Lecture 10: Master impressions for dentures (the basics and advanced techniques)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are different impression materials? (8)
Alginate
Silicones - light/medium/heavy body
Silicone putty
Zinc oxide eugenol
Impression compound
Impression plaster
Materials have different properties that we should be aware of to minimise what?
errors in the final cast
When do properties of impression materials change?
when they set
Before setting compare the viscosity of the impression materials mentioned at the start:
low, medium and high viscosity (3 in each category)
High viscosity:
Impression compound
Heavy bodied silicone
Silicone putty
Medium viscosity:
Zinc oxide and eugenol
Medium bodied silicone
Alginate (thick mix)
Light viscosity:
Alginate (thin mix)
Impression plaster
Light bodied silicone

After setting in the tray
rigid (3) elastic/flexible
rigid:
Impression compound
impression plaster
zinc oxide eugenol
Elastic/flexible:
silicones (varies based on body type)
colloids (alginates)

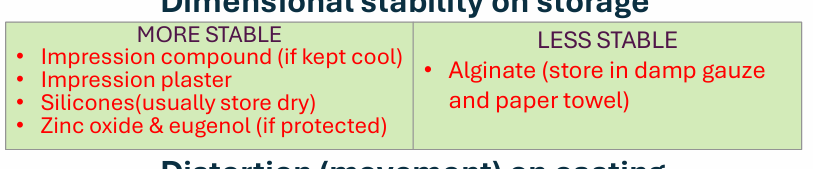
Dimensional stability on storage?
stable (4)
less stable (1)
more stable:
Impression compound (if kept cool)
Impression plaster
silicones (usually store dry)
zinc oxide eugenol (if protected as surface is fragile)
less stable:
Alginates - store in damp gauze and paper towels
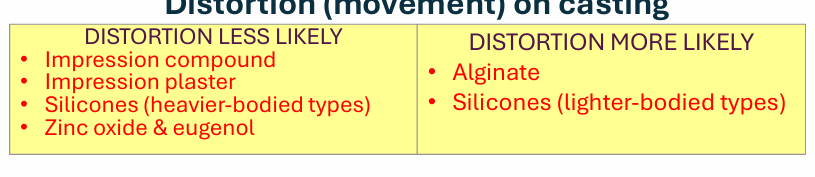
Distortion on casting?
distortion more or less likely?
less likely:
impression compounds
impression plaster
zinc oxide eugenol
silicones - heavier bodied types
more likely:
alginates
silicones (lighter bodies types)
how does the viscosity of the impression material have an effect from high to low? (2)
high viscosity - less surface detail and greater pressure on underlying oral structures
lower viscosities - more surface detail and less pressure on underlying oral structures
setting in a rigid and elastic/flexible state is/not good when there is the presence of what?
rigid - not good in presence of hard tissue undercuts
elastic/flexible - good for hard tissue undercuts
Dimensional stability , if low means you should ideally do what?
more dimensionally stable means you can cast much later while the less stable impression materials need to be cast much sooner
Distortion/ movement - what implications does this have?
Impression materials that have less distortion means they are more rigid when casting while the one’s that are more likely to distort are less rigid when casting so need support in thin sections
an accurate cast results in what?
a better fitting denture
What are possible sources of error on final cast? (10)
wrong type
instructions
flexible tray
rinse off
storage
correct stone
air bubbles
excess liquid
disturbing before set
damaging

What were the steps in casting again and tips
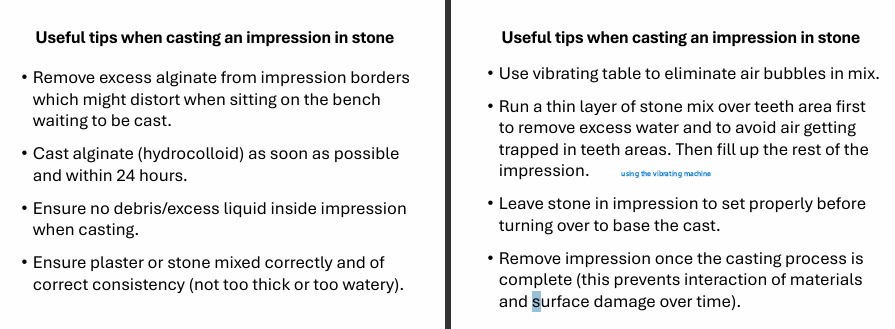
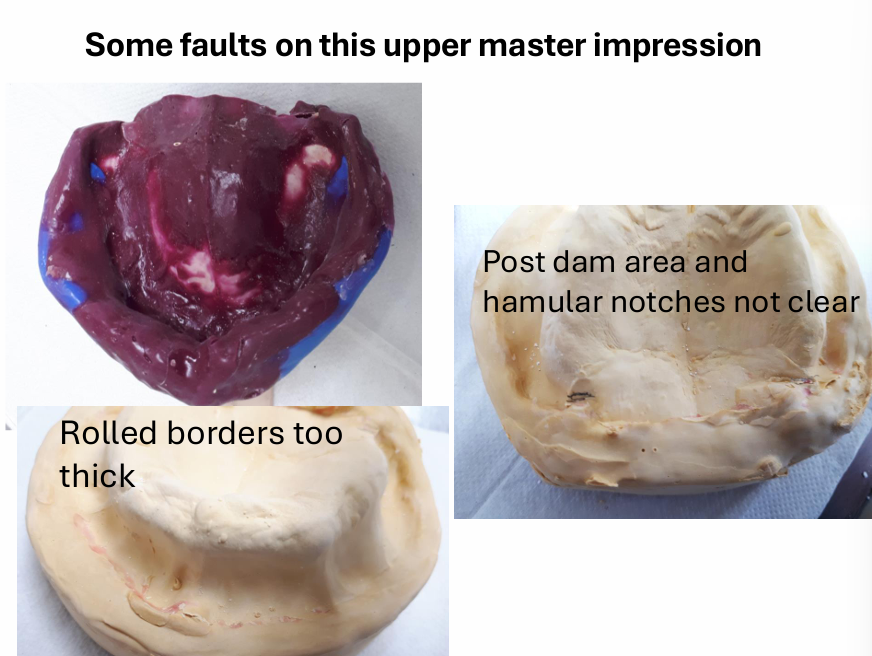
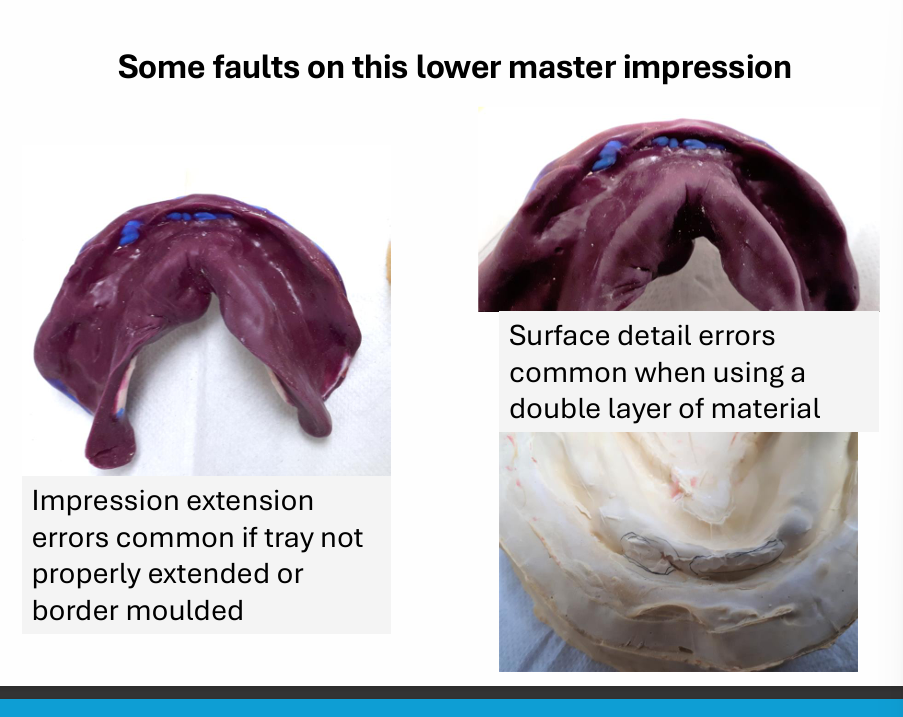
What must be done correctly in order to make an accurate master impression?
Need a fairly accurate primary impression first - on which we make a special tray
Why do we want the primary impression to be as accurate as possible * (5)
keep an accurate and permanent record of dentition at various stages of treatment
to be able to examine the occlusion when patient is not there
to examine the shape of the natural teeth and supporting tissue in more detail, for designing partial cobalt chrome dentures
to make accurate diagnostic wax-ups when planning to build up teeth for tooth wear cases
construct better fitting impression trays - special trays
What are the trays that we initially use called? and what is their problem?
Stock trays
are not well-fitting
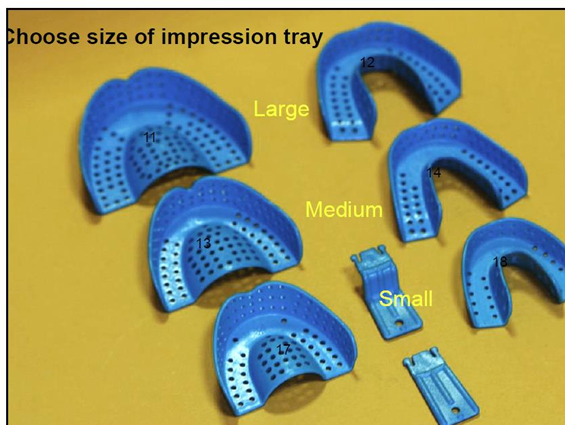
How do you know if the stock tray is the most appropriate size? (4)
what could you ask the patient to do?
it is comfortable to place in the mouth
it sits against the teeth occlusal surfaces both sides of the mouth
it covers all areas of the mouth to be recorded - or it can be extended with wax
There is room inside the tray so that you can move it from side to side slightly - alginate should be 2-3 thick
to bite on a sheet of wax and use this print as a guide to tray size
how may you modify the borders of the tray?
what could you add to the impression if they are partially dentate?
Trays are not a precise fit so may need to modify the border with wax
when there are teeth missing it is useful to adapt the stock tray using silicone putty
the impression is then completed with alginate covering the wax/putty and tray
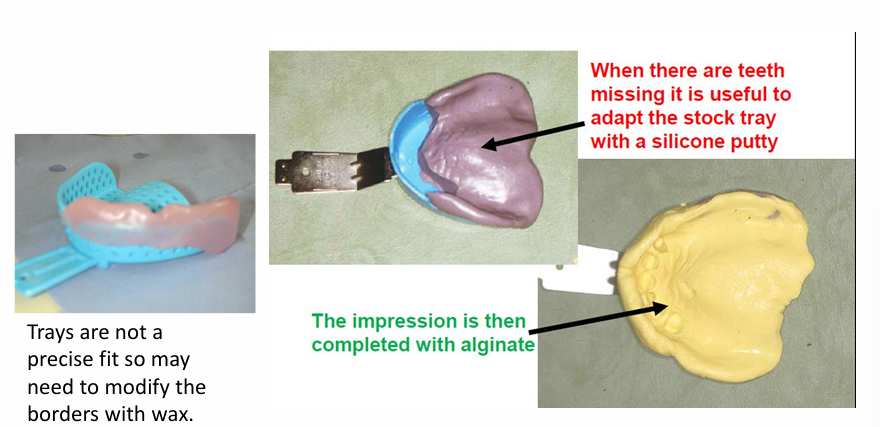
Why do we add wax and putty extension?
pushes the alginates where you want it to go
supports alginate in thin sections
Putty - reduces the thickness of alginate where the teeth are missing so alginate distortion is reduces after setting and on storage
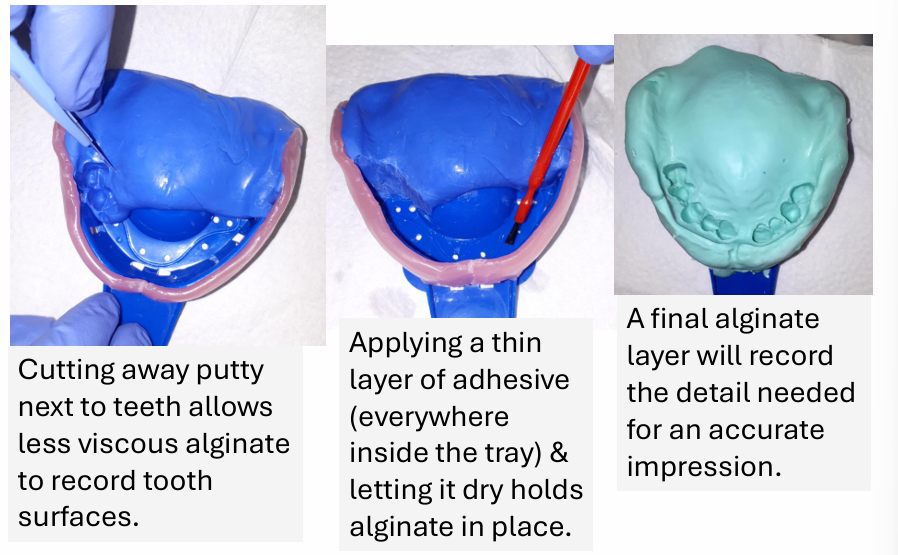
When you add the putty what must you do to get a an accurate impression?
You cut away the putty to leave some room for the less viscous alginate to get a more detailed impression of the teeth

This tray is for which type of patient?
Edentulous patient
where can we add wax and do we need putty?
we can still add wax to the borders to extend the trays
don’t normally need to add putty on the inside of the stock tray when there are no natural teeth
What are some patient considerations for any denture impression * (8)
look where the impression is going when seated in the pts mouth
pt upright
take the lower impression first so they get used to it
avoid overloading impression tray
putty/wax to clock out/pre-fill large spaces means less alginate
faster setting material for gaggy patients
pt breathes/distractions
do not remove impression material until it has set

Why do we take a master impression?
a master impression is usually more accurate than a primary impression
How is the master impression made?
special tray
How is the master impression tray more accurate? (4)
the special tray is made to fit the patient’s mouth much better than the stock tray
the special tray usually covers all the areas we need to record accurately for the denture and less modifications needed
a thin and even layer of impression material reduces the risk of impression material distortion
a thick layer of impression material can lead to more distortion because there is more of it
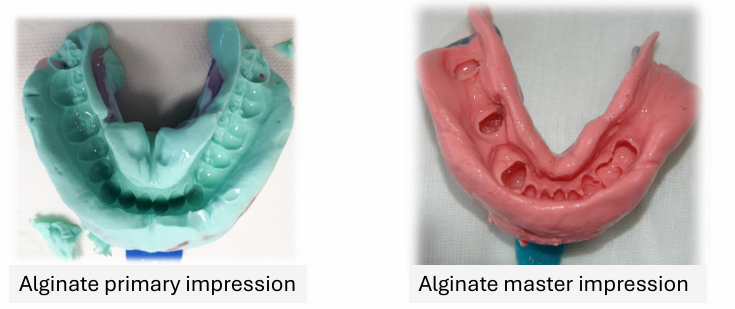
Compare primary and master impression (3)
On master, all teeth and ridges are recorded more accurately and impression borders are less bulky
On master impression, the impression material is thinner and so less likely to distort
on master impression the fit surface of the denture should be more accurate making it more comfortable and more stable - less wobbly
Before you make a special tray what do you draw on the primary cast?
draw an outline on the primary cast, this pencil outlines represents the denture bearing area - which is the soft tissue that will support the denture
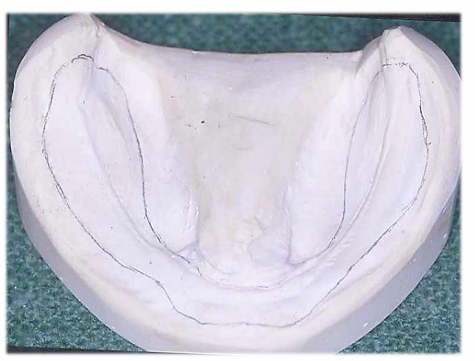
The special tray will what to the pencil outline?
the special tray follows the pencil outline
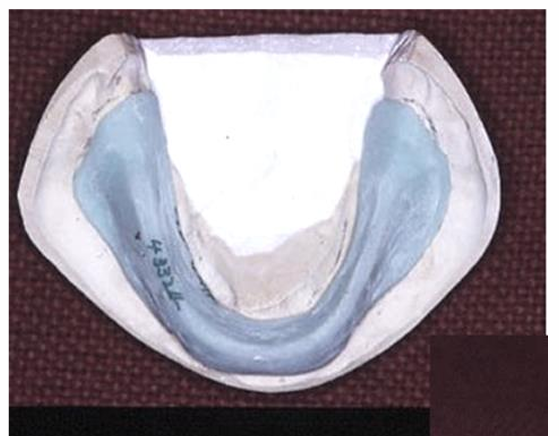
in the mouth, the edge of the tray should be what?
about 2 mm from the deepest part of the sulcus all around the tray
special trays, what are the 2 types - for edentulous and then for edentulous and patients with natural teeth ()
Close-fitting - edentulous only
Thin space underneath the tray - edentulous and patients with natural teeth
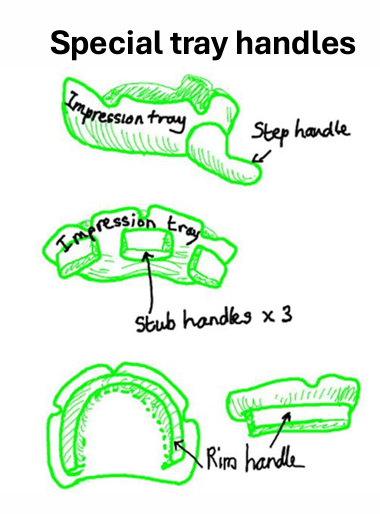
what type of handles on the special tray for pts with natural teeth and edentulous?
step handles for patients with (or without) natural teeth
stub or rim handles only for edentulous patients
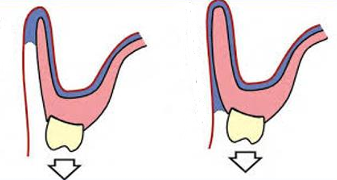
Compare the denture flange, which has the better seal?
where else in an denture do you need a good seal
the denture on the right has a better seal
air cannot pass up the sulcus and into the denture, this can cause the denture to dislodge
a denture flange that is too thin does not work as well as one that fills the width of the sulcus
the post dam - in between the hamular notch- you scrape a m shape at the back so more material goes in for extra support at the back as here is no sulcus posteriorly, this digs in the vibrating line area at the back of the mouth where the tissue is more compliant
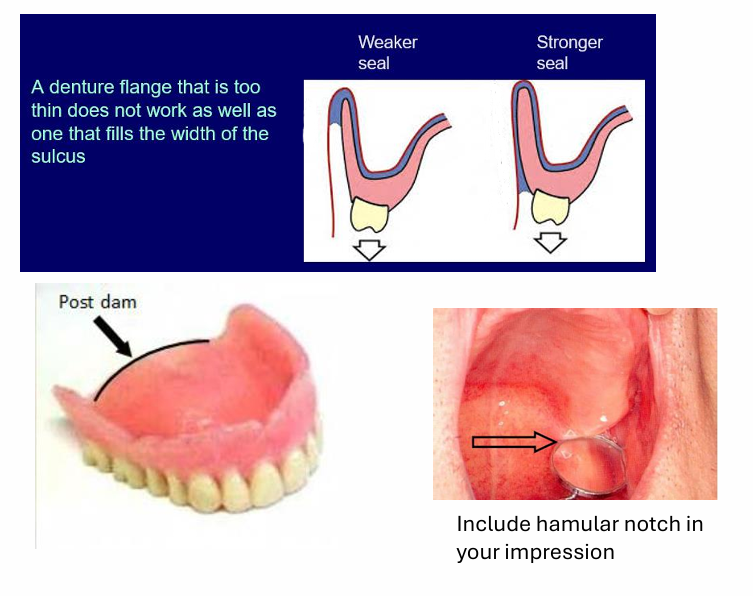
What shape should the impression border be?
a correct border means what?
over-extended tray borders can be fixed how?
under-extended tray borders can be fixed how?
The impression border should be the same shape as the patients’ sulcus - when cheeks and lips moving slightly
means the final denture is more stable when the cheeks and lips move
trimmed if too long - acrylic bur
material added along the edge
What materials can be added for fixing the border moulding? (3)
what happens after border moulding?
green stick
self-curing resin
silicone putty
the final impression spreads over the top of the border moulding

What must you avoid squashing in the mouth?
frenal attachments - otherwise the finished denture will traumatise these areas
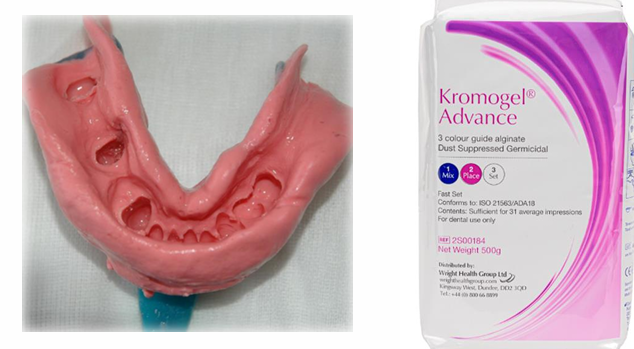
What impression material is used for taking master impression in special trays of a partially dentate patient and why not silicone?
hydrocolloid - alginate
this is to prevent the impression getting stuck, as these can get stuck in the patients’ mouth if there are natural teeth
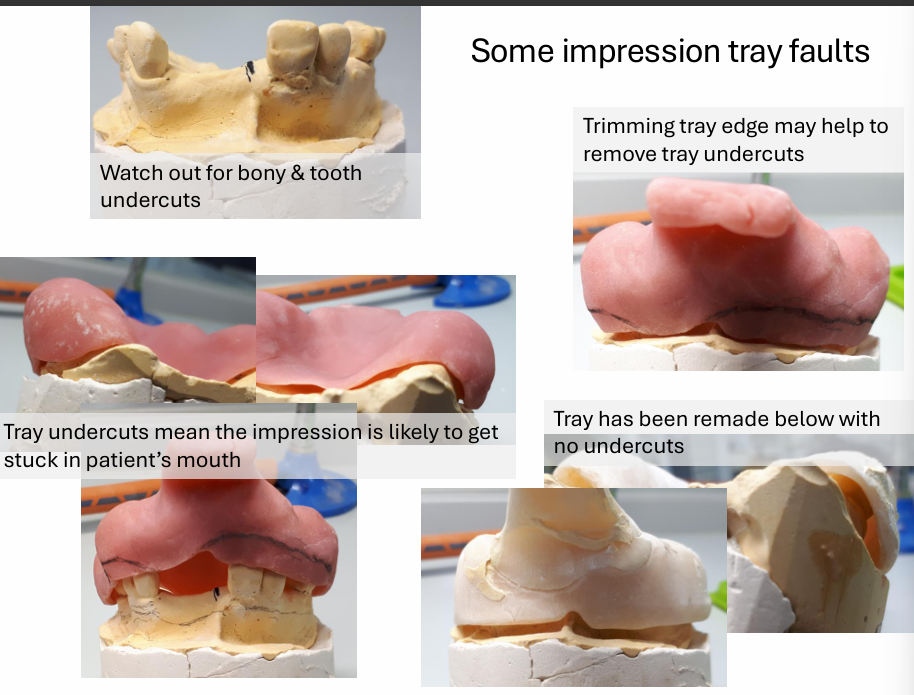
Why are undercuts in the primary cast for when making a special tray a problem?
this undercut will be transferred onto the special tray
tray undercuts mean the impression is likely to get stuck in the patient’s mouth
trimming tray edge may help to remove tray undercuts
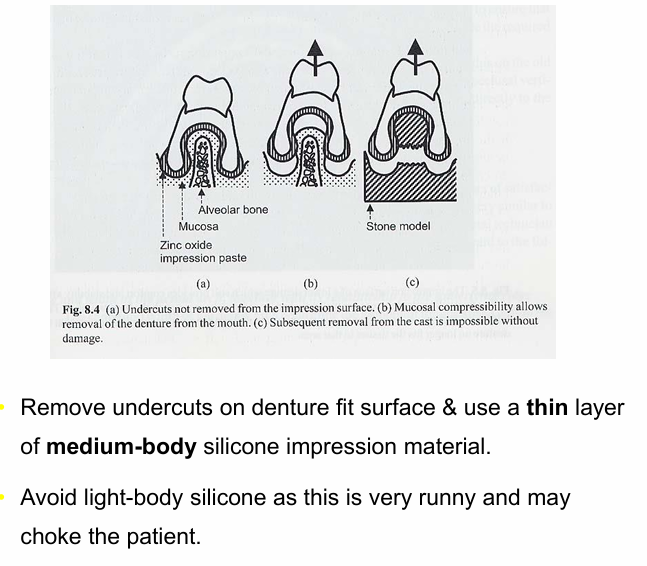
what impression material should you use for edentulous patients?
medium-body silicone - alginate acceptable but makes it more difficult to cast impression borders well
What type of silicone do you not use?
light-bodied silicone for denture impression as it is very runny and may end up being swallowed
when could you use light body ?
reline impressions, use a thin layer to avoid this problem - however medium-body works just as well if applied thinly
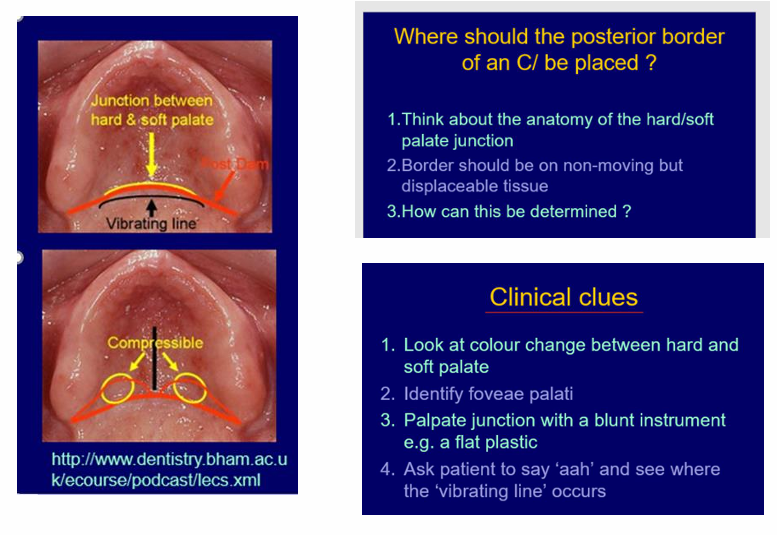
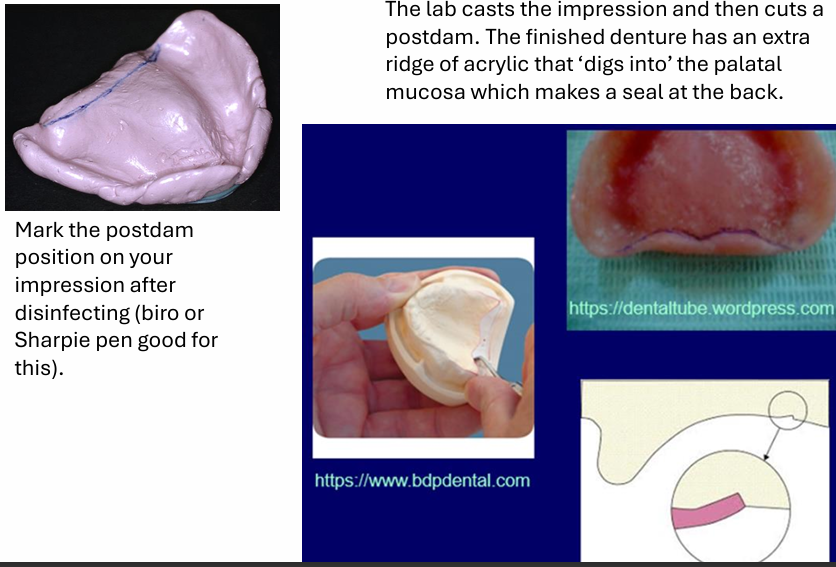
What should you mark on the disinfected impression for an upper complete denture and where?
what are some clues to finding this area?
Mark the post dam area
border should be on non-moving but displaceable tissues
look at the colour change between hard and soft palate
identify fovea palati
palpate junction with a blunt instrument
ask patient to say ahhh and see where the vibrating line occurs
when you mark the post dam position on your impression after disinfecting, what happens next?
the lab casts the impression and then cuts a post dam. the finished denture has an extra ridge of acrylic that ‘digs into’ the palatal mucosa which makes a seal at the back
What type of bases are made for edentulous and partial dentures?
edentulous - often heat-cured clear acrylic bases bases from the master impression - can also make temporary bases
for partial dentures - always use temporary bases
What are the steps in disinfection and storage of impressions?

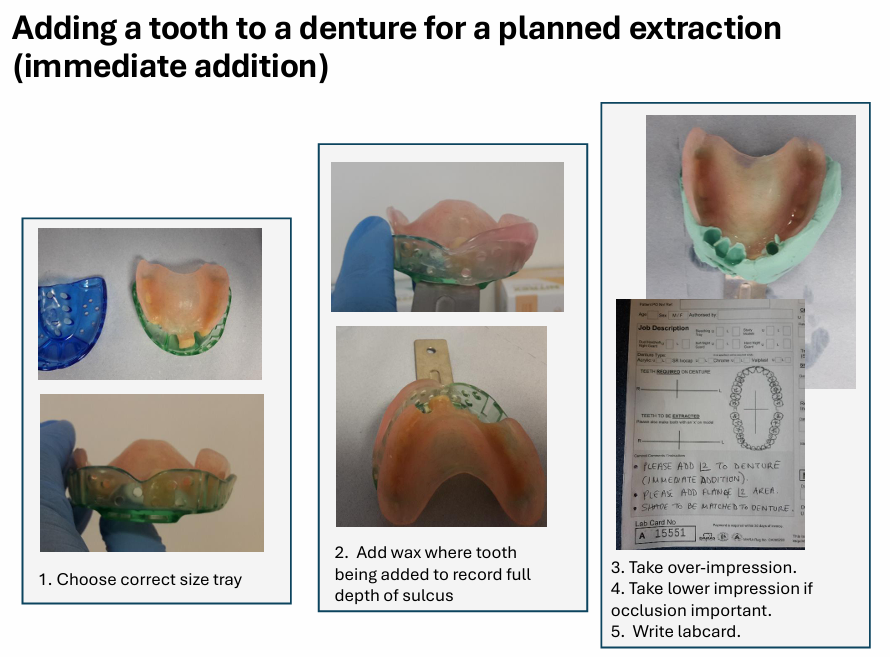
What are over - impressions?
choose the correct size tray
add wax where tooth being added to record full depth of sulcus
take over-impression
take lower-impression if occlusion important
write lab card
the tooth to be extracted will be removed from the cast and an artificial tooth added to the
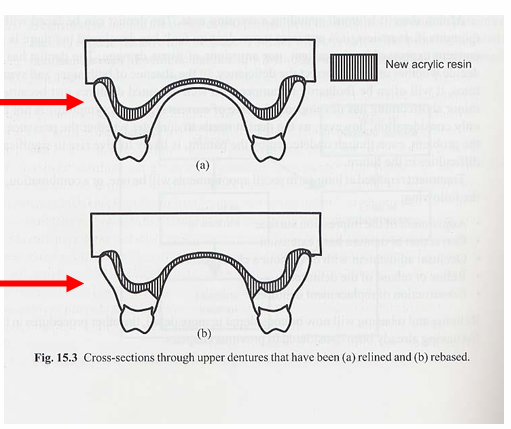
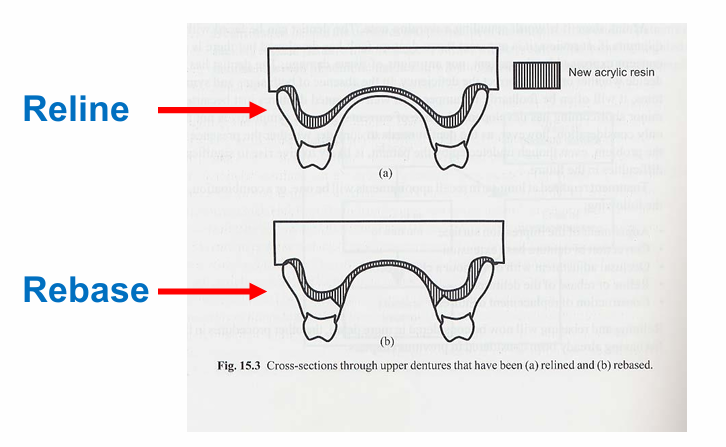
What is denture relining?
where a new fit surface is added to a denture to make it fit against the tissues more accurately
more successful in complete dentures - can be attempted with partial dentures
What is denture rebasing?
similar to reline, but the base material is almost completely replaced in the palate area. only works with complete dentures not partial dentures
What type of impression is needed for both a relining and rebasing?
reline impression
Which is which?
what must you warn the patients about this procedure?
warn them that it is an irreversible change which may not work
What is the technique for impressions taking for relines?
remove undercuts and use a thin layer of medium-body silicone impression material
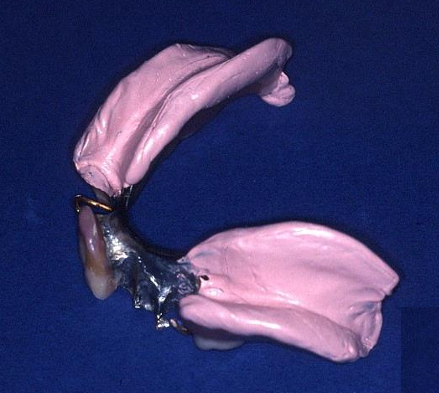
What is this image showing? (2
reline impression
for a /P
with free-end saddles
What are 2 methods that can be used to avoid extracting mobile teeth in impressions?
Blocking out tooth undercuts - prior to impression taking
a digital scan can be used to record the shape o the teeth and supporting tissues where teeth are very mobile
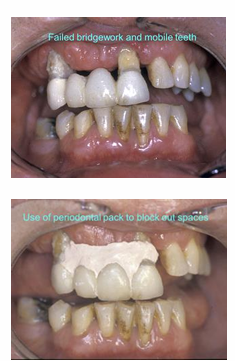
What is the problem with digital scans?
digital scans do not record the sulci very well which is why we don’t use them routinely for dentures
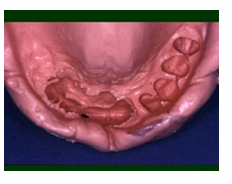
What is selective displacement?
apply more pressure on one area of the oral tissues and less pressure on another area
What 2 situations would you use selective displacement?
free-end saddles
flabby ridges
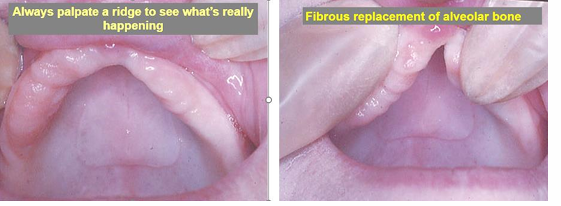
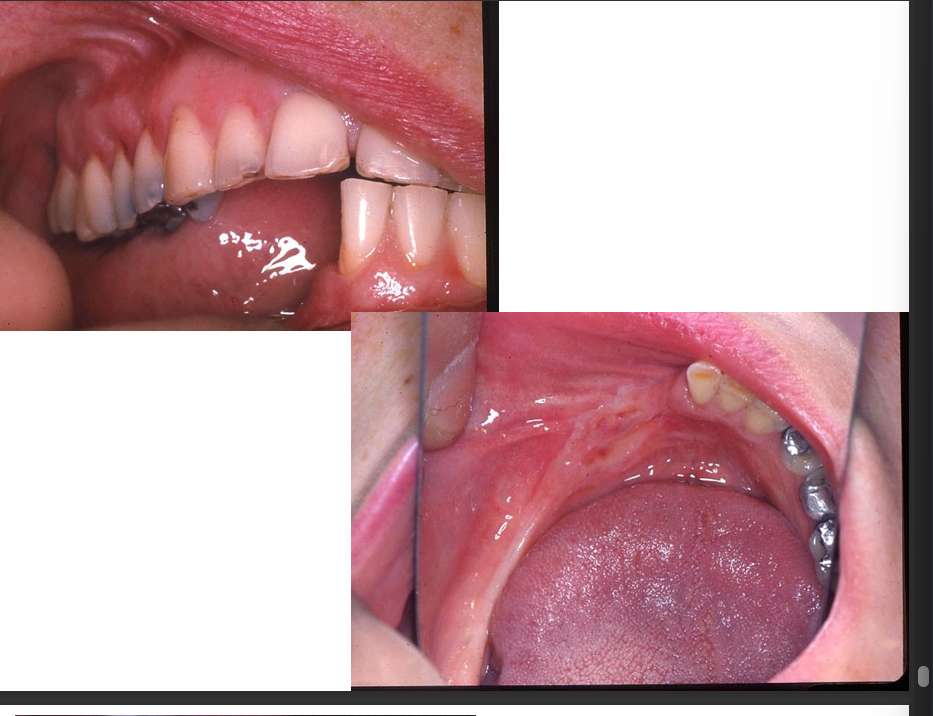
What is this image showing/
flabby ridge, fibrous replacement of alveolar bone
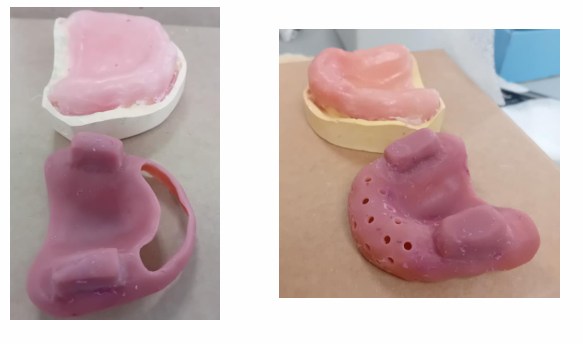
how can these trays help?
the window
the perforations - allow the impression to put less pressure on this mobile tissue
Why are dentures with free-end saddles a problem?
Greater problem on which arch?
Because of the dual nature of the support - teeth and alveolar ridge
Mandibular dentures greater problem
Periodontal membrane and mucosa have different displaceabilities causing denture to tip
Potential damage to abutments and to alveolar ridge
patients experience denture movements during function - when biting
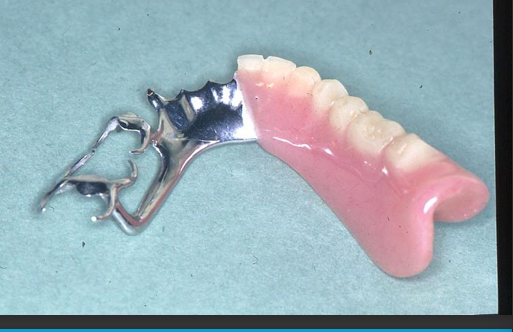
How do you take an impression in this case?

How is the cold cure base achieved?
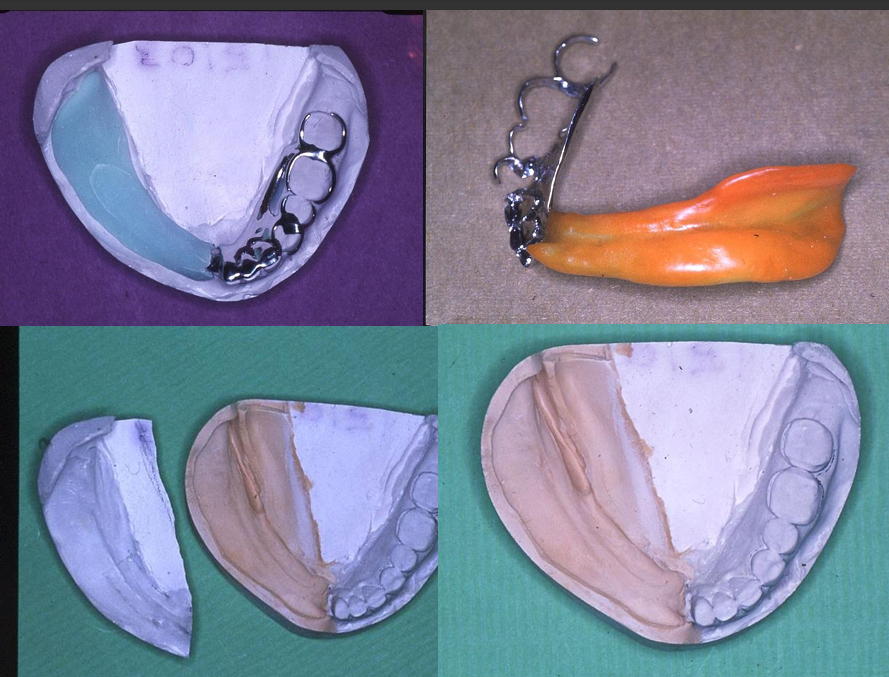
How can you take an impression to record the patient’s oral mucosa shape over a period of time (during one day)
Functional impression
viscogel impression inside fit surface of complete denture
let patient wear it for a day or so and then they give it back to you to send to lab for casting up master impression
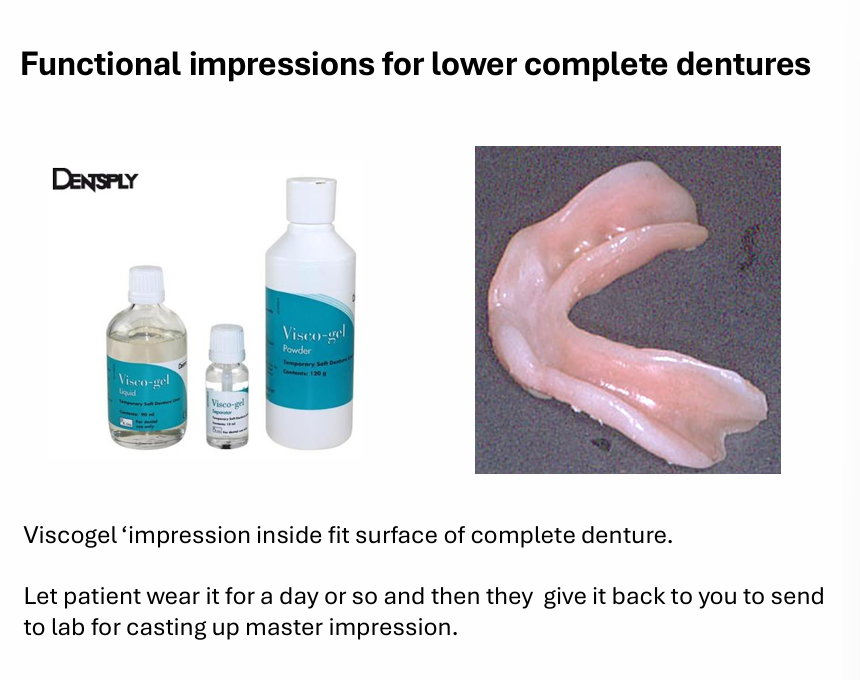
Functional impressions are used for which arches?
edentulous arches usually the lower to try to achieve a more comfortable fitting surface
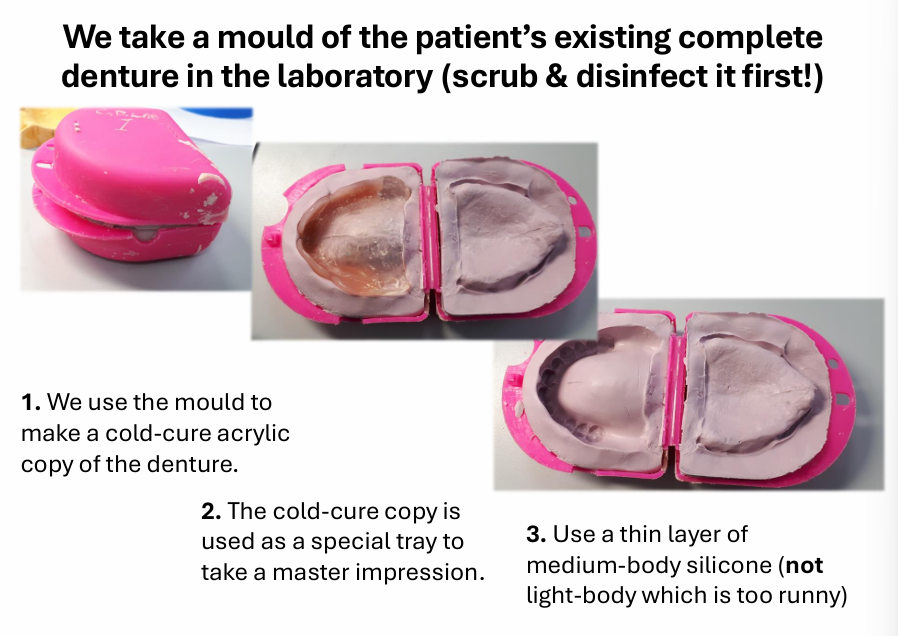
when making a copy complete denture, what do you use as a special tray?
cold-cure acrylic copy
How do you do this?