Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Overview
1/455
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
456 Terms
Amino Acid
Molecule with amino and carboxyl functional groups.

Alpha Carbon
Central carbon in amino acids with four groups.
R Group
Side chain that defines amino acid properties.
Proteinogenic Amino Acids
20 amino acids encoded by human genetic code.
Chiral Center
Carbon atom with four different substituents.
Optically Active
Substance that rotates plane-polarized light.
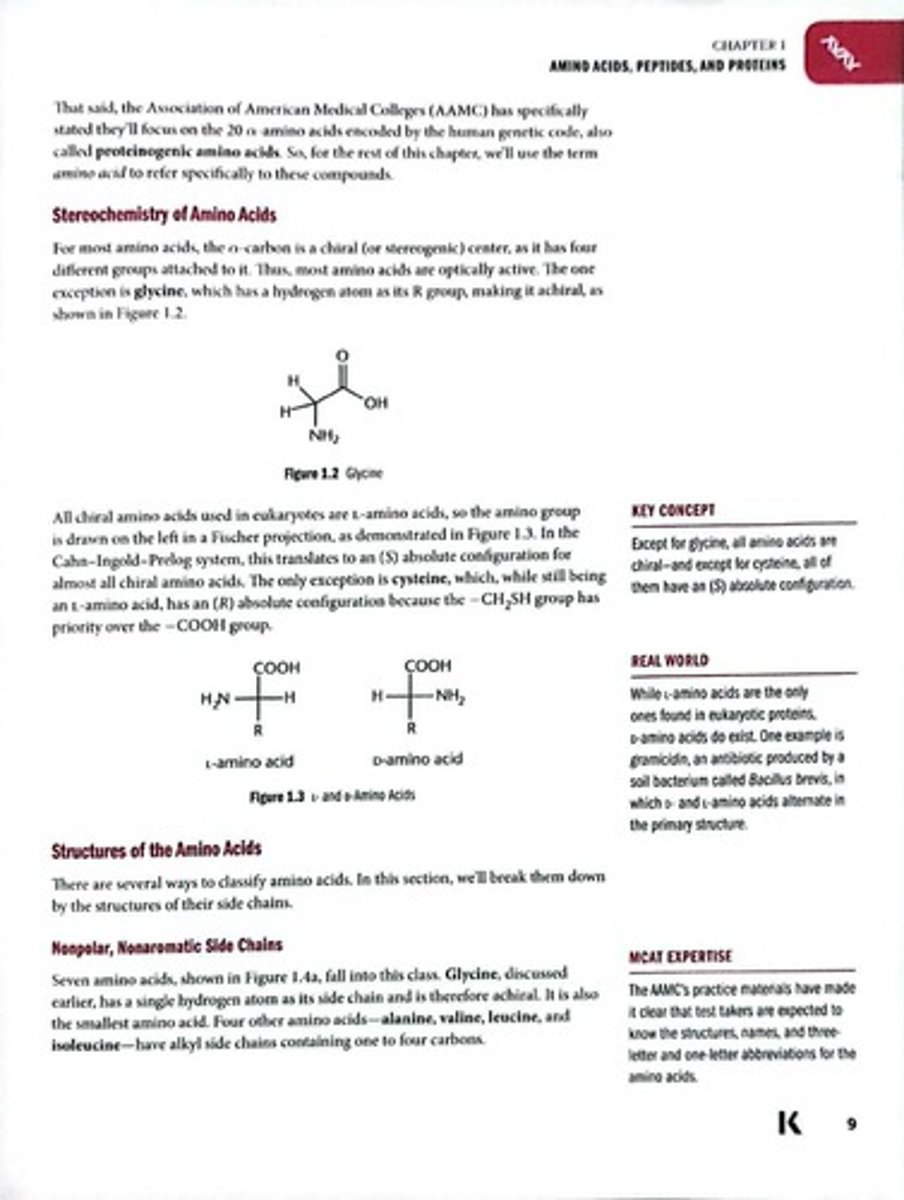
Glycine
Smallest amino acid, achiral with hydrogen side chain.
L-Amino Acids
Amino acids with amino group on left in Fischer projection.
D-Amino Acids
Amino acids with amino group on right in Fischer projection.
Cysteine
L-amino acid with (R) absolute configuration.
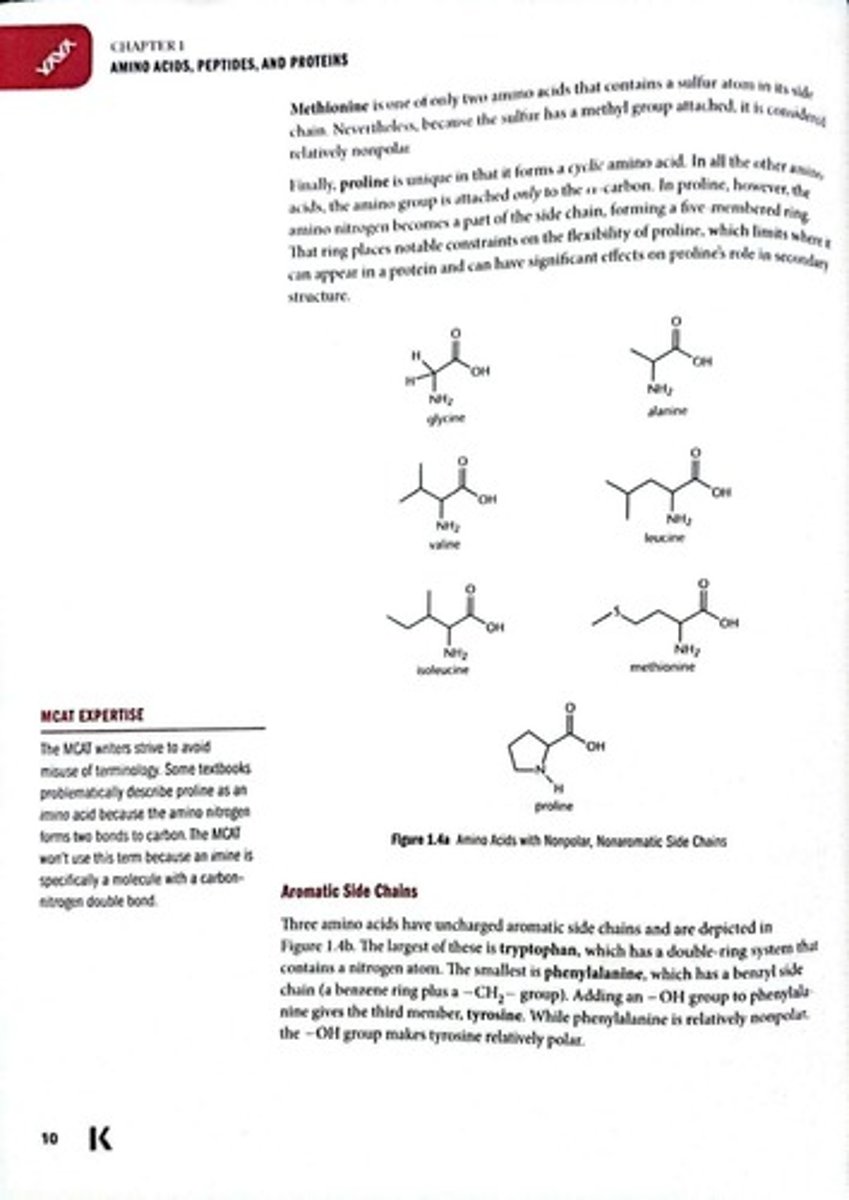
Methionine
Amino acid containing a sulfur atom.
Proline
Cyclic amino acid with unique structure.
Nonpolar Amino Acids
Amino acids with hydrophobic side chains.
Hydrogen Atom
One of the four groups attached to alpha carbon.
Carboxyl Group
Functional group (-COOH) in amino acids.
Amino Group
Functional group (-NH2) in amino acids.
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger in the nervous system.
Ornithine
Amino acid involved in urea cycle.
Valine
Branched-chain amino acid with hydrophobic properties.
Leucine
Essential branched-chain amino acid.
Isoleucine
Branched-chain amino acid with two stereoisomers.
Alanine
Nonpolar amino acid with a methyl side chain.
Amino Acid Classification
Grouping based on side chain structures.
Flexibility
Proline's structure limits protein flexibility.
Amino Nitrogen
Nitrogen in amino acids that bonds to carbon.
Imine
Molecule with a carbon-nitrogen double bond.
Tryptophan
Largest amino acid with a double-ring system.
Phenylalanine
Smallest amino acid with a benzyl side chain.
Tyrosine
Phenylalanine with an added hydroxyl group.
Serine
Amino acid with a polar hydroxyl side chain.
Threonine
Similar to serine, with an additional methyl group.
Asparagine
Amino acid with an amide side chain.
Glutamine
Similar to asparagine, with an additional carbon.
Negatively Charged Side Chains
Amino acids with charges at physiological pH.

Aspartic Acid
Deprotonated form is aspartate, an acidic amino acid.
Glutamic Acid
Deprotonated form is glutamate, an acidic amino acid.
Charged Side Chains
Amino acids with positively or negatively charged groups.
Lysine
Amino acid with a terminal primary amino group.
Arginine
Contains three nitrogen atoms in its side chain.
Histidine
Amino acid with a proton-gaining side chain.
Hydrogen Bonding
Interaction between polar side chains in proteins.
Sulfur vs. Oxygen
Sulfur's bonds in cysteine are longer and weaker.
Aromatic Side Chains
Amino acids with uncharged aromatic side chains.
Imidazole
A ring structure containing two nitrogen atoms.
pKa
pH at which half of molecules are deprotonated.
Protonation
Addition of a proton to a molecule.
Deprotonation
Removal of a proton from a molecule.
Physiologic pH
Normal body pH, approximately 7.4.
Hydrophobic Amino Acids
Amino acids that repel water, e.g., alanine.
Hydrophilic Amino Acids
Amino acids that attract water, e.g., lysine.
Alkyl Side Chains
Long carbon chains in hydrophobic amino acids.
Titration Curve
Graph of pH versus the amount of titrant.
Amphoteric Species
Substances that can act as acids or bases.
Ionizable Groups
Functional groups that can gain or lose protons.
Acidic Group
Carboxylic acid group in amino acids.
Basic Group
Amino group in amino acids.
Protonated Form
Form of a molecule with an added proton.
Deprotonated Form
Form of a molecule without a proton.
pKa1
pKa for the carboxyl group, around 2.

pKa2
pKa for the amino group, between 9 and 10.
Physiological Conditions
Normal biological environment affecting amino acid behavior.
Nucleophilic Attack
Reaction where a nucleophile attacks a substrate.
Zwitterion
A molecule with both positive and negative charges, neutral overall.
Acidic pH
pH below 7, where amino acids are positively charged.
Neutral pH
pH around 7, where zwitterions exist.
Basic pH
pH above 7, where amino acids are negatively charged.
Carboxylate group
Deprotonated form of the carboxylic acid group (-COO-).
Titration
Process of adding a base to an acid to determine pKa.

Buffer solution
Solution that resists changes in pH near its pKa.
Equivalents
Amount of acid or base in titration relative to solute.
Fully protonated
State where all acidic groups are protonated.
Half-deprotonated
State where half of the acidic groups are deprotonated.
Conjugate base
The species that remains after an acid donates a proton.
Conjugate acid
The species formed when a base accepts a proton.
Internal salts
Salts formed within a molecule, like zwitterions.
Protonated amino group
Amino group in its +1 charged form at low pH.
Deprotonated carboxyl group
Carboxyl group in its -1 charged form at high pH.
pH of human blood
Normal physiological pH, approximately 7.4.
Milk of magnesia
Antacid with a pH around 10.5, affecting amino acids.
Isoelectric Point (pI)
pH where molecule is electrically neutral.
Buffering Phase
pH remains constant during titration.
Acidic Amino Acids
Have lower isoelectric points.
Basic Amino Acids
Have higher isoelectric points.
Peptide Bond
Covalent bond linking amino acids.
Dipeptide
Peptide consisting of two amino acid residues.
Tripeptide
Peptide consisting of three amino acid residues.
Hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of a compound due to water.
Trypsin
Enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds.
Chymotrypsin
Enzyme that hydrolyzes peptide bonds.
pKa Values
Used to calculate isoelectric points.
Equivalents of Base
Amount of base added in titration.
Protonated State
State where a molecule has gained protons.
Oligopeptide
Peptide with up to 20 amino acid residues.
Polypeptide
Long chain of amino acids, over 20 residues.
Amino Terminus
Free amino end of a peptide chain.
Carboxy Terminus
Free carboxyl end of a peptide chain.
Condensation Reaction
Reaction forming peptide bonds, releasing water.
Amide Bond
Bond formed between carbonyl and nitrogen groups.
Electrophilic Carbonyl
Carbonyl carbon that attracts nucleophiles during bond formation.
Nucleophilic Amino Group
Amino group that attacks carbonyl in peptide formation.