L13 Nervous System Structure Through Development (Imported from Quizlet)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
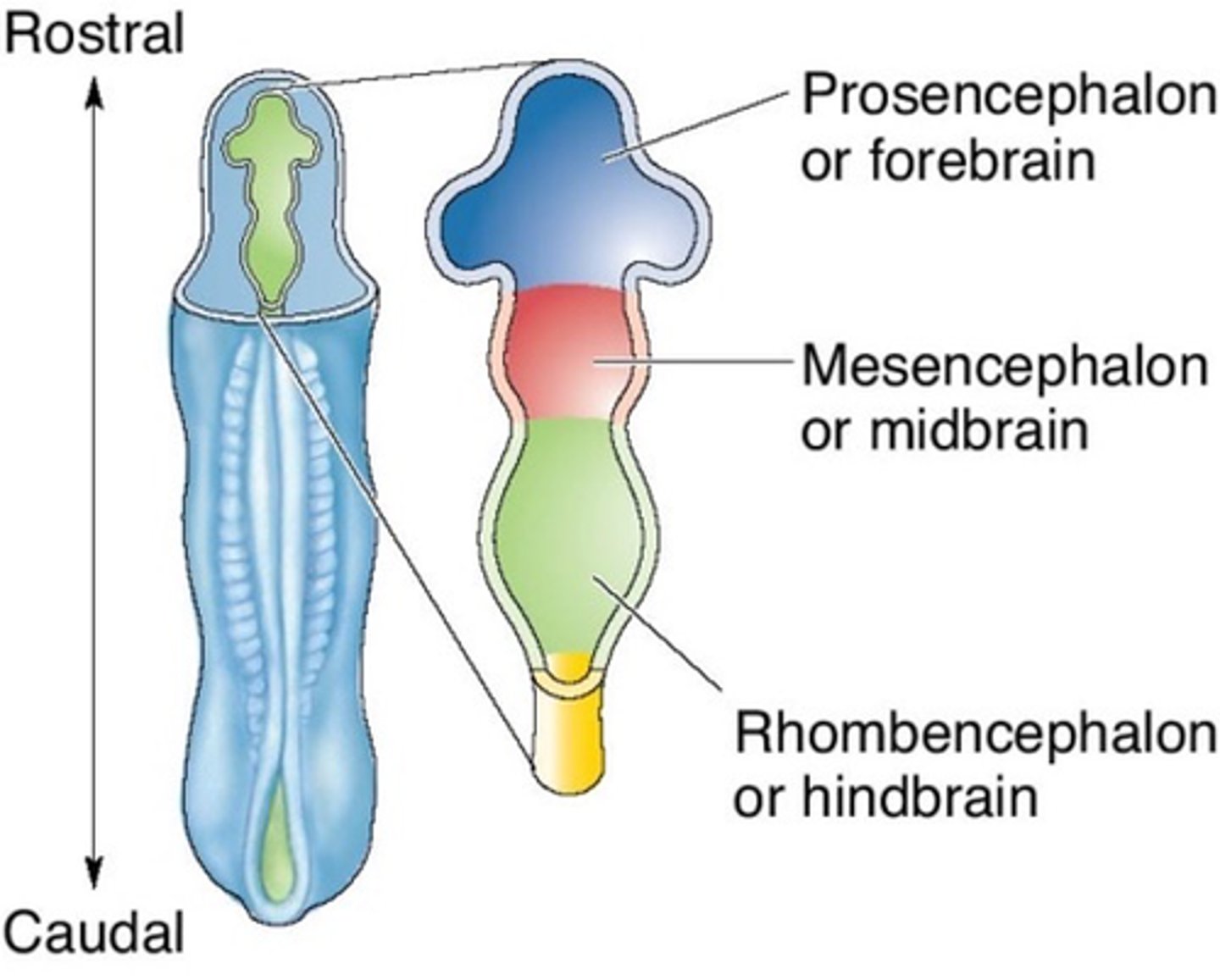
Forebrain
What part of the brain is labelled in blue in this image?
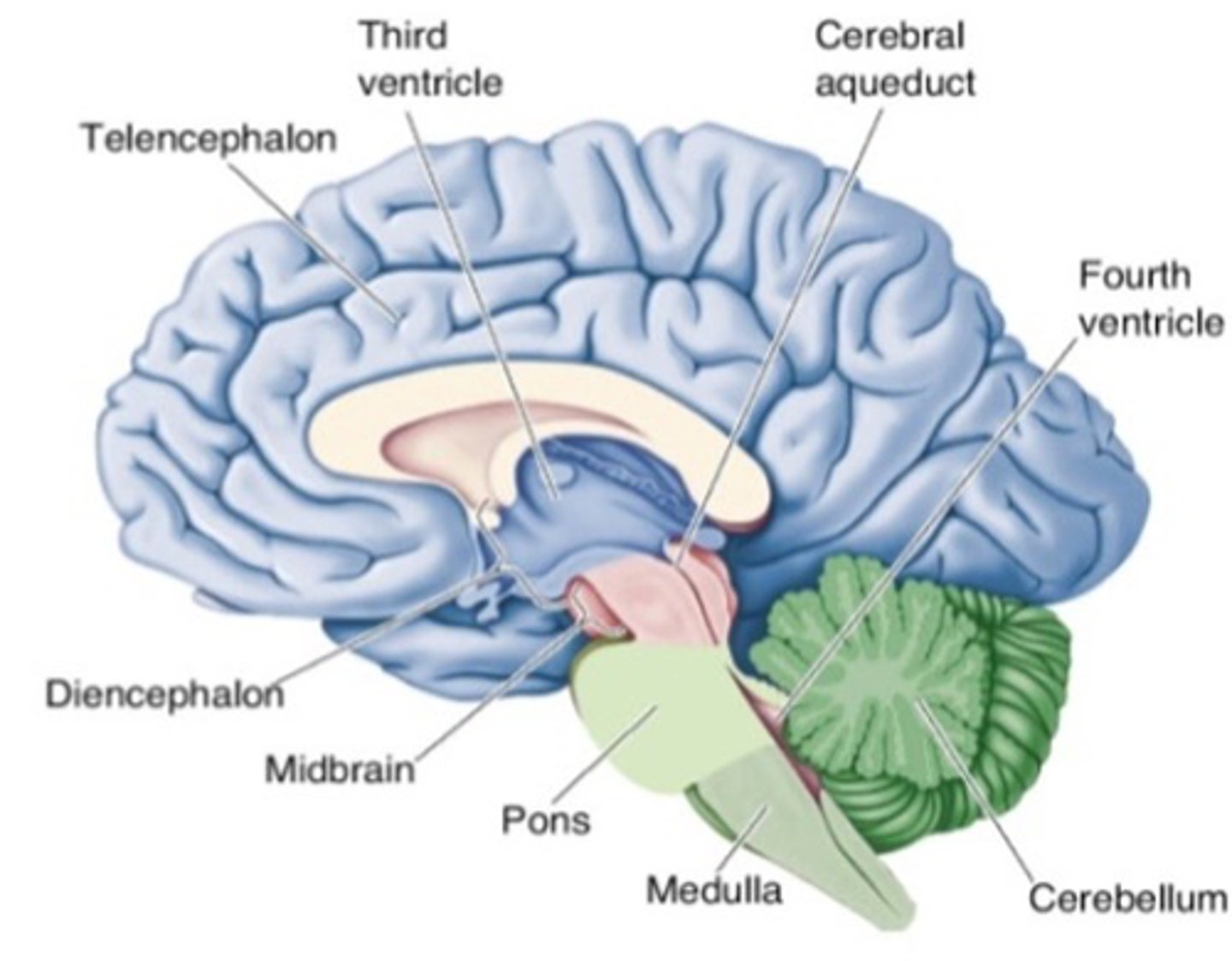
Midbrain
What part of the brain is labelled in pink in this image?
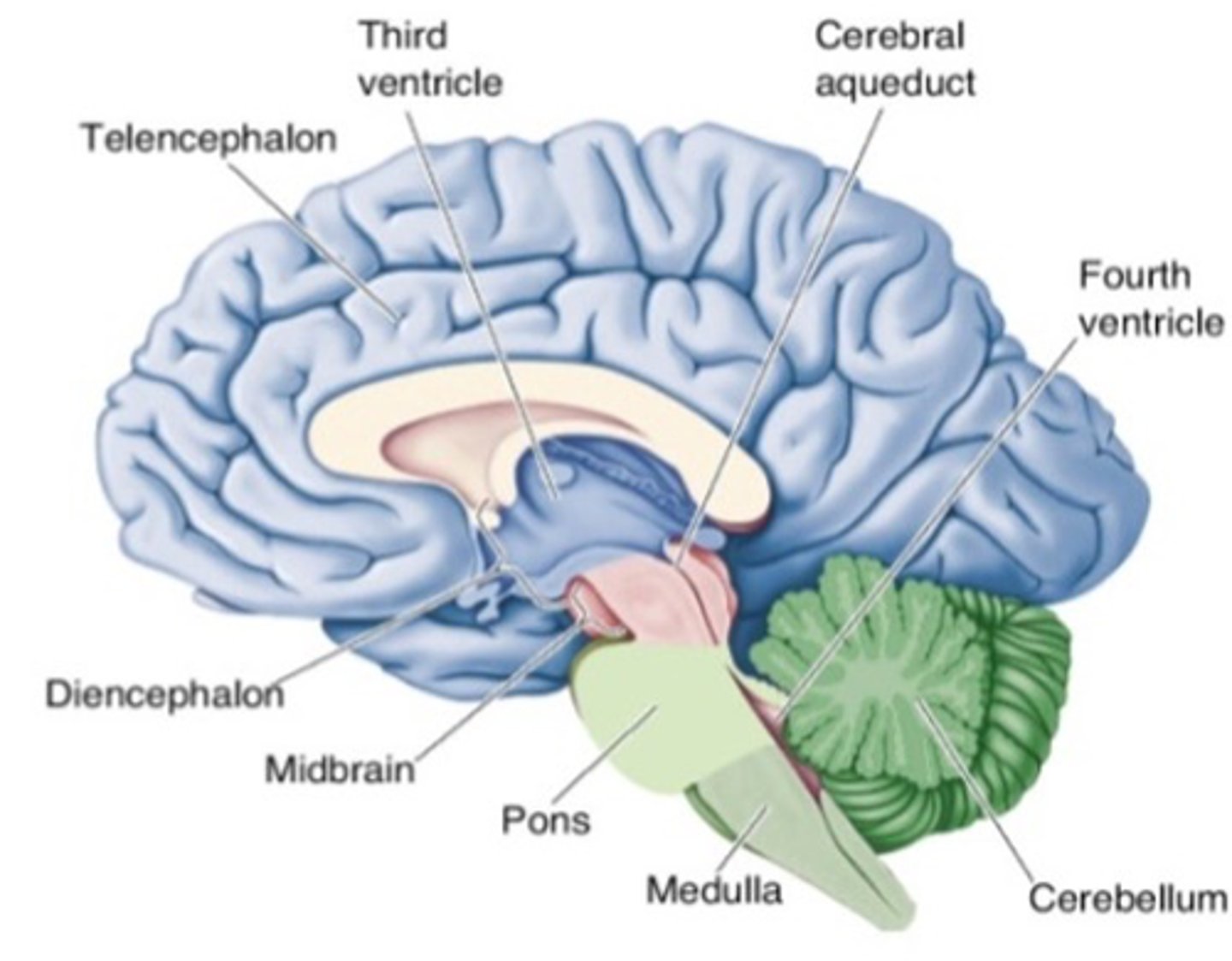
Hindbrain
What part of the brain is labelled in green in this image?
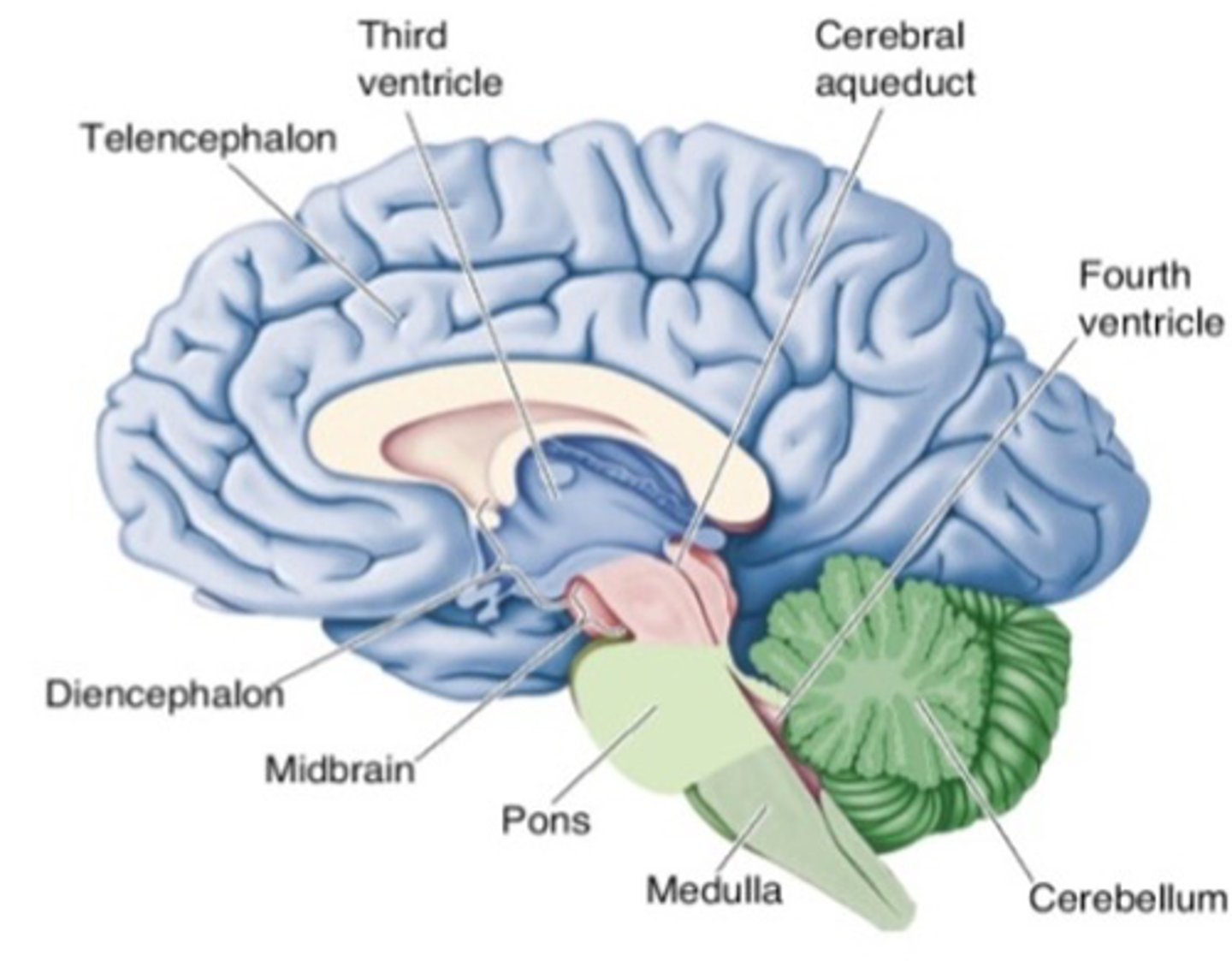
~17 days
At around how many days old does the neural plate form?
Lining of viscera
What does the endoderm form?
Bones and muscles
What does the mesoderm form?
Skin and nervous system
What does the ectoderm form?
The neural plate
The nervous system develops from what?
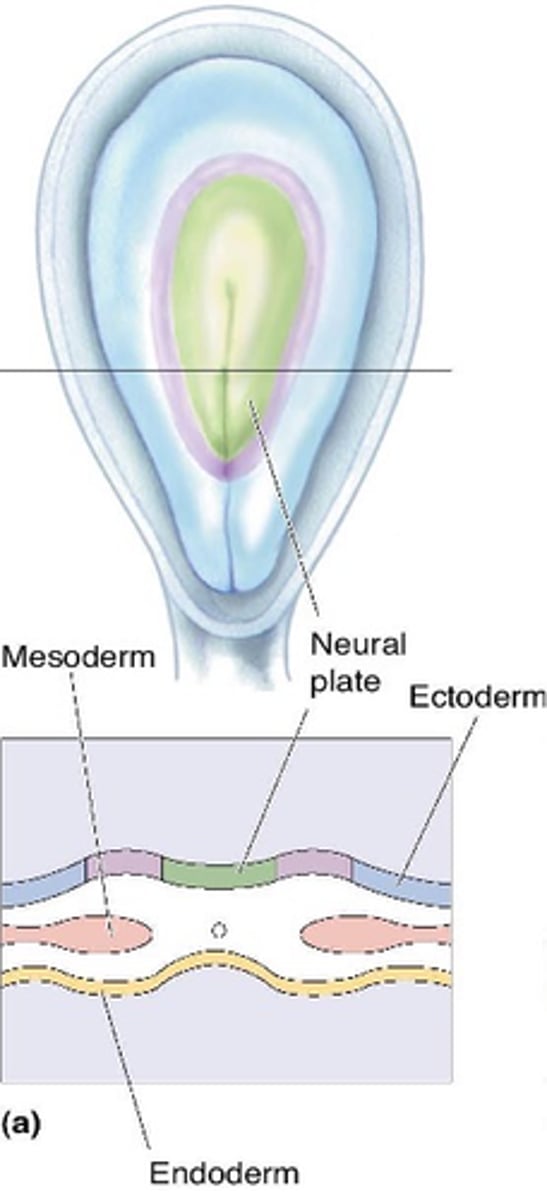
~22 days old
At around how many days old does neurulation occur?
5
Goes from being flat plate to being a tube in ~_ days
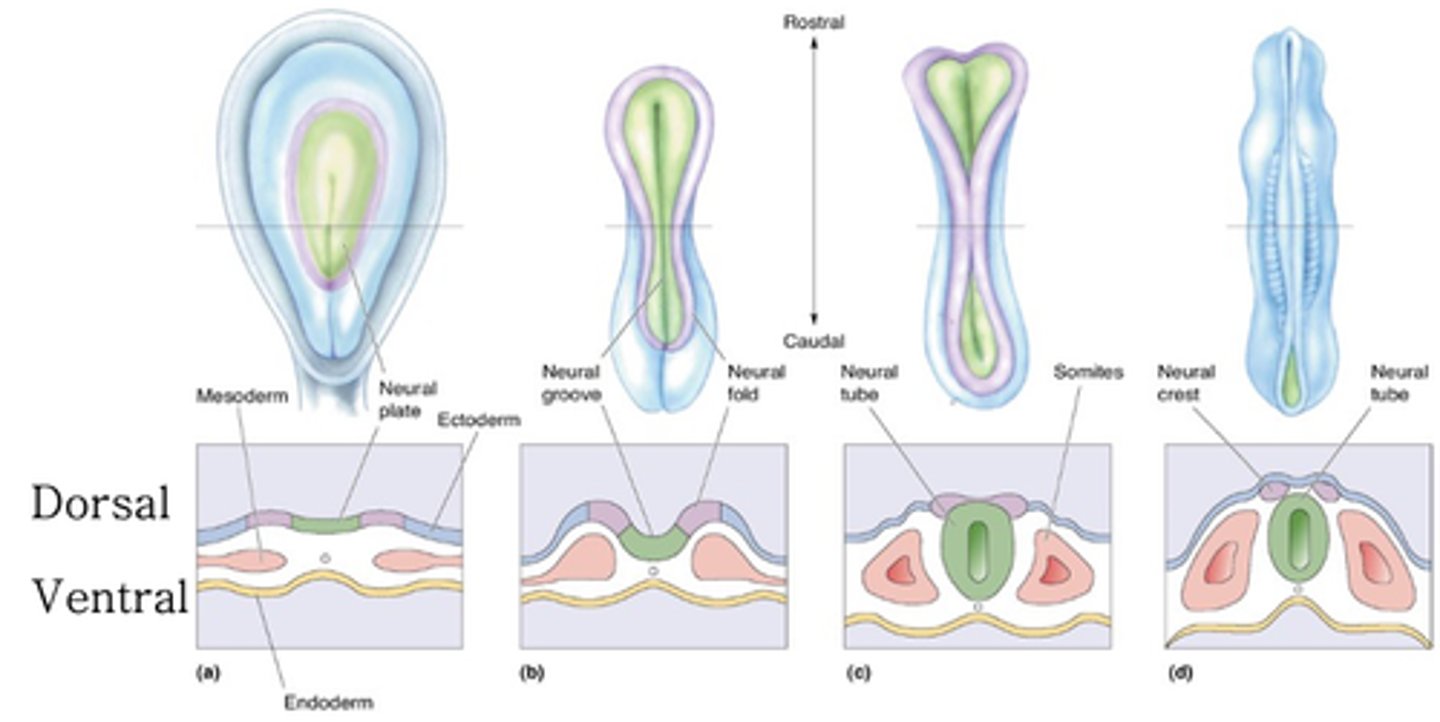
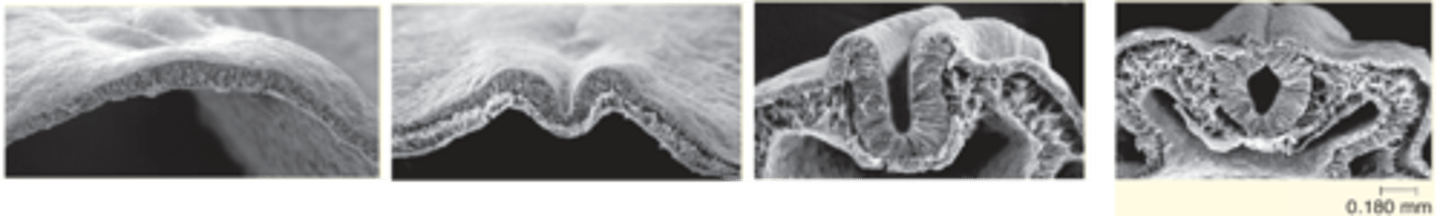
Neural groove, folds, tube, crest
The neural plate forms ________ ______ and _______ which then goes on to form neural ____ and neural ____
Neurons of the CNS
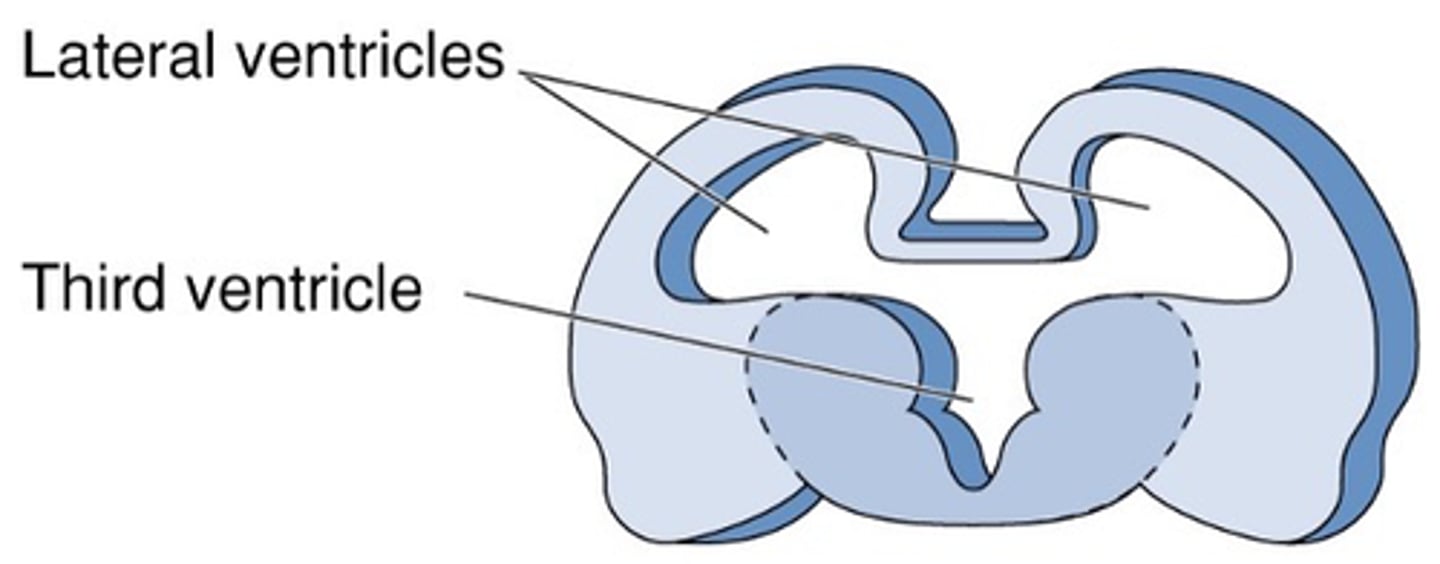
Ventricular system
What does the neural tube become?
Cells of the PNS
What does the neural crest become?
Ventricular cavity
The tube formed in neurulation becomes the ___________ _______
Sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion
Autonomic neruons (e.g. post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons, enteric neurons)
What neurons could form from the neural crest?
Chromatin cells, Schwann cells
What non-neurones derive from the neural crest?
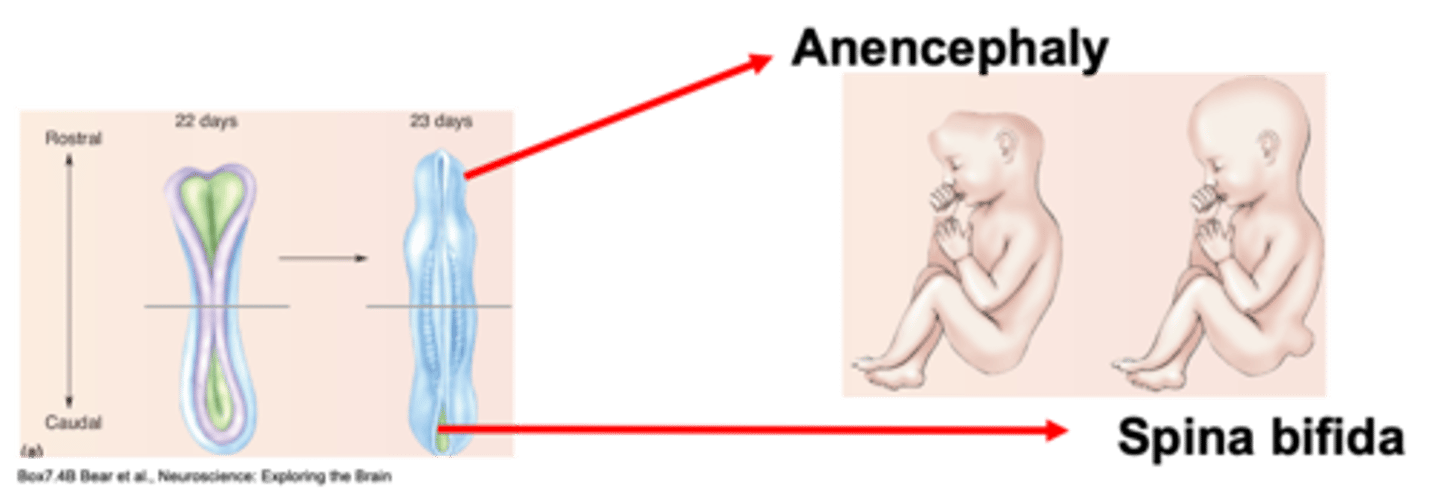
Failure to appropriately close the neural tube
Specific sequences of gene expression - influenced by environment
Folic acid = 90% reduction in the chance of neural tube defects = influences DNA synthesis
Why are women advised to take folic acid when trying to conceive and during pregnancy?
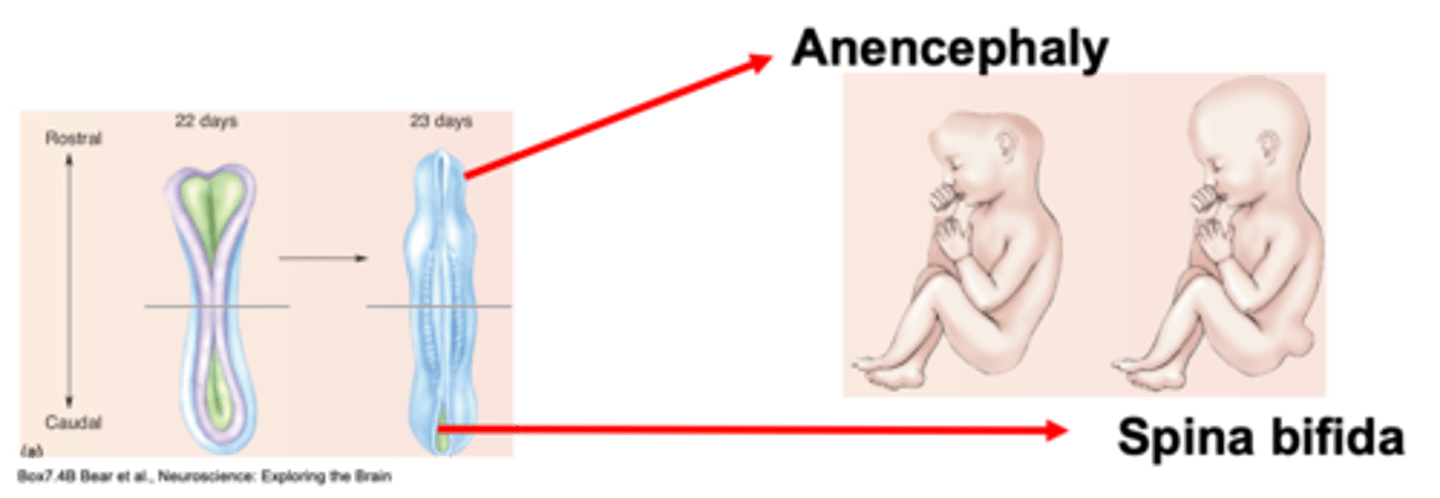
Anencephaly (fatal)
A defect closing at the top, rostrally, where the brain develops is known as ...?
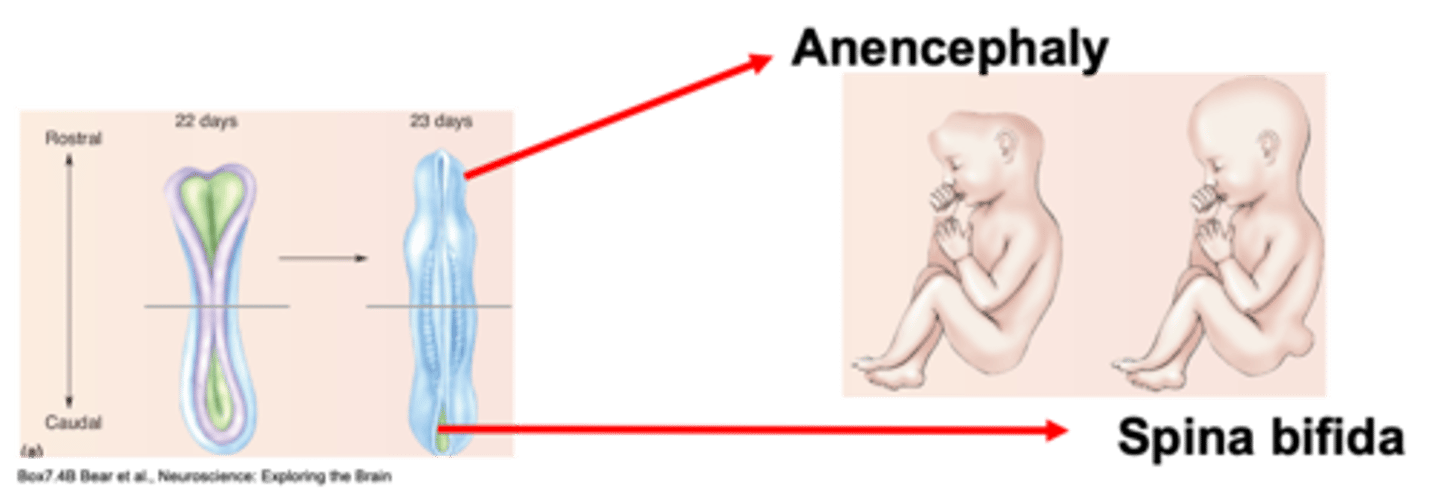
Spina bifida
A defect at the caudal part of the neural tube where spinal cord develops is known as ...?
Differentiation
What happens after neurulation?
Where tissue changes into separate ones
What happens in differentiation?
3 primary brain vesicles
Secondary brain vesicles of the forebrain
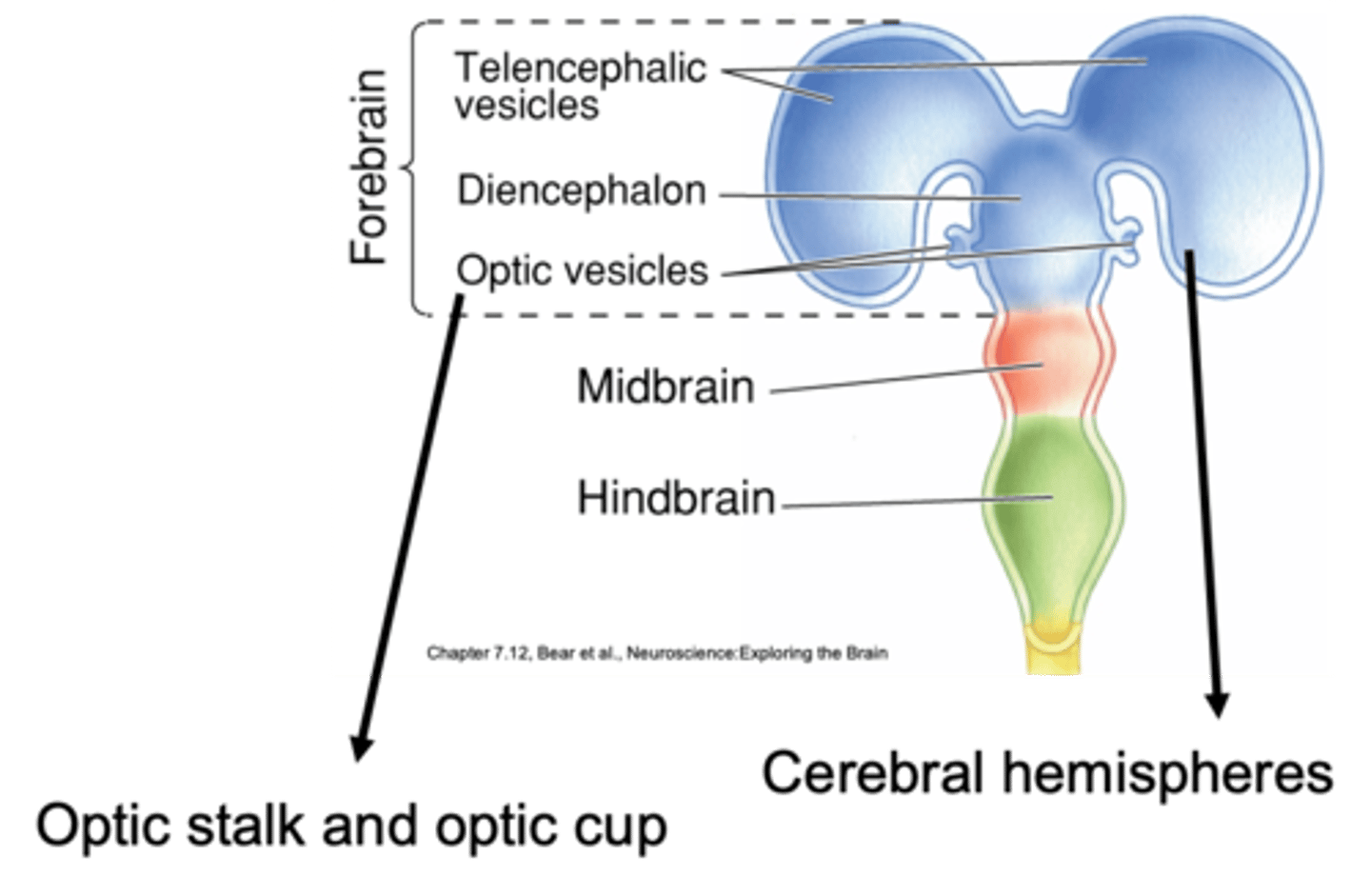
Optic stalk develops to the optic nerve, which is composed of axons of retinal ganglion neurons
Optic cup becomes the retina
What do the optic stalk and optic cup develop into?
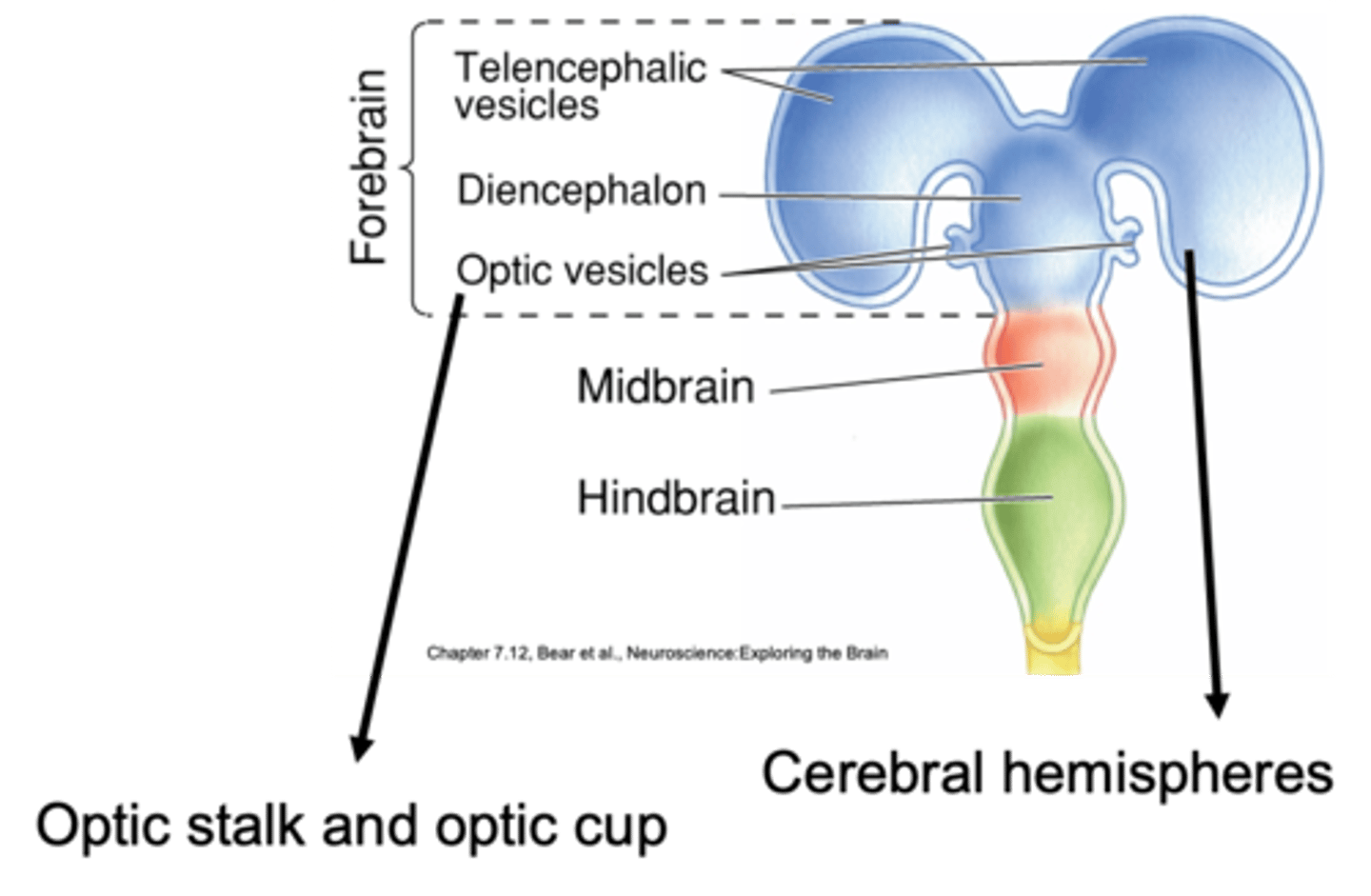
Houses neurons that receive information from the nose, process smell
What are olfactory bulbs?
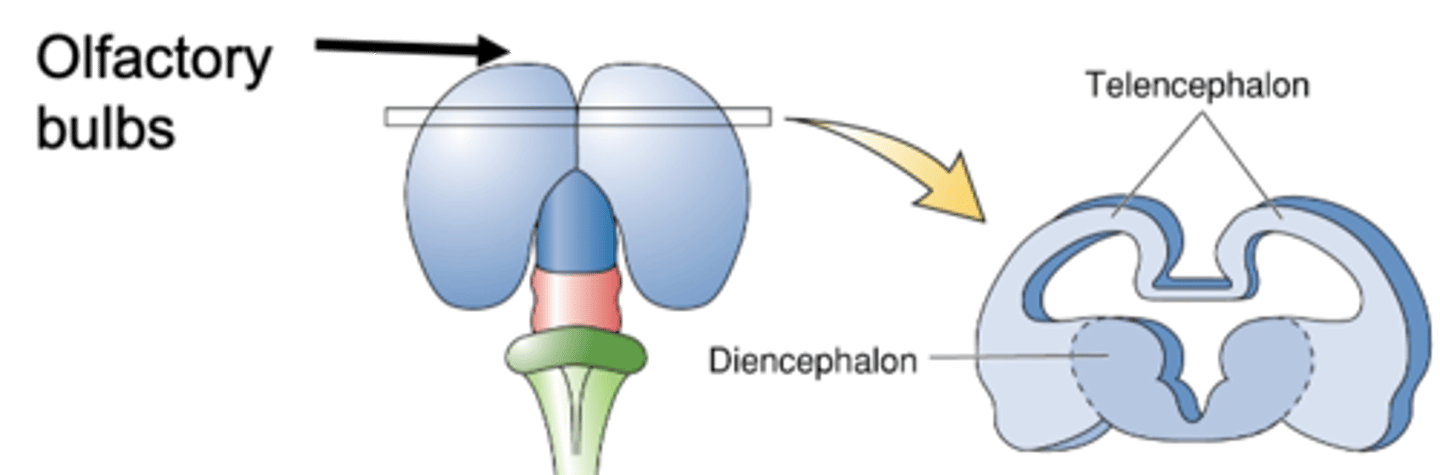
Forebrain differentiation: Main division
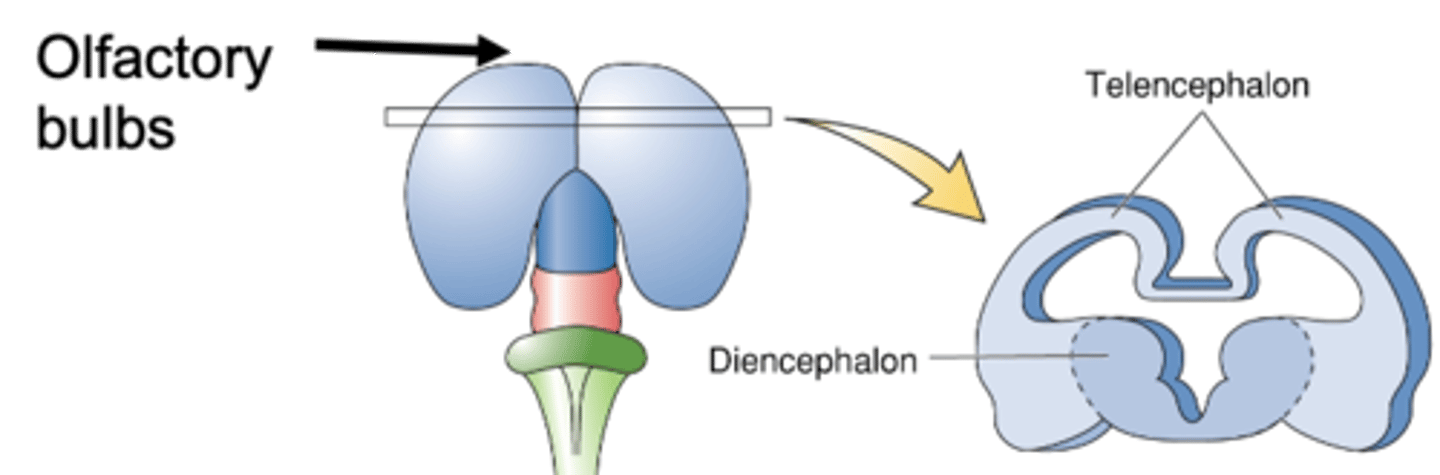
Forebrain differentiation: Ventricles
Forebrain differentiation: Grey matter
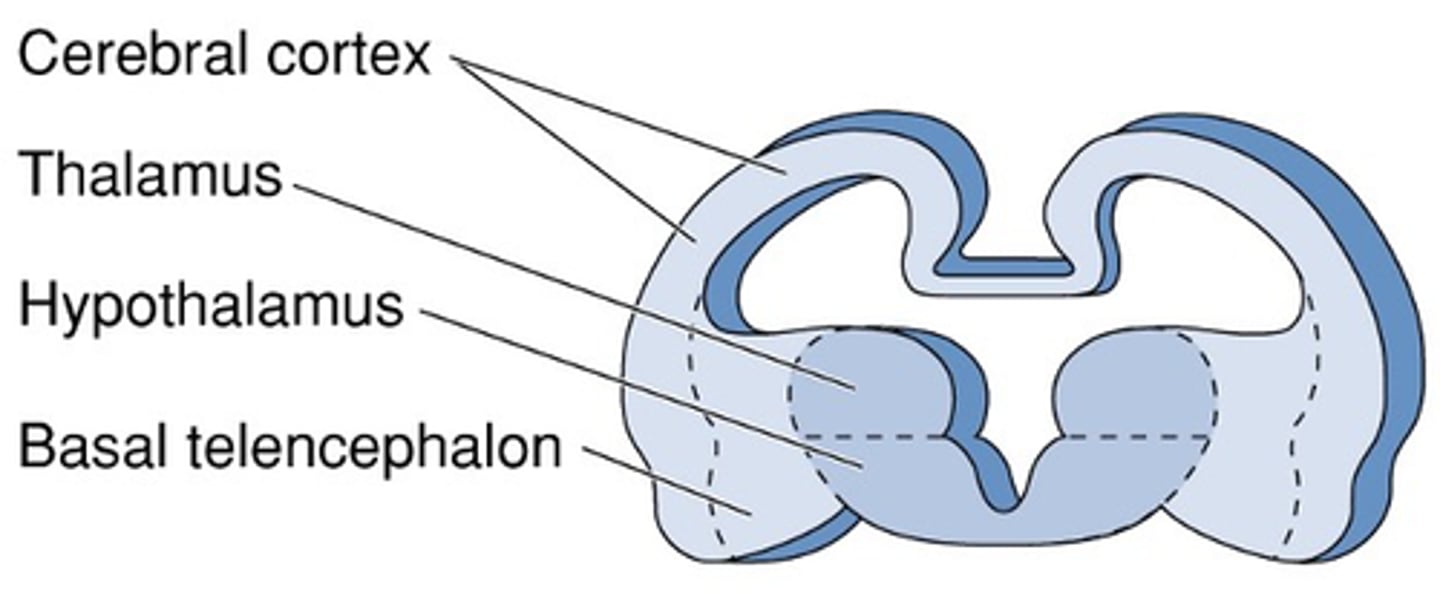
Forebrain differentiation: White matter
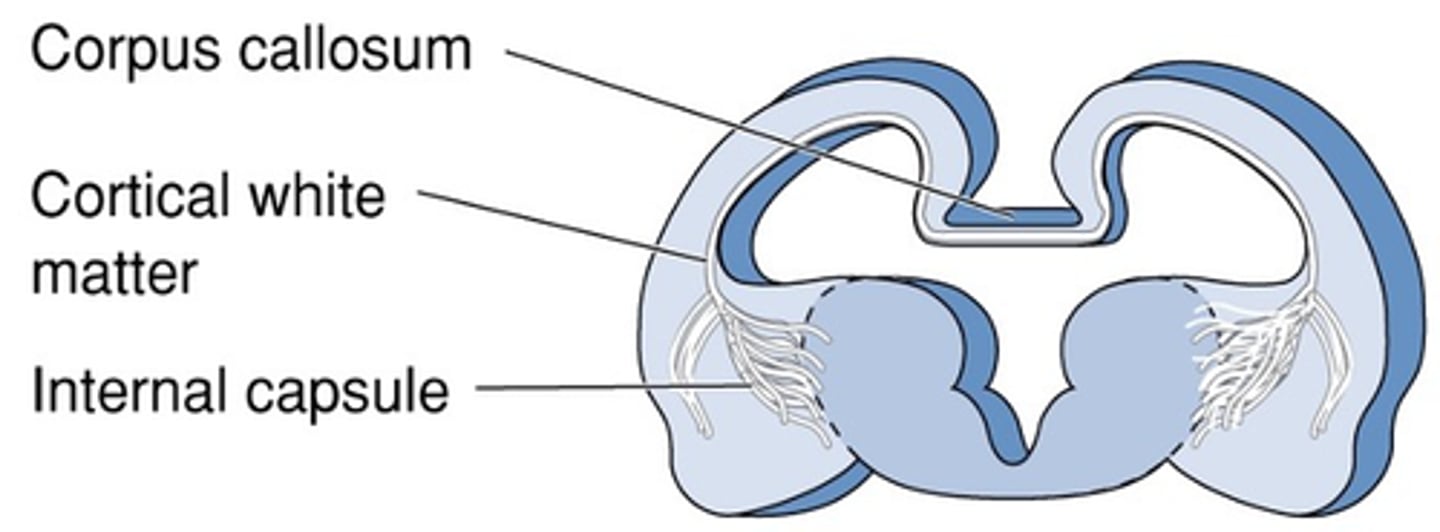
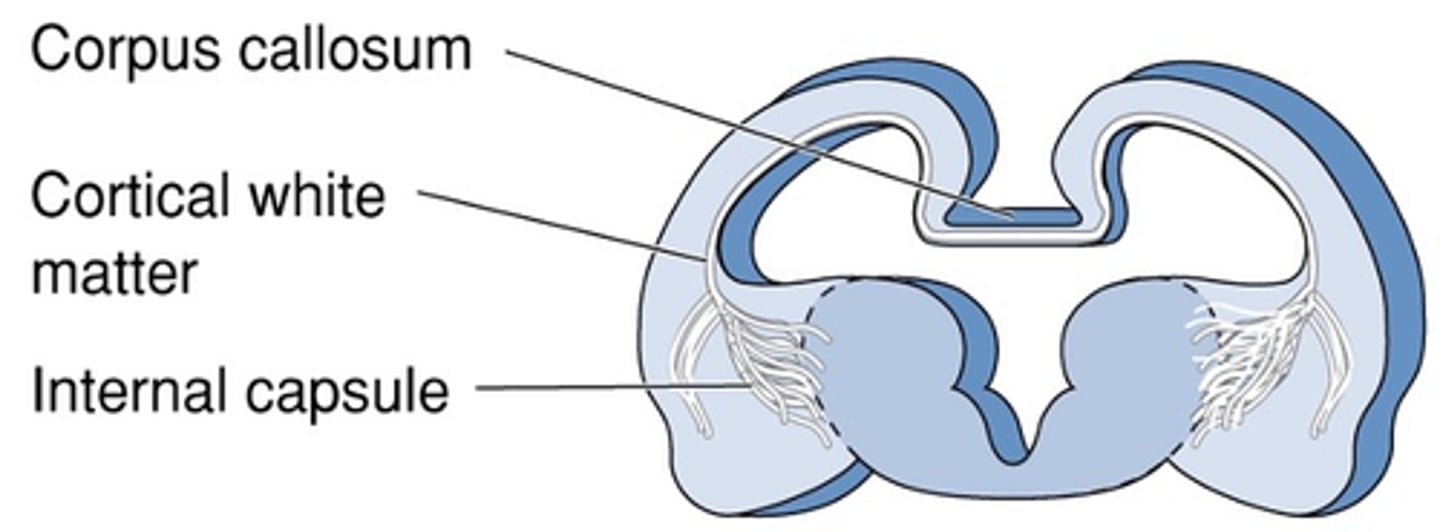
Gateway to and from the cerebral cortex
What is the internal capsule?
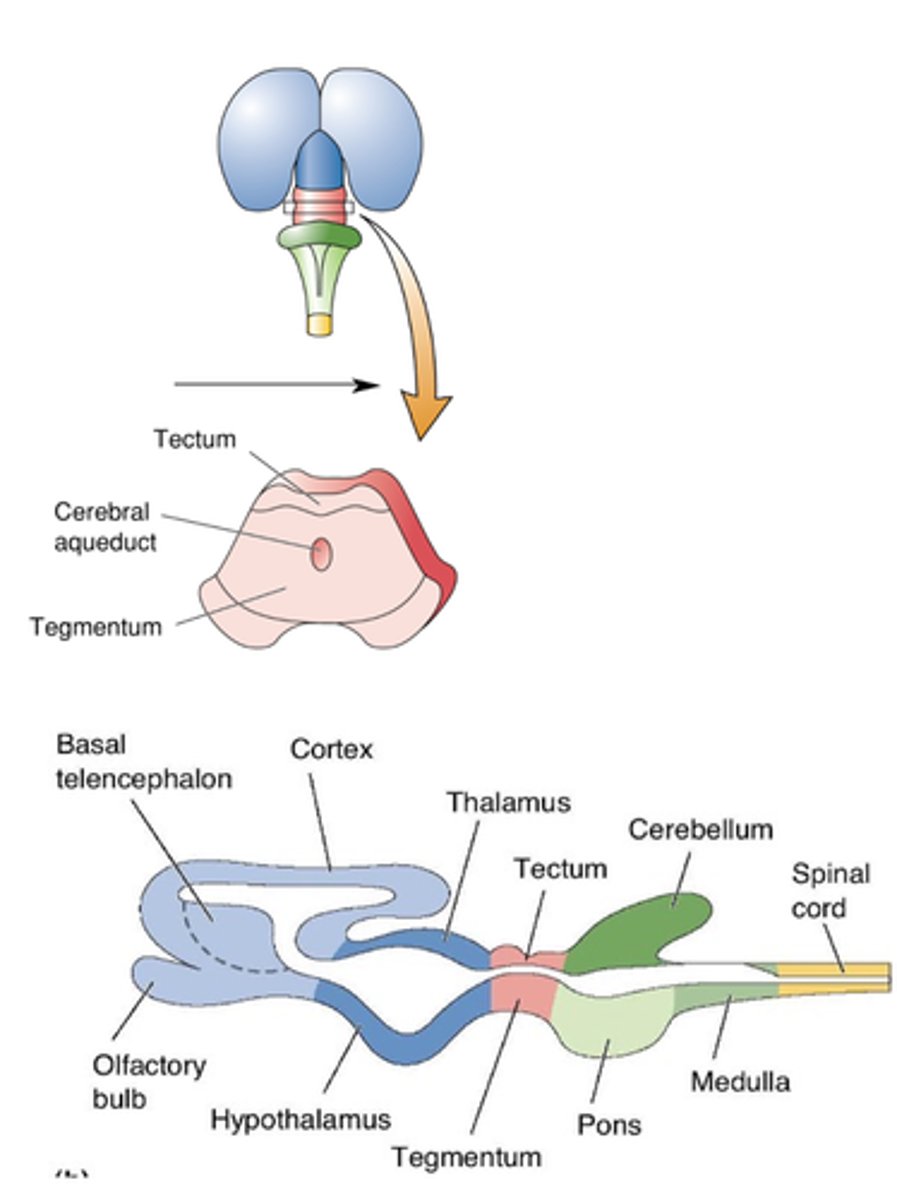
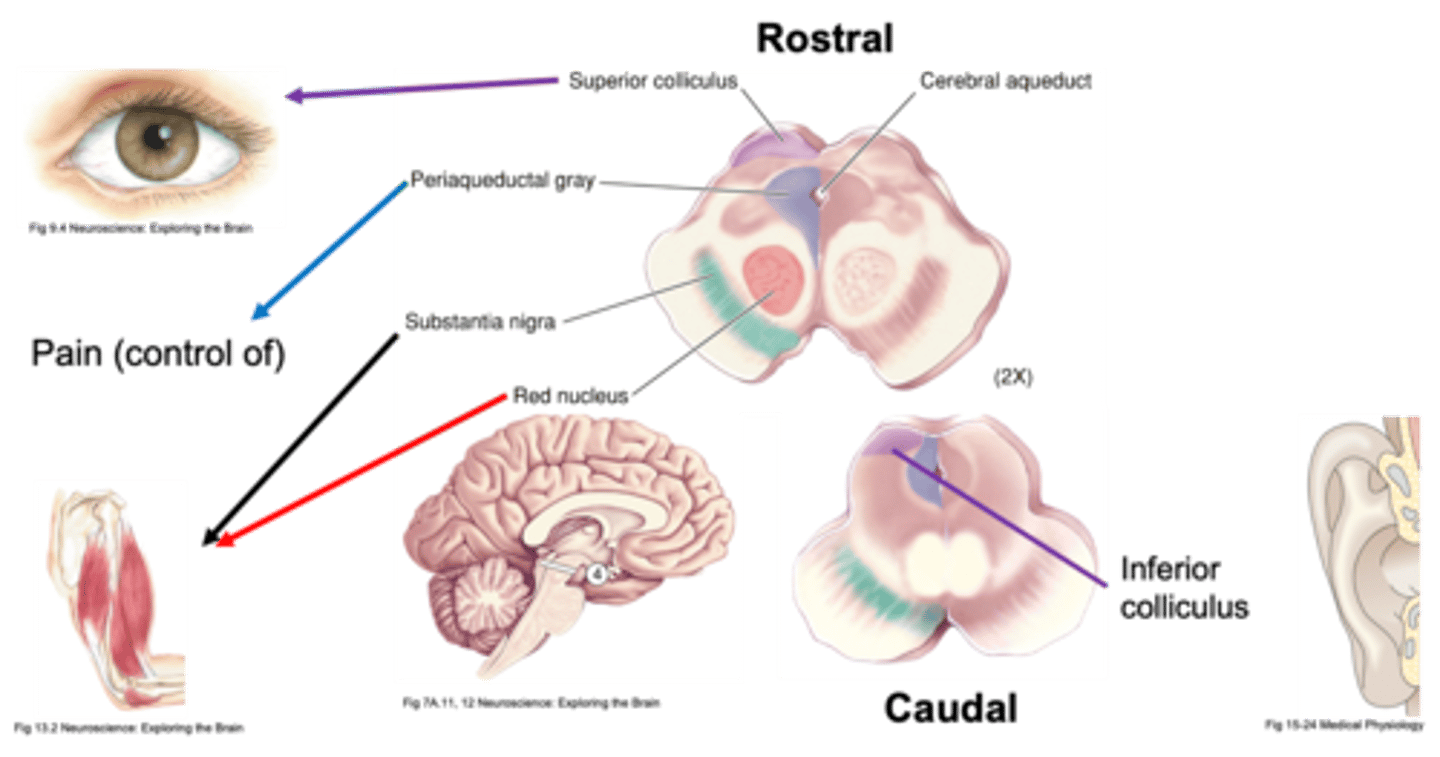
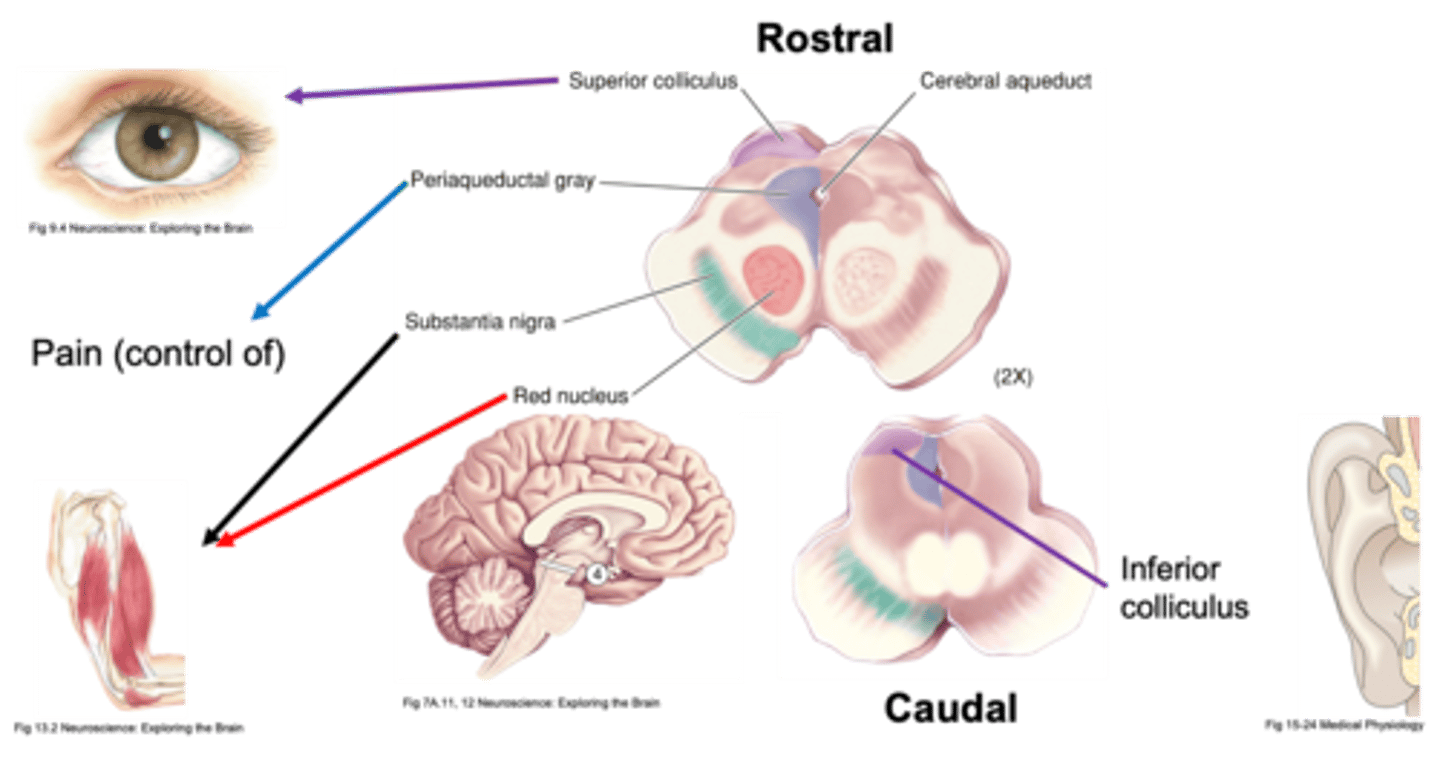
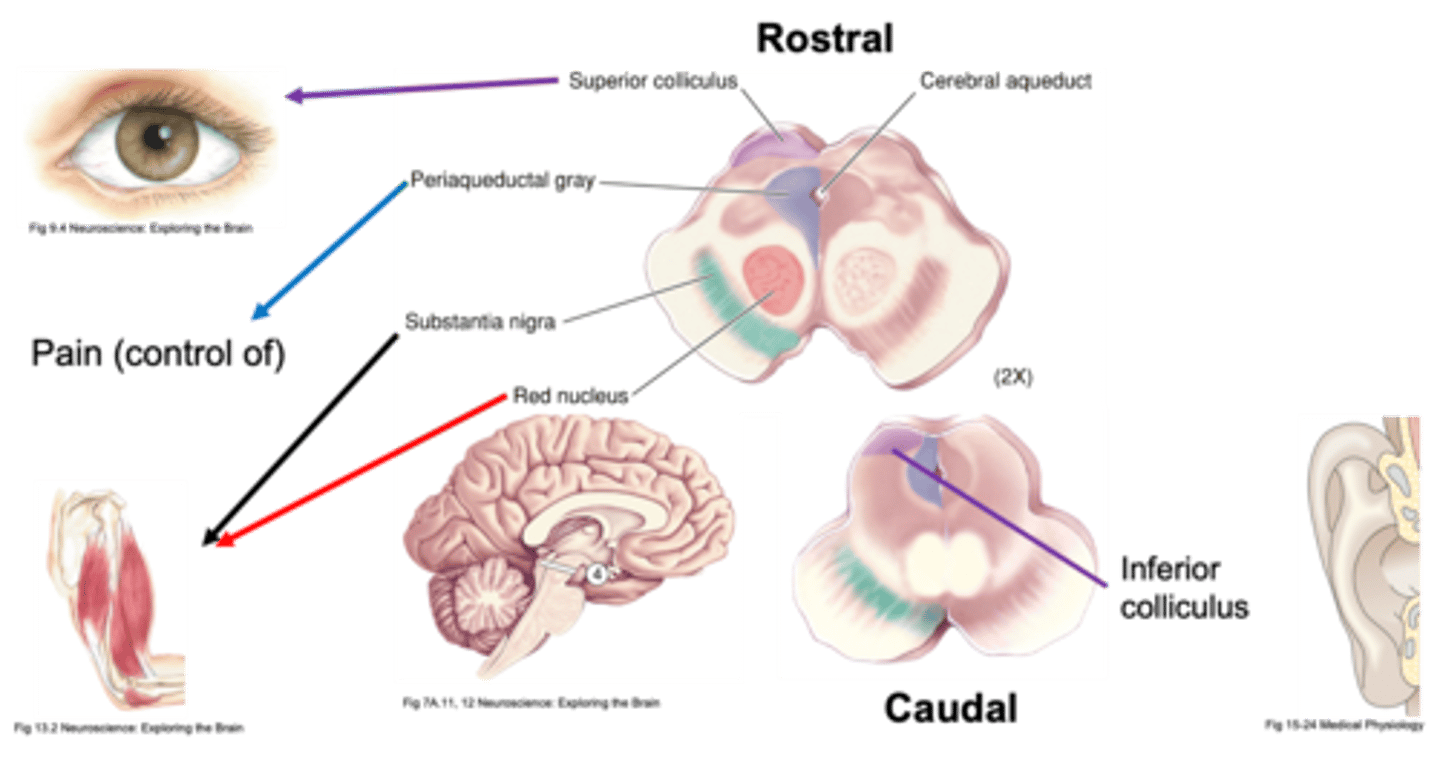
Midbrain differentiation
Processes vision
What does the superior colliculus do?
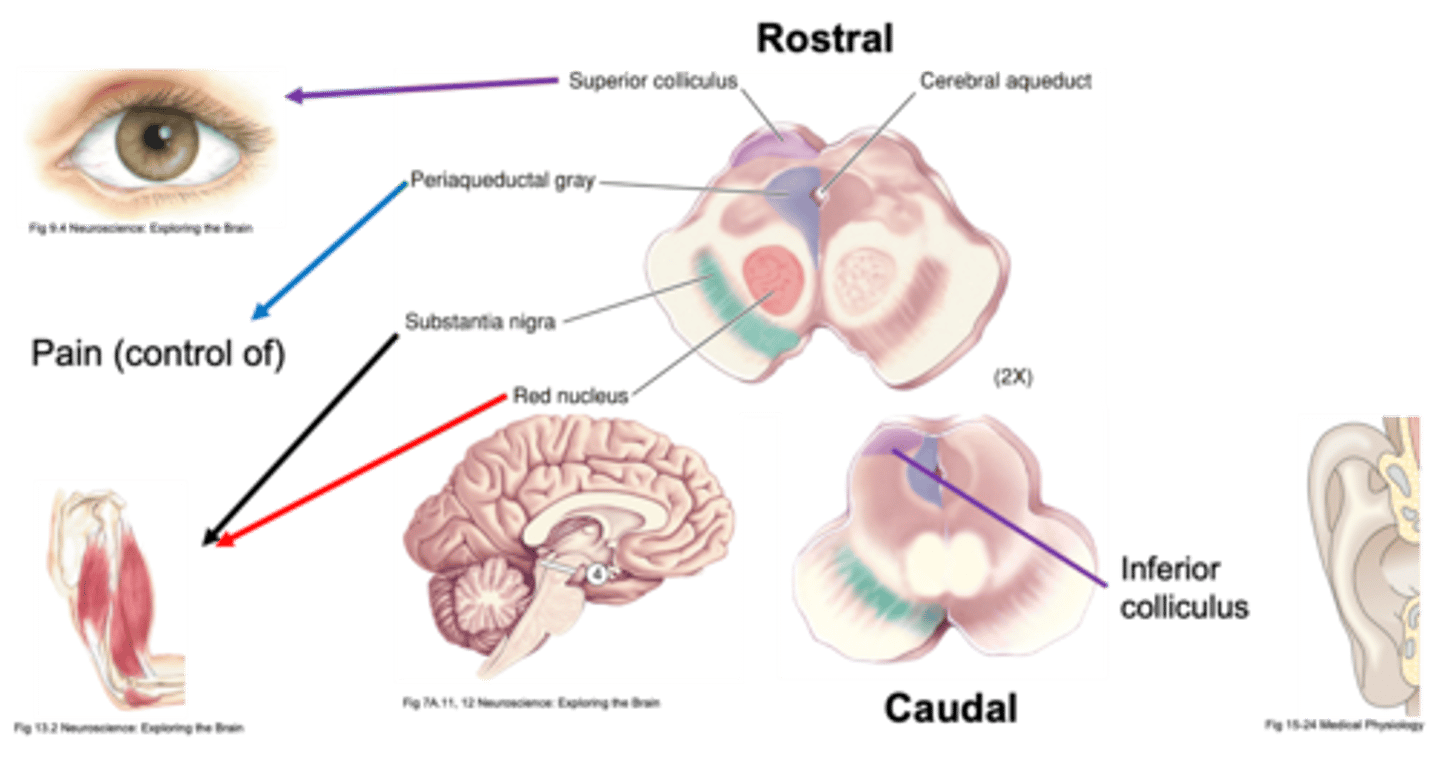
Processes audio
What does the inferior colliculus do?
Sensory processing and voluntary movement
What does the midbrain have roles in?
Substantia nigra and red nucleus
What parts are involved in movement in the midbrain?
Controls pain
What does periaqueductal grey do?
Pons, medulla and cerebellum
What make up the hindbrain?
Rhombic lips, cerebellum, neurons
__________ ______ grow to form _________ - smaller volume than central hemispheres but the same number of _________
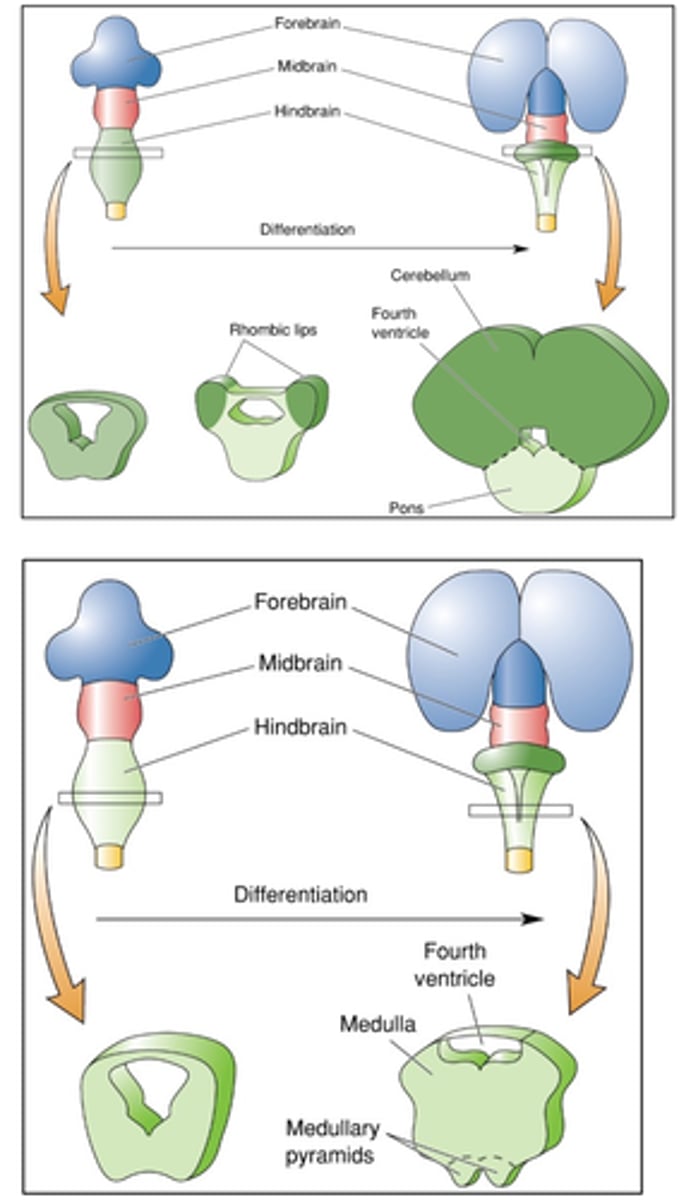
Pons
What is ventral to cerebellum?
Medulla
What is caudal to hindbrain?
Co-ordinates movement, balance and posture
What does the cerebellum do?
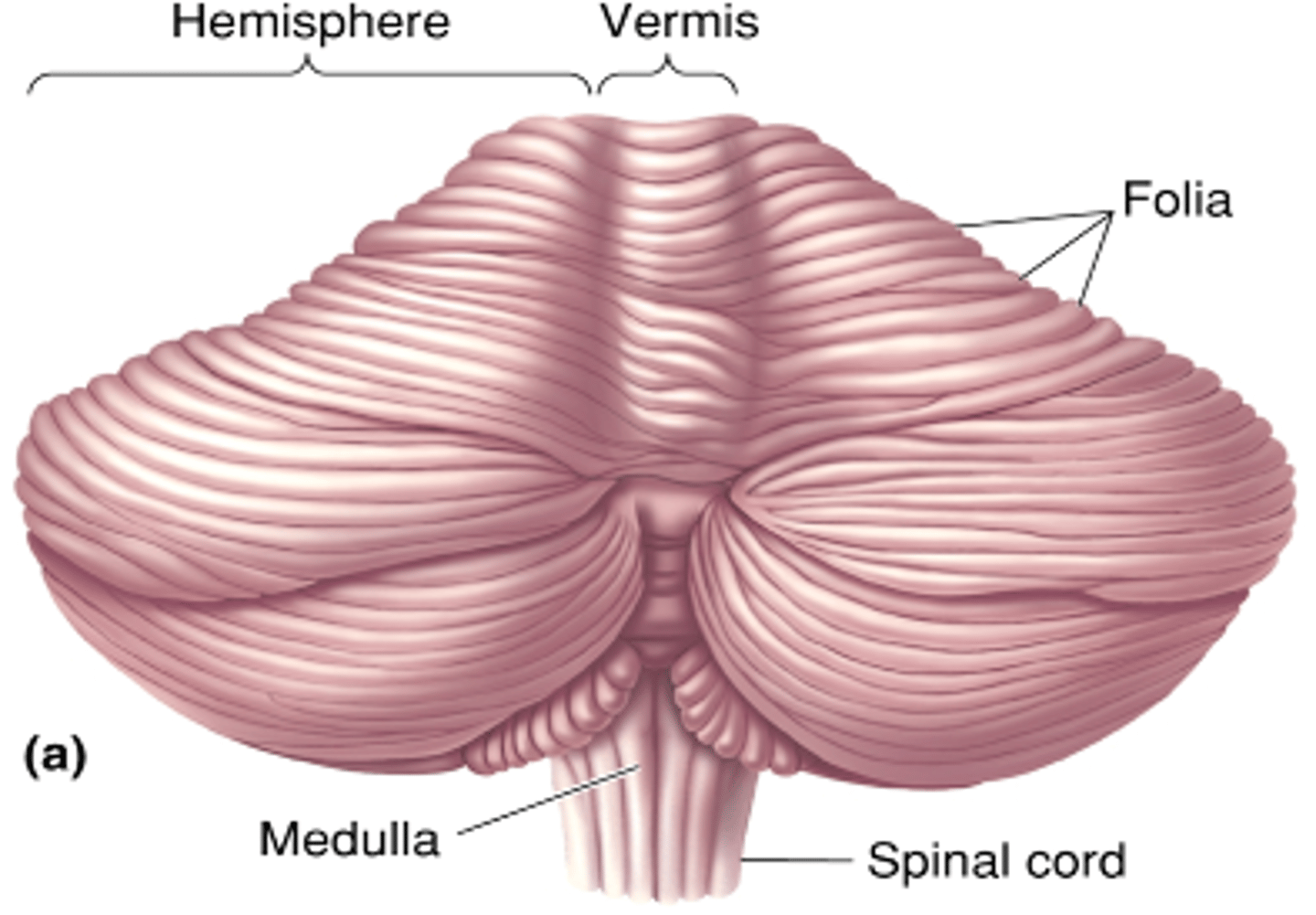
10, 50
In the cerebellum, there's __% CNS volume: __% CNS neurones
Vestibulocerebellum
What is the oldest part of the cerebellum that controls balance?
Spinocerebellum
What part of the cerebellum has muscle stretch receptors?
Cerebrocerebellum
What part of the cerebellum receives projections from sensorimotor cortex and controls motor coordination?
Hemispheres, vermis
The cerebellum is made up of two ____________ with a structure in the middle called _______
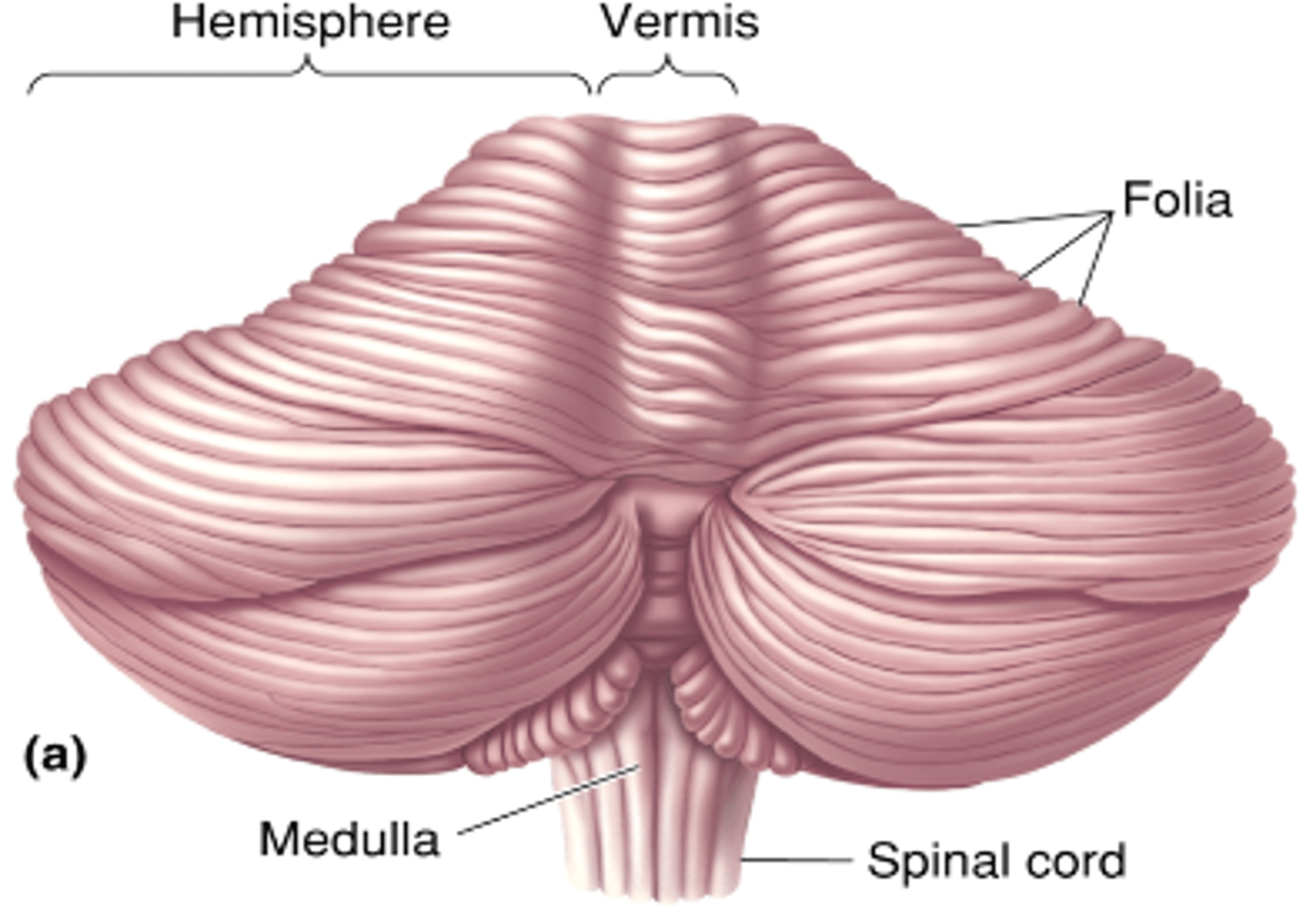
Folium
What is a single fold called?
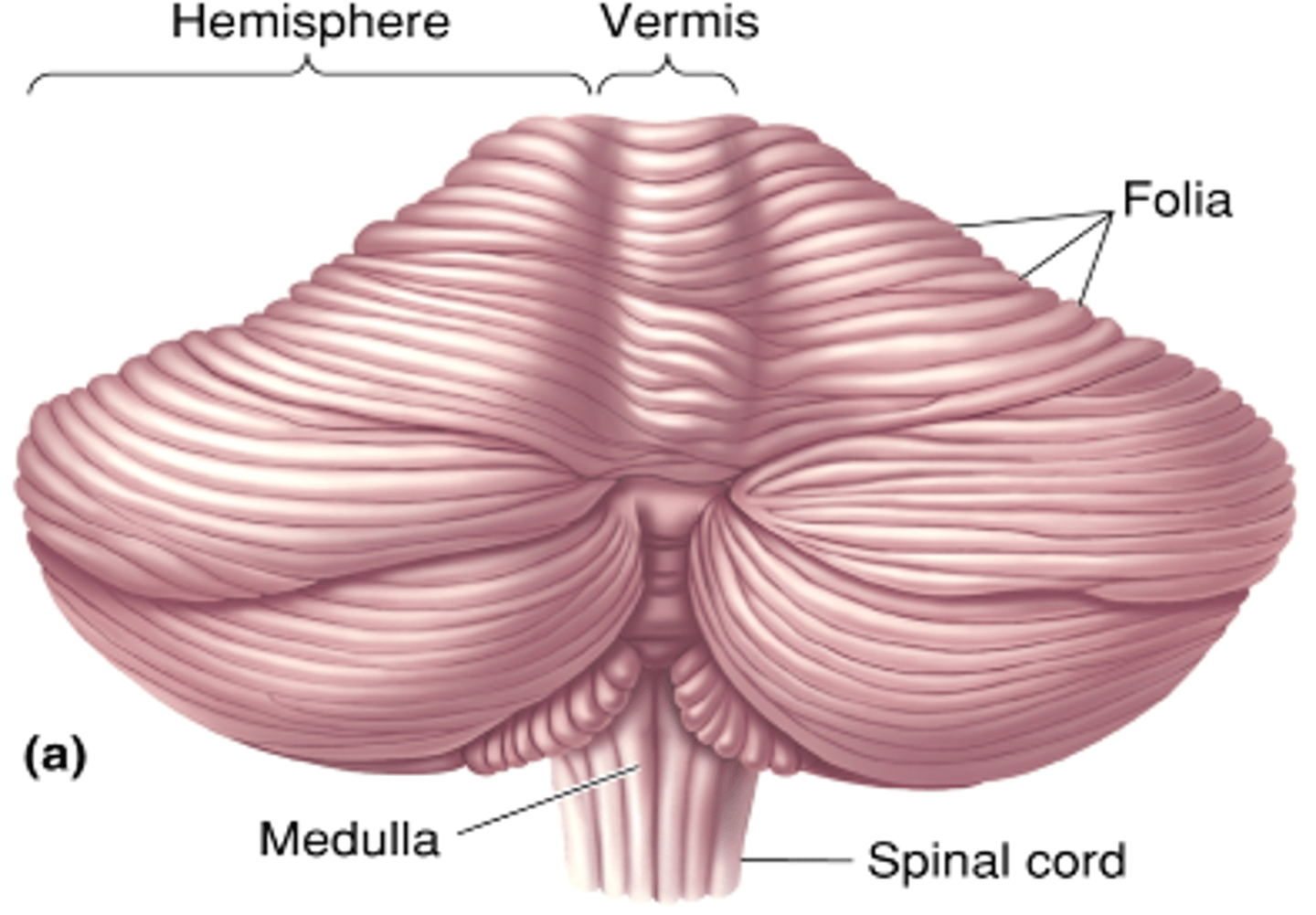
Folia
What are multiple folds called?
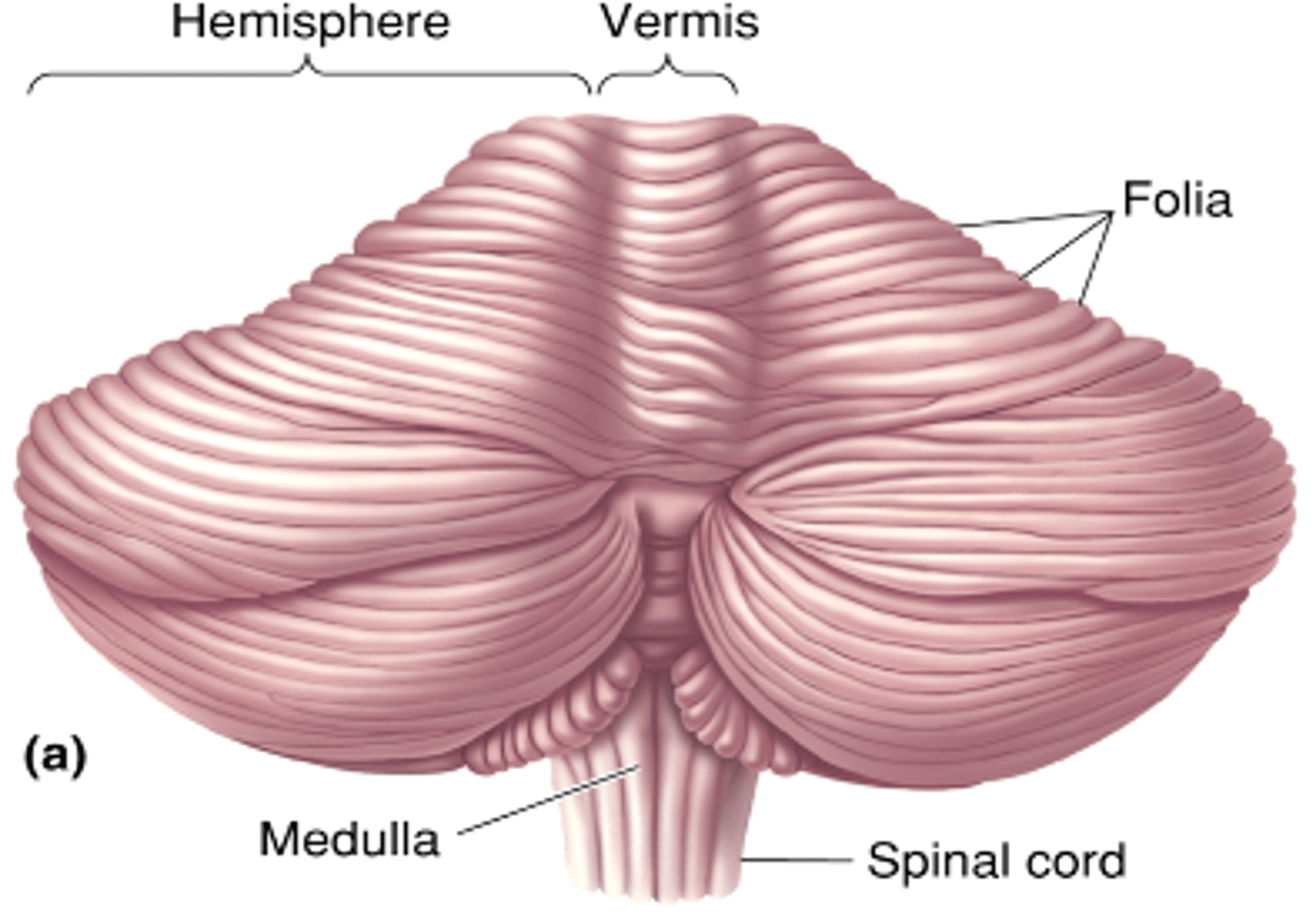
Pons, deep cerebellar nuclei
Information fed into the _____ and then fed out through the _____ ___________ ________
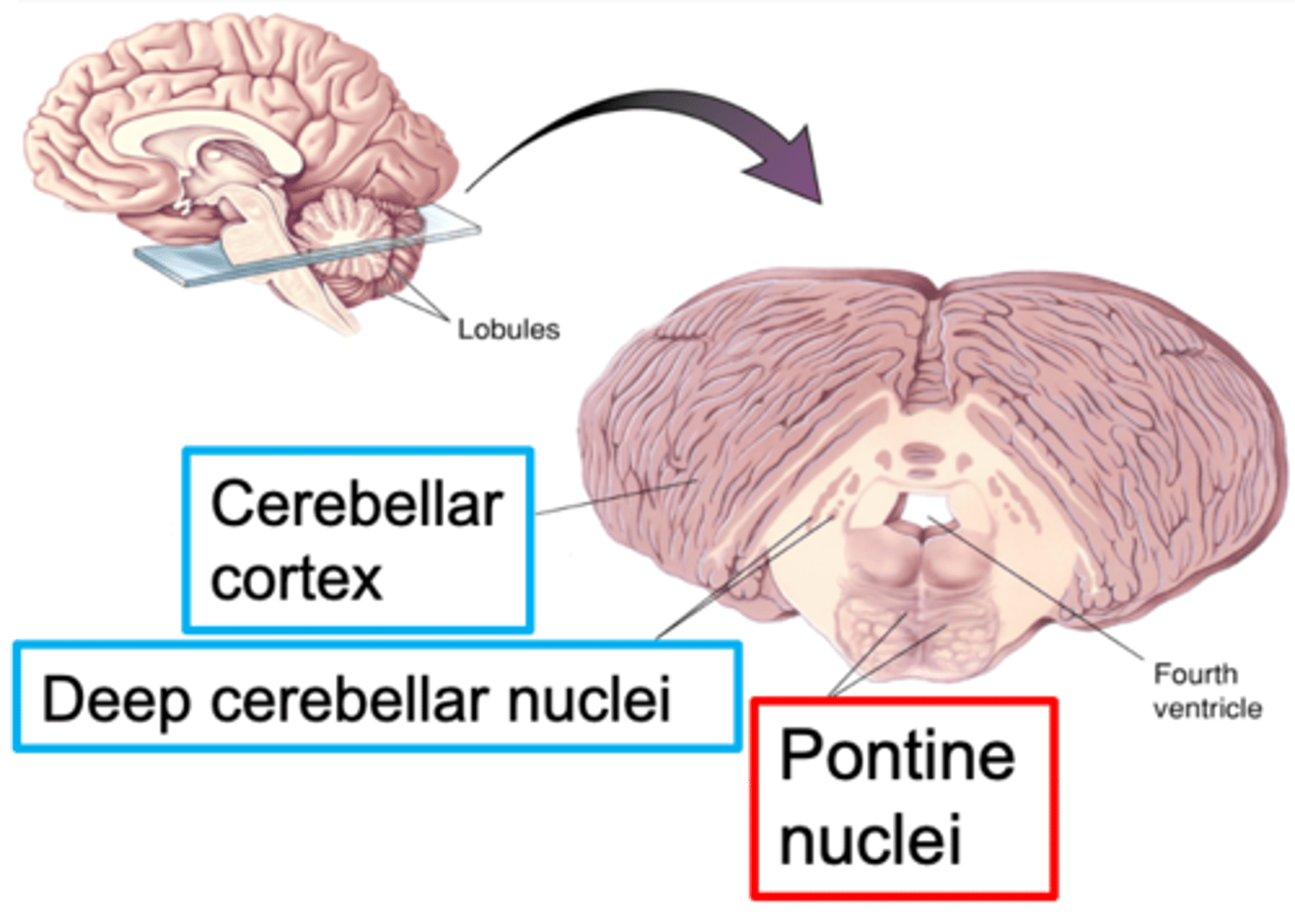
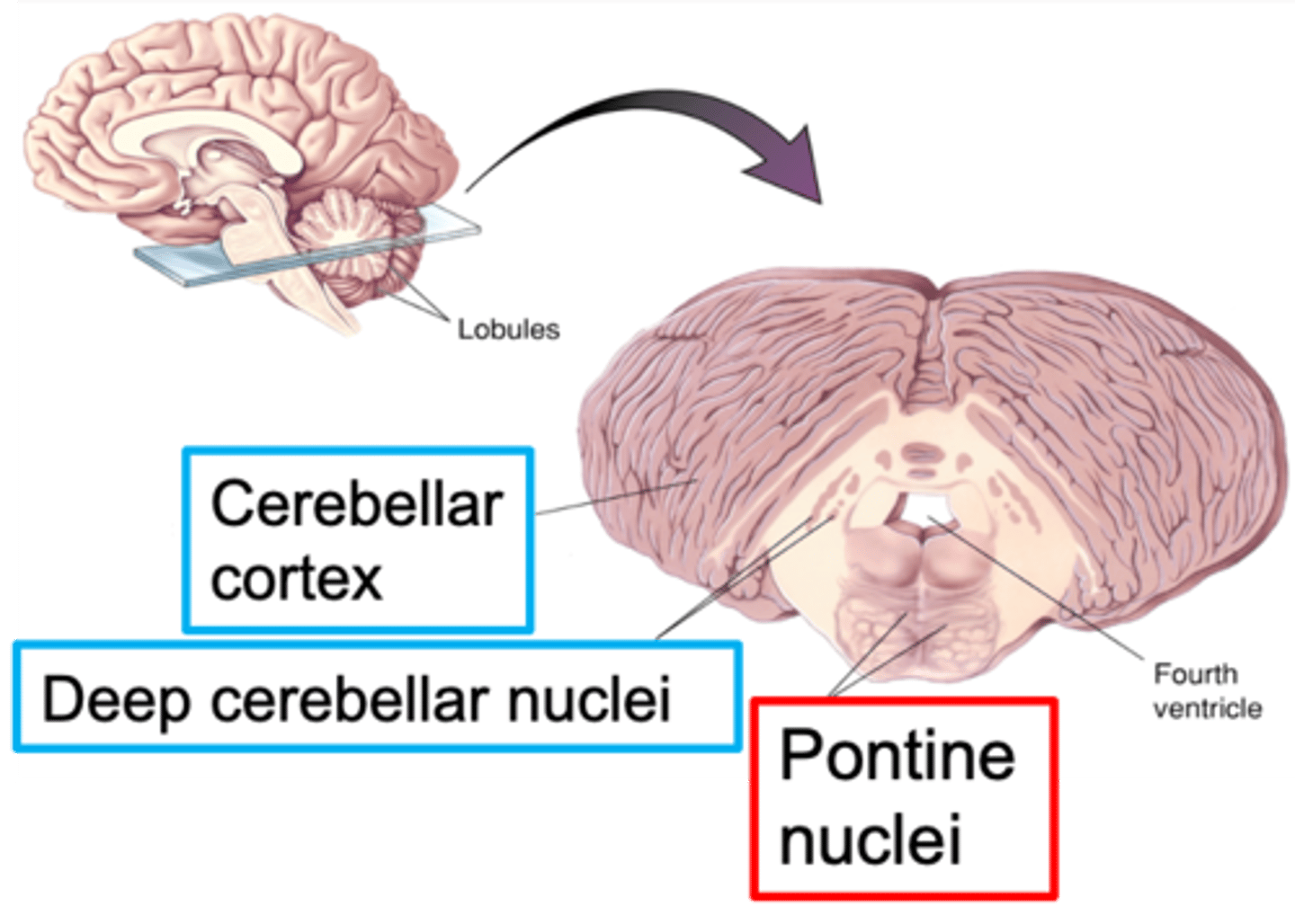
Nuclei of the pons
What are pontine nuclei?
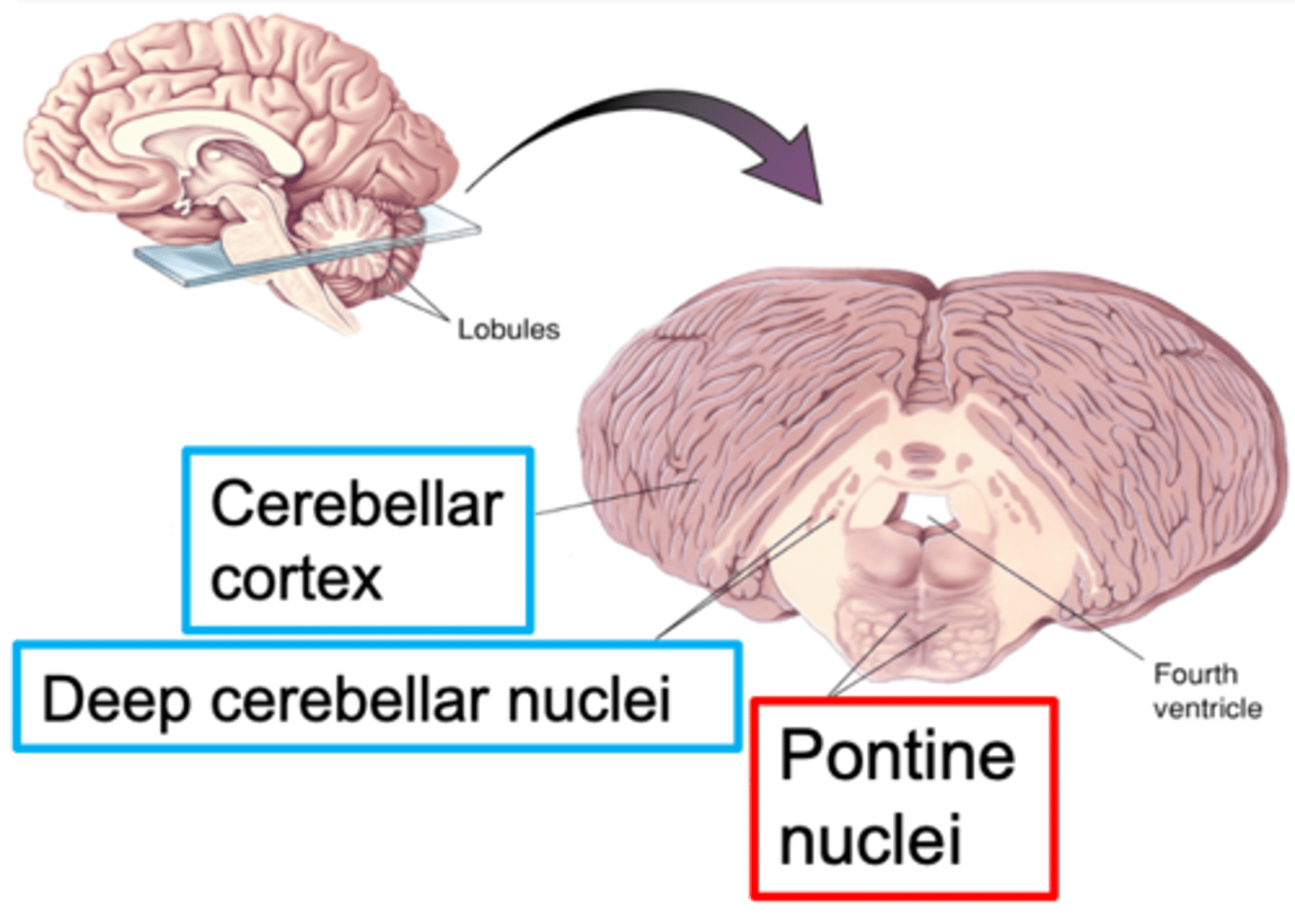
White
________ matter tracts from pontine nuclei
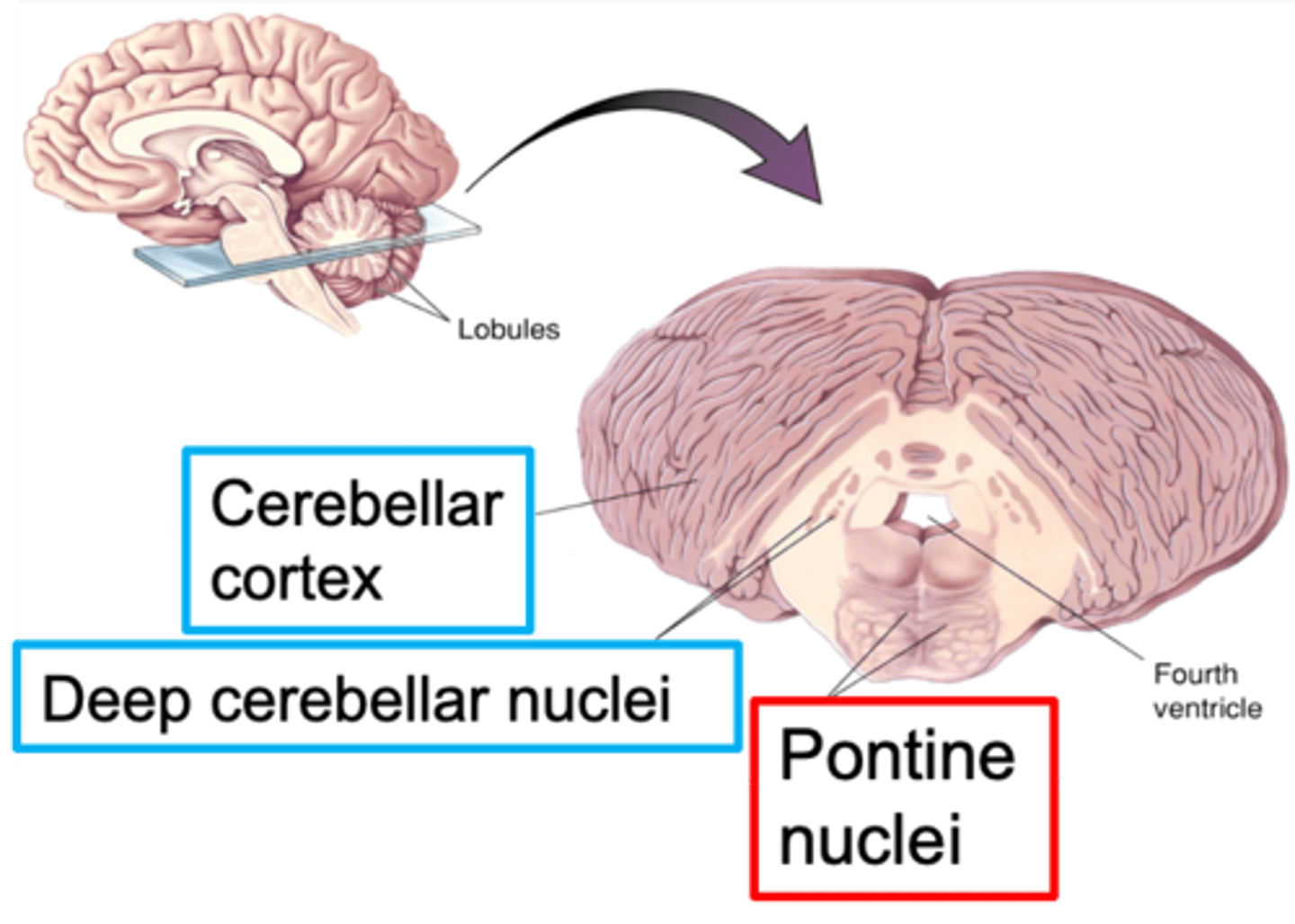
Grey
_______ matter area called the deep cerebellar nuclei
1:40
What is the ratio of neuronal outputs to inputs?
Due to purkinje cells with huge dendritic trees
Why is there a lot of integration in the cerebellum?