15 bandaging and open wound management large animal
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
5 days
When does granulation tissue appear in the wound healing process?
4-6 days
When does epithelialization occur in the wound healing process?
FIRST STOP BLEEDING
What is always your FIRST GOAL when performing an initial exam for wound management in large animals?
1. b. history
2. j. initial exam, blood loss?
3. a. patient restraint
4. i. visual assessment
5. h. clean wound/surrounding tissue
6. g. wound anesthesia
7. k. wound exploration/lavage
8. l. wound debridement
9. f. wound closure
10. e. wound dressing
11. d. bandage
12. c. aftercare
Put the steps in order of large animal wound management (she's lengthy i know):
a. patient restraint
b. history
c. aftercare
d. bandage
e. wound dressing
f. wound closure
g. wound anesthesia
h. clean wound/surrounding tissue
i. visual assessment
j. initial exam, blood loss?
k. wound exploration/lavage
l. wound debridement
Physical exam
What should you perform on EVERY patient?
If the horse has gotten a tetanus shot within 2 mo. no booster needed (anything over 2 months needs a tetanus toxoid booster)
You are managing a horse with a wound. If the horse has gotten a tetanus shot within _________ months, no booster is needed.
Teiler's disease (a viral hepatitis that affects horses, aka serum hepatitis)
What is the risk of using tetanus anti-toxin in large animals?
Twitch and tranquillizers (Ace, Alpha 2 agonists like Xylazine and Detomidine, opoids like butorphanol)
Name a few restraint mechanisms for horses:
Xylazine, detomidine
Name the alpha 2 agonist (drugs which stimulate alpha 2 adrenergic receptors which decrease sympathetic nervous system = low bp, hr, etc.) drugs which are used as tranquilizers in horses?
Could be synovial structure involvement, blood supply could be involved like jugular vein or carotid artery
Why do you need to be concerned with wound location in large animals?
10^5 organisms/gram of tissue
How many organisms typically have to be involved per gram of tissue for a wound to be considered "infected"?
Foreign material present in wound, necrotic tissue, hematoma, blood supply compromise, immunosuppression
Typically, 10^5 organisms per gram of tissue are needed for a wound to be considered "infected". Name some instances where, if these things happen, less bacteria will be needed for infection.
2 inches
How far around a wound should you clip the hair?
Alcohol (on open wounds)
What antiseptic should you NOT use to clean wounds?
FALSE: most lacerations are sutured with the horse STANDING
TRUE OR FALSE: Most lacerations are sutured with the horse in lateral recumbency.
Use lidocaine/mepivacaine and local blocks (peripheral nerve block)
Why can you suture most lacerations standing in horses? What can you use?
10-15 psi (achieved using 18 ga needle on 35 or 60 mL syringe) using saline or lactated ringers
What pressure (in psi) is typically used to lavage horse wounds? What solution is used?
Perform synoviocentesis, sample the fluid, pressurize the structure, and inject antibiotics (amikacin).
ALSO you can inject sterile saline. EX: if you have a wound on the medial side, sterilely prep and insert needle with saline on LATERAL side. if it communicates with the joint, saline will come out of the wound on the medial side. if it doesn't communicate saline will come shooting back out of your needle on the lateral side
When exploring a wound in a large animal, how can you determine if there is synovial involvement?
Amikacin
Which antibiotic do you inject into a wound if you suspect there is synovial involvement?
1. sharp (with scalpel)
2. mechanical (wet-to-dry bandages, but NOT once epithelization has started)
3. autolytic (moist wound healing, WBC/enzymes degrade necrotic tissue)
What are the 3 most common mechanisms of wound debridement in large animals?
DO NOT DO once epithelization has started, around 4-6 days
At what stage of the healing process should you not use mechanical debridement in large animals?
To debride superficial layer
What is sharp debridement used for?
Observe clean versus serrated cuts (ex metal versus barbed wire). If there is higher energy on impact, there will be more tissue damage and vascular compromise
Why is it important to know the mechanism of injury when managing horse wounds?
Give tetanus toxoid (tetanus vaccine to prevent) AND tetanus anti-toxin (treatment for tetanus)
You go to a farm to treat a horse with a wound. The owner has just gotten the horse and does not know anything about its vaccine history. What should you do?
1. primary
2. delayed primary
3. delayed secondary
4. second intention healing
Name the 4 types of wound closure
Primary
Which type of wound closure is done immediately (within first 12 hours) and the owner should be warned of possible dehiscence
Delayed primary
Which type of wound closure is done within 3-5 days of the injury, before granulation tissue forms and after a period of debridement. There may be mild to moderate contamination
Delayed secondary closure
Which type of wound closure is done after granulation tissue is present, though exuberant granulation tissue must be excised first. This is not common
Second intention healing
Which type of wound closure is not actually closed by the veterinarian, as is often present with large wounds after granulation tissue is present. There may be chronic, contaminated, skin loss. Likely to dehisce (inform owner)
1. Jackson-Pratt
2. Penrose
What are the two different types of drains used in large animal to prevent accumulation of exudate that will compromise closure?
Jackson-Pratt
This type of drain is considered "closed", and fluid is sucked away from the surgical site so the device does not have to be ventral
Penrose
This type of drain is considered "open", and must be placed in the most ventral location as it uses gravity to drain fluid out of the lowest point
Nonabsorbable mono: nylon (ethilon) and polypropylene (prolene)
What suture material should you use in superficial skin in a horse?
Simple interrupted
What suture pattern should you use in non-tension areas in a horse?
Vertical mattress and near-far-far-near
What suture pattern should you use in high tension areas in a horse?
Gauze: wet-to-dry bandages, 4x4 gauze, or Kerlix AMD
What wound dressing is appropriate to use when you want to debride heavily contaminated and exudative wounds in large animals?
Gauze (Kerlix AMD) used to debride heavily contaminated and exudative wounds
What type of wound dressing (which can be used in primary layer) is this and on what type of wounds should it be used?

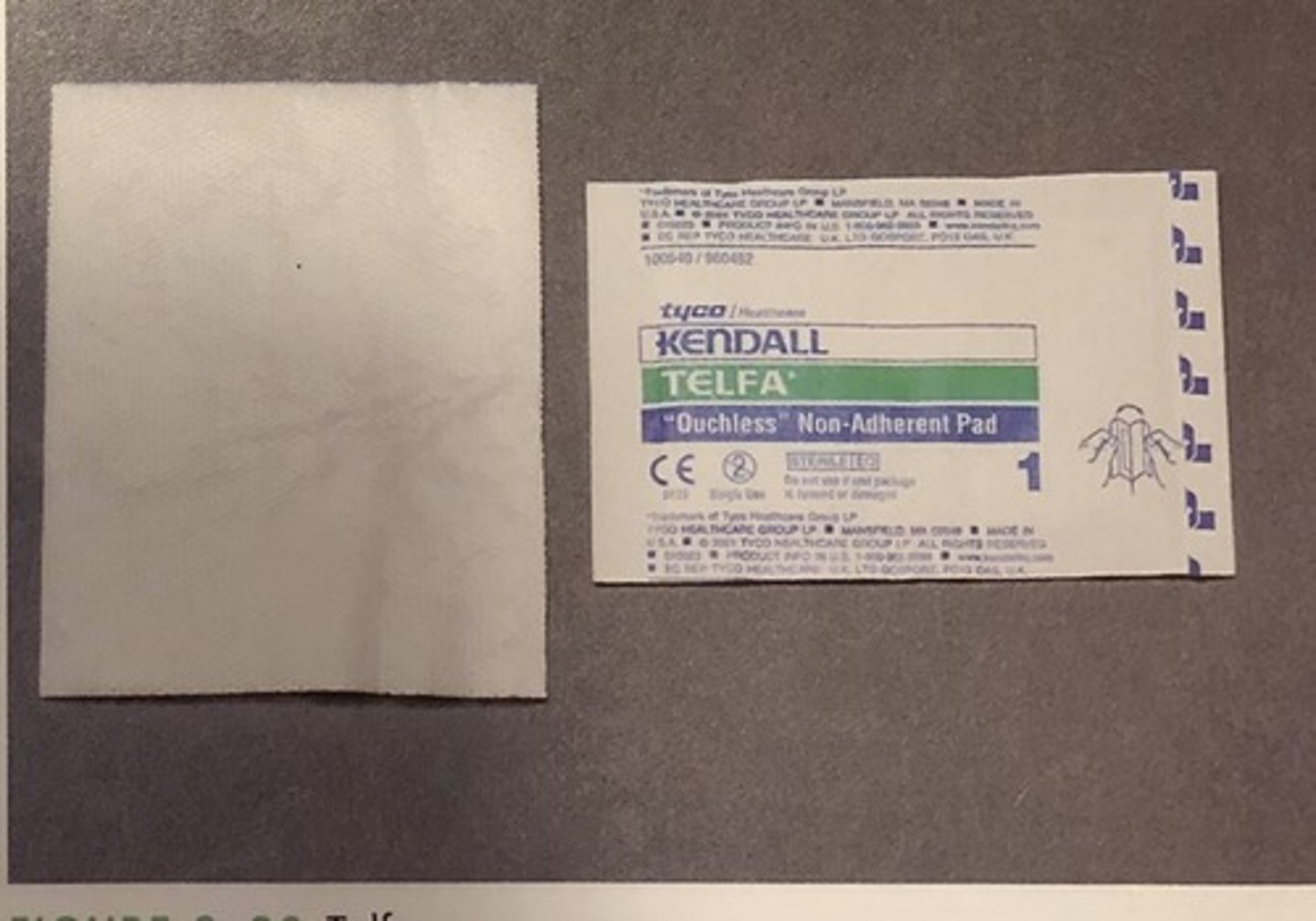
Telfa pads
What wound dressing is appropriate to use over surgical wounds or suture wounds, as it is nonadherent and nonocclusive?
This is TELFA, used on surgical or sutured wounds
What type of wound dressing is this and on what type of wounds should it be used?
Hypertonic saline dressing (Curasalt)
What wound dressing is appropriate to use for aggressive wound debridement but only within the first few days?
Calcium Alginate (Curasorb)
What dressing is appropriate to use for moderately exudative wounds or over substantial tissue loss, as it creates a gel which promotes moist wound healing?
ON LEFT LIMBS: counterclockwise
ON RIGHT LIMBS: clockwise
(imagine a swimmer doing a breaststroke)
In which direction should you bandage horse limbs? Left? Right?
Start medially
On which side of the leg should you start when bandaging equine limbs? Medial or lateral?
1. wear gloves and apply nonadherent first layer
2. hold in place with kling gauze, LOOSELY wrapped
3. apply thick outer bandage
4. apply brown gauze TIGHT over thick bandage to decrease edema
5. Apply vet wrap over brown gauze, make sure there are no wrinkles
6. place Elasticon loosely to the top and bottom margins of the vet wrap to prevent debris from getting into the bandage
Describe how to apply veterinary equine bandages
Standing wraps (support while standing in stable/transport), polo wraps (during exercise), pillow wraps (thick additional padding often under standing wraps)
Name a few re-usable bandage materials often used by owners
Not enough padding, wrapped in wrong direction
What is the issue with this bandaging technique?
uneven pressure, swipes, and poor application
What is the issue with this bandaging technique?
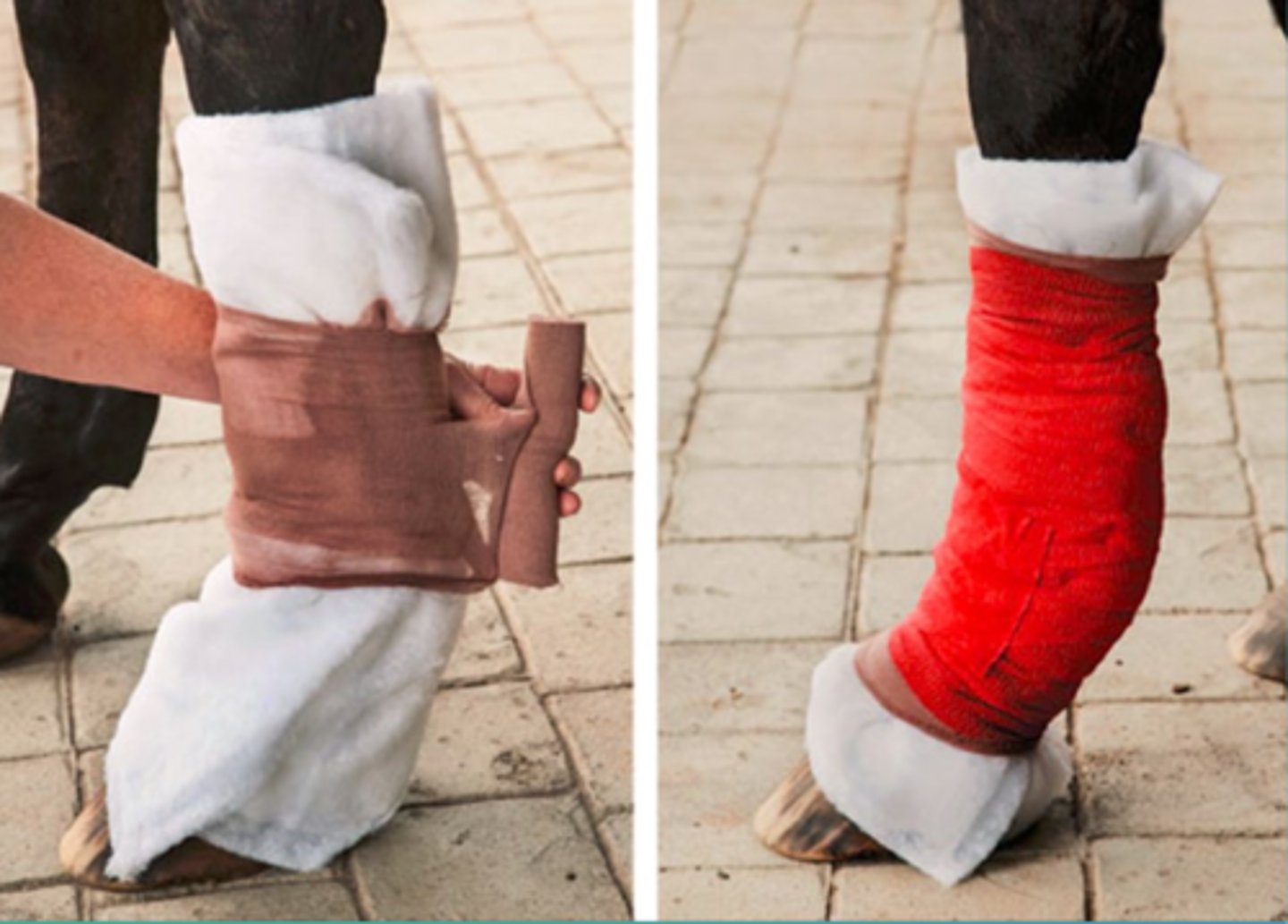

Figure eight the bandage, racing stripe with elasticon, use gauze to pad accessory carpal and point of hock
How can you minimize pressure over bony prominences over joints?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE: When splinting horse legs proper padding is very important as PVC pipes and duct tape are often used
Wrap tight on hoof, loose on skin with LOTS of duct tape on bottom of foot. ALSO do not make too tight over coronary band or you may have to cut it down
When bandaging the hoof, what is important to remember?
1. exuberant granulation tissue formation
2. pressure sores
3. bandage bows (extensor/flexor tendon inflammation due to too little padding or being wrapped too tightly)
Name a few complications of bandaging horses?
Multiple bandages are applied one on top of the other to provide maximum support and protection
What is a "stack wrap"?
Essentially acts as a crutch, putting the pressure on the claw which is uninjured and elevating the injured side
Why do you apply "claw blocks" to cattle on the UNAFFECTED claw?
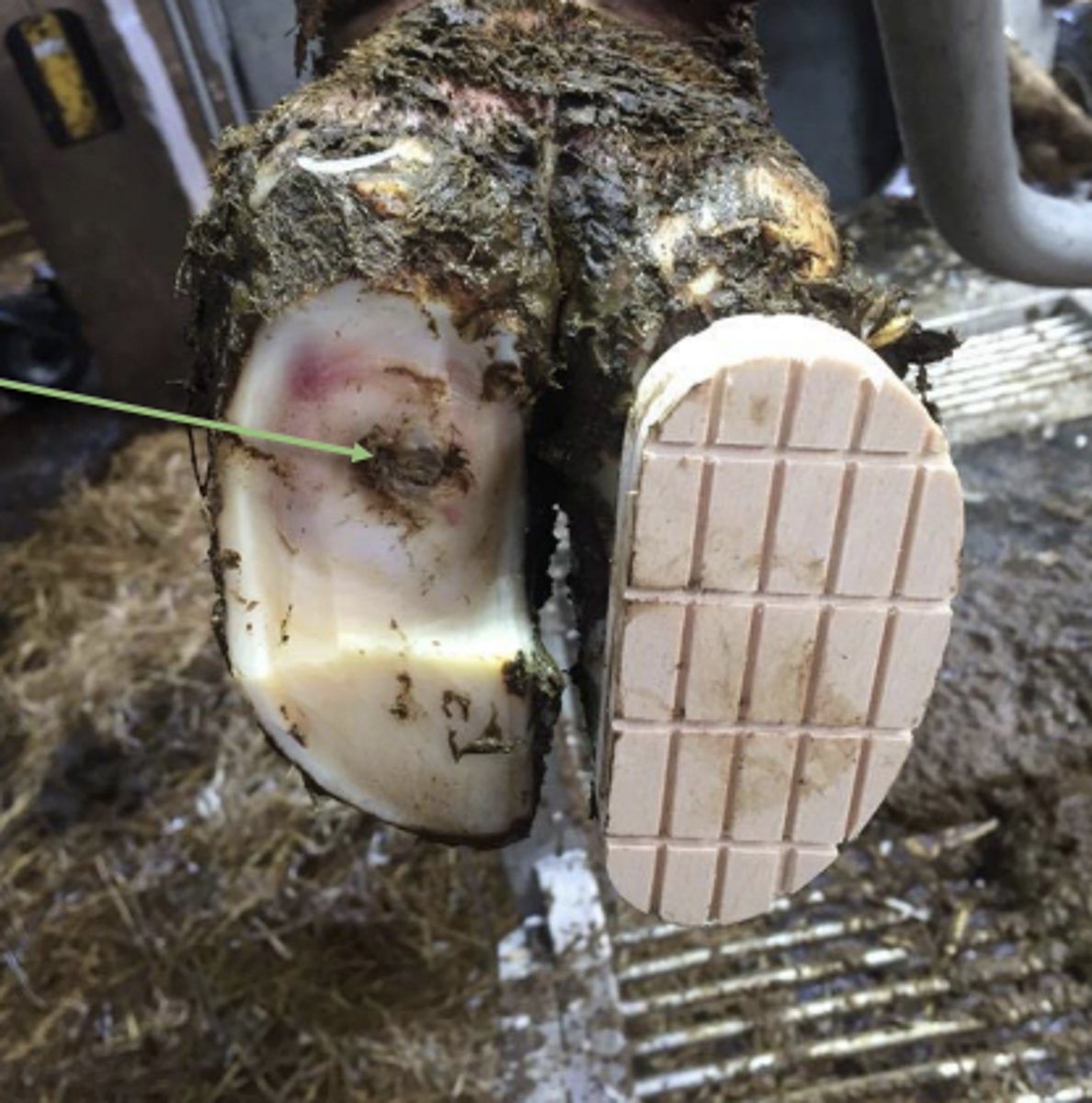

Dew claws
What is one structure on cattle that horses do not have which you have to be aware of so you do not wrap directly over them as it could be painful with too much pressure?
1. dehiscence (WARN OWNERS EVERY TIME)
2. exuberant granulation tissue aka proud flesh
3. involvement of synovial structures
4. bone sequestrum
5. cellulitis
Name the complications of wound healing in large animals:
Distal limbs (carpus, tarsus and below)
Where do you most commonly see proud flesh?
Sharp debridement, topical steroids, skin grafting
Name a few ways to treat proud flesh?
Horses
Proud flesh is more common in horses or cows?
TIME: prognosis is better if treated early
What is the biggest factor with synovial structures being involved with wounds in horses?
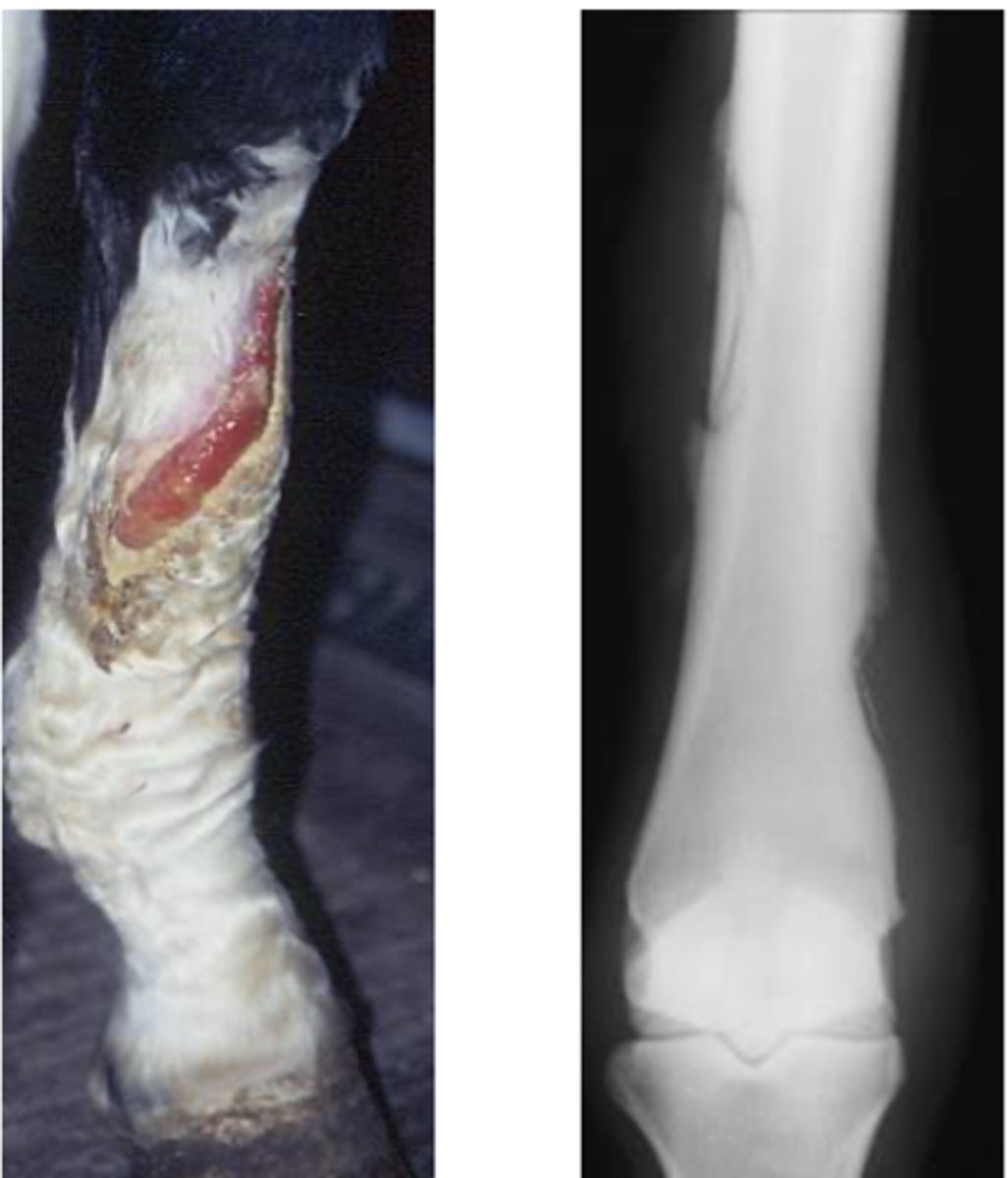
Bone sequestrum
You see a nonhealing wound and do an x-ray to see this. What is happening?
Cellulitis
This complication of wound healing occurs when there is severe wound edema in limbs associated with a relatively small wound, typically because of infection of the subcutaneous tissues
AGGRESSIVE therapy: systemic antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, bandaging
Name some treatments for equine cellulitis