisation can be shown in smaller areas
P - more expensive than others
P - poor temporal resolution
E - has around a 5 second time-lag so actual patterns cannot be recorded in real time
evaluate electroencephalography (EEG)
P - high temporal resolution
E - can detect at resolution of a single millisecond. so useful in conditions diagnosis eg. epilepsy (random bursts of brain activity).
P - generalised data
E - information from thousands of neurons. so cannot pinpoint neural activity exactly. so activity cannot be distinguished from the origin and adjacent locations
evaluate event related potential
P - ERPs are more specific than EEGs.
E - ERPs are are taken from EEG measurements, have excellent temporal resolution (better than fMRI)
E - so is used to measure cognitive functions and deficits
P - lack of standardisation
E - methodology differs between research studies
P - conditions
E - background noise must be removed and extraneous material must be removed - difficult to achieve
evaluate post-mortem examinations
P - provided foundation for research
E - broca and wernicke relied on post mortems before neuroimaging was possible
P - observed damage origin
E - could be due to unrelated trauma or decay
P - ethics
E - consent is difficult as family member would have to - can’t always give informed consent whilst grieving
what are circadian rhythms
Biological processes that cycle in a 24-hour period, eg, sleep cycle or core body temperature
what are is another name for the bodies internal clock
endogenous pacemakers
what are exogenous zeigebers
external changes that effect biological rhythms, such as light and temperature.
what is an infradian rhythm
A biological rhythm that occurs over a period longer than 24 hours, such as the menstrual cycle or seasonal affective disorder.
what is an ultradian rhythm
A biological rhythm that occurs in less than 24 hours, such as the sleep cycle.
what is meant by a free-running cycle
A biological rhythm that is not influenced by external cues, such as light or temperature, and continues at its natural pace.
outline research studies into exogenous and endogenous studies
Siffre (1962) - examined the impact of isolation on circadian rhythms by living in a cave for two months, finding that his biological clock naturally settled to one beyond the 24-hour cycle (roughly 25 hours). But still continued to sleep and wake regularly
Aschoff and Wever (1976) - studied participants in a WW2 bunker without natural light, finding that most had circadian rhythms between 24 and 25 hours (bar one - 29 hours) supporting the existence of endogenous clocks.
Simon Folkard (1975) - 12 people lived in a dark cave for 3-weeks but went to bed when the clock said 11:45 and woke when it said 7:45. Researches gradually increased the speed of the clock covertly from 24 to 22 hours. only one Ps was able to adapt to the shorter cycle. This shows that exogenous zeitgebers cannot easily override free-running circadian rhythms.
what is the SCN
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a group of cells in the hypothalamus that regulates circadian rhythms by responding to light signals and controlling the release of hormones like melatonin.
evaluate circadian rhythms
Shift work - COUNTERPOINT - research was correlational
medical treatment
individual differences
shifting the school day
gender bias
research not generalisable
strengths of circadian rhythms
P - shift work studies
E - Boivin(1996) found that night shift workers experienced a lighter incidence level at around 6am - a circadian trough - as concentration levels are down. as well as higher rates of heart disease
E -so proves that the cycle is represented in real life and generalisable environments - COUNTERPOINT
P - Medical treatment
E - has lead to the field chronotherapeutic or how treatments can be administered to best suit a patients biological rhythms. e.g. aspirin for heart attacks is taken at night as heart attacks are most common in the morning
E - so it can improve the effectiveness of treatments
P - Shifting school start times
E - 2014 - Research shows that later start times can improve academic performance and reduce sleep deprivation in adolescents.
E - This highlights how adjusting schedules in accordance with circadian rhythms can lead to positive outcomes.
limitations of circadian rhythms
COUNTERPOINT -
P - these studies used correlational methods
E - so it is difficult to establish whether these changes were caused by the disruption of the sleep-wake cycle or if its due to environmental factors such as seclusion from socialising and an altered eating pattern as a result of the lifestyle change
E - so could not be as important as they claim
P - individual differences
E - most studies done on small samples. Czeisler et al (1999) found individual differences between sleep cycles ranging from 13-65 hours
E - so the research of some participants cannot be applied to everyone’s biological rhythms
outline procedure of Reinberg (1967) study into infradian rhythms
woman who spent 3 months in a cave with a small lamp for light.
outline findings of Reinberg (1967) study into infradian rhythms
her menstrual cycle shortened from 28 days to 25.7 days
So with the lack of light (exogenous zeitgeber) her infradian rhythm changes
this suggests that external factors have an effect on infradian rhythms
evaluate Reinberg (1967) study into infradian rhythms
only one participant
menstrual cycle varies naturally
research support
outline procedure of Russell et al (1980) study into infradian rhythms
sweat (pheromones) were taken from one group and applied to the upper lip of a separated second group
outline findings of Russell et al (1980) study into infradian rhythms
the study found that the menstrual cycles of women who were exposed to these pheromones synchronized with the cycles of the donor.
evaluate Russell et al (1980) study into infradian rhythms
small sample size affected generalizability
supports the role of pheromones in synchronizing cycles
questions about ecological validity of laboratory settings
factors effecting cycle - stress, weight, age, diet
outline Penton-Volk et al (1999)
study into infradian rhythms, where women expressed a preference for feminised faces at the least fertile stages of the cycle, but more masculine faces at fertile points.
so women’s sexual drive/ behaviour is effected by their infradian rhythms
what is SAD
Seasonal Affective Disorder
a depressive disorder triggered by reduced sunlight during winter months.
what are the symptoms of SAD
low mood
fatigue
irritability
social withdrawal
changes in sleep and appetite
lack of interest in in life
what type of circadian rhythm is SAD
SAD is classified as a circannual rhythm (annual cycle)
which hormone contributes to SAD
Melatonin - sleepy hormone, triggered by a lack of light stimuli
this is thought to have a knock-on effect on serotonin levels
what are the four steps
light exposure triggers signal from retina to superchiasmatic nucleus (pacemaker)
signal relayed by the pineal gland
pineal gland secretes melatonin
too much melatonin may effect serotonin levels
evaluate SAD
P -real world application
E - light therapy where a persons body clock is stimulated by artificial light has helped to reduce the SAD symptoms in 80% of Ps - Sanassi (2014)
E - so proves that a lack of light, and melatonin production causes depressive symptoms
COUNTERPOINT
E - Rohan et al (2009) recorded a relapse rate of 46% the following winter after light therapy, compared to the 23% relapse rate of those who received CBT.
E - so not purely hormone based
evaluate the menstrual cycle
P - evolutionary basis
E - can be explained by natural selection, synchronisation would have been advantageous as it would allow women to get pregnant at the same time, so if any women died in childbirth, others were lactating and could support the orphaned baby.
E - so suggests that the trait would help avoid selection pressures and would be inherited
P - methodological limitations
E - research into synchrony were full of confounding variables, such as stress, diet, exercise/fitness ect. so explains why other studies have failed to replicate - 1993
evaluate infradian rhythms
P - improved understanding
E -has helped to understand the age related changes to sleep patterns. SWS reduces with age, so growth hormones are reduced in older people, as they are produced in the SWS.
E - this can be applied to understanding lower energy in older people and treated with relaxation and medication.
P - the sleep lab
E - little extraneous variables as in a controlled lab environment.
E - however, the artificial settings may not reflect true sleep patterns.
P - individual differences
E - variation between participants. tucker (2007) found variation between the duration of each sleep stage. - particularly stages 3 and 4. tucker determined these differences to be biologically determined.
E - so the results and research has limited generalisability.
what are the 5 stages of the sleep cycle
light sleep - easily woken, and brain waves are high frequency and have a short amplitude (alpha waves)
the alpha waves continue but there are occasional random changes in the pattern called sleep spindles
and 4. then enter deep sleep or slow wave sleep (SWS) when the brain waves are delta waves - lower frequency and higher amplitude.
X
REM sleep - body is paralysed but brain activity almost mimics the awake mind. the brain produces theta waves and includes rapid eye movement - REM
what type of rhythm is the sleep cycle
ultradian - as its duration is less than 24 hours
what is the SCN
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a small region of the hypothalamus that regulates circadian rhythms by responding to light information and helping to control the sleep-wake cycle.
outline research into SCN in animals
DeCoursey et al (2000)
destroyed the SCN connections in 30 chipmunks who were then returned to the wild and observed for 80 days
sleep wake cycle disappeared in all before the end of the study and many had been killed by predators
Ralph et al (1990)
found that when they bred mutant hamsters with a 20-hour circadian rhythm and transplanted their SCN into normal hamsters, the recipients exhibited the same 20-hour rhythm, indicating the SCN's role in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
what is the pineal gland
The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland located behind the hypothalamus that produces melatonin, so is an endogenous mechanism
what is melatonin
a hormone produced at the end of the day and is inhibited in the day (light stimulus)
can cause SAD if too much - during the winter
evaluate endogenous pacemakers
P - beyond the master clock
E - peripheral oscillators are circadian rhythms influenced by the SCN but not directly and also act independently. Damiola (2000) showed how changing feeding patterns of mice could alter the circadian rhythm in the liver by up to 12 hour, whilst leaving the SCN rhythm unaffected.
E - so there are other complex influences on the sleep-wake cycle
P - ethics
E - animal studies are ethically flawed as removed the SCN understanding that it would negatively impact their chance of survival - also a permanent change
P - interactionist system
E - cannot be studied in isolation. so influenced by others, but no one is completely alone so solo studies (Siffe) are not generalisable