8.1 Strategic direction
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Ansoff matrix- strategic direction
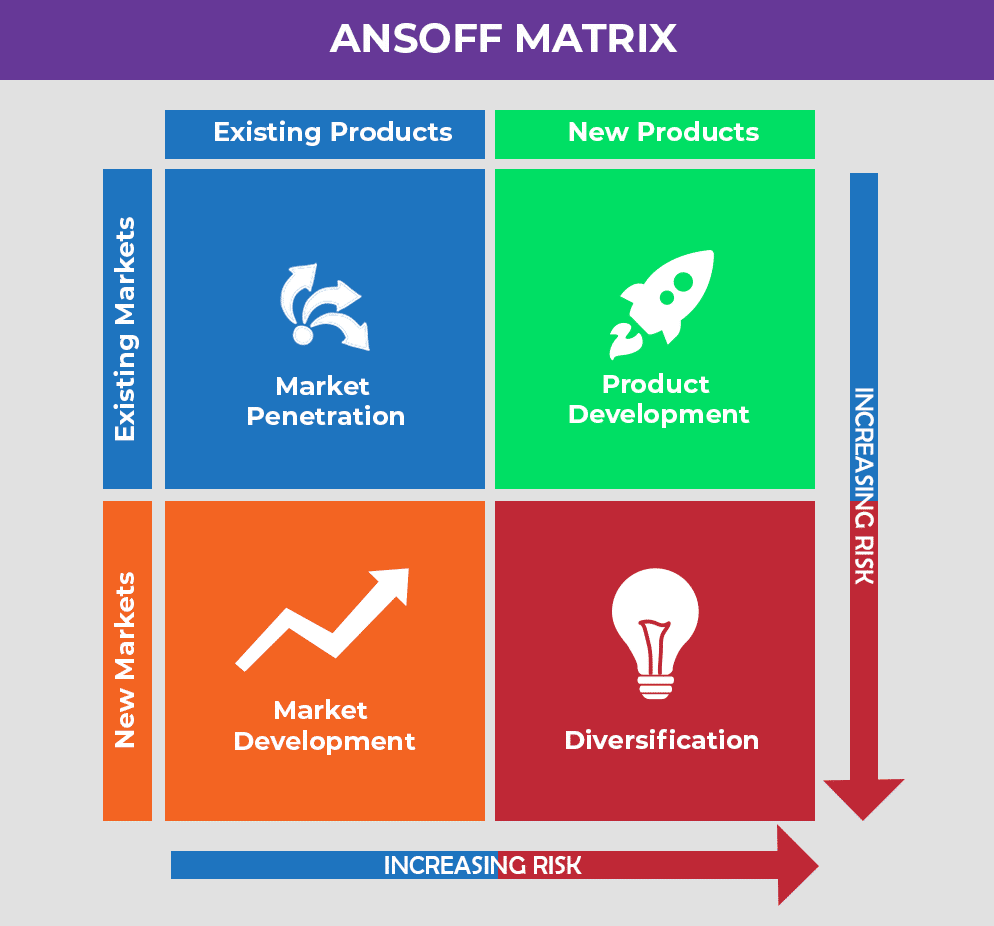
market penetration
selling more of an existing product to an existing market
low risk low reward
approaches
gain MS from competitors
encourage customers to buy or consume more
changes to marketing mix
extension strategies
ADV market pentration
low risk – uses what the business already knows
quick results – easier to increase sales to current customers
builds brand loyalty – strengthens position in the market
efficient use of resources – no need for new product development
DIS market penetration
competitors reactions
short term
market may already be saturated
may not be cost effective
market development
attracting new markets to buy existing products
approaches
enter a new international markets (risky)
move from B2B to retail
move to a new market segment
ADV market development
expands customer base – reaches new regions or demographics
increases revenue potential – opens up new sales opportunities
spreads risk – not dependent on one market
can be cost-effective – if using the same product with small changes
DIS market development
lack of knowledge of customers
product may not be accepted, desired or understood
business may not understand new market
alienation of current customers (separation)
product development
selling new products to existing customers
must be a proactive market leader for this
approaches
launch improved version of existing product
introduce complementary product to develop a range
adapt product to suit a target market within a market
ADV product development
meets changing customer needs – keeps business relevant
builds on existing relationships – easier to sell to loyal customers
can increase customer spend – offering more to the same audience
improves brand image – seen as innovative
DIS product development
high R and D cost
competitor reactions
risk of cannibalisation (decreased in demand for a company’s original product in favour of its new product)
may shorten product life cycle
diversification
selling new products to a new market
high risk high reward
related diversification - potential synergies
unrelated diversification - no relation between markets
approaches
R and D into new products and market research
take over of another business
ADV diversification
high growth potential – taps into entirely new opportunities
spreads risk – not tied to one product or market
can boost brand reach – if successful, increases visibility
can take advantage of trends – enters fast-growing areas
DIS diversification
high risk as 2 elements are unknown
relies on heavy investment
cultural differences may exist
brand image diluted
limitations of Ansoff
some categories are grey areas
assumes 2 diagonal strategies have equal risk
may not take external factors into account
strategic direct
the markets a business chooses to compete in and the products/services it offers
factors effecting which markets a business should compete in
market size and growth potential – bigger or growing markets offer more opportunities
customer needs and behaviour – must match what the business can offer
level of competition – high competition may reduce chances of success
economic conditions – stable economies are often safer for investment
cultural factors – values, habits, and preferences must align
accessibility – includes transport, communication, and distribution channels
factors that influence which products to offer
customer demand – products should solve a real need or problem
company strengths and resources – products must match what the business can do well
profitability – should have good profit margins and sales potential
competition – must offer something better or different than rivals
technology trends – products should keep up with or use new technologies
cost of production – must be affordable to make and sell
brand fit – products should match the company’s image and values