CMS Final: Cardio pt. 1
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
what is the best diagnostic study to diagnose valvular disorders?
TTE or TEE echo
RILE mnemonic
right →inc with inspiration
left → inc with expiration
which type of murmurs are always pathologic?
diastolic
what are the diastolic murmurs?
AR, PR, MS, TS
what are the systolic murmurs?
AS, MR, VSD, PS, TR, MVP
what are the continuous murmurs?
venous hum, pericardial friction rub, PDA
what are the acyanotic congenital heart disease with L→R shunt?
ASD
VSD
PDA
these can develop eisenmeger's complex if uncorrected!!
what are the acyanotic congenital heart defects without outflow obstruction?
PS
AS (bicuspid)
coarctation of aorta
What are cyanotic heart defects?
1. Eisenmeger's
2. Ebstein's anomaly
3. tetralogy of Fallot
4. transposition of the great vessels
when do cyanotic heart defects typically appear?
childhood
Which murmur radiates to the axilla?
mitral regurgitation
which murmur: opening click + mid-systolic murmur @ LUSB?
PS
which murmur: crescendo-decrescendo early diastolic @ LUSB
PR
+ Graham steell murmur
which murmur: high pitch blowing holosystolic @ LLSB?
TR
which murmur: harsh crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur that increases with valsalva?
HOCM
which murmur: continuous musical hum, loudest @ right infraclavicular region?
venous hum
which murmurs increase with valsalva?
HOCM and MVP
which murmur: holosystolic left parasternal murmur with thrill at LLSB?
VSD
which murmur: continuous machine-like murmur in left infraclavicular region?
PDA
which murmur: fixed split S2 with mid-systolic murmur at LUSB?
ASD
which systolic murmur is best heard at the left upper back?
coarctation of the aorta (CoA)
which murmur: harsh, diamond shaped, crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection @ RUSB?
AS
PLUS paradoxical split of S2
which murmur: high-pitched blowing early diastolic decrescendo murmur at LLSB/RLSB?
AR
which murmur: diastolic rumble at apex?
austin flint (AR)
which murmur: opening snap and low-pitched diastolic rumble at apex in LLD position?
MS
which murmur: holosystolic, high pitched murmur at apex/radiates to L axilla?
MR
which murmur: mid-systolic click + late systolic murmur at apex?
MVP
which grade of murmur?: audible but faint
2
which grade of murmur?: loud with a thrill
grade 4
which grade of murmur: moderately intense without thrill?
grade 3
which grade of murmur: so loud you don't need a stethoscope and thrill?
grade 6
which murmur radiates to carotids?
AS
what is the triad of symptoms associated with AS?
angina
syncope
exertional dyspnea
what disorder is pulsus parvus et tardus seen in?
AS
what is the etiology of congenital AS?
bicuspid valve
where is AR best heard? when does it increase?
erb's point
increases when patient leans forwards and exhales
which abnormal pulses are associated with AR?
1. corrigan's = large carotid pulsation
2. water hammer = wide PP
3. pulsus alternans = weak and strong
4. quincke's sign = flashing of blood during systole
5. pulsus bisferians = single central pulse wave with 2 peaks and mid-systolic dip
Which troponins are cardiac specific? which is more specific for MI?
T and I
I is more specific to MI
which cardiac enzyme appears in 6-12 hrs, peaks at 24 hrs, and is gone after 3-4 days?
CPK
which cardiac enzyme shows up in 3 hours and remains for up to 2 weeks?
Troponin
first line!
which cardiac enzyme shows up in 2 hrs and clears after 20-36 hrs?
myoglobin
(nonspecific--reacts to any muscle damage)
which cardiac enzyme appears in 24 hrs, and clears after 8-9 days?
LD/LDH
which cardiac enzyme is elevated if ventricles are stretched/dilated? what is a significant lab value for HF?
BNP
>400 = significant
which test evaluates the tunica media for plaque buildup?
carotid intima media thickness (CIMT)
can CIMT determine how much plaque burden there is?
NO! (this was a giveback on exam 1)
which test assesses if the heart can perform in an active dynamic state?
stress test
which test can evaluate the degree of plaque burden or accumulated calcium?
CAC
which diagnostic test is used for infective endocarditis?
TEE
if a IVDA has acute infective endocarditis, what is the likely etiology?
s. aureus
if a patient has subacute infective endocarditis, what is the likely etiology?
S. viridians
affects already damaged heart (congenital, prosthetic valve, RF)
what are symptoms associated with infective endocarditis?
janeway lesions
oslers nodes
roths spots
splinter hemorrhage
+ signs of infection
Janeway lesions vs. oslers nodes: which is painful?
oslers nodes
"No pain jane"
which valve is most affected by acute rheumatic fever?
mitral 75%
aortic 25-30%
What is the JONES criteria for Rheumatic fever?
presence of 2 major manifestations
or
1 major manifestation + 2 minor manifestations
what are the major jones criteria?
Carditis
Chorea (CNS involvement)
Erythema marginatum
Polyarthritis
Subcutaneous nodules
what is the minor jones criteria?
PEACH Fever
Prolonged PR interval
ESR raised
Arthralgias
CRP increased
Hx of previous rheumatic fever or RHD
+fever
a patient presents with fever and polyarthritis. ESR is elevated. what is the diagnosis and treatment?
ARF → penicillin
What is the DUKE Criteria?
for IE
2 major OR 1 major and 3 minor OR 5 minor
Major: Two positive blood cx, new regurgitant murmur, vegetation on ECHO
Minor: Fever, vascular phenomena, positive blood cx of uncommon pathogen, immunologic phenomena (Osler, Janeway, Roth), predisposing factor (surgery/procedure, IVD)
What causes fixed splitting of S2 in ASD?
increased pressure from L → R; longer for pulm valve to close bc of an increased preload
what is Eisenmenger's complex?
Initial L → R shunt causes pulmonary hypertension
if uncorrected, eventually causes R → L shunt leading to cyanosis/HF/infections
what is defined as communication between the aorta and pulmonary artery?
PDA
what is the treatment for PDA?
Indomethacin (NSAIDs)
what is a common complication of CoA?
berry aneurysm (can lead to circle of willis bleed)
if a patient has forceful upper extremity pulses, but weak/delayed lower extremity pulses, what would you expect to see on a CXR?
CXR → rib notching or figure 3 sign
dx is coarctation of the aorta
what is defined as fibrotic narrowing of the aorta distal to the left subclavian artery?
coarctation of the aorta
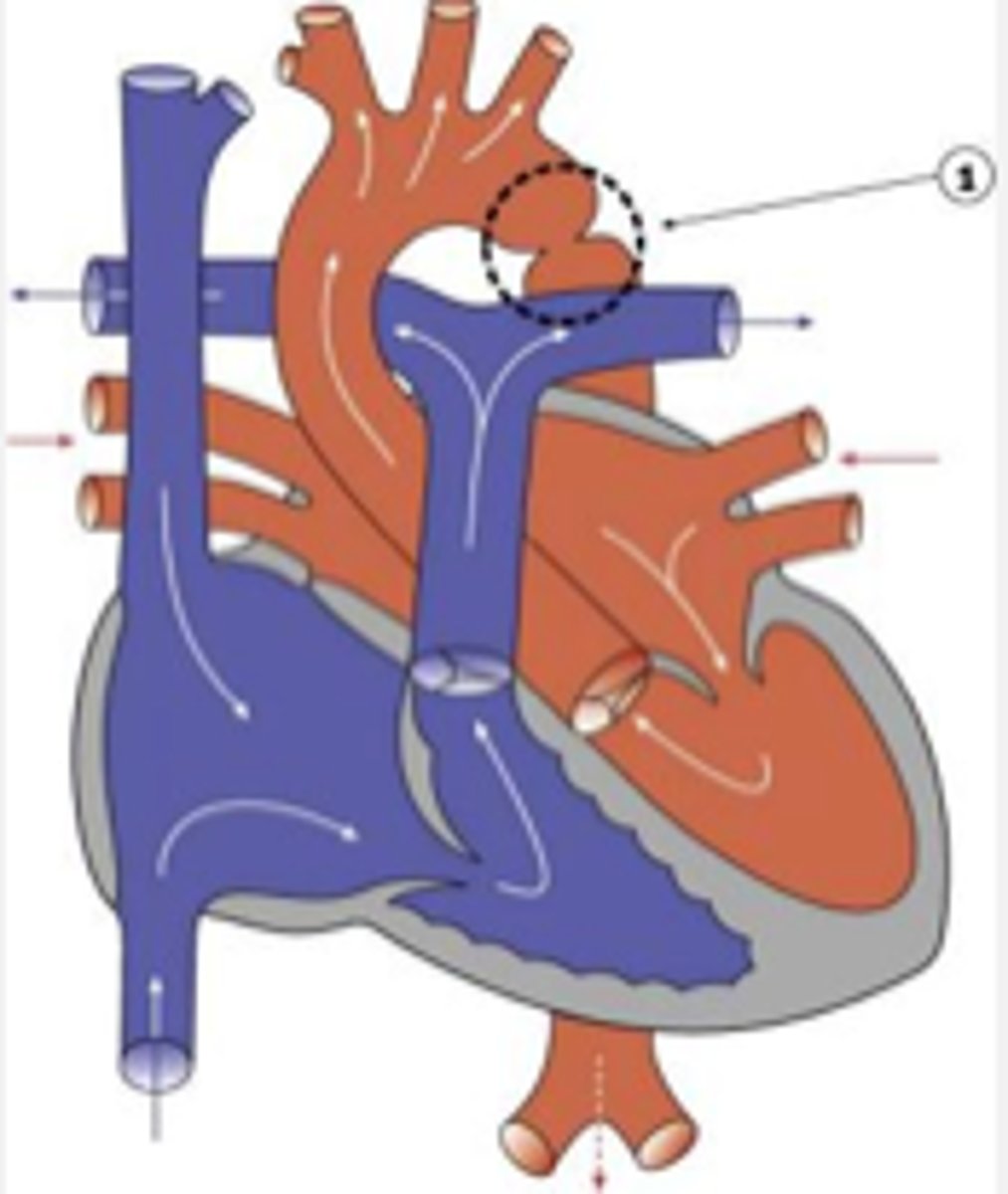
what valvular disorder is tetralogy of fallot associated with?
pulmonic stenosis
what are the 4 components of tetralogy of fallot?
PROV:
P=pulmonic stenosis
R=RVH
O=overriding aorta
V=VSD (L→R shunt)
which condition has a soft P2 and harsh systolic ejection click?
tetralogy of fallot
which valvular defect has risk factor of down syndrome?
VSD
what does Eisenmenger's cause?
R→L shunt → increased blood flow to pulm artery → vaso-occlusive disease (pulm HTN)
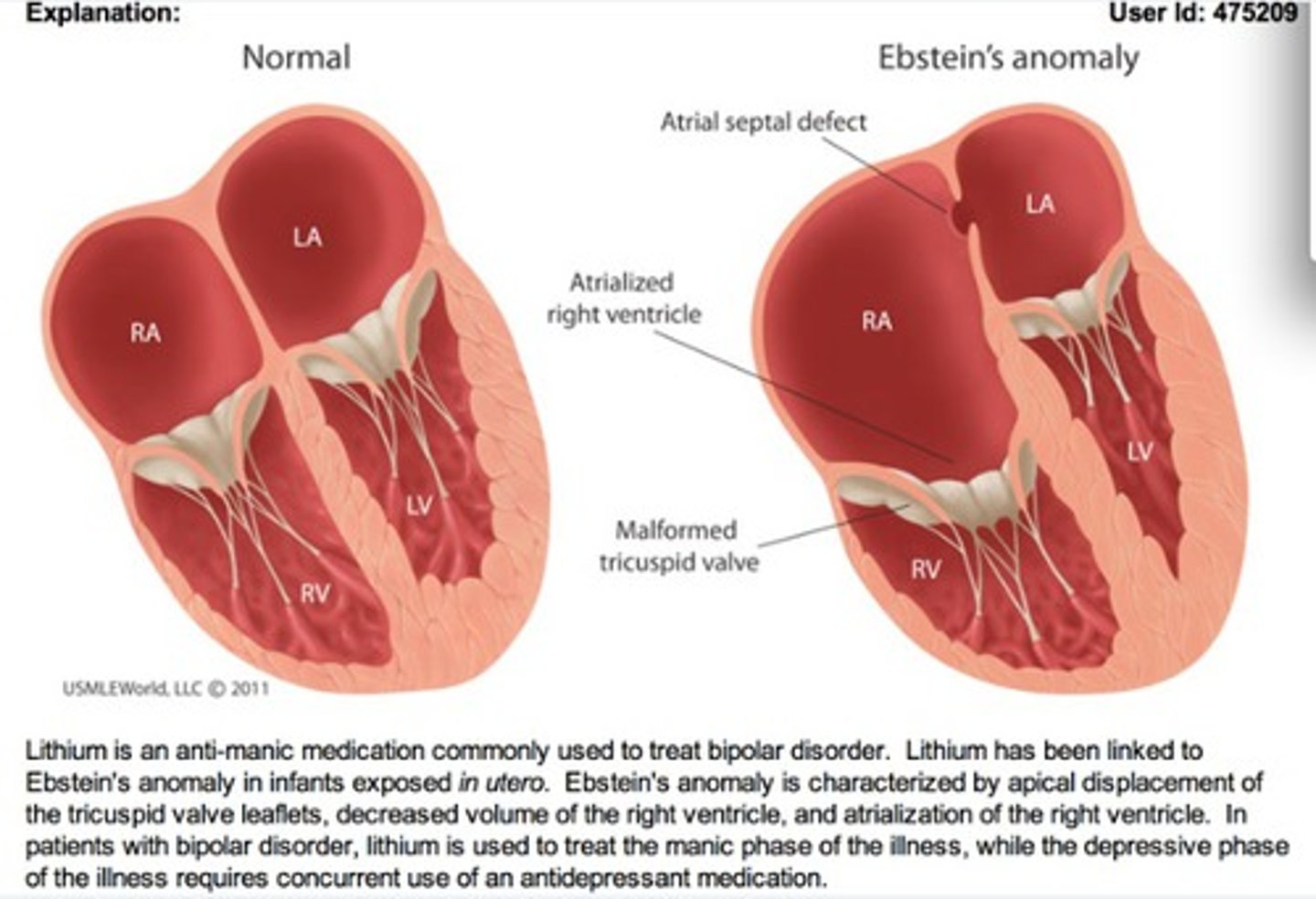
what is an atrialized right ventricle known as?
ebstein anomaly
RA embeds intself into RV → RAP increases
what valvular disorders is ebstein's anomaly associated with?
ASD and PFO
what occurs when the aorta and pulmonary artery are switched?
transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
what is the term to describe when valves can't open fully due to narrowing?
stenosis
what is the term to describe when valves do not close efficiently, causing backflow of blood?
regurgitation
what is the definitive treatment for murmurs/valvular disorders?
valve replacement
which murmur is associated with Ortner's syndrome?
MS → enlarged LA compresses recurrent laryngeal nerve
(ortner's = hoarseness)
A tall, slender female patient presents to your clinic complaining of palpitations and atypical CP. On exam, you hear a midsystolic click and late systolic murmur at the apex. Valsalva increases the murmur. What is your suspected dx?
MVP
what is the MC cause of sudden death in young people?
HOCM
What is the S4 heart sound?
"atrial gallop"
Stiff/hypertrophic ventricle (aortic stenosis, restrictive cardiomyopathy)
What is the S3 heart sound?
it may occur during passive filling of the ventricles due "sloshing" on the ventricular walls and is a low-pitched sound
which valvular disorder is associated with rheumatic fever?
MS
what valvular disorder has the symptoms: palpitations, HF, and dyspnea?
MS →"PHD"
what is the most common congenital form of TR?
ebstein's anomaly
which type of endocarditis is seen in patients with lupus?
libman-sacks
which valve is more likely to be affected by endocarditis in patients who are IVDAs?
tricuspid valve
what cardiac conditions require prophylaxis for dental procedures for infective endocarditis?
- prosthetic valve
- previous IE
- unrepaired congenital heart disease
- cardiac transplant
NOT FOR VALVULAR DISORDERS!
what is the MC type of ASD?
patent foramen ovale (PFO) → can cause stroke in young adults
which valvular disorder is Afib likely seen in?
ASD
R vs L heart failure: JVD, hepatojugular reflex, pitting edema?
RHF
R vs. L heart failure: pulm edema, crackles and rhonchi, bibasilar rales, orthopnea (pillow talk)?
LHF
what is seen on CXR in LHF?
blunting at costophrenic angle d/t buildup in lungs
Orthopnea is:
difficulty breathing when lying down
Trepopnea
dyspnea in LLD position
platypnea
dyspnea in upright position
Which class of HF is described as:
No limitation of physical activity.
class 1
which class of HF is described as: slight limitation of activity but comfortable at rest or with mild exertion
class 2
which class of HF is described as: marked limitation of activity, only comfortable at rest
class 3
which class of HF is described as: any physical activity brings on discomfort and symptoms occur at rest
class 4
pulsus paradoxus is seen in which condition?
cardiac tamponade (this was on the exam)