All of the Topics in Biology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
1
New cards
What are the seven classifications of living things?
Movement, Respiration, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition, Irritability
2
New cards
What is movement?
When an organism goes from one place to the next
3
New cards
How do plants move?
They turn towards the light and grow their roots into fertile soil
4
New cards
What is respiration?
Plants and animals using oxygen in the air to turn food into energy
5
New cards
What is the formula for respiration? (Using the formula version of the equation)
O₂ + C₆H₁₂O₆ \= CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
6
New cards
What is the process of the growth of plants (from seed)?
Germination
7
New cards
What is reproduction?
When an organism makes a copy of themselves
8
New cards
What is excretion?
The removal of waste products in the body
9
New cards
What is taxonomy?
The branch of science concerned with classification
10
New cards
What are living things classified in?
Hierarchical system
11
New cards
What are the seven classifications of living things in order?
Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
12
New cards
Who developed the two naming systems for classifications of living things?
Carolus Linnaeus
13
New cards
What is the two word naming system used to classify a species called?
Binomial Nomenclature
14
New cards
How is binomial nomenclature written?
Underlined if handwritten, he genus is capitalized,
15
New cards
What 2 examples of monera?
E-coli, Salmonella
16
New cards
Where are protists mainly found?
In water
17
New cards
Which is the only single-cellular fungus?
Yeast
18
New cards
How do fungi reproduce?
Through spores
19
New cards
What are the cell walls of fungi made of?
Chitin
20
New cards
What phylum is an animal with a backbone in?
Chordata
21
New cards
What are the five classes that Phylum Chordata is divided into?
Mammals, Birds, Fish, Reptiles, Amphibians
22
New cards
What are the four classes that Phylum Arthropoda is divided into?
Arachnids, Myriapods, Insects, Crustaceans
23
New cards
Are fish cold or warm blooded?
Cold blooded
24
New cards
What kind of eggs do fish lay?
Jelly like eggs
25
New cards
Where do amphibians live?
In both water and land
26
New cards
How do amphibians fertilize eggs?
Externally
27
New cards
Are amphibians cold or warm blooded?
Cold blooded
28
New cards
What is the skin of reptiles like?
Dry and scaly
29
New cards
What kind of fertilization do reptiles do?
Internal fertilization
30
New cards
Describe the eggs of birds.
Hard shelled
31
New cards
Are birds cold or warm blooded?
Warm blooded
32
New cards
Are mammals cold or warm blooded?
Warm blooded
33
New cards
What do mammals have on their bodies?
Hair or fur
34
New cards
What does sessile mean?
Attached to a surface, cannot move
35
New cards
What are the simplest animals?
Sponges
36
New cards
List 3 characteristics of Porifera.
Asymmetrical; No true tissues or organs; Can regenerate
37
New cards
What is another name for Cnidarians?
Stinging celled organisms
38
New cards
What are the stinging cells in cnidarians called?
Cnidocytes
39
New cards
What are the (scientific) names for the types of worms?
Platyhelminthes, Nematodes, Annelids
40
New cards
What is the other name for Platyhelminthes?
Flat worms
41
New cards
What is the other name for nematodes?
Round worms
42
New cards
What is the other name for annelids?
Segmented worms
43
New cards
What is an example of a flat worm?
Tapeworm
44
New cards
What is an example of a round worm?
Hookworm
45
New cards
What is an example of a segmented worm?
Earthworm
46
New cards
What do earthworms do? (List 2 things)
Aerate the soil improving structure and moisture holding Helps with decomposition
47
New cards
What are three groups of mollusks?
Gastropods, Bivalves, Cephalopods
48
New cards
What are the 3 main parts of the plant?
Leaf, Stem, Roots
49
New cards
What are the 4 groups in the non-flowering plants?
Mosses and Liverworts, Ferns, Algae, Gymnosperms
50
New cards
What are the simplest plants?
Mosses
51
New cards
How do mosses reproduce?
With spores
52
New cards
Where are mosses found?
In damp places
53
New cards
How do ferns reproduce?
With spores
54
New cards
Where are ferns found?
In damp places
55
New cards
Describe the leaves of a fern?
Feathery
56
New cards
Where are algae found (where in the ocean)?
Attached to rocks or floating on water
57
New cards
How do the male vs female cones look on a gymnosperm?
Male cones are in clusters and female cones are scattered
58
New cards
What are the vascular tissues in a plant?
Xylem and Phloem
59
New cards
What does xylem do?
Transport water and dissolved minerals
60
New cards
What does phloem do?
Transport food
61
New cards
What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms?
Cones
62
New cards
Where can gymnosperms be found?
In dry or cold places
63
New cards
What is the flowering plant called?
Angiosperms
64
New cards
What are the leaves of a monocot vs dicot like?
Monocots have narrow leaves with parallel veins and Dicots have broad leaves with branching veins
65
New cards
What kind of roots do monocots and dicots have?
Monocots have fibrous roots and dicots have tap roots
66
New cards
What is the pistil?
The female part of the flower
67
New cards
What does the pistil consist of?
Stigma, style, ovules, and ovary
68
New cards
What is the stamen?
The male part of the flower
69
New cards
What does the stamen consist of?
Anther and Filament
70
New cards
What does the petals do?
Provide color and scent to the flower to attract pollinators
71
New cards
What is the sepal and what does it do (2 things)?
A small leaf like structure that houses unopened buds and supports and protects the reproductive parts of the flower
72
New cards
What does the receptacle do? (List 3 things)
Holds flower parts together; Houses the ovary; Holds the nectary (which produces nectar)
73
New cards
What does the anther do?
Produces pollen cells
74
New cards
What does the filament do?
Holds up the anther
75
New cards
What does the stigma do?
Catch pollen with its sticky outside
76
New cards
What does the style do?
Connects the stigma to the ovary
77
New cards
What does the ovary do?
Stores the ovules (this is where fertilization occurs)
78
New cards
What does the ovule do?
Contain the egg cells
79
New cards
Where are the sperm cells in the flower located?
In pollen grains
80
New cards
Which part of the flower becomes the fruit and the seed?
The ovary becomes the fruit and the ovules becomes the seed
81
New cards
What is a pedicel?
A stalk or stem that supports a (whole) flower
82
New cards
Look at a diagram of a flower and study that. Or else🔪.
Ok fine
83
New cards
When the flower’s son left for college, what did he say? - Good luck, I be-leaf in you
Ha ha ha, funny joke
84
New cards
What is pollination?
The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma
85
New cards
What are the 2 types of pollination?
Self pollination and cross pollination
86
New cards
What is self pollination?
When the pollen is transferred to the stigma of the same flower (of the same plant)
87
New cards
What is cross pollination?
When pollen from one flower is transferred to the stigma of a different flower (on different plants of the same species)
88
New cards
What is fruit and seed dispersal?
The spreading of seeds and fruits away from the parent plant
89
New cards
List 4 facts about wind pollenated flowers that are different from insect pollinated flowers.
They have small flowers with no scent or nectar;
The anthers are large and hang out of the flower;
They produce large quantities of lightweight pollen;
They have feathery stigma outside the flower to trap flying pollen
The anthers are large and hang out of the flower;
They produce large quantities of lightweight pollen;
They have feathery stigma outside the flower to trap flying pollen
90
New cards
List 4 facts about insect pollinated flowers that are different from wind pollinated flowers.
They have large brightly colored flowers with a nectar scent;
The anthers are smaller and firmly attached to the filament;
They produce smaller quantities of pollen with spiky patterns (to stick to insects);
They have flat sticky stigma inside the flower
The anthers are smaller and firmly attached to the filament;
They produce smaller quantities of pollen with spiky patterns (to stick to insects);
They have flat sticky stigma inside the flower
91
New cards
What are 2 benefits of fruit and seed dispersal?
Colonizes new areas, and Prevents overcrowding
92
New cards
What are 5 methods of seed (and fruit) dispersal?
Clinging to Animals, Wind currents, Eaten by animals, Explosive mechanisms, Water currents
93
New cards
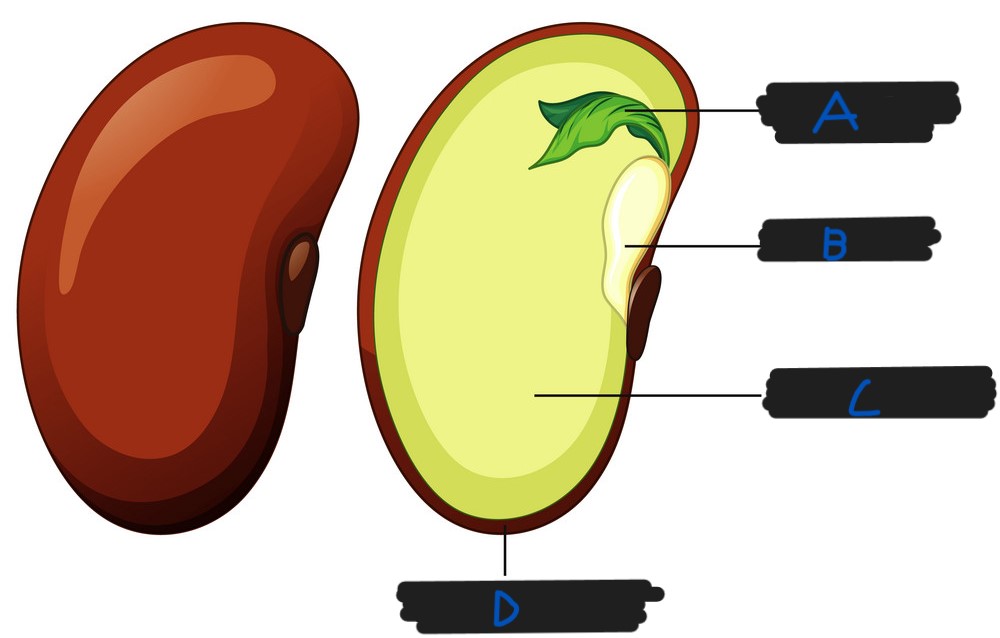
What part of the seed is labelled A?
Embryo
94
New cards
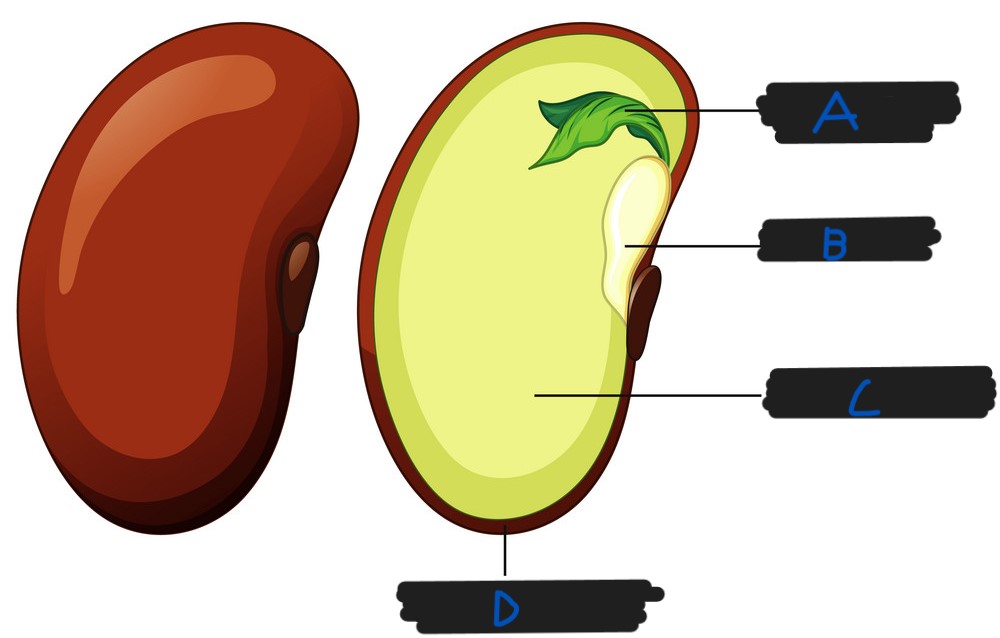
What part of the seed is labelled B?
Radicle
95
New cards
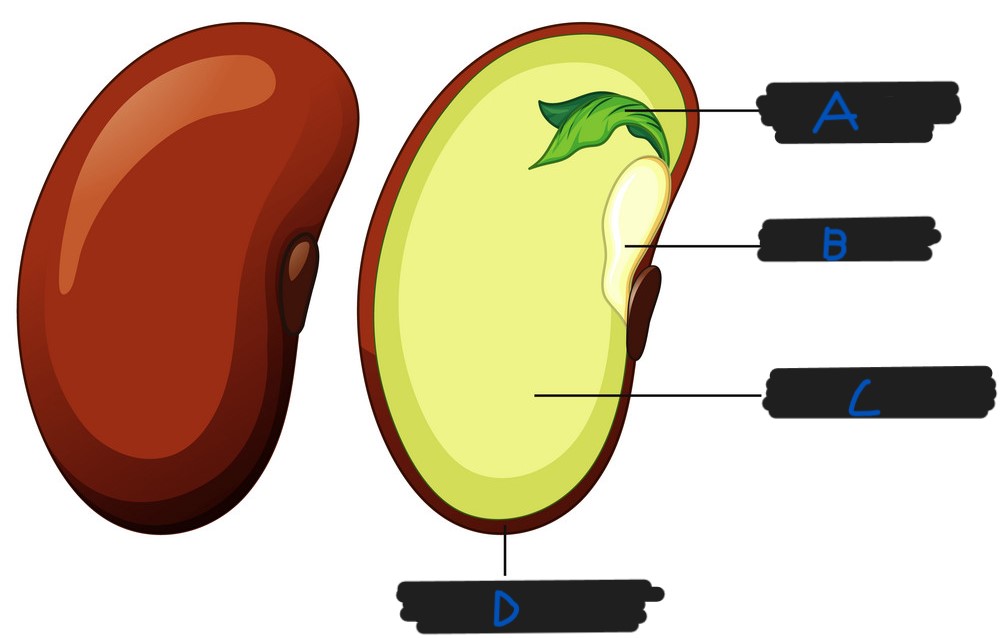
What part of the seed is labelled C?
Cotyledon
96
New cards
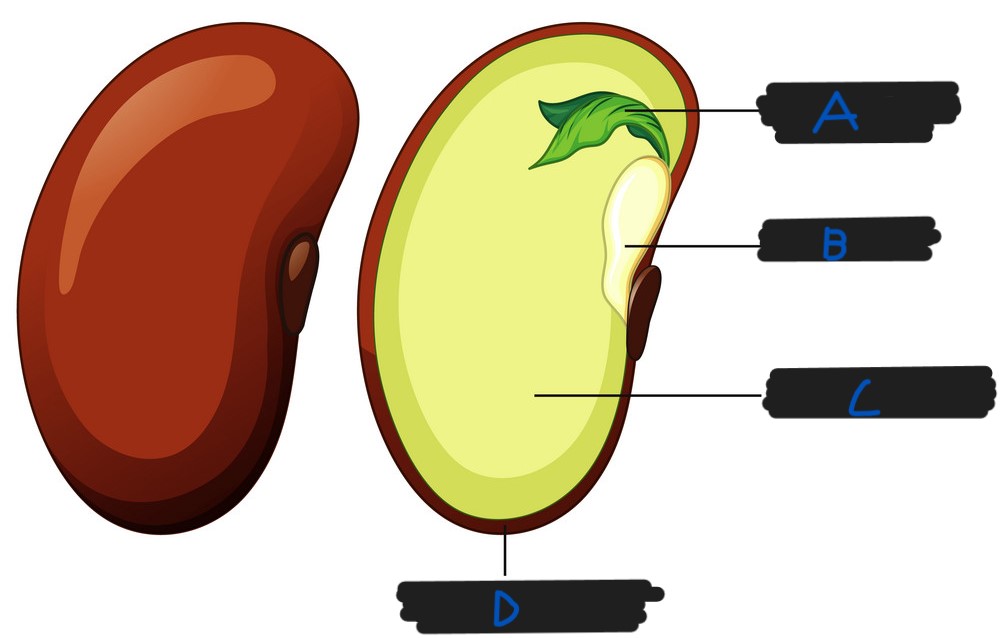
What part of the seed is labelled D?
Seed coat
97
New cards
Which part of the seed shoots out first?
Radicle
98
New cards
Which part of the seed contains the food?
Cotyledon
99
New cards
Bonus question: List 4 functions of water in a plant.
Removes waste products;
Helps cool down the plant;
Transports essential minerals to the plant;
Is needed for vital chemical reactions in the plant
Helps cool down the plant;
Transports essential minerals to the plant;
Is needed for vital chemical reactions in the plant
100
New cards
What does soil consist of?
Rocks, sand, clay, plant and animal remains, and fungi