4.2 Marketing planning
Introduction
- Marketing planning: process of formulating appropriate strategies and preparing marketing activities to meet marketing objectives.
Marketing mix
Marketing mix: key decisions that must be taken in the effective marketing of product.
- 4Ps:
- Product: what you sell. It could be a physical good, services, consulting, etc.
- Price: how much do you charge and how does that impact how your customers view your brand?
- Promotion: where do you promote your product/service? Where do your ideal customers go to find information about your industry?
- Place: how do your customers find out about you? What strategies do you use and are they effective?
Coordinated marketing mix: key marketing decisions complement each other and work together to give customers a consistent message about the product.
Differences between market segments and target markets
Market segment: sub-group of a market made up of consumers with similar characteristics, tastes and preferences.
Target market: market segment that a particular product is aimed at.
Market segmentation and consumer profile
Market segmentation: identifying different segments within a market and targeting different products or services to them.
Consumer profile: quantified picture of consumers of a firm's products, showing proportions of age groups, income levels, location, gender and social class.
Ways which markets may be segmented in
- Geographic differences: strategy used to target products/services at people who live in or shop at, a particular location. It works on the principle that people in that location have similar needs, wants and cultural considerations.
- Demographic differences: strategy used to target products/services at people based on their age, education and gender.
- Psychographic differences: strategy used to target products/services at people based on their attitudes, interests, personality, values, opinions and lifestyle of your target market.
Difference between niche market and mass market
- Niche market: small and specific part of a larger market.
- Niche marketing: identifying and exploiting a small segment of a larger market by developing products to suit it.
- Mass market: market for products that are often standardized and sold in large quantities.
- Mass marketing: selling the same products to the whole market with no attempt to target groups within it.
Product position map or perception map: graph that analyses consumer perceptions of each of a group of competing products in respect of two product characteristics.
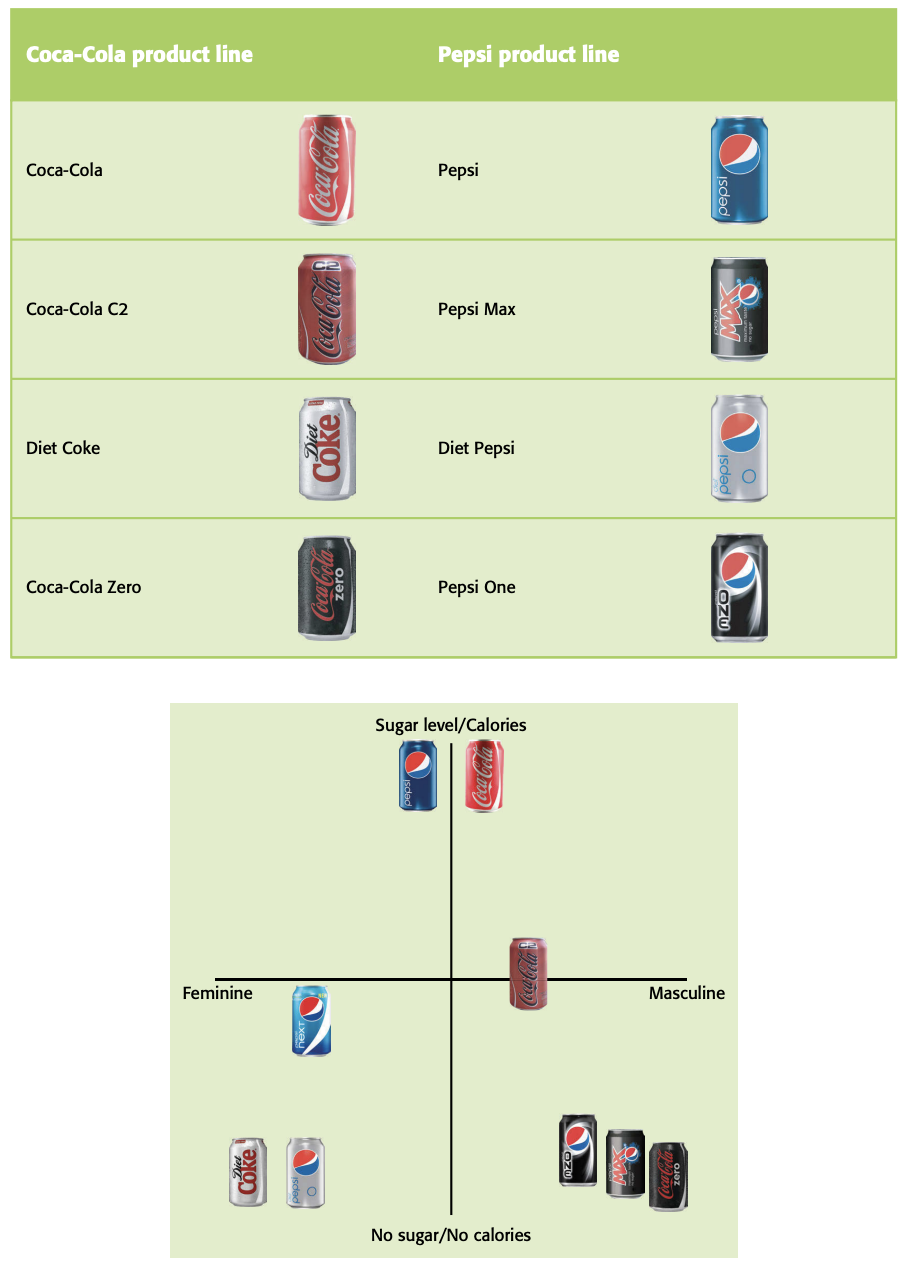
Unique selling point/proposition (USP): factor that differentiates a product from its competitors, such as the lowest cost, the highest quality or the first ever product of its kind; a USP could be thought of as “what you have that competitors don’t”.