RADIOGRAPHIC POSITIONING FOR DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING - Fill in the Blank Flashcards
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards cover central ray and image receptor basics, projections, planes, body positions, decubitus, position vs. projection, and common radiographic rules.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Central Ray
the imaginary line in the middle of the X-ray beam spectrum.
image receptor
The is the device that receives the energy of the X-ray beam as it passes through the body and formulates an image.
anatomic position
Patients should always be in
Anterior
front
posterior
back
Coronal (Frontal) plane
anterior; posterior
Axial (Horizontal) (Transverse) plane
superior; inferior; slice
Sagittal (Longitudinal) plane
left and right
Median (Midsagittal) plane
equal
AP projection
CR enters anterior and exits posterior of part/body
PA
CR enters posterior and exits anterior surface of part/body
Oblique
angled stance where neither sagittal not coronal plane is perpendicular to IR
Position and projection are .
opposite
SID
distance between the X-ray tube (source) and the image receptor
OID
distance between the and the image recepto object (the body)
Axial projection
central ray angled more than 10 degrees along the long axis of the body.
A tangential projection
directs the central ray to the outer margin of a curved surface to a body part just under the skin and project it to the IR.
Decubitus positions
patient is laying down and central ray is horizontal and parallel to the floor
the three primary decubitus positions are .
Lateral Decubitus, Dorsal Decubitus, Ventral Decubitus
Dorsal decubitus means lying on the surface.
back
Ventral decubitus means lying on the surface.
stomach
lateral projection
CR enters lateral surface and exits to the opposite lateral surface part/ body; side to side projection
A typical radiographic study requires a minimum of projections.
two
When a joint is in prime interest area, a minimum of projections is required.
three
In anatomic position the patient is facing you, and their right will appear on you
left
For hands and feet, digits are always orientated
up
Evaluation criteria
Positioning; exposure factors, all pertaining anatomy
positioning rules exceptions
post-reduction upper and lower limbs; pelvis study projection unless a hip injury is suspected; abdomen (KUB)
Position
placement of body (part) in relation to IR. or The body (part) as seen by the IR
Projection
path of the central ray as it enters and exits the body; path of the central ray as it excited the x-ray tube and goes through the patient to the IR
How much projections are required
two
exam
shot
procedure
ongoing and dynamic
recumbent
laying down
How can a patient be viewed in recumbent
dorsal, ventral, lateral
radiographer
HC professional that does diagnostic imaging and radiation therapies
A.L.A.R.A
As low as reasonable achievable
What does alara do
avoid radiation exposure that doesnt serve a direct need or benefits exam
In ALARA what are the fundemental principles
Time, distance, sheilding
Interaction with patient
explain procedure; let patient do as much as possible
dressing patient
No metals or thick plastic
Motion control
image is blurry or has loss of significant fine
Stopping motion control
use tape, sponges, stands
gondal shielding
shielding patients for all exams thats not pelvis and abdomen
collimators
adjustable filter in x-ray tube controlling field size
Must haves in a picture
date, name or ID number, Maker, industry ID
4 quadrents of the abdomen
RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
Nine regions of the abdomen
R hypochondrium, epigastric, L hypochondrium , R lumbar, umbilical, L lumbar, R iliac, hypogastric, L iliac
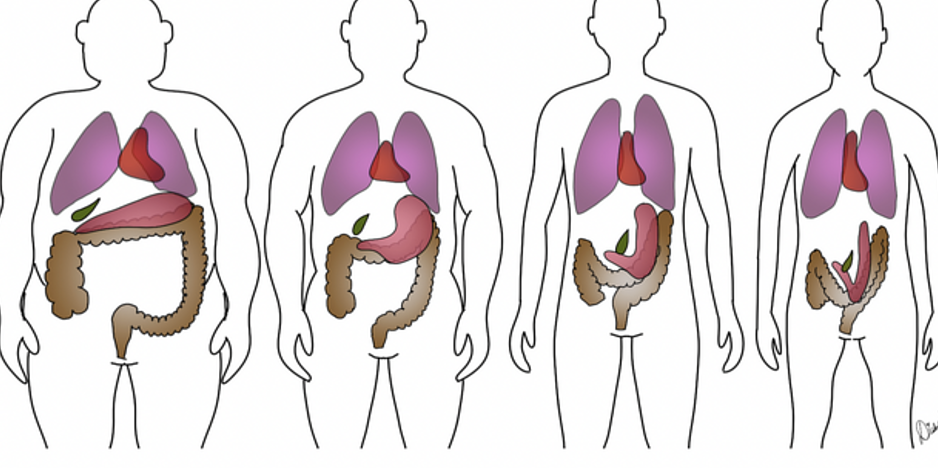
4 types of body habitus
important bc it may change positioning
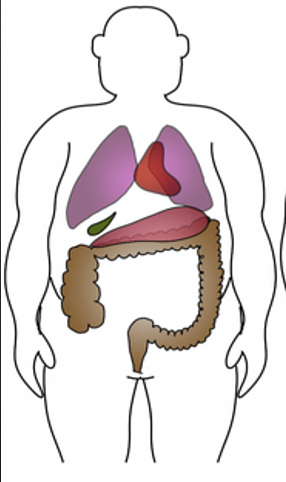
build: massive
abdomen: long
Thorax: short, broad, deep
pelvis: narrow
5% hyperstheic
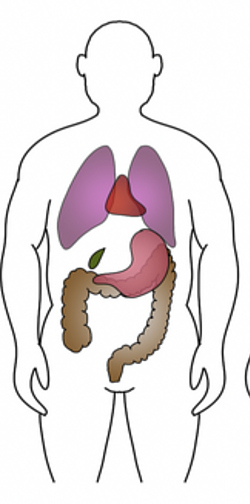
build: moderately heavy
abdomen: moderately long
thorax: moderately short, broad and deep
pelvis: relatively small
50% sthenic
intermediate between asthenic and sthenic; most difficult to classify
35% hyposthenic
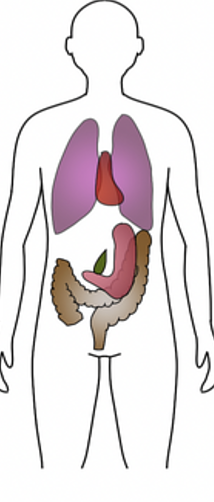
build: frail
abdomen: short
thorax: long, shallow
pelvis: wide
10% Asthenic
proximal
towards center of body
distal
away from center of body
planter
sole of feet (posterior)
dorsum
top of feet (anterior)
AP hand
palm of hand
PA hand
back of hand
Another name for PA hand
dorsum
AP oblique
CR enters anteriorly and exits posteriorly to rotated part/body
PA oblique
enters posteriorly and exits anteriorly to rotated part/body
AP axial
angled CR enters anteriorly and exits posteriorly
PA axial
angled CR enters posteriorly and exits anteriorly
AP axial oblique
Angled CR enters anteriorly and exits posteriorly to rotated part/body
PA axial oblique
angled CR enters posteriorly and exits anteriorly to rotated oblique part/body