MCAT Biology - Embryogenesis and Development
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Ultrasonography
a radiographic technique performed by placing a probe that emits high-frequency sound waves near the tissue to be examined
fertilization
the formation of a diploid zygote from the union of a sperm and an ovum
ampulla
the widest part of the fallopian tube where fertilization occurs
acrosomal apparatus
tube-like structure when sperm comes into direct contact with the secondary oocyte’s cell membrane
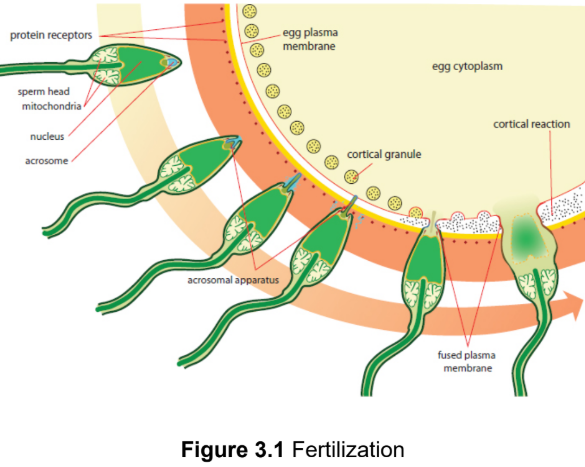
cortical reaction
a release of calcium ions depolarize the membrane of the ovum to prevent fertilization of the ovum by multiple sperm cells and increases the metabolic rate of the newly formed diploid zygote
zygote
the diploid cell resulting after fertilisation
fertilization membrane
depolarized and impenetrable membrane of the secondary oocyte
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins
fertilization of two different eggs released during one ovulatory cycle by two different sperm; each placenta (may grow onto each other), chorion, amnion; as genetically distinct as regular siblings
Monozygotic (identical) twins
a single zygote splits into two; may share placenta, chorion, placenta; genetic material/genomes identical
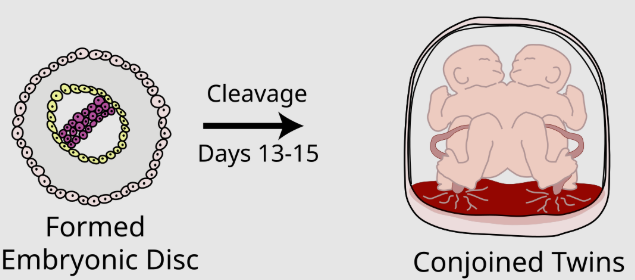
conjoined twins
two offspring are physically attached due to poor division of zygote
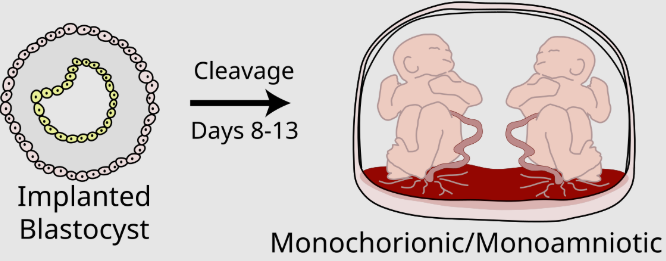
Monochorionic/monoamniotic twins
share the same amnion and chorion
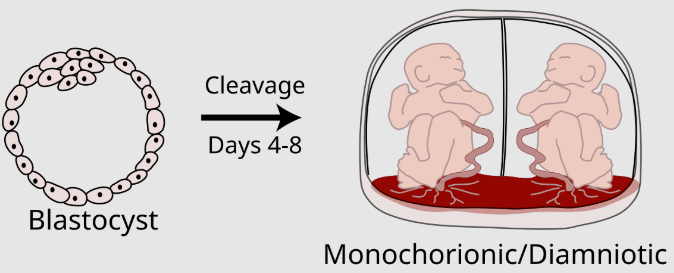
Monochorionic/diamniotic twins
each have their own amnion, but share the same chorion
Dichorionic/diamniotic twins
each have their own amnions and chorions
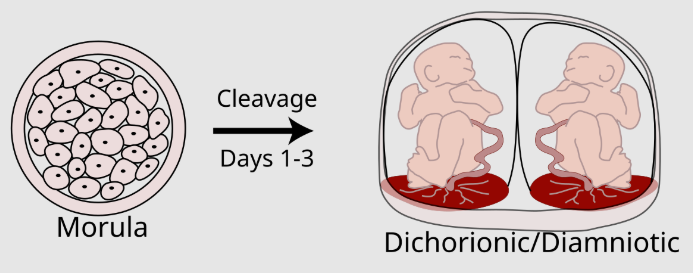
cleavage
zygote undergoes rapid mitotic cell divisions and becomes an embryo; increases two ratios: the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic (N:C) ratio and the surface area-to-volume ratio (more, smaller cells = same radius)
Indeterminate cleavage
results in cells that can still develop into complete organisms; totipotency
Determinate cleavage
results in cells with fates that are already determined; committed to differentiating into a certain type of cell
Differentiation
the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one, changing the structure, function, and biochemistry of the cell to match the cell type
morula
solid mass of cells causing by embryonic cleavage; Latin for ‘raspberry"‘
blastulation
morulas turns into blastula
blastula
a hollow ball of cells with a fluid-filled inner cavity
blastocoel
the fluid-filled inner cavity of a blastula/blastocyst
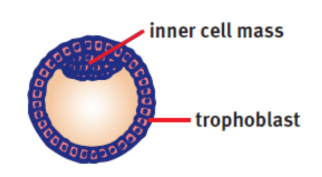
blastocyst
mammalian blastula; consists of trophoblast and inner cell mass
inner cell mass
gives rise to the organism; protrudes into the blastocoel
trophoblast
give rise to the chorion and placenta; surround the blastocoel
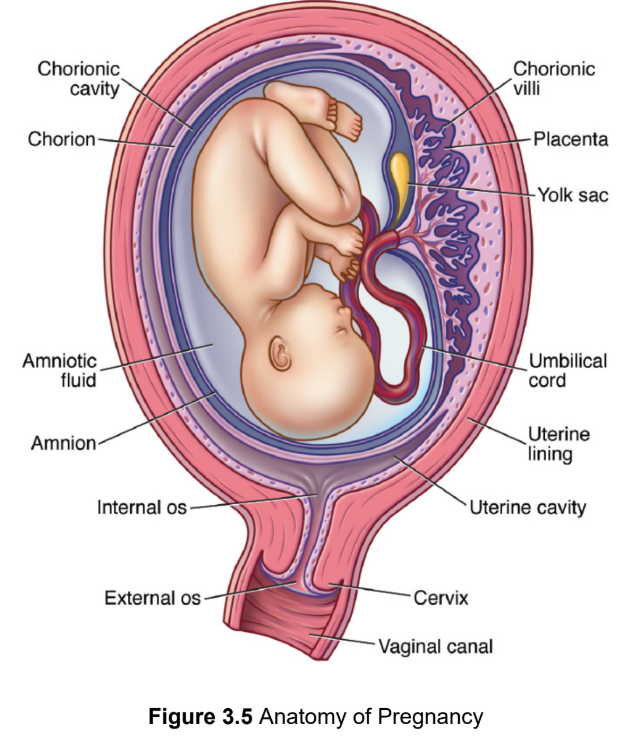
chorion
extraembryonic membrane that develops into the placenta
chorionic villi
microscopic finger-like projections that penetrate the endometrium; support maternal-fetal gas exchange, form from trophoblasts
umbilical cord
two arteries and one vein encased in a gelatinous substance that connects the embryo to the endometrium
ectopic pregnancy
blastula implants outside the uterus; >95% in the fallopian tube; often a surgical emergency
yolk sac
supports and nourishes embryo before placental site of early blood cell development
allantois
early fluid exchange between the embryo and the yolk sac; forms part of the umbilical cord
amnion
a thin, tough membrane filled with amniotic fluid that acts as a shock absorber and contains fetal cells that can be examined for chromosomal abnormalities as well as sex determination
Amniocentesis
process of aspirating amniotic fluid by inserting a thin needle into the amniotic sac; test for sex determination and chromosomal abnormalities
gastrulation
the generation of three distinct cell layers; occurs after implantation
gastrula
blastula after invagination and differentiation
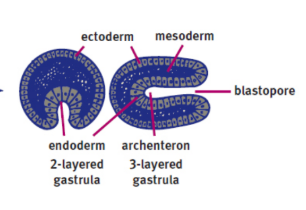
archenteron
the membrane invagination into the blastocoel; develops into the gut
blastopore
the opening of the archenteron
deuterostomes
blastopore develops into the anus
ex. humans
protostomes
blastopore develops into the mouth
primary germ layers
three layers of cells in the gastrula
ectoderm
outermost layer of gastrula; gives rise to the integument
epidermis
hair
nails
epithelia of the nose, mouth, lower anal canal
lens of the eye,
nervous system (including adrenal medulla)
inner ear
mesoderm
middle layer of gastrula
musculoskeletal
circulatory
excetory
gonads
mucular and connective tissue layers of of the digestive and respiratory systems and the adrenal cortex
endoderm
innermost layer of gastrula
the epithelial linings of the digestive and respiratory tracts
lungs
pancreas
thyroid
bladder
distal urinary tracts
parts of the liver
selective transcription
only the genes needed for that particular cell type are transcribed
induction
the ability of one group of cells to influence the fate of nearby cells
inducers
by chemical substances which diffuse from the organizing cells to the responsive cells
organizing cells
cells that secrete inducers
responsive cells
cells that receive and respond to inducers
neurulation
development of the nervous system
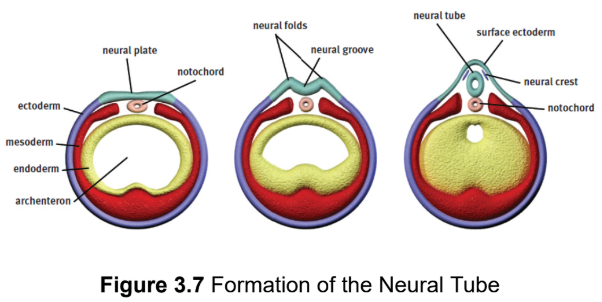
notochord
a rod of mesodermal cells; forms along the long axis of the organism like a primitive spine; induces a group of overlying ectodermal cells to slide inward to form neural folds surrounding a neural groove
neural tube
gives rise to the central nervous system
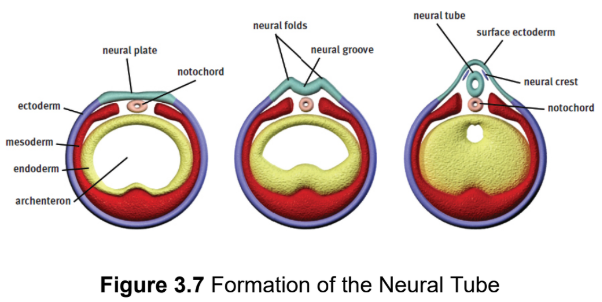
neural crest cells
migrate outward to form the peripheral nervous system (including the sensory ganglia, autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla, and Schwann cells) as well as specific cell types in other tissues (such as calcitonin-producing cells of the thyroid, melanocytes in the skin, and others); found at the tip of each neural fold
spina bifida
some or all of the spinal cord may be exposed to the outside world as result of a failure of the neural tube to close; range from no significant distress to death; prevented by folate supplements
anencephaly
the brain fails to develop and the skull is left open as result of a failure of the neural tube to close; universally fatal; prevented by folate supplements
Teratogens
substances that interfere with development, causing defects or even death of the developing embryo; will not have the same effect on every embryo or fetus
ex. alcohol, prescription drugs, viruses, bacteria, environmental chemicals including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
pregnant individuals with diabetes and hyperglycemia
fetus that is too large to be delivered and that could become hypoglycemic soon after birth due to synthesising lots of insulin to compensate for high levels of sugar in utero
specification
initial stage of cell specialization in which the cell is reversibly designated as a specific cell type
determination
the iireversible commitment of a cell to a particular function in the future
morphogens
specific molecules secreted by neighbouring cells that cause neighboring cells to follow a particular developmental pathway
ex. transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), sonic hedgehog (Shh), and epidermal growth factor (EGF)
stem cells
cells that have not yet differentiated or that give rise to other cells that will differentiate
potency.
determines the tissues a particular stem cell can differentiate into
totipotent
greatest potency; can differentiate into any cell type
ex. embryonic stem cells
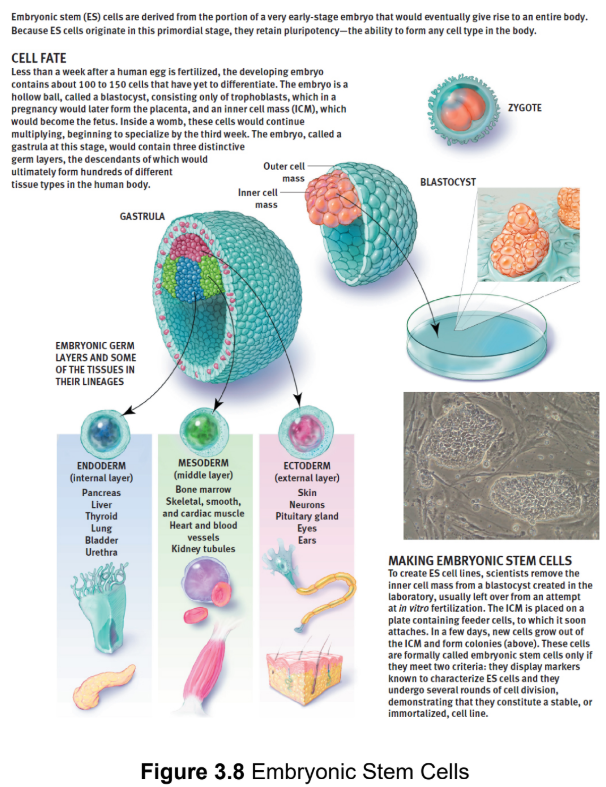
pluripotent
differentiate into any cell type except for those found in the placental
structures; blastocyst/gastrula
multipotent
can differentiate into multiple types of cells within a particular group
ex. hematopoietic stem cells - capable of differentiating into all of the cells found in blood, but not skin, nerve, or muscle
responder
cell that is induced
competent
able to respond to the inducing signal
Autocrine
signals act on the same cell that secreted the signal
Paracrine
signals act on cells in the local area
Juxtacrine
signals do not usually involve diffusion, but involve a cell directly stimulating receptors of an adjacent cell
endocrine
signals involve secreted hormones that travel through the bloodstream to a distant target tissue
growth factors
highly specific peptides that promote differentiation and mitosis in certain tissues
ex. PAX6 is expressed in the ectoderm of the head → optic vesicle approaches the overlying ectoderm producing this factor → development of the lens of the eye is induced → triggers the optic vesicle → forms the optic cup → becomes the retina
reciprocal development
two-way induction
Cell Migration
Cells must be able to disconnect from adjacent structures and go to their correct location
ex. anterior pituitary gland originates from a segment of oral ectoderm and must migrate from the top of the mouth to its final location just below the hypothalamus
Apoptosis
programmed cell death; allows recycling of materials; prevents the release of
potentially harmful substances into the extracellular environment.
ex. fingers are originally webbed during development of the hand unril extra sells under go apoptosis
apoptotic blebs
the cell undergoes changes in morphology during apoptosis and divides into many self-contained protrusions
apoptotic bodies
blebs break apart into smaller pieces that are then digested by other cells
necrosis
a process of cell death in which a cell dies as a result of injury; internal substances can be leaked, causing irritation of nearby tissues or even an immune response
Regenerative capacity
the ability of an organism to regrow certain parts of the body
ex. liver - high; heart - low; kidney - moderate
complete regeneration
the lost or damaged tissues are replaced with identical tissues
ex. salamanders & newts (extensive clusters of stem cells)
incomplete regeneration
the newly formed tissue is not identical in structure or function to the tissue that has been injured or lost
ex. humans (scars)
Senescence
biological aging at the cellular and organismal level; results in the failure of cells to divide, normally after approximately 50 divisions in vitro
telomeres
ends of chromosomes; contains lots of guanine and cytosine to prevent DNA from unravelling; difficult to replicate so they shorten during each round of DNA synthesis
telomerase
reverse transcriptase that is able to synthesize the ends of chromosomes, preventing senescence; allows cells to divide indefinitely and may play a role in the survival of cancer cells
fetal hemoglobin (HbF)
greater affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin (primarily HbA); assists with the transfer (and retention) of oxygen into the fetal circulatory system
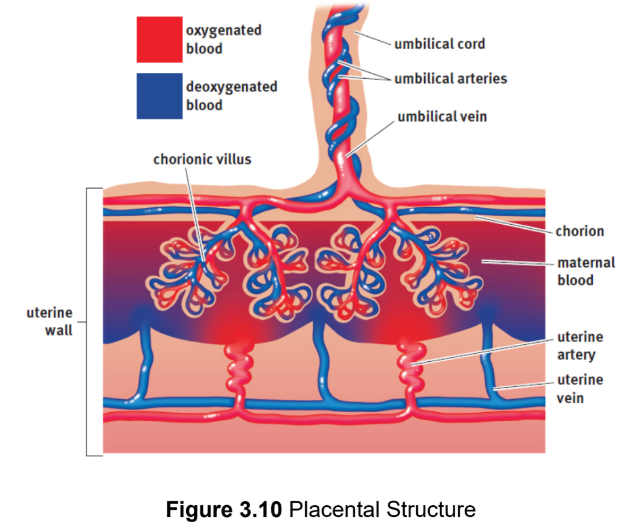
placenta
organ where nutrient, gas, antibodies and waste exchange between fetus and parent occurs; depends on the close proximity of the embryonic and maternal bloodstreams, facilitating diffusion between them without mixing; Fetal lungs do not function until birth
TORCHES infections
pathogens small enough to cross the placental barrier by diffusion
TOxoplasma gondii, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, HErpes or HIV, and Syphilis
umbilical arteries
carry blood away from the fetus toward the placenta; deoxygenated
umbilical vein
carries blood toward the fetus from the placenta; oxygenated
fetal shunts
pattern of blood flow in the heart that deviates from the normal circuit of the circulatory system to actively directblood away from sensitive organs while they develop
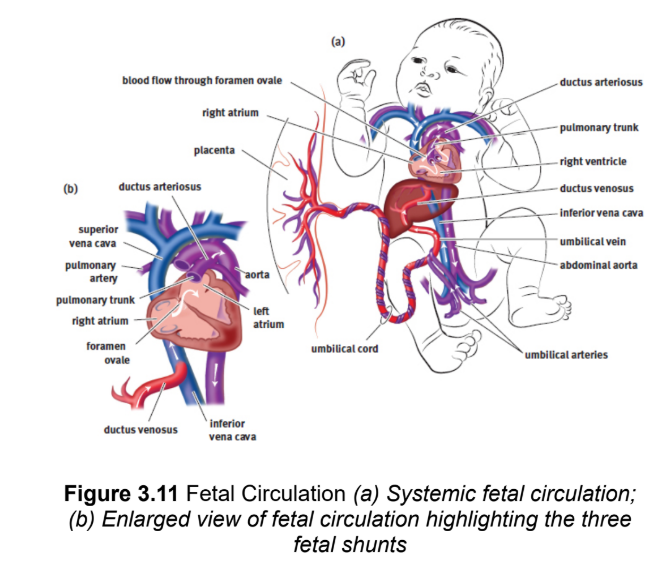
foramen ovale
one-way valve that connects the right atrium to left atrium; allows blood entering the right atrium from the inferior vena cava to flow into the left atrium instead of the right ventricle, and thereby be pumped through the aorta into systemic circulation directly; right side higher pressure until birth - reverse
ductus arteriosus
shunts leftover blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta
ductus venosus
shunts blood returning from the placenta via the umbilical vein directly into the inferior vena cava, bypassing the liver (smaller hepatic arteries exist)
Human gestation length
280 days, three trimesters
generally: larger animal, larger gestational period
first trimester
organ development
herat beat - 22 days
eyes, gonads, limbs, liver
5 weeks - 10 mm
6 weeks - 15 mm
7 weeks - cartilaginous skeleton begins to harden into bone
8 weeks - most of the organs have formed, the brain is fairly developed, embryo → fetus
3 months - 9 cm long
Second Trimester
moves in amniotic fluid
face looks human
toes an finegrs elongate
6 months - 30 - 36 cm
Third Trimester
continued rapid growth and further brain development
transport of antibodies to fetus
growth rate slows
less active
parturition
vaginal childbirth; accomplished by rhythmic contractions of uterine smooth muscle
prostaglandins
oxytocin
peptide hormone associate diwth childbirth, breatfeeding, and emotional attachment
birth process
the cervix thins out and the amniotic sac ruptures - water breaking.
strong uterine contractions result in the birth of the fetus
the placenta and umbilical cord are expelled
afterbirth
expulsion of the placenta and umbilical cord