ECON FINAL
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Economics
The study of purposeful (goal oriented)) human behavior
cultural mandate
God’s directive to dominate the earth
positive statements (used in econ)
what is
normative statements
what ought to be
skepticism
attempts to render doubtful every position
relativism
truth and falsity are product of differing convention and frameworks
empiricism
we have no source of knowledge other than sensory experience
apriorism
knowledge is independent of experience
Christian apriorism
mental categories that are implanted in us by God
praxeology
studies preferences ;denotes our preferred method of completing everyday tasks or our approach to solving problems
human action
Ends
the purpose for acting
means
the things used to achieve ends
ideas
what you apply means to, to achieve an end
rational
purposeful behavior
scarcity
ends outnumber means
scarce
something that is both desirable and in limited supply
rare
something that is in limited supply, but which lacks desirability
ex ante
before the fact
ex post
after the fact
positive economics
the branch of economic analysis that describes the way the economy actually works
oppurtunity cost
the value of the alternative that must be forgone as the result of choosing to achieve a certain end
economize
to try to achieve the ends with the least means
subjective value
the worth of a good or service as determined by its usefulness to the buyer
economic good
the means used to satisfy an end
consumer good
directly serviceable means for satisfying ends
producer good
indirectly serviceable means for satisfying ends
production structure
a visualization of the relationship between consumer goods and producer goods
marginal utility
the utility one receives from the marginal unit of a good
the law of marginal utility
there is an inverse relationship between the quantity of a good and the marginal utility of that good
land
all natural resources used to produce goods and services
labor
human effort directed toward producing goods and services
capital goods
goods that are used in producing other goods rather than being bought by consumers
marginal unit
the next unit gained or given up
utility
the capacity to be useful and provide satisfaction
the law of diminishing returns (the law of too many cooks in the kitchen)
when all other inputs are held constant the increase in output attributable to the variable input eventually falls
labor theory of value
the belief that all value in produced goods is derived from labor
discipline of repeated dealings
if you don’t deal with me today as I expect ill refuse to deal with you tomorrow
direct exchange
the trading of goods for other goods or services without the use of money
involuntary exchange
interaction lacking consent
voluntary exchange
interaction based on consent
protectionism
the practice of shielding a country’s domestic industries from foreign competition by taxing them
paternalism
people are mistaken abut their own best interests
ownership
necessary for exchange
absolute advantage
when ones party is better at producing a good than another party
autarky
economic self sufficiency
division of labor
different people specializing at producing different goods
specialization
focusing of a specific task to the exclusion of ither possible tasks
private property
property owned by an individual
doux commerce thesis
exchange cultivates the virtues that underpin free and prosperous societies
the capitalist peace
the idea that advanced capitalist societies do not choose to go to war against one another
exchangeability
permits economic goods to be allocated to their most highly valued users
excludability
the ability to prevent other users from consuming some piece of property
accountability
individuals bear the cost/reap the benefits of their actions
tragedy of the commons
individuals '“over consume” a good due to the lack of private property rights
private predation
burglary, looting, mugging ect.
public predation
takings, confiscating taxation, regulation, inflation, etc.
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
money
commonly accepted medium of exchange
economic calculation
producer comparing revenues/costs to determine weather profit/loss has been made
demand
relates different quantities of a good a buyer is willing to purchase at each price
maximum buying price
largest amount of money valued less than the relevant unit
demand curve
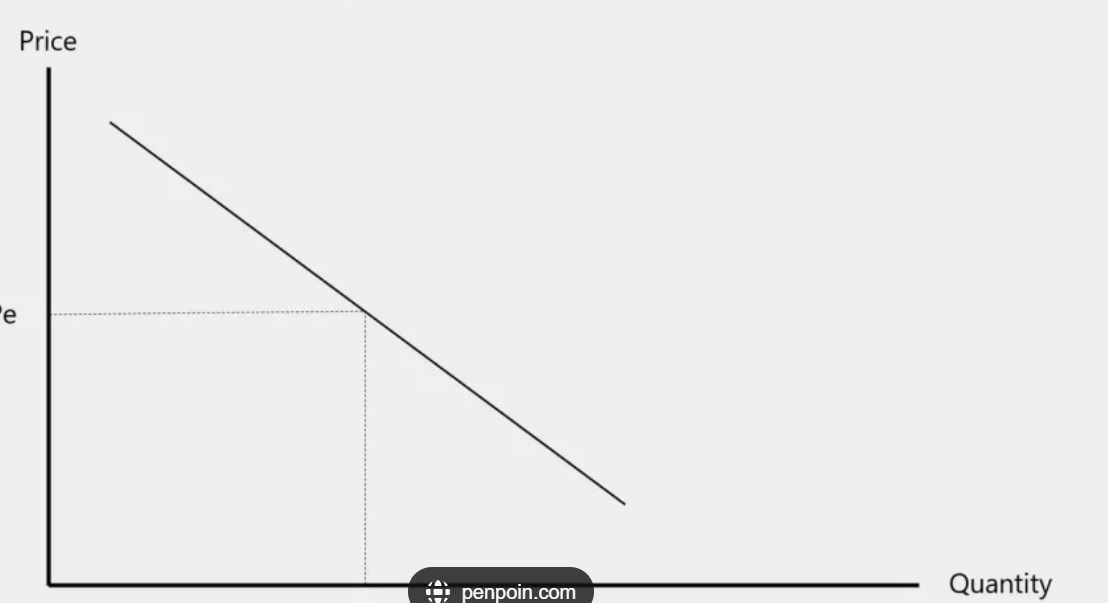
the law of demand
there is an inverse relationship between the hypothetical price of a good and the quantity of that good a person will buy ceteris paribus
ceteris paribus
all other things held constant
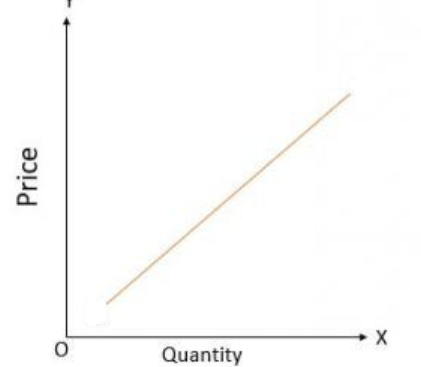
supply
related different qualities of a particular good an individual is willing and able to supply at very given price
min selling price
smallest amount of money valued more then relevant unit
the law of supply
there is a positive relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good, supplied ceteris paribus
most eager buyer
the person willing to pay the most for the good
most eager seller
the person willing to accept the lowest price for a good
supply curve
equilibrium price
the price at which there is no excess demand or excess supply
excess demand
quantity demanded>quantity supplied (shortage)
excess supply
quantity supplied>quantity demanded (surplus)
the law of one price
for any good there will (eventually) be only one market price which is paid and received ceteris paribus
arbitrage
attempting to profit by buying low and selling high
the role of prices
price allocate resources to their highest valued users
elasticity
a measure of sensitivity/responsiveness to change in prices
elastic demand
a situation in which consumer demand is sensititve to changes in price
inelastic demand
a situation in which an increase or a decrease in price will not significantly affect demand for the product
total expenditure
P*Q
increase in demand
demand curve shifts right
decrease in demand
demand curve shifts left
complements
goods used to jointly achieve some desired end
SUBSTITUTE
good consumed in place of some other good
increase in supply
curve shifts right
decrease in supply
curve shifts left
increase in consumer income
-willing and able to buy more at each price
- increase in demand
-demand curve shifts right
production
creation of value
consumption
destruction of value
saving
sacrificing present consumption
plain saving
storing up consumer goods so they can be consumed in the future
investment
the transfer of saved resources to lengthen the production structure
capitalist saving
sacrificing consumption to lengthen the production structure
time preference
the intensity of the preference for current over future consumption
positive time preference
humans always prefer present consumption to later consumption
duration of servicableness
the period of time for which a capital good continues yielding services
capitalist
individual who saves income/invest the formation of capital goods
entrepreneur
undertakes production by combining factors of production to produce a final product to sell for income
total revenue
price of unit times the quantity of the unit sold