EQ3- How are human rights used as arguments for political + military intervention?
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
4 geopolitical interventions to address human rights issues
Development aid
Trade embargos
Military aid
Indirect + direct military action
Development aid + example
Financial aid given to developing countries to promote human rights.
given by multilateral + bilateral aid
UN General assembly asked wealthy countries to commit 0.7% GNI a year to aid- only 6/20 met target in 2015, UK made it a legal requirement in 2015
EXAMPLES
UK announced £100M 3 year package in 2022
designed to support Ukraine economy + reduce its reliance on gas imports from Russia, and countries taking in its refugees e.g. Moldova
Trade embargo + example
A ban that restricts trade with a particular country
encourages country to change actions or their economy will decline
often used in response to perceived threats to international security or for countries with a record of human rights abuses
EXAMPLES
EU imposed arms embargo, incl. technology military services
encourage cease to actions in Ukraine as they threaten territorial integrity + independence of Ukraine
Military aid + example
Countries provide money, weapons or military training to another country’s official army to help stop human rights abuses e.g. terrorism, overthrow a dictator
sometimes given to opposition groups fighting for democracy against authoritarian gov’s
EXAMPLES
US aid packages to Ukraine worth $775M each included rockets, ammunition, drones, etc in 2022
helps defence across long term
Indirect military action + example
Military equipment provided unofficially by 1 country to another/ military/rebel group within a country
done in support of 1 side of a civil conflict
EXAMPLE
2017 British army personnel trained Nigerian forces to improve security + fight Islamic militant group Boko Haram
Direct military action + example
Armed forces from 1 country engaged in conflict to another
EXAMPLE
2003- USA+UK among a coalition of countries sent troops + carried out airstrikes in Iraq against gov of Saddam Hussain
Who promotes geopolitical intervention and how?
IGO’s- UN, EU, WB, WTO
impose trade embargos, put conditions on aid, express disapproval of HR abuses
NGO’s- Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch
campaign for protection of human rights, petition+ lobbying of authoritarian gov’s e.g. free protestors imprisoned unfairly, encourage IGO’s and govs to intervene in HR abuses
e.g. Amnesty International campaigns with local NGO’s in Afghanistan to try improve education for women
National governments
Why is it difficult for IGO’s, NGO’s and governments to agree on action?
could be due to political + economic purposes/ self-interest e.g. oil reserves
e.g. UK performed airstrikes in Libya 2011 to protect civilians, but it is claimed it was to gain access to more oil reserves
risk of intervention could lead to wider conflict + injury to civilians
cutting off aid could reduce countries ability to support citizen’s basic needs
organisations/ countries involved could have different aims e.g. increase global influence or protecting human rights
How do Western Governments use human rights as a basis for intervention?
Offering aid with conditions attached e.g. give aid if they improve the education of women
Negotiating trade agreements e.g. lowering import tariffs
Military intervention for serious breaches of HR
How does human rights interventions challenge national sovereignty?
One nation interferes with governance of another.
Create tension between national sovereignty + R2P (states have responsibility to protect their populations from genocide, war, etc, and the international community has responsibility to assist).
Libya 2011- challenge to national sovereignty
PROBLEM: civil war erupted against Gaddafi (ruler) who violated HR + funded global terrorism.
INTERVENTION: UN authorised bombing raids by France + UK in support of civilians + rebels under R2P. Gaddafi was then killed.
NATIONAL SOVEREIGNTY CONCERNS: 5 countries on UN security councils were concerned there was insufficient evidence for interference.
Real reason for interference was regime(gov) change- NATO decided who should rule, instead of the nation.
Libya has 10th largest oil reserve- could be for this reason.
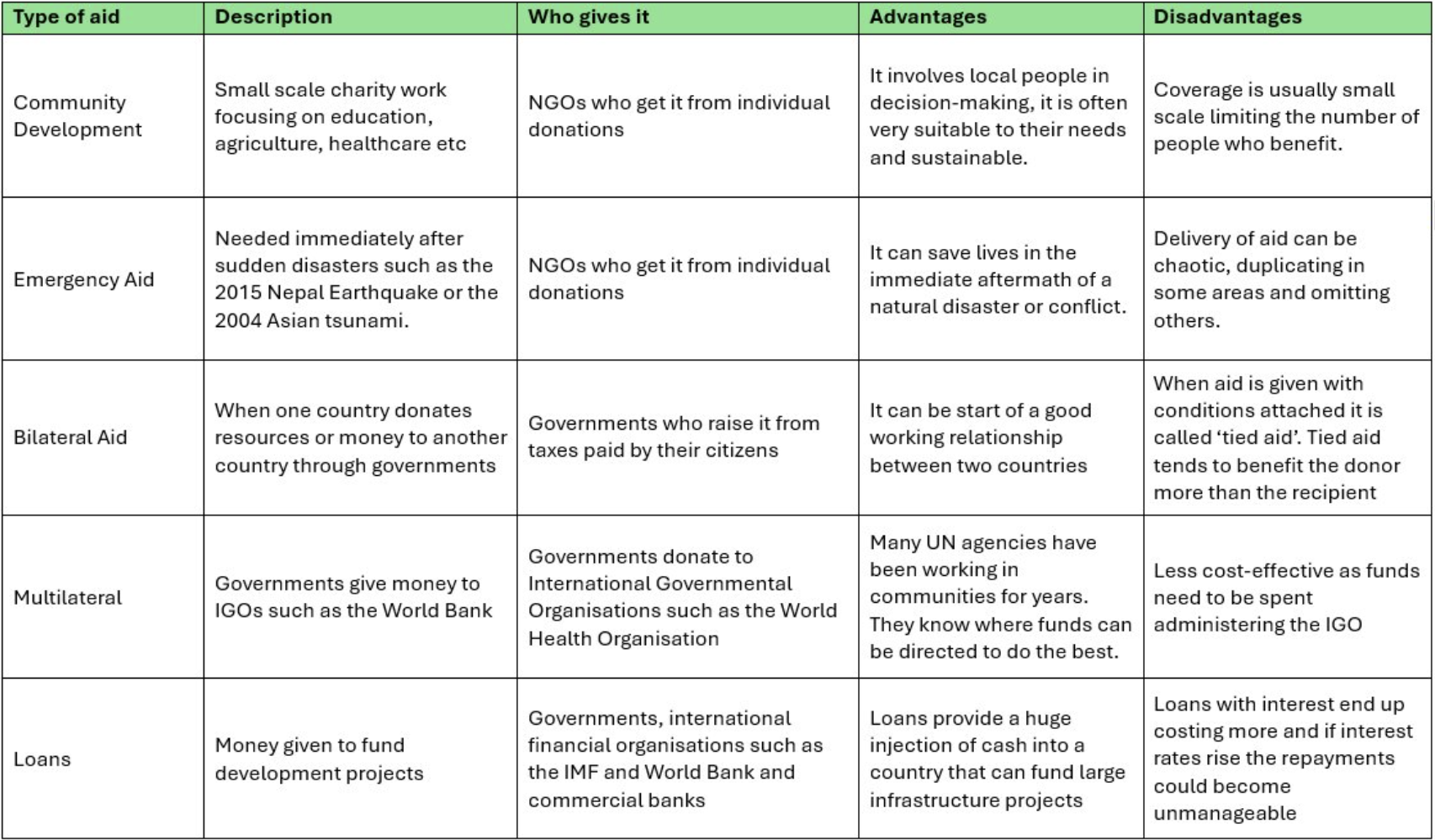
Types of development aid
Community development
Emergency aid
Bilateral aid
Multilateral aid
Loans
Development aid pros+cons
Failure of aid in Haiti
NEED FOR AID
2010 earthquake left 220k dead + 1.5M homeless
outbreak of cholera in tent cities killed >9k ppl
AID
over £12bn aid pledged by gov’s, IGO’s (UN), NGO’s (Red Cross + Oxfam)
money was used in diff ways e.g. emergency shelters + restore access to clean water
CONCERN
2yrs after, 500k still lived in temporary shelters with no electricity plumbing, sewerage
condition for ½ money to be spent within 18 months, but only 40% spent
gov + NGO’s were unable to coordinate + use money effectively
Example of loans as development aid- WB in Uganda
$230M in aid to help with issues e.g. building resistance to climate change
-conditions: Uganda had to meet 197 separate conditions before given funding
-environment: prioritise economic development over environment- leads to displacement of indigenous groups + environmental degradation
Success of development aid in Africa
Malaria
increased funding $1.7bn allowed more malaria control interventions
international aid programmes (Net for Life)
global death rate from malaria fell 25% between 2000-20, preventing 6.2M deaths
areas with high coverage- bed nets+treatment programmes, have recorded ↓ by 50% e.g. Tanzania, Zambia
Gender equality
45% UN bilateral aid targeted to gender equality
WB target on S+E African primary aged girls- 25M more enrolled than early 2000
loans + microfinances- 68% ↑ in earnings
still 10% difference in labour force participation between men+women
Problems with development aid
Aid dependency- hinders development
gov relies on money instead of fixing tax systems/ raising revenue to self-fund development projects + basic services
long-term development planning is difficult- amount of aid received is uncertain
Corruption + inequality
used by political elite to ensure they remain in power + repress citizens- buying votes e.g. Zambian former president 2009 charged with embezzling $12M aid money
minority groups pay price for misuse of aid through reduced access to services, increased costs
Impact of economic development on the environment, minority groups + human rights
Niger Delta oil production
Environment | Minority groups | HR |
40M litres spilled every year across delta- pollute ground+surface water, and soil Mangrove forests regularly damaged | Access to clean water limited due to oil spills Traditional livelihoods (fishing, agriculture) damaged by oil spills- disrupt traditions+make ppl poorer | Conflict over oil reserves led to human rights abuses- Nigerian military burnt down Ogoni tribe villages, making 300k homeless |
Accounts for 70% export revenue, oil accounts for $10bn per year
What is land grabbing?
Acquisition of large areas of land in developing countries by domestic + TNC’s, gov’s, + individuals. Land may be taken over + not paid for.
used as a resource for bribes- land is the greatest asset
Impact of economic development on env, minority groups, HR.
Land grabbing in Kenya
more soil degradation, deforestation, loss of biodiversity
↑ chance of food insecurity due to focus on commercial agriculture over food production
85% people rely on agriculture for livelihoods- reduces rights to decent standard of living + food
Examples of military intervention driven by geopolitical interests, but justified by HR
1995 NATO intervention Bosnia
air + bombing campaign against Bosnian Serbs who attacked muslims
HR justification: Serb leader convicted genocide + war crimes, 8k Bosnian Muslims killed
geopolitical interest: NATO did not want Bosnian war+conflict spilling over into other European countries, destabilising the region
2003 invasion in Iraq
US-led coalition incl. UK, Poland, Australia, invaded Iraq + overthrew regime
HR justification: Saddam Hussein authoritarian rule- mass killings, WMD e.g. chemical weapons, torture against Kurds+Shiites
geopolitical interest: safeguard oil supply from the Middle East
Example of military aid to support countries with questionable HR records
Saudi Arabia + UK
SA has an undemocratic regime, poor women’s rights e.g. fathers are default guardians of children
UK has supplied SA with $23bn in weapons since 2015
due to trading relationship- SA has invested over £60bn in UK
provided military support to SA who supported Yemen gov fight against rebel groups
has led to HR violations- bomb attacks of civilians, 17.5k deaths+injuries
What is the ‘War on Terror’ + its HR justifications?
A global battle against terrorist organisations.
USA sent troops to Iraq + Afghanistan, unapproved by the UN
justified by: Iraq holds weapons of mass destruction, concerns over more terrorist attacks e.g. 9/11, protecting human rights e.g. Saddam Hussein’s rule in Iraq, defend USA
How did the USA violate human rights + the UDHR during the war on terror?
US soldiers tortured prisoners in Iraq
those accused of being terrorists were flown to Guatanamo Bay- tortured + held without trial for years
organisations like Al-Qaeda used this violation to recruit new members, and ↑ risk of captured Americans for harsher treatment