Exam 1 - Chemistry
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Classify matter into types based on compositions (Chapter 1 - OB)
Recognize different types of properties and use these properties to help identify substances (Chapter 1 - OB)
Differentiate between physical & chemical changes (Chapter 1 - OB)
Explain the difference between matter, mass, and weight (Chapter 1 - OB)
Differentiate between hypothesis, theories, & laws (Chapter 1 - OB)
Recognize measurement systems and types (Chapter 1 - OB)
Determine the number of sig figs in a number or measurement (Chapter 1 - OB)
Round to the correct number of sig figs after a calculation (Chapter 1 - OB)
Write equivalencies between metric units using the numerical values of prefixes (Chapter 1 - OB)
Write conversion factors between metric units, metric & U.S. units, from context, and from percents (Chapter 1 - OB)
Types of Matter (Chapter 1)
Matter is anything that occupies space (has volume) and has mass, includes particles
2 types:
Pure Substance
Element
Compound
Mixture
Homogenous
Heterogenous
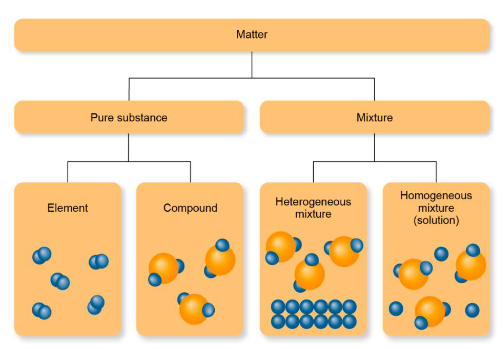
Type of Matter: Pure Substance (Chapter 1)
Element: made of a single type of atom, existing in its natural state
Example: copper
Compound: made of more than one type of atom (element)
Example: copper(II) chloride
Types of Matter: Mixture (Chapter 1)
Made of more than one substance, physically combined, sitting together
Homogenous mixture
Heterogeneous mixture
Types of mixtures: Homogenous mixture (Chapter 1)
Uniform in composition, cannot see the different components (molecules)
Example: broth
Types of mixtures: Heterogeneous mixture (Chapter 1)
Not uniform in composition, can see the different components
Example: stew
Substance Matter - Practice (Chapter 1)
Salt
M&M’s
Food coloring
Caffeine Molecule
Aluminum Can
Coffee
Compound
Heterogeneous mixture
Homogeneous mixture
Compound
Element
Homogeneous mixture
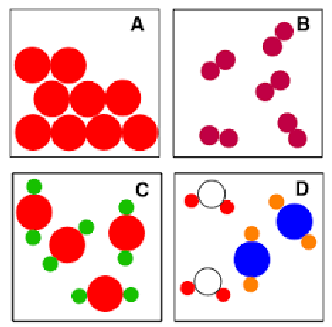
Particle Diagrams (Chapter 1)
A
B
C
D
Element
Element (diatomic)
Compound
Mixture (likely heterogeneous)
Types of Properties (Chapter 1)
Intensive
Extensive
Types of Properties: Intensive (Chapter 1)
Amount doesn’t matter, is a property of the substance no matter the size of the sample (part of the substance)
Luster (shine), density
Types of Properties: Extensive (Chapter 1)
Amount matters, size of the sample dictates property, measurements matters
Carat, mass
Properties Practice (Chapter 1)
Size
Density
Flammability
Boiling point
Extensive
Intensive
Intensive
Intensive
Types of Properties & Changes: Physical (Chapter 1)
Properties: Characteristics that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance
Bread dough is pale in color, has a squishy texture, smells of flour
Changes: changes that alter the appearance of substance, but not its identity, process (Melting, Dissolving)
Rolling or flattening changes shape
Solid, Liquid, Gas
Types of Properties & Changes: Chemical (Chapter 1)
Properties: Characteristics (reaction) that describe the ability of a subtense to change into a different substance
Bread dough is sensitive to heat
Changes: Changes that alter the identity of a substance, giving it new physical and chemical properties (React)
Baking turns dough into bread, outside becomes brown and crusty
Makes compounds from different types of elements
Practice: Chemical or Physical Properties / Changes (Chapter 1)
Properties:
Yellow
Reacts with acid
Boils at 100°C
Change:
Burning
Melting
Dissolving
Properties:
Physical
Chemical
Physical
Change:
Chemical
Physical
Physical
Mass (Chapter 1)
Amount of matter
(Measured as weight)
Metric Unit: gram (g)
SI unit: kilogram (kg)
Weight (Chapter 1)
Force of gravity acting on matter
Measured same, but weight would be different on other planets/the Moon
Parts of the Scientific Method Practice- Observation, hypothesis, experiment, or conclusion (Chapter 1)
a. My sunflower grows best with moderate watering
b. My sunflower is not growing
c. My sunflower needs more water to grow
d. I am going to water my sunflower every other day
a. Conclusion
b. Observation
c. Hypothesis
d. Experiment
Hypotheses (Chapter 1)
Untested ideas based on observations
When metal gains weight as it turns to a powder, air is added to it
Theory (Chapter 1)
Explanation for something based on many experiments by many scientists that has been accepted by the scientific community
Oxygen theory of combustion: when metals burn in oxygen from the air combines with the metal to make a new substance
Law (Chapter 1)
Statement about something that is upheld consistently
Law of conservation of mass: matter cannot be created nor destroyed
Metric System (Chapter 1)
Used in science, health professions, most other countries, has values based on powers of 10
International system of units (SI): official system of measurement used throughout the world
Both systems used in chemistry, depending on context
Volume (Chapter 1)
The amount of space a substance takes up
Metric unit:
Liter (L)
SI unit:
cubic meter (m³)
Length (Chapter 1)
How long an object is
Metric & SI unit:
Meter (m)
Temperature (Chapter 1)
How hot an object is
Metric unit:
degrees Celsius (°C)
SI unit:
Kelvin (K)
Time (Chapter 1)
How long it takes for something to occur
Metric & SI unit:
seconds (s)
Taking Measurements (Chapter 1)
Measurements can only be as precise as the device the measurements came from
Identify the smallest increment marked on the device
Estimate one place past markings
Precision (Chapter 1)
Repeatability or how finely a device measures
How close the data is to aeach other
Accuracy (Chapter 1)
How close to correct (to true value)
Sigficant Figures Rules (Chapter 1)
Any zeros to the left of all nonzero are not significant
Ancy zeros between significant digits are significant
Any zeros to the right of all nonzero digits in a number with decimal places are significant
Any zeros to the right of all nonzero digits in an integer are uncertain, but assume are not significant if no further information
All digits in the coefficient of a number in scientific notation are significant
Sig. Figs. Practice (Chapter 1)
2056.0
0.000193
1860
5
3
3
Rounding with S.F. (Chapter 1)
Determine how many s.f. are allowed, look at digit just past the last allowed digit — if greater than or equal to 5, if less than 5, round down
Rounding with S.F. Practice (Chapter 1)
Round to 2 s.f.: 2060
Round to 3 s.f.: 0.0102549
Round to 2 s.f.: 100
Round to 3 s.f.: 2193.5
Round to 1 s.f.: 0.000356
2100
0.0103
1.0 × 10³
2193.5
0.0004
Adding/Subtracting S.F. (Chapter 1)
Look for least number of decimal places (least precise) value — this is number of decimal places the answer can have
Adding/Subtracting S.F. Practice (Chapter 1)
1.234 + 4.1 =
78 - 42.6 =
107.2 + 6.58 =
99 - 37.1 =
5.3
35 (no decimal places)
113.8
62 (no decimal places)
Multiplying/Dividing S.F. (Chapter 1)
Look for least number of s.f. — this is number of s.f. the answer can have
Multiplying/Dividing S.F. Practice (Chapter 1)
1500 × 2.63 =
0.153/0.006102 =
218 × 0.003 =
4.7 × 106 / 952=
3900 (2 s.f.)
25.1 (3 s.f.)
0.7 (1 s.f.)
4900 (2 s.f.)
2-Step Math with S.F. Practice (Chapter 1):
Determine how many centimeters are in 8.4 inches.
Determine how many meters the value above represents
8.4 in. x 2.54 cm/1 in. = 21.336 → 21.3 cm (should be 2 s.f., keep 3 for now)
21.3 cm x 1 m/100 cm = 0.21 m (round to correct s.f. based on numbers provided — 2 s.f.)
2 - Step Math with S.F. Practice Part 2 (Chapter 1)
(482 - 15.4)/26
(0.021 + 0.95)(1.2)
17.61/(2.4 - 0.81)
482 - 15.4 = 467
467/26 = 18 (2 s.f.)
0.021 + 0.95 = 0.97
0.97 × 1.2 = 1.2 (2 s.f.)
2.4 - 0.81 = 1.6
17.61/1.6 = 11 (2 s.f.)
Metric Units (Chapter 1)
A base unit represents a type of measurement such as length or mass
A prefix is part of the name of a metric unit that precedes the base unit and specifies the size of the measurement
We can place a prefix in front of any metric unit to increase or decrease its size by some factor of 10
The relationship of prefix to unit is expressed by replacing the prefix with its numeral value, ex. kilo = 1000, 1 kilometer = 1000 m
Metric Equivalencies Practice (Chapter 1)
1 L = ? mL
1 g = ? ng
1 um = ? m
1 g = ? kg
1000 mL or 10³
1 × 109 ng
1 × 10-6 m
1 × 10-3 kg
Conversion Factors (Chapter 1)
A fraction that shows an equivalency between 2 units
Values from the metric system are exact numbers — don’t count towards sig. figs.
“Per” means fraction bar
A percent can be written as a conversion factor out of 100 total objects
Examples:
1000 g/1 kg or 1 kg/1000 g
10 × 10-9 L/1 nL or 1 L/1 × 10-9 nL or 1 L/1 × 109 nL or 1 ×109 nL or 1 L
14% of the paperclips were purple:
14 purple paperclips/100 paperclips
Special volume equivalency: 1 cm³ = 1 mL
1 cm³/1 mL or 1 mL/1 cm³
Conversion Factors Practice (Chapter 1)
Write 2 conversion factors for the relationship between each set of units
Grams and milligrams
Liter and deciliters
Meters and gigameters
18% of the pens were blue
1 g = 1000 mg or 0.001g = 1 mg
1 g/1000 mg or 1000 mg/1 g or 0.001 g/1 mg or 1 mg/0.001g
1 L = 10 dL or 0.1 L = 1 dL
1 L/1 dL or 10 dL/1 L or 0.1 L/1 dL or 1 dL/0.1 L
1 Gm = 1 × 109 m or 1 × 10-9 Gm = 1 m
1 Gm/ 1 × 109 m or 1 × 109 m/1 m or 1 × 10-9 Gm/1 m or 1 m/1 × 10-9 Gm
18 blue pens/100 pens
Unit Conversions Practice Part 2 (Chapter 1)
How many inches are in 72.4 feet? (1 ft = 12 in.)
How many cups is 0.0125 gallons? (1 Gallon = 4 quarts, 8 pints, 16 cups)
72.4 ft x 12 in/1 ft = 869 in
0.0125 gal x 16 cups/1 gal = 0.200 cups
Metric Unit Conversion Practice Part 3 (Chapter 1)
How many nanometers are in 5.3 m?
The volume of a liquid is 250 uL. What portion of a gigaliter is this?
The mass of an object is 25.61 g. How many mg is this?
How many megameters are represented by 450 cm?
5.3 m x 109 nm/1 m = 5.3 × 109 nm
250 uL x 1 L/106 uL x 1 GL/109 L = 2.5 × 10-13 GL
450 × 1 m/100 cm x 1Mm/10-6 Mm
Mixed Unit Conversions Practice (Chapter 1)
If you drive 13.27 miles, how many centimeters have you traveled? (1 in = 2.54 cm, 1 mi = 5280 ft)
An object is measured to have a mass of 126.4 g. How many pounds is this? (1 lb = 0.4536 kg)
13.27 mi x 5280 ft/1 mi x 12 in/1 ft x 2.54 cm/1 in = 2.136 × 106 cm
126.4 g x 1 kg/1000 g x 1 lb/0.4536 kg = 0.2787 lb
Compounds Units Practice (Chapter 1)
A boat travels at 45 miles per hour. What is this speed in km/min? (1 mi = 1.609 km)
You buy some candy that costs 55 cents per pound. What is the price of the candy in dollars per kilogram? (1 lb = 0.4536 kg)
45 mi/1 h x 1.609 km/1 mi x 1 h/60 min = 1.2 km/min
55 cents/1 lb x 1 lb/0.4536 kg x 1 dollar/100 cents = 1.2 dollars/kg
Squared or Cubed Units (Chapter 1)
When a conversion factor has to be squared or cubed, both the numbers and units in the numerator and denominator must be squared or cubed
A useful conversion factor 1 mL = 1 cm³
Squared or Cubed Units Practice (Chapter 1)
A volume is measured as 1.625 L. What is this volume in m³?
A unit pressure is pounds per square inch (psi). How much is 34.1 psi in g/cm²? (1 lb = 0.4536 kg, 1 in = 2.54 cm)
The density of aluminum is 2.7 g/cm³. What is this density in dg/L?
The volume of a cube is determined to be 46.2 mm³. What is this volume in uL?
1.625 L x 1000 mL/1 L x 1 cm³/1 mL x (1 m/100 cm)³ = 0.001625 m³
34.1 lb/1 in² x 0.4536 kg/1 lb x 1000 g/1 kg x (1 in/2.54 cm)² = 2.40 × 10³ g/cm²
2.7 g/1 cm³ x 10 dg/1 g x 1 cm³/1 mL x 1000 mL/1 L = 27000 dg/L
46.2 mm³ x (1 cm/10 mm)³ x 1 mL/1 cm³ x 1 L/1000 mL x 106 uL/1 L = 46.2 uL
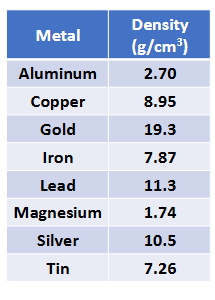
Density (Chapter 1)
= mass/volume or d = m/V
Always the same for a given pure substance
Density Practice (Chapter 1)
Calculate the volume of a sample of aluminum with a mass of 13.7 g.
3.58 L of an unknown substance has a density of 7.87 kg/L. Find the mass of the sample. Identify the substance (1 kg/L = 1 g/mL)
The mass of an unknown substance is 84.9 g and it takes up a volume of 1.169 × 10-5 m³. Identify the substance.
270 = 13.7/V → 2.70V = 13.7 → V = 13.7/2.70 = 5.07 cm³
7.87 = m/3.58 → 7.87 × 3.58 = 28.2 kg Iron
84.9 g/1.169 × 10-5 m³ x (1 m/100 cm)³ = 7.26 g/cm³ Tin
Temperature Formulas (Chapter 1)
Tc = 5/9 (TF -32)
TF = 9/5 TC +32
TK = TC + 273.15
Temperature Practice (Chapter 1)
Convert 195°F to °C (Tc = 5/9 (TF -32))
A liquid is measured to be 14.9°C, what is this temperature in kelvin? (TK = TC + 273.15)
What is 402 K in °F? (TF = 9/5 TC +32)
90.6°C
288.1 K
264°F