Natural Killer Cells
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
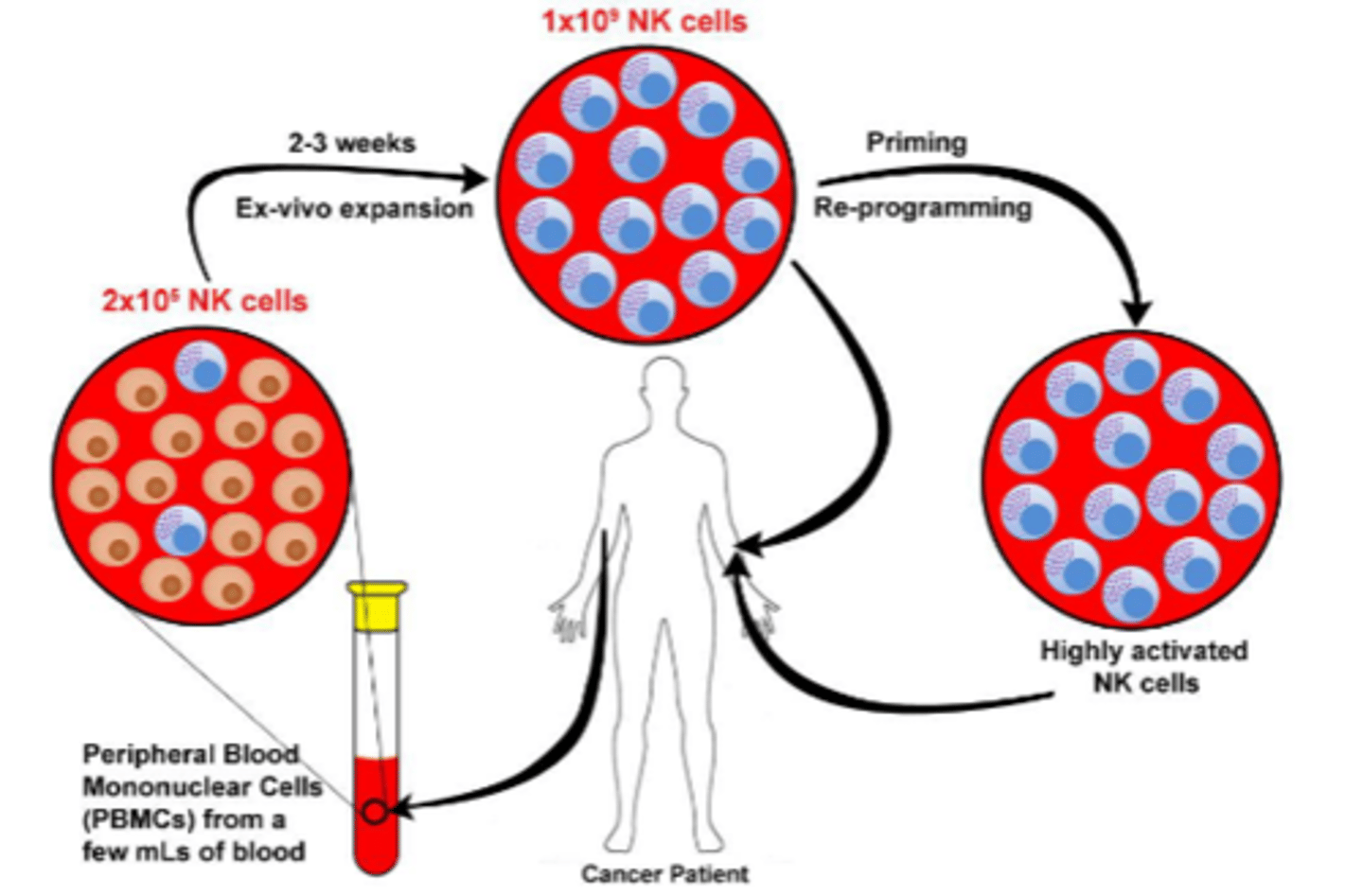
1. blood is taken from the host
2. NK cells are purified in the sample
3. NK cell activtion -> production of a lot of NK cells
4. NK cells are incubated with cytokines and re-programmed with certain targets in order to find certain targets
5. NK cells are administered back to host for elimination/minimizing of tumors
Describe Natural Killer Cell Immunotherapy
blood
spleen
liver
Where are NK cells found?
they migrate in large numbers when an inflammatory reaction is underway
When do NK cells migrate to tissues?
no
Do NK cells have antigen receptors like T and B cells?
1. chemotactic receptors
2. cytokine receptors
3. adhesion receptors
3 types of receptors found on NK cells
bind to chemokines released by other cells to move to area of infection
What is the function og chemotactic receptors on NK cells?
activate NK cells
What is the function of cytokine receptors on NK cells
adhere to endothelium of blood vessels to enter tissue and leave blood vessel
What is the function of adhesion receptors on NK cells
Large granular lymphocytes (LGL)
What is another name for NK cells
they resemble lymphocytes -> have large nucleus
Why are NK cells called LGL's?
cytotoxic granules
What do NK cells contain
bone marrow
Where do NK cells originate from?
~1 week
How long do NK cells live for?
innate immunity
***however some of them have memory capabilities
What arm of immunity are NK cells a part of?
CD56
CD16
CD3
3 markers for ID of NK cells in vitro of mice and humans?
Fc receptor
What kind of receptor is CD16?
CD2+
CD8+
CD3+
NKp46
4 markers for ID of NK cells in vitro of pigs
CD335
NKp46
2 markers for ID of NK cells in vitro of cattle
1. kill virus infected cells, tumor cells, and stressed cells **abnormal cells
2. cytokine and chemokine production
2 main roles of NK cells in innate immunity
IFN-gamma
TNF-aplha
IL-17
IL-22
4 cytokines and chemokines are produced by NK cells
regulate the function of other cells
What is the end goal of cytokine and chemokine production?
the abnormal cells alter expression of certain cell surface markers
How are abnormal cells detected by the NK cells?
Major HIstocompatability Complex (MHC1)
What do normal cells express on their surface to protect them from NK cells?
only nucleated cells
Is MCH class 1 found on all normal cells?
it is supressed
In nucleated cells that are infected, what happens to their MHC class 1?
they often fail to express MHC 1
How are tumors detected by NK cells
tumors are smart! They are learning to express MHC1!
Problem with tumors and MHC 1
MHC 1 chain related A (MICA)
MHC 1 chain related B (MICB)
Rae-1
H60
What is expressed on stressed cells to tell the NK cells that something is wrong
they have 2 types of recognition receptors
How do NK cells recongize these abnormal cell expressions?
1. activating receptors
2. inhibitory receptors
2 types of recognition receptors found on NK cells
by a balance between signal of their activting and inhibitory receptors
How are NK cells regulted?
recongize stress proteins on the cell surface and lead to the killing of the target cells
What is the function of activating receptors
recognized MHC 1 and preserves the target cell
What us the function of inhibitory receptors?
activating signals are typically blocked by inhibitory signals -> if the call is expressing MHC 1 they will be preserved regardless of if they are presenting stress proteins
How do activating and inhibitory receptors regulate the NK cells?
Killer cells immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIRs)
CD158
MCH1 receptors in humans, cattle, dogs, and pigs
Killer Cell lectin-liek receptors (KLRs)
MHC 1 receptors in mice, rats, and horses
type1 transmembrane proteins
What type fo receptors are KIRs?
leokocytes immunoglobulin like receptors (LILRs)
NKp46
2 other important members of the type 1 transmembrane protein receptor family
NK cells
subset if lymphocytes
What 2 cells are KIRs expressed on?
NK cells
leukocytes
What 2 cells are LILRs expressed on?
NK cells
What is NKp46 expressed on?
NKG2D
Special lectin-like receptor expressed on NK cells
stress proteins:
MICA
MICB
ULBP
Rae-1
MULT1
H60
What does NKG2D recognize
this overides the inhibitory signal through MHC 1 and permis NK cell cytotoxicity
What happens when NKG2D binds to a high amount og stress proteins expressed on a cells surface?
gamma-delta T cells
Where else is NKG2D expressed?
it is the only activating receptor that is known to overise the dominating inhibitory signal
What is special about NKG2D
1. lysis of infected, stressed, or transformed cells
2. activation of macrophages through secretion of cytokines
2 effector functions of NK cells
IL-12
What chemokines are released by macrohage to pull NK cells to it?
INF-gamma
What cytokines are released by NK cells to activate and increase the killing capacity in the macrophage?
1. perforin dependent mechanism
2. CD95/CD95L (Fas/FasL) mechanism
3. CD16 killing pathway
3 NK cell cytotoxicity mechanisms
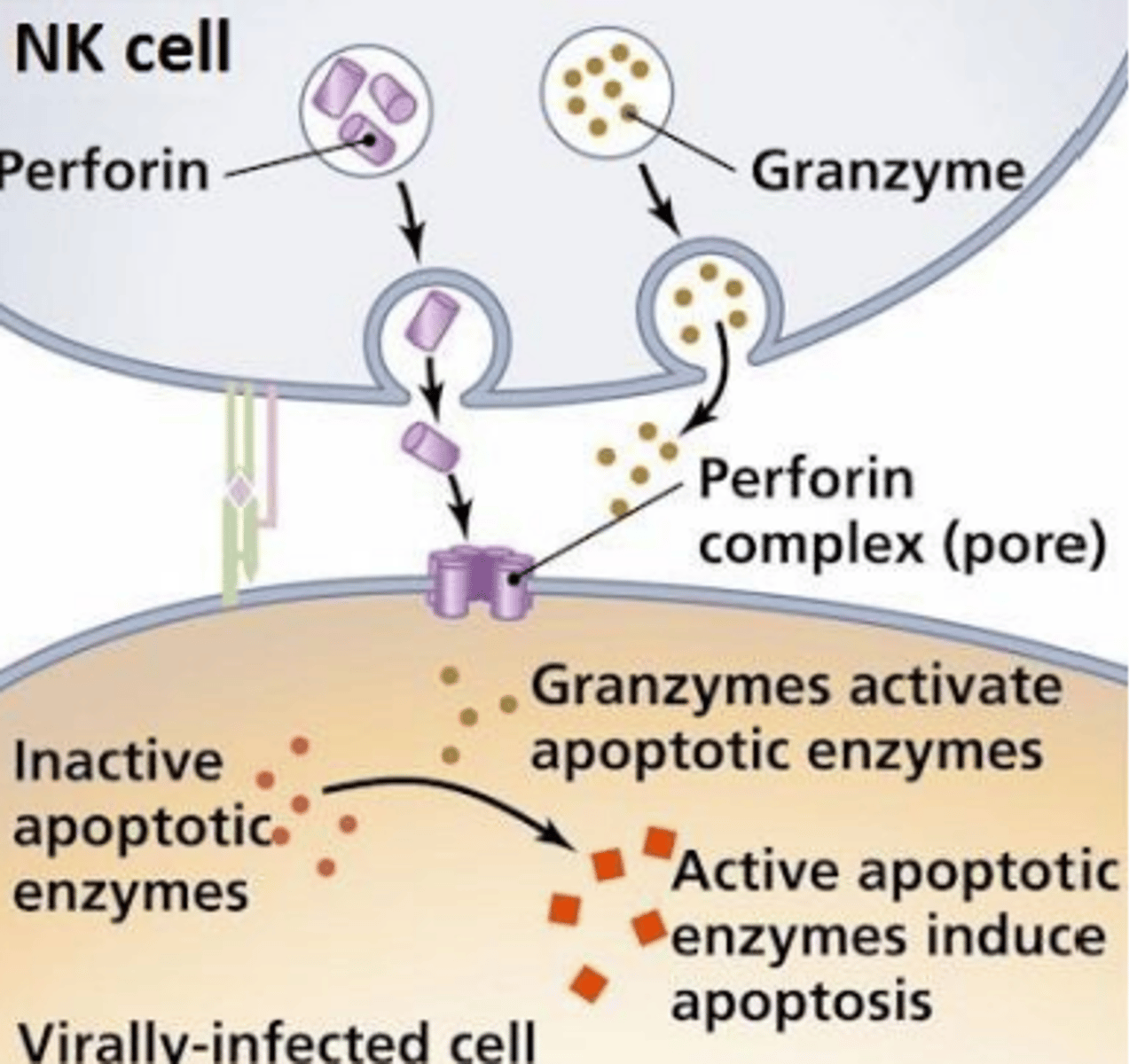
1. NK cell is triggered by activating receptor and released perforin (protein) from its pranules
2. perforin combines to create a lesion in the target cell membrane called the perforin channel
3. Granulysin, NK-lysin, and fragmentin are released from cytotoxic granules and are passed through perforin channels
4. Granzymes and protease induce apoptosis of the target cell
Perforin dependent mechanism
1. CD95L are expressed on NK cell surface
2. CD95 are highly expressed on target cells
3. binding of CD95L to CD95 induced apoptosis of the target cell
CD95/CD95L (Fas/FasL) mechanism
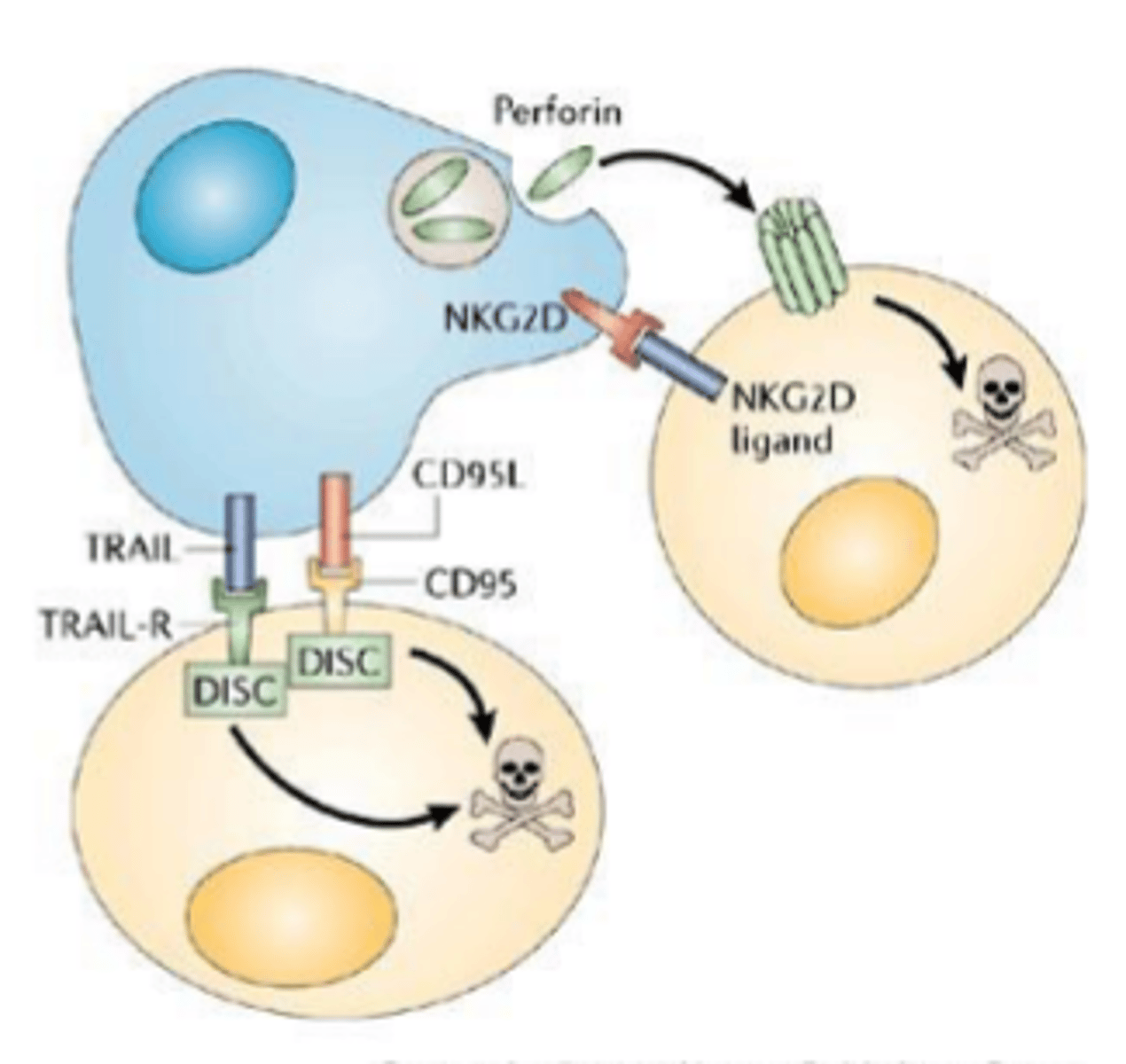
antibodies - CD16 is an Fc recepros
What is the CD16 killing pathway depending on
1. FAB side of antigen binds to an antigen on an infected cell
2. NK cells bind to the Fc side of the antibody using CD16 Fc receptors
3. after binding the NK cell will start cytotoxicity actions
CD16 killing pathway
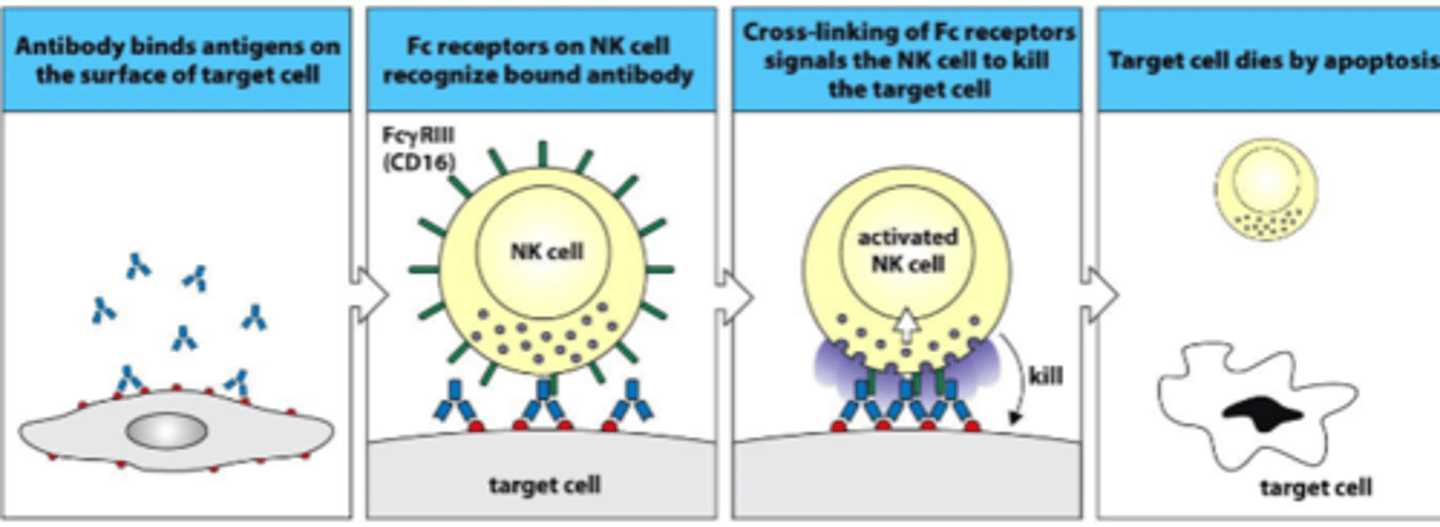
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity ADCC
What is another name for the CD16 killing mechanism
IL-1
IL-2
IL-12
IL-15
IL-18
IL-21
type 1 IFN
type 2 IFN
What cytokines activate NK cell activity
lead to efficient killing
What do cytokines lead to in NK cells
lymphokine activate killed cells (LAK)
When in vitro, NK cells are isolated and treated with cytokines which turns them into
they are highly cytotoxic cells that have the potential to be used in immunotherapy of tumors
What is the consequence of NK cells being activated into lymphokine activated killed cells (LAK)
Foot and mouth disease in swine
What is an example of a virus that can inhibit NK cell cytotoxocity?
they are simialr to NK cells and t lymphocytes
Why are NKT cells special
alpha/beta TCR
NK1.1
other KLR family receptors
potentially CD4- or CD8-
What 4 things can be expressed on the surface of NKT cells?
glycolipid antigens on bacteria
What do NKT cells recognize
IL-15
What cytokine activated NKT cells?
link the T cell system and NK cells
What is the main function of NKT cells?
allergies
antitumor immunity
autoimmunity
antimicrobial immunity
What immune roles do they play a part in?
Natural killer dendritic cells
-dendritic cells that share some properties with NK cells
What are NK DCs?
NK1.1
CD11c
What 2 markers do NK DCs express?
a NK cell marker
What kind of marker is NK1.1?
DC marker
What kind of marker is CD11c
spleen
liver
lymph nodes
thymus
Where are NK DC found in the body?
1. they spntaneously lyse tumor cells
**NK cell function
2. present antigen to naive T cells
**DC function
What are the 2 action of NK DCs?
IFN gamma
What is produced in arge amounts by NK DCs?
TLR 9
What stimulates NK DC to produce IGN gamma
they link the innate and adaptive immunity
Why are NK DCs so important