Materials and Processing Metals Flashcards
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are the main 4 categories of materials.
Polymers
Metals
Ceramics
Composites
What are composites?
A combination of 2 or more categories of materials.
What are Polymers?
Polymers are large molecules (macromolecules) formed by the repetition of smaller chemical units called monomers, often resulting in long chains. They are typically organic (carbon-based).
What are some properties of metals?
They are typically strong, ductile (can be drawn into wires), malleable (can be hammered into thin sheets), and have high thermal and electrical conductivity. They are relatively dense and have high melting points.
Nonorganic
Crystalline Structure
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Alloys (A combination of two or more metals)
What are some properties of polymers?
Generally lightweight, flexible or relatively weak, and are good electrical and thermal insulators. They have low melting/softening points compared to metals and ceramics.
Organic
Carbon Chains
Wide range of mechanical properties
What are some properties of ceramics?
They are extremely hard, brittle (shatter easily), possess very high melting points, and are excellent thermal and electrical insulators.
Nonorganic
Cristalline Structure–loosely packed
High Compression Strength
Low tensile strength
Porous
Can be Good insulators and/or conductor (or semiconductors)
Full range of magnetic properties
What are some properties of Composites?
They are designed to achieve a desirable combination of properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and fatigue resistance.
Combination of 2 or more materials
Particulate composites
Fiber reinforcement composites
Matrix composites
What are two main types of polymer and what is their definition?
Thermoplastics (e.g., polyethylene) soften upon heating and can be reshaped repeatedly.
Thermosets (e.g., epoxy) harden permanently upon initial heating and cannot be re-melted.
What is ultimate strength?
The maximum stress a material can withstand under tension (being pulled) or compression (being squeezed) before it breaks or fractures. It is a critical limit used in structural design, often calculated as the maximum load divided by the original cross-sectional area.
What is Flexibility?
The ability of a material to bend or deform easily without breaking or suffering permanent damage. In technical terms, a material's flexibility is often represented by the inverse of its stiffness (low Young's modulus). Materials like polymers (plastics) are often chosen for their high flexibility.
What is Machinability and what is it associated with?
A measure of how easily and economically a material can be cut, drilled, milled, or otherwise shaped by subtractive processes (machining). Good machinability is associated with:
Low cutting forces and power consumption.
Long tool life (less tool wear).
Good surface finish.
What is Density:
The mass per unit volume of a material, often measured in g/cm^3 or kg/m^3.
What is Durability:
The ability of a material to withstand wear, stress, and deterioration over time and in various service environments (like heat, cold, or high load cycles). It is a broad measure that incorporates many other properties, including fatigue strength and resistance to degradation.
What is Thermal expansion?
The tendency of matter to change in volume (most commonly length) in response to a change in temperature. It is quantified by the coefficient of thermal expansion ($\alpha$).
What is Electrical conductivity?
The material's ability to conduct an electric current. High conductivity (metals like copper and aluminum) is essential for wiring and circuitry. Low conductivity (polymers, ceramics) is required for electrical insulators.
What is thermal Conductivity?
The material's ability to transfer heat. High thermal conductivity is needed for heat sinks, while low conductivity is required for thermal insulation.
What is resistance to corrosion?
The material's ability to resist degradation (chemical or electrochemical attack) when exposed to a specific environment (like moisture, salt, acids, or oxygen).
What are two things that always impact your product, no matter what you are making.
Cost
Time
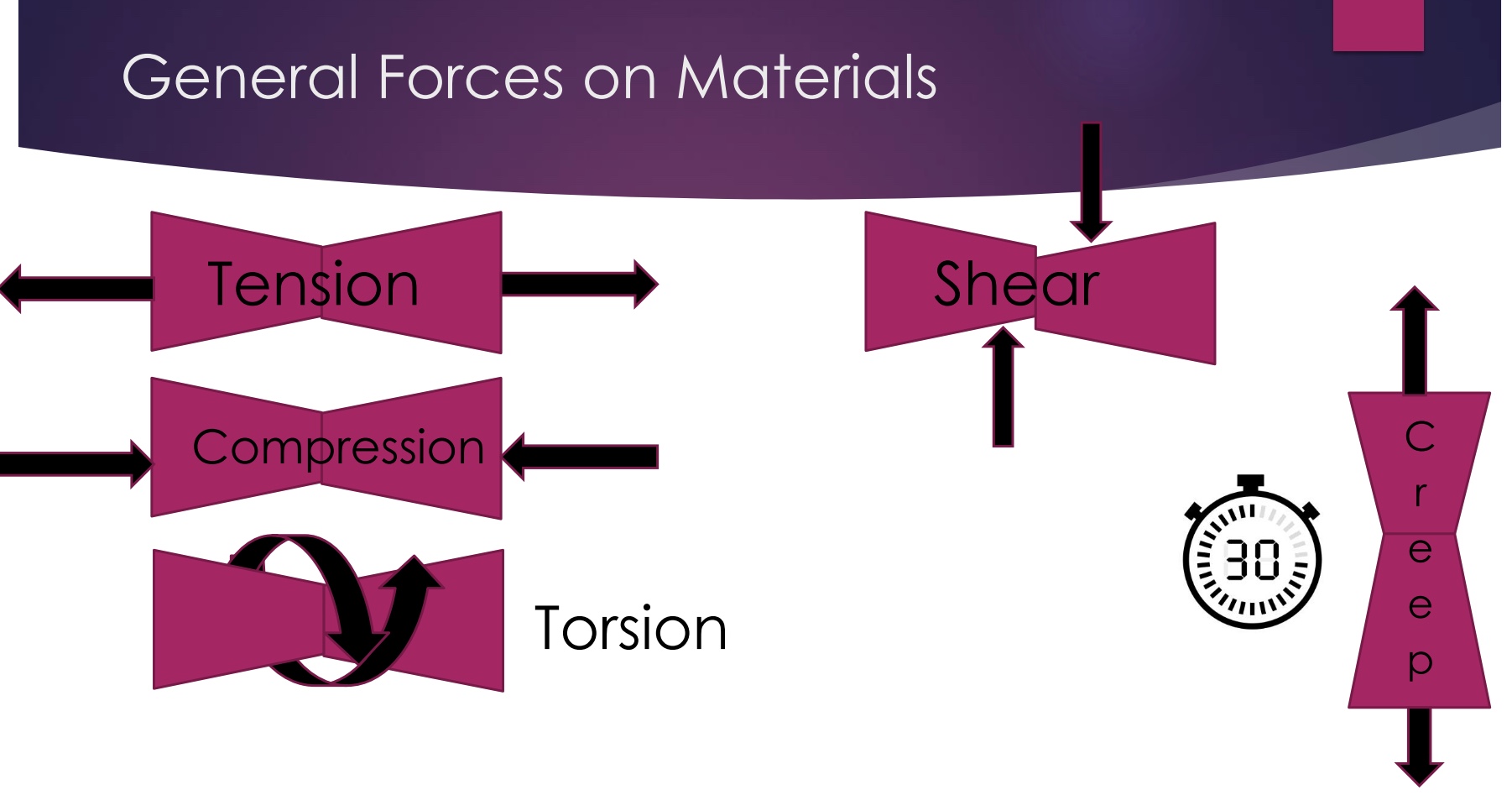
What are the general forces on materials?:
Tension
Compression
Torsion (Twisting)
Shear
Creep (force acting on a material over time)
What is Hardness?
The ability of a material to resist localized plastic deformation (a permanent change in shape), typically from indentation, scratching, abrasion, or cutting.
What is Toughness?
Toughness: The ability of a material to absorb energy and undergo plastic (permanent) deformation before fracturing or breaking. It is a combination of a material's strength and its ductility. (A material can be tough but not hard)
What is Ductility?:
The ability of a material to deform plastically under tensile stress (when pulled) without fracturing. It is the property that allows a material to be drawn out into a thin wire or filament. (its flexibility or bendability)
What is Malleablility?:
The ability of a material to deform plastically under compressive stress (when hammered or rolled) without fracturing. It is the property that allows a material to be flattened into thin sheets.
What is Elasticity?
The ability of a material to return to its original size and shape after a distorting force or stress has been removed.
Whic materials are good conductors and which materials are insulators?
Metals are good conductors while polymers and ceramics are usually insulating materials.
What are alloys?
A substance or material that has 2 or more metals.
What are the two main categories of metals and their definitions?
Ferrous: based on (contain) Iron (like steel, cast iron)
Nonferrous: Are NOT based on (contain) Iron (like Aluminum, Copper, gold, magnesium, nickel, silver, tin, titanium, zinc).
What are some examples of ferrous metals?
steel
cast iron
What are some examples of nonferrous metals?
Aluminum,
Copper,
gold,
magnesium,
nickel,
silver,
tin,
titanium,
zinc
What are the two main categories of metal casting and their definitions?

Expendable Casting (Mold can be used only once (then it breaks) and is cheap).
Permanent Casting (Mold can be used multiple times, is more expensive, and product is smooth, or "shelf ready”).
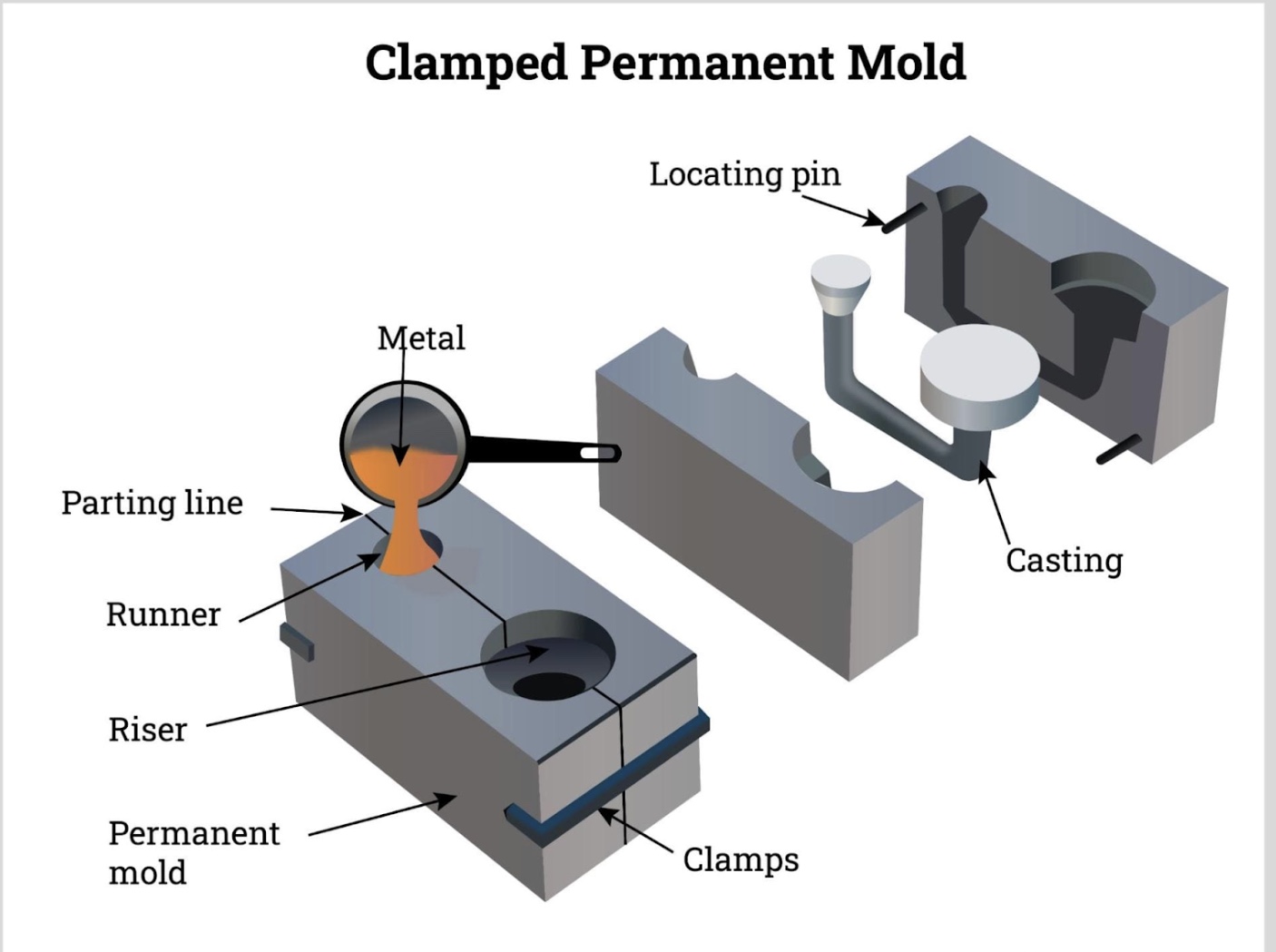
What is forming and what are some types of forming?
Plastic deformation causing the metal to stretch, compress or bend.
Cold forming.
Hot forming.
Roll forming.
Thread roll forming.
What is material separation and what are some processes used for material separation?
Material separation: Using shear force to remove material.
Milling
Engine Lathe
Drill
Saw
How are speed and feed rate different in material separation/
Feed Rate:
Feed rate: rate at which the cutting tool is coming in contact with the material. OR referring to the amount of material being removed over time.
Speed:
Referring to the rpm (rotational speed).
What are three main benefits of cutting fluids?
The three core functions are:
heat dissipation (cooling),
friction reduction (lubrication),
debris removal (chip evacuation),
What are some examples of cutting tool materials?
Carbon steel
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
Carbides
Titanium
Cobalt
Diamond (the strongest)
What are some examples of single point tools (1 cutting surface)?
Engine/Metal Lathe
Turning (moving along the axis of the material)
Facing
Boring (makes the hole precise)
what are some examples of multipoint cutting tool materials (multiple cutting surfaces)?
Drilling
Milling
Sawing
Filing
Thread cutting
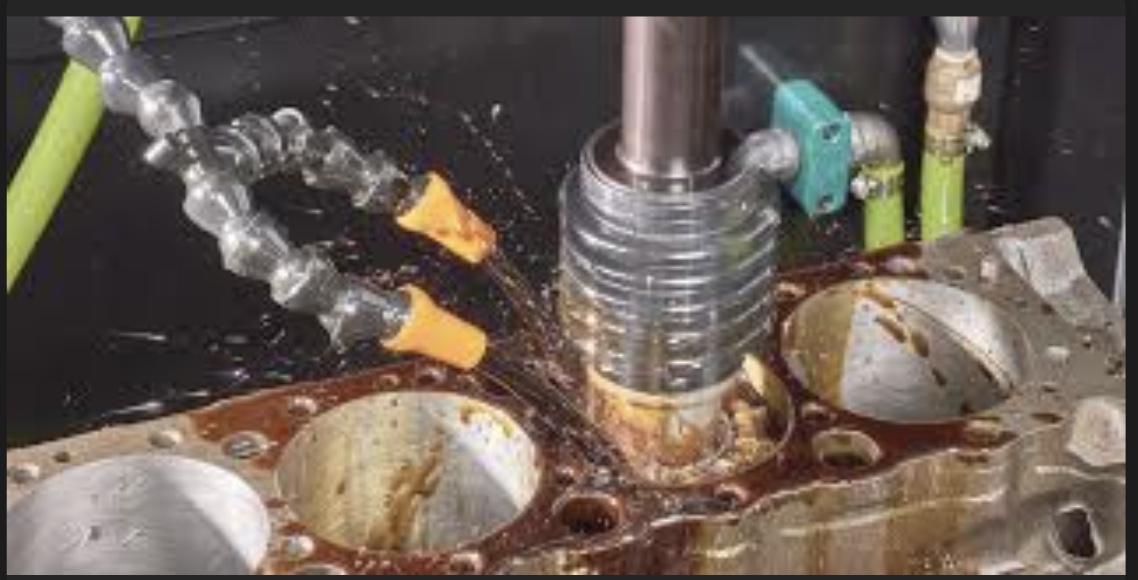

Abrasive machining and picture.
Grainy text
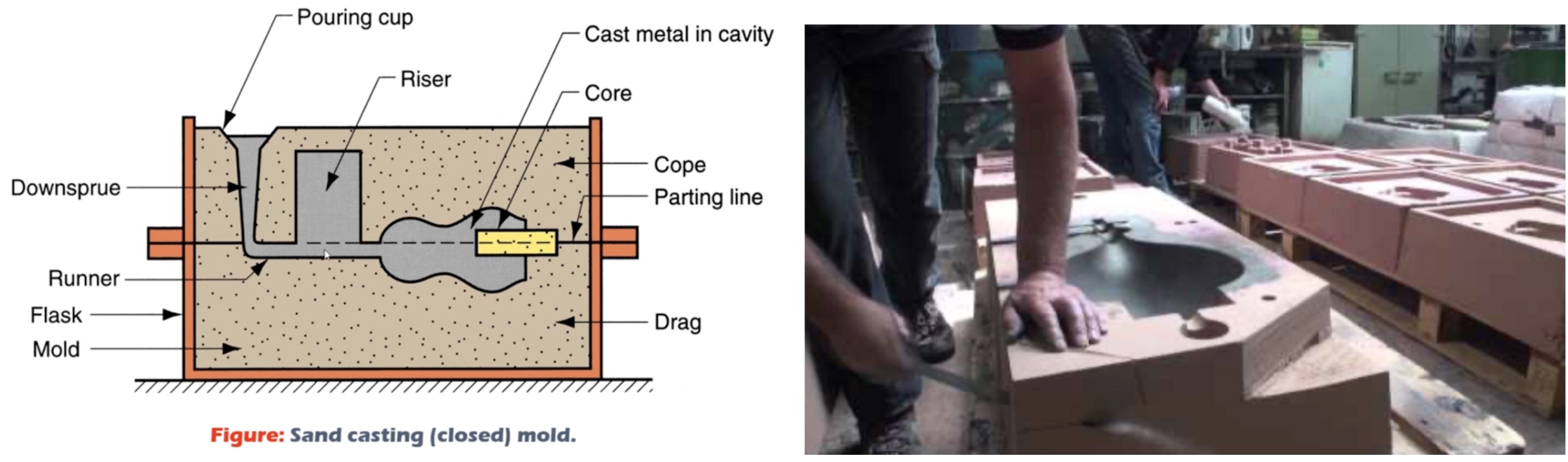
Sand casting definition and picture.

Bolt

Screws


Nails

Pins
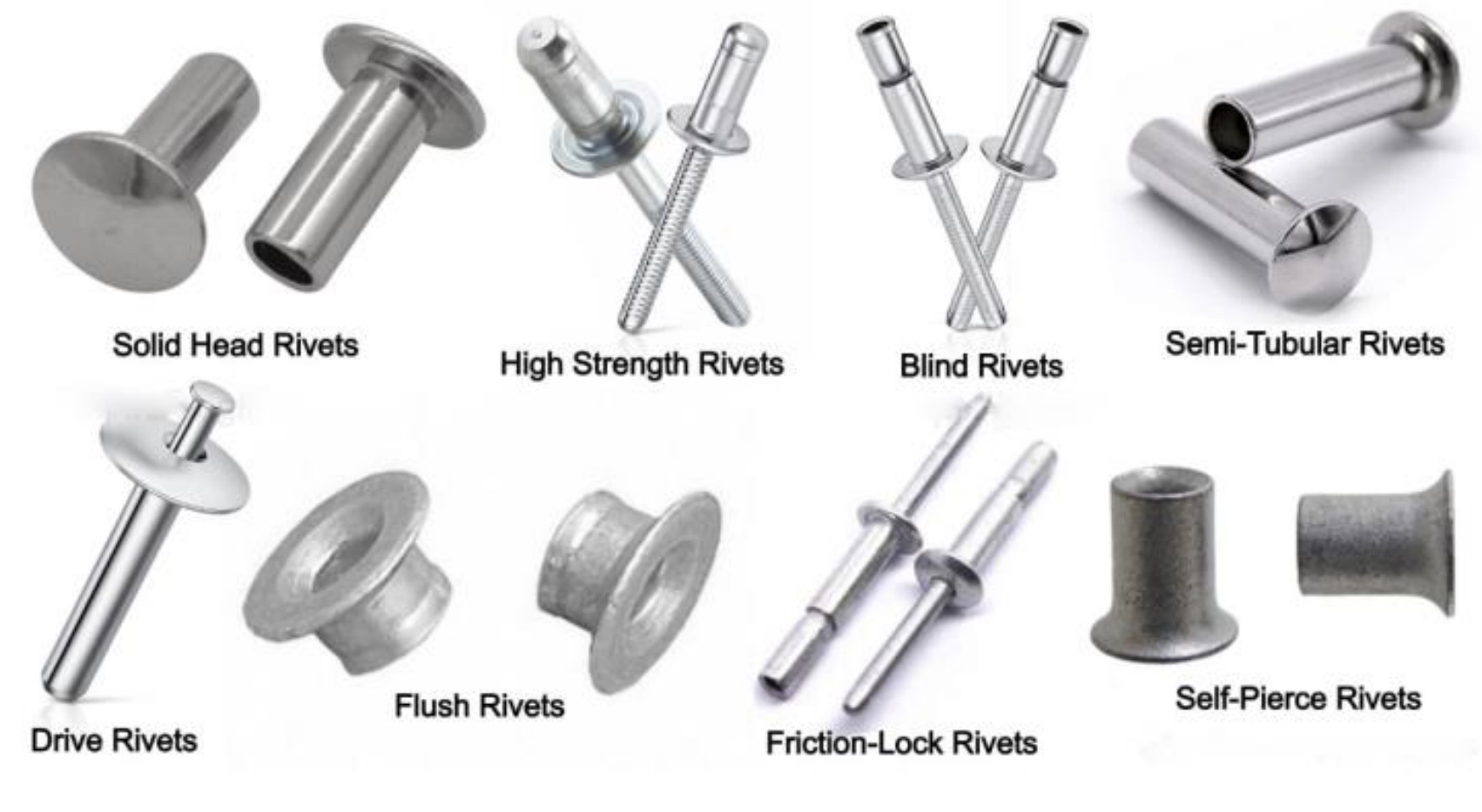

Rivets

Rings and Clips
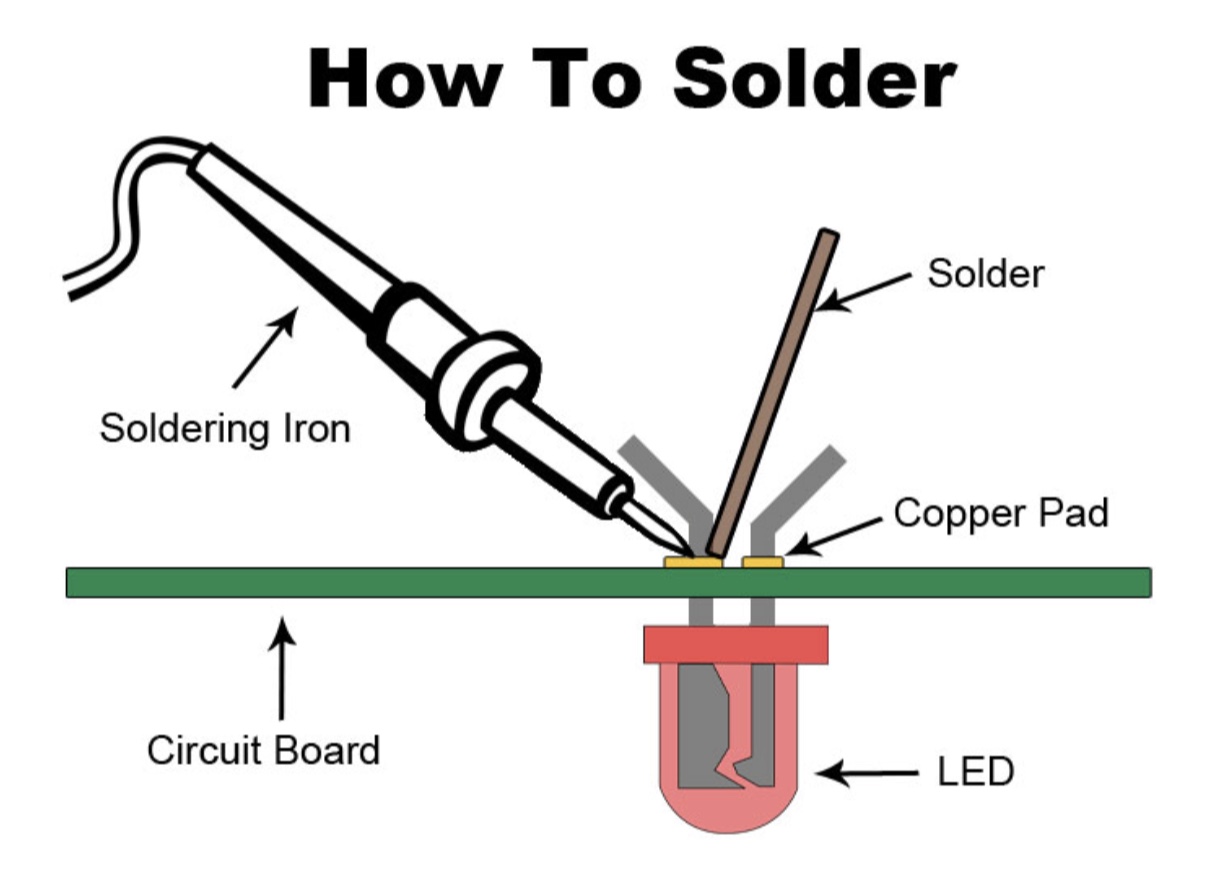
Soldiering
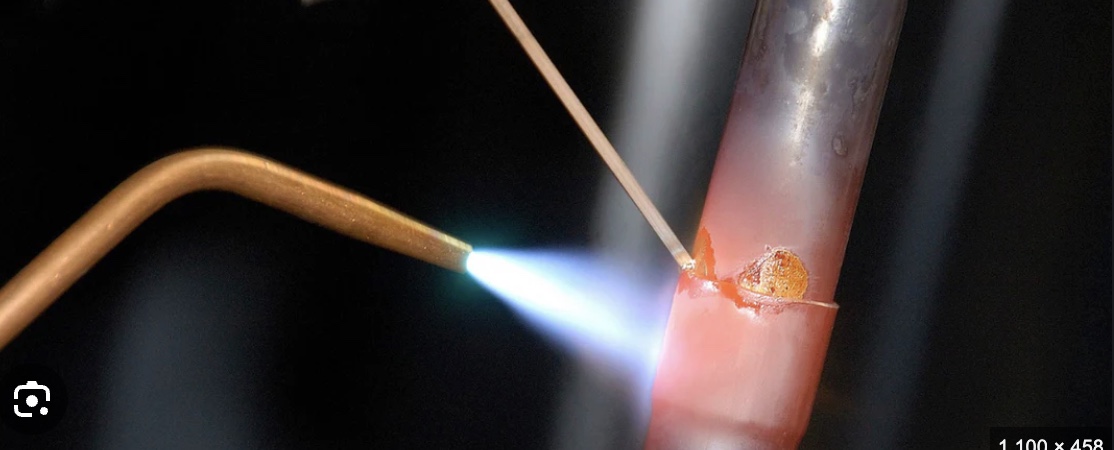
Brazing
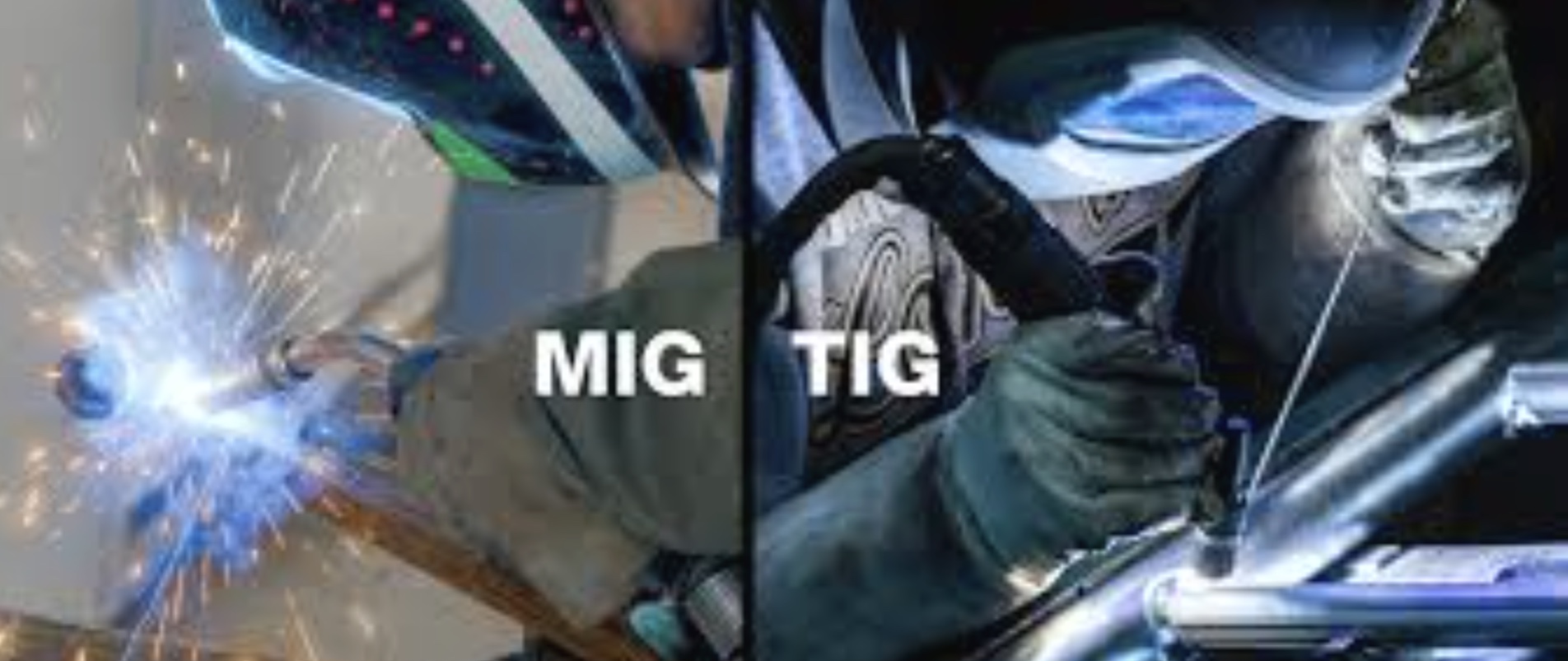


Speed faster
Welding MIG
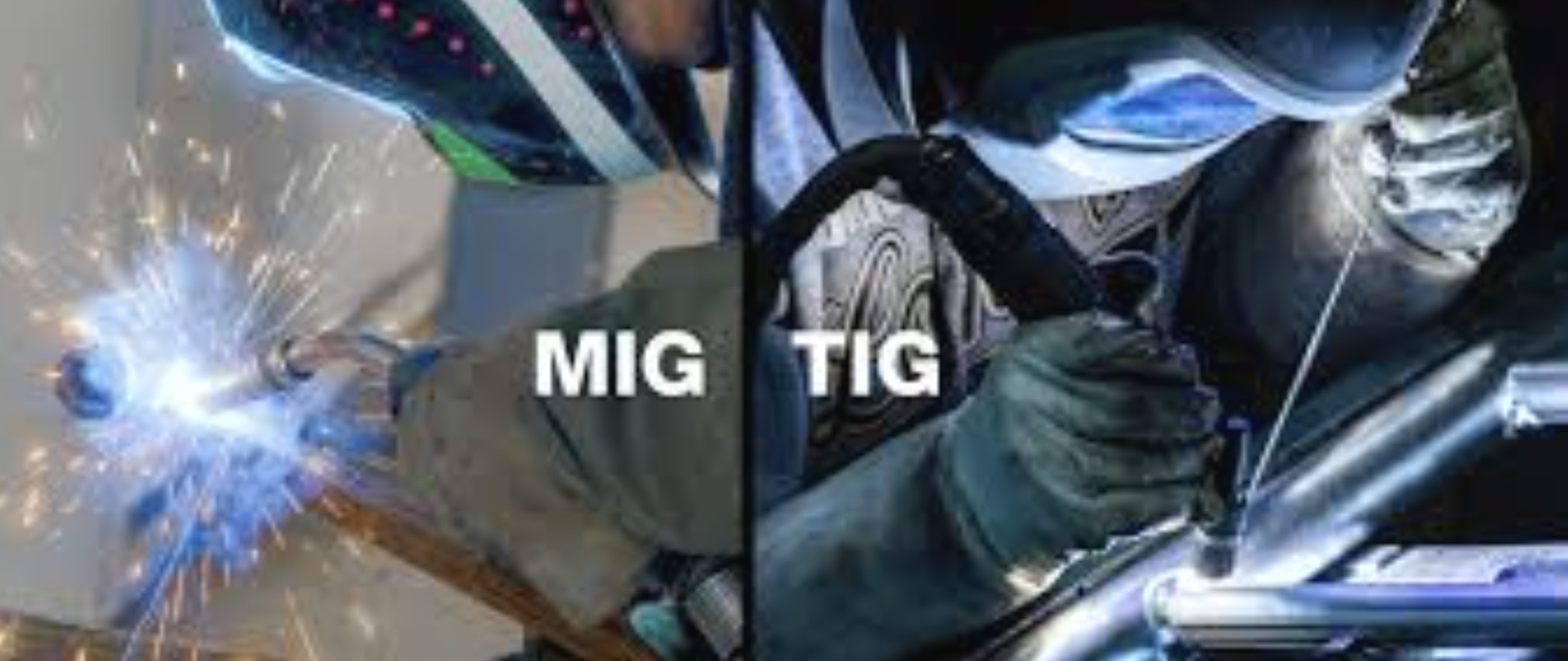

Better control/quality
Welding TIG

Welding Arc/stick
WHAT 2 THINGS (PROPERTY CHANGES) HAPPEN TO STEEL WHEN YOU INCREASE THE AMOUNT OF CARBON?
The higher the percentage of Carbon, the harder the metal.
As hardness increases, brittleness also increases.
WHAT ARE SOME ADVANTAGES OF LOW CARBON STEEL?
The advantage of low carbon steel is that it is very cheap and available. Also very flexible.
High ductility and malleability, making it easily formed and welded.
What force is used for material separation?
Shear force is used for material separation.
What does cohesion use to bond its materials together?
cohesion uses heat and/or pressure to bond its materials together.
What does Adhesion use to bond its materials together?
Adhesion uses glue and/or epoxy to bond its materials together.

Copper
Aluminum
Steel
Brass
Bronze

Shell mold Casting
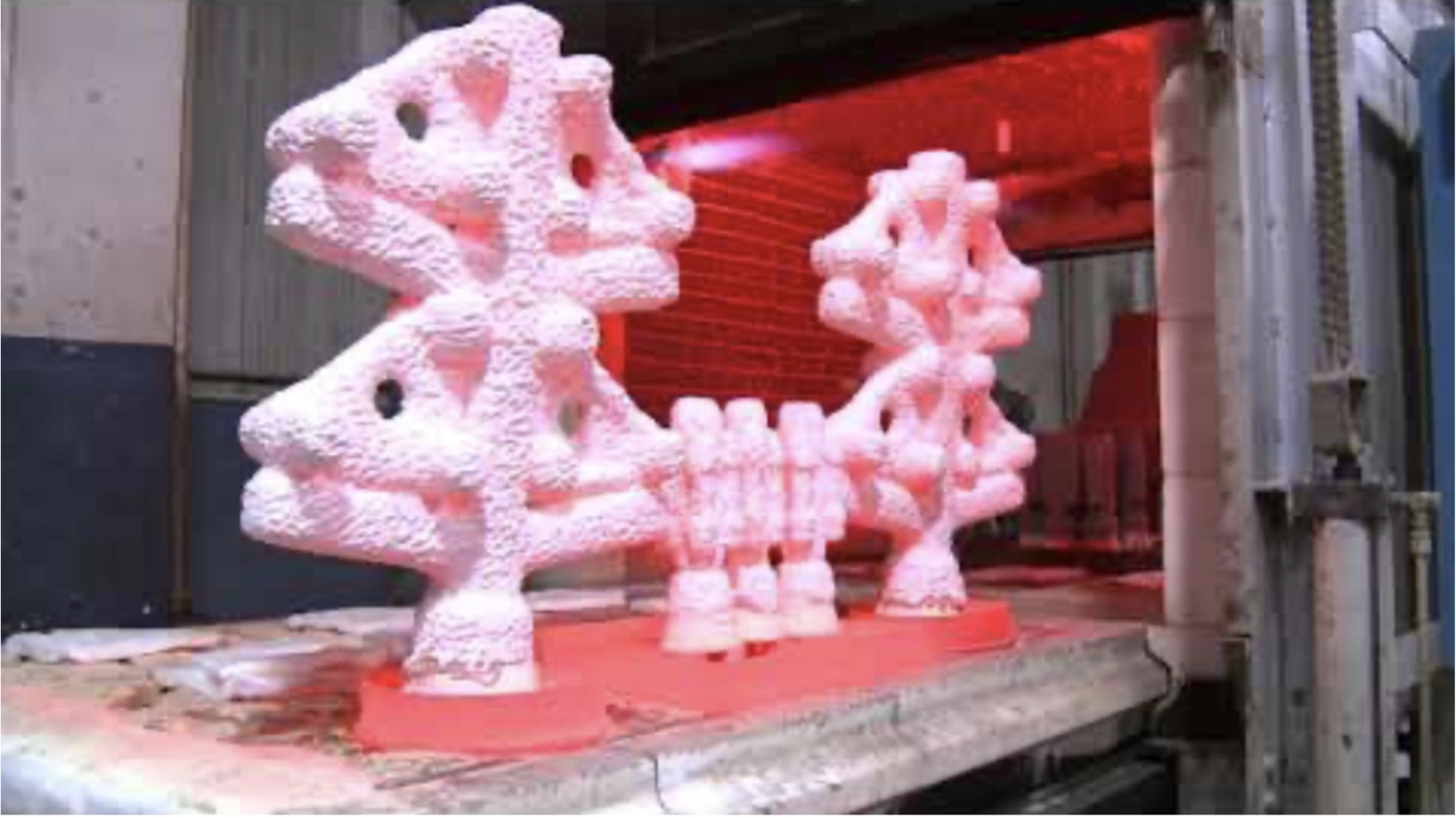

Investment Casting/Lost - wax casting
Bending, drawing, and freezing
Stainless or Carbon steel
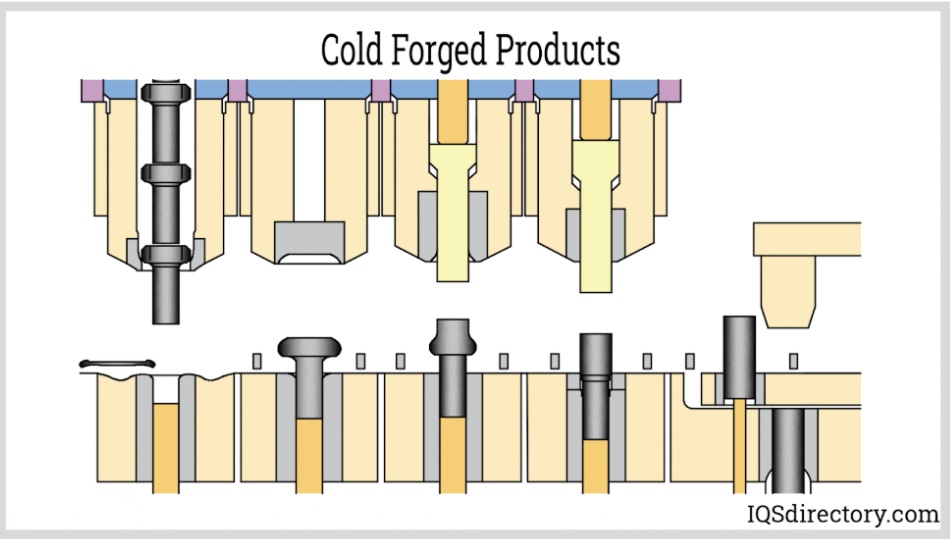
Cold forming
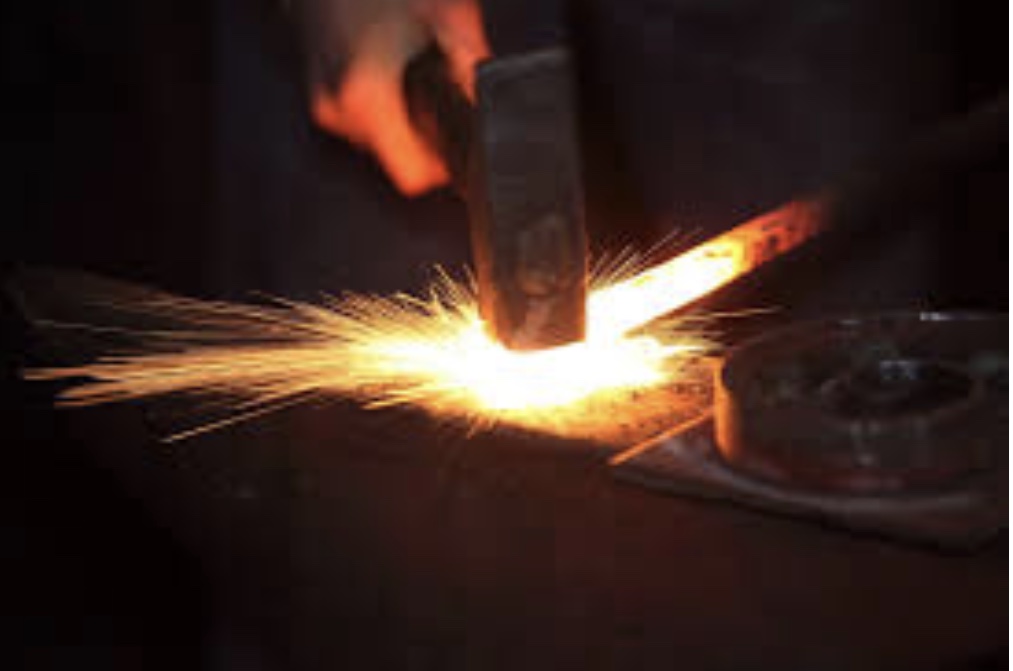

Hot forming
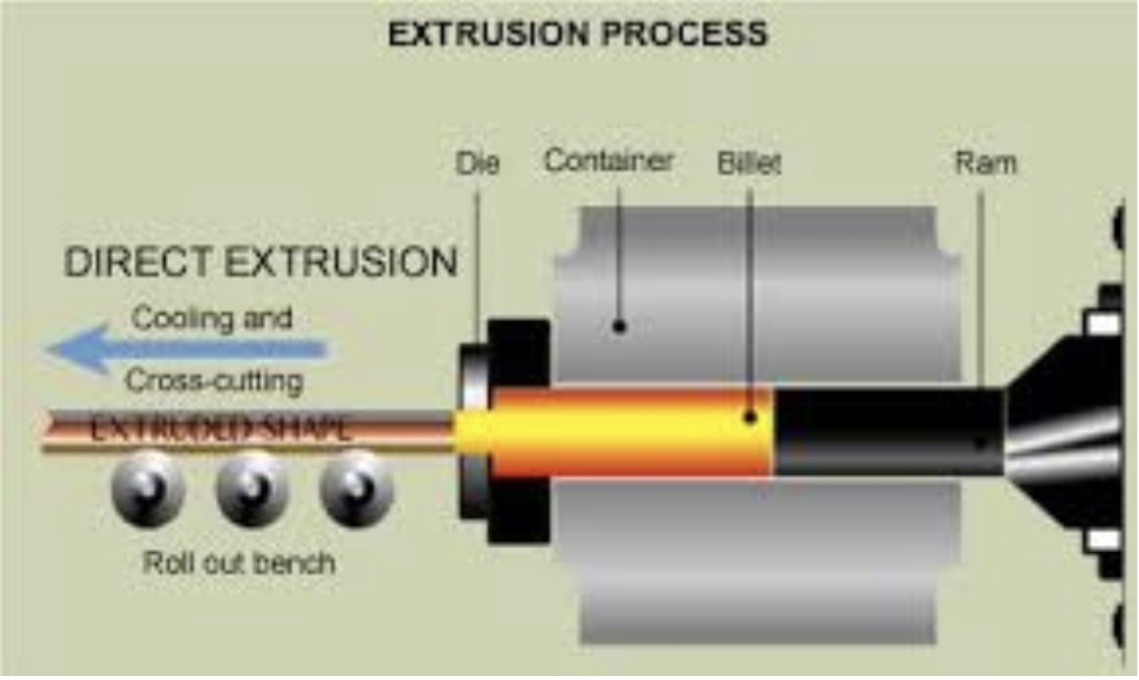
Metal extrusion
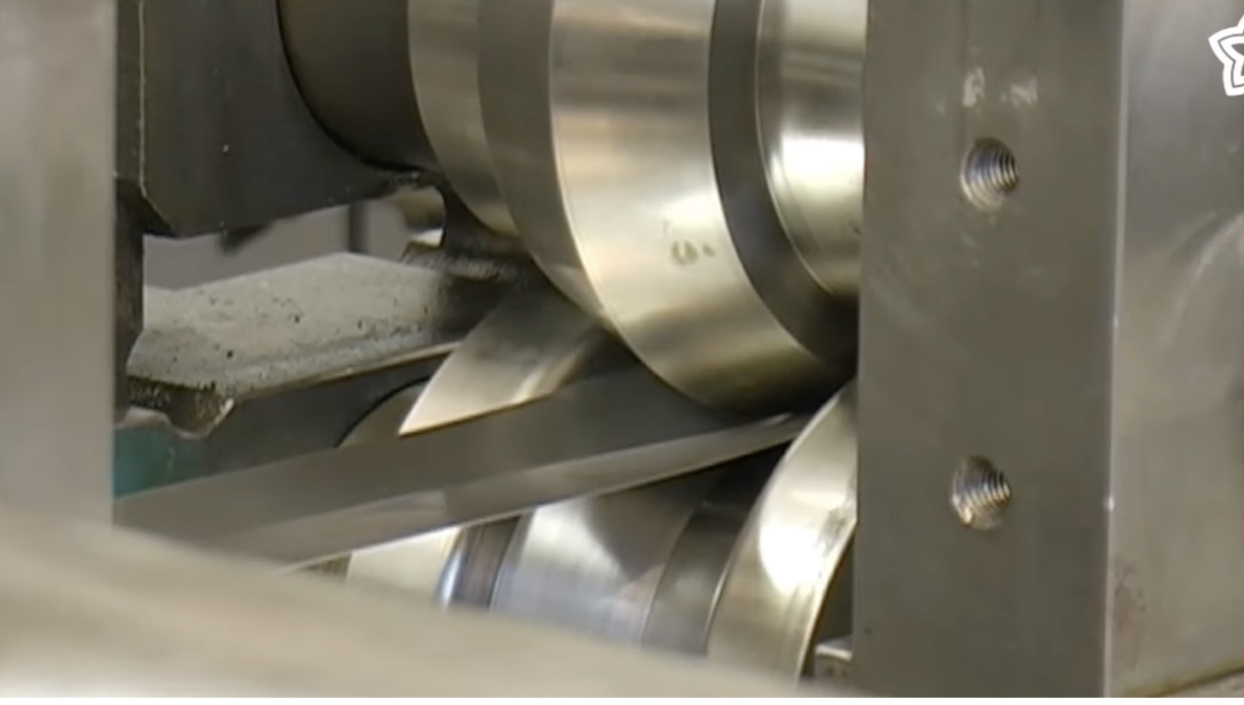

Roll forming
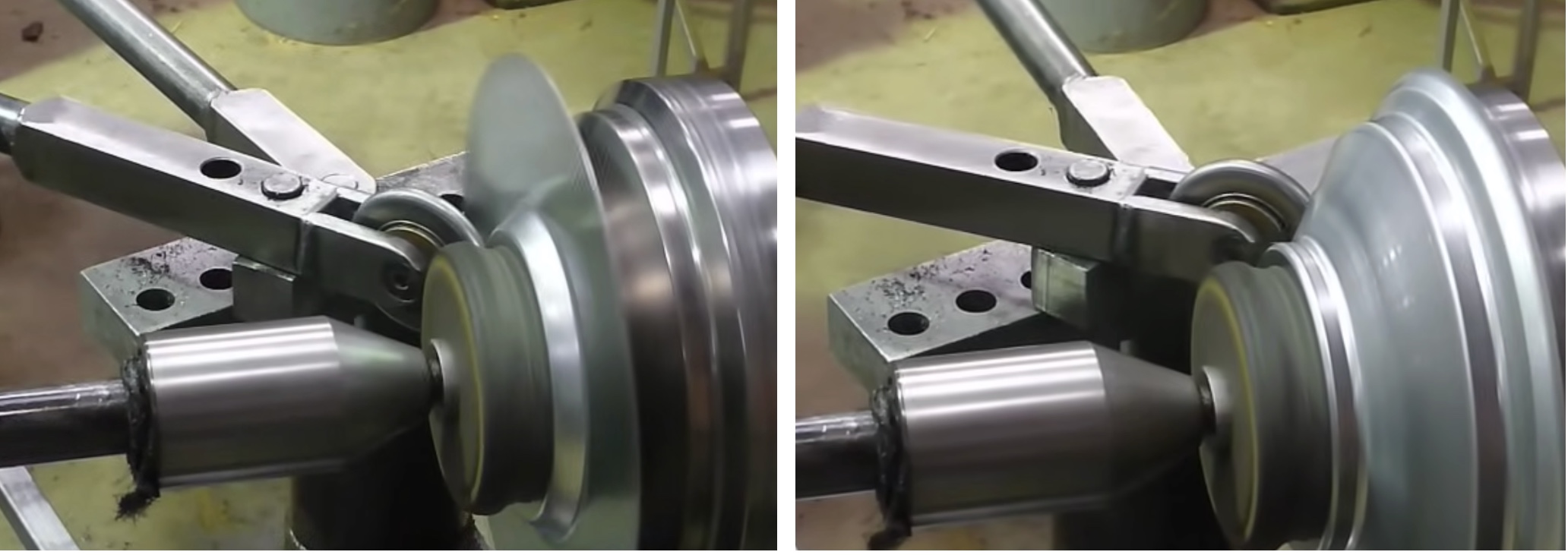

Spin Forming
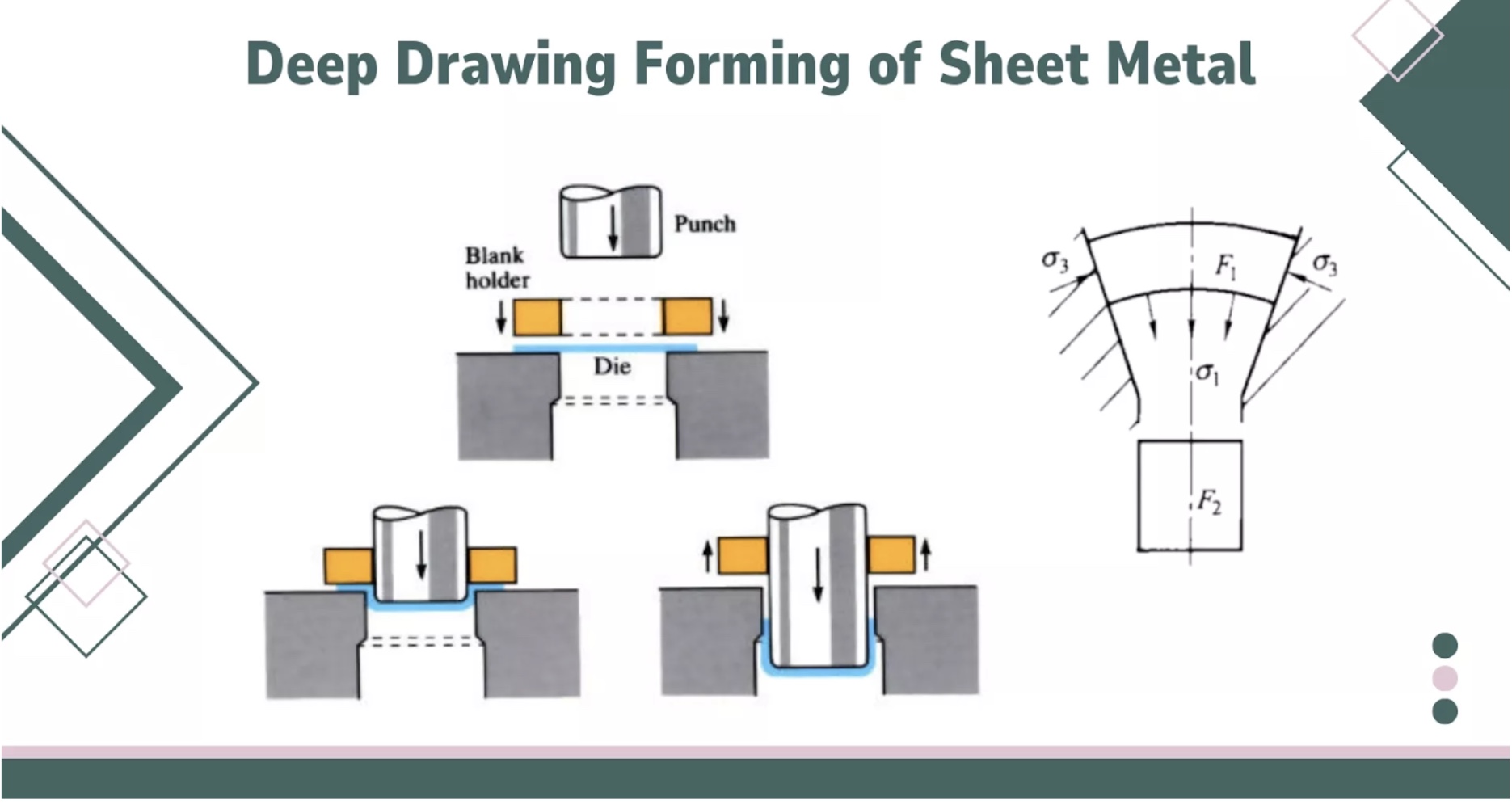
drawing
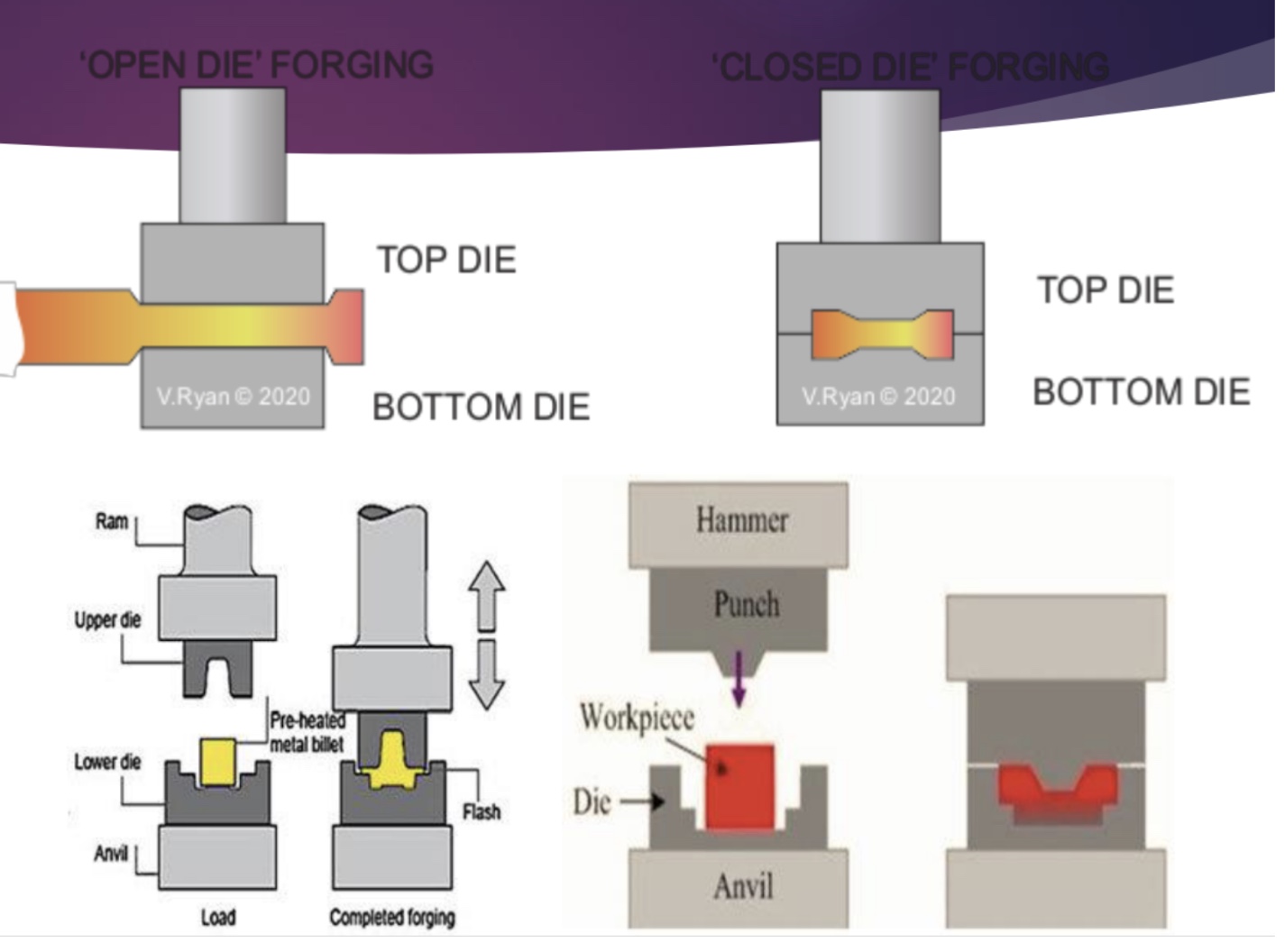
Die
Buffing
Spot wielding
Miling
Lathe
Grinding
Polishing
General forces on materials