Overview of Brain Anatomy and Functions
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Gyrus
A ridge on the surface of the brain.
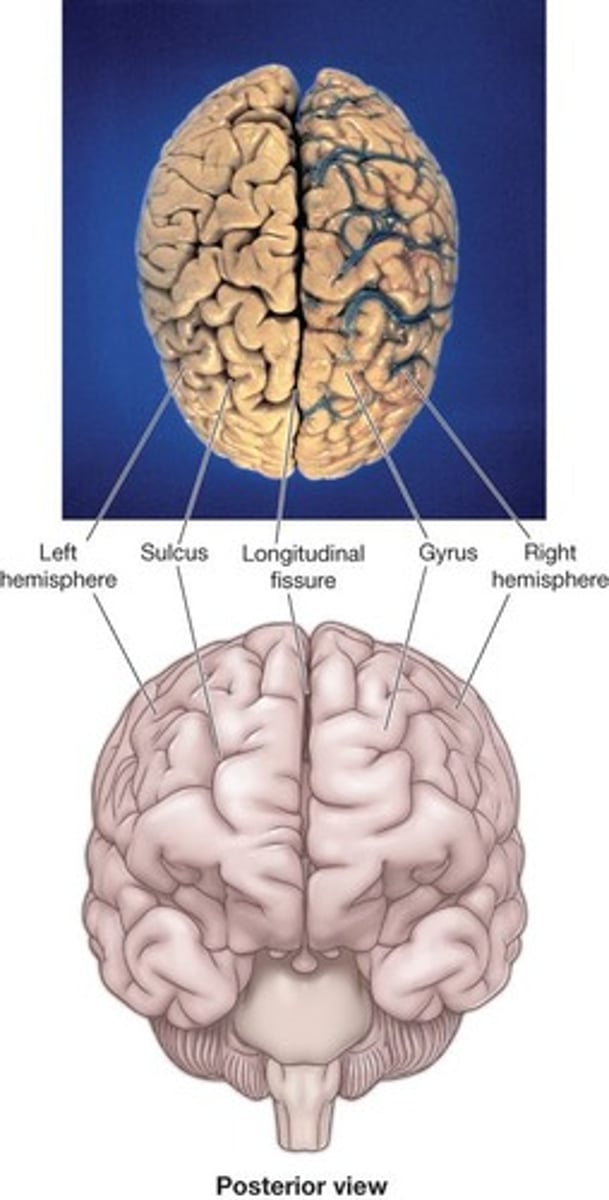
Sulcus
A groove on the surface of the brain.
Fissure
A deep groove that separates major brain regions.
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions.
Diencephalon
The part of the brain that includes the thalamus and hypothalamus.
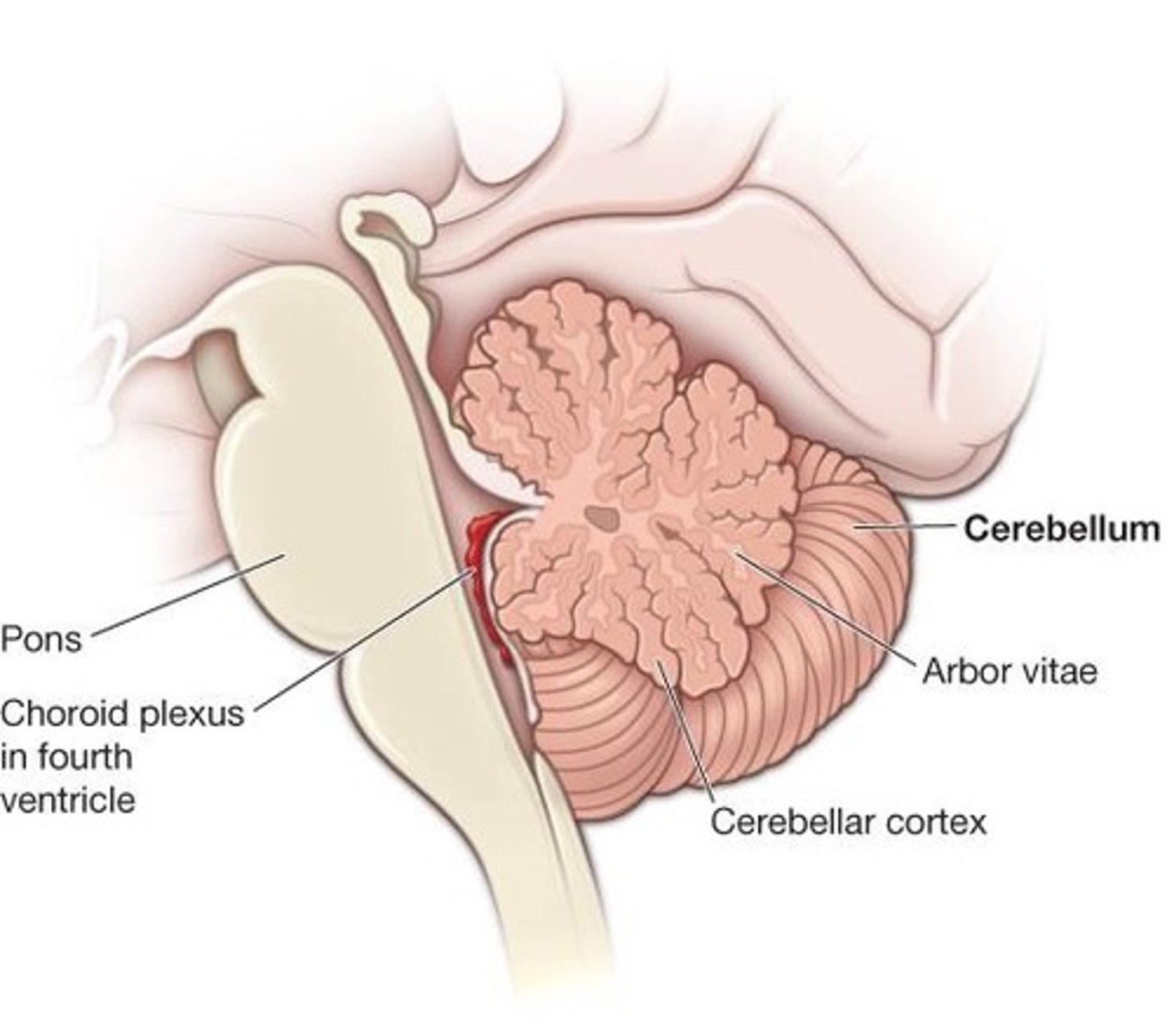
Cerebellum
The part of the brain that coordinates voluntary movements.
Brainstem
The part of the brain that controls basic life functions.
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for rational thoughts, decisions, some language, and personality.
Parietal Lobe
Responsible for sensory (touch) interpretation.
Temporal Lobe
Responsible for auditory interpretation.
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for visual interpretation.
Insula
Responsible for taste interpretation.
Primary Cortical Areas
Areas that directly decode sensory stimuli.
Association Cortical Areas
Areas that associate sensory stimuli with memories.
Longitudinal Fissure
The deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres.
Lateral Sulcus
The groove that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
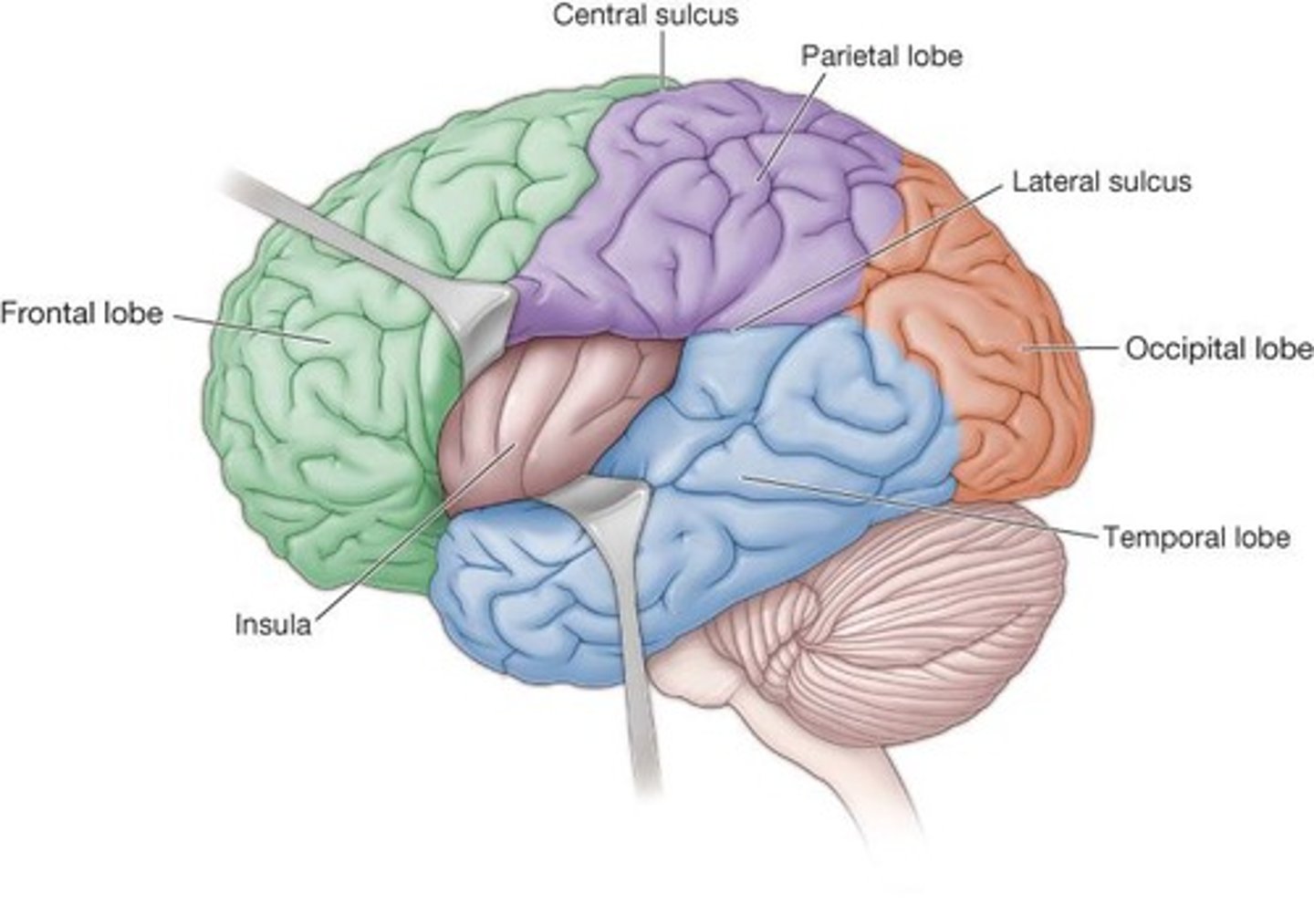
Central Sulcus
The groove that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
Transverse Fissure
The groove that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum.
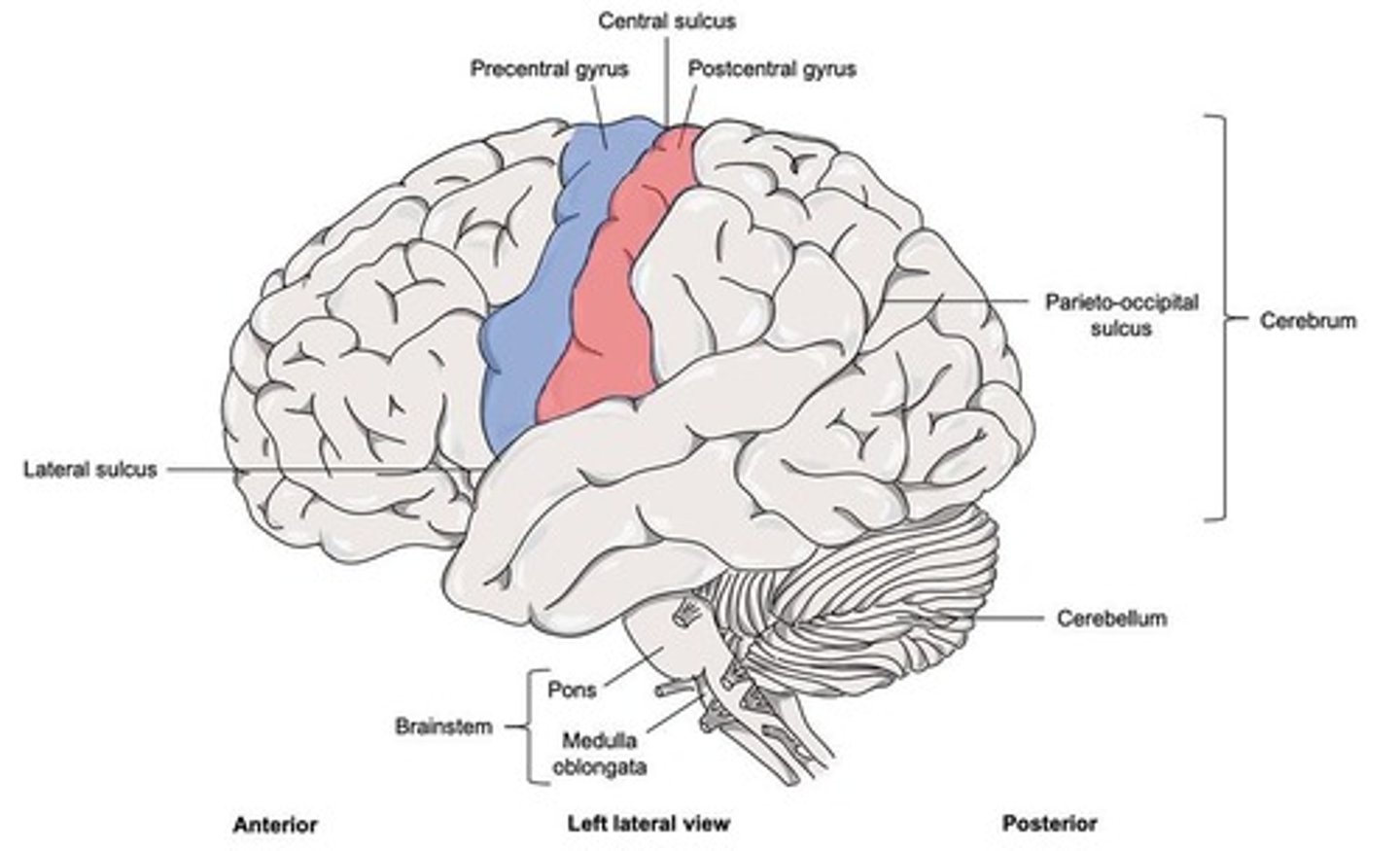
Precentral Gyrus
The gyrus located anterior to the central sulcus, involved in motor control.
Postcentral Gyrus
The gyrus located posterior to the central sulcus, involved in sensory processing.
Cortex
The outer layer of the brain, involved in high-level functions.
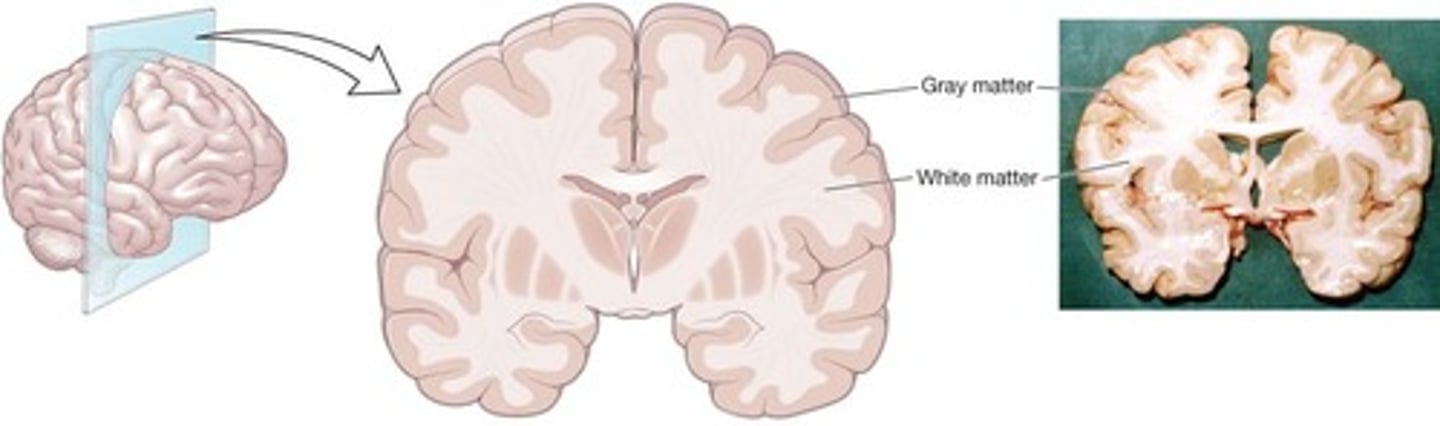
White Matter
Myelinated axons in the brain.
Cerebral Nuclei
Collections of cell bodies in the CNS, also known as basal nuclei.
Gray Matter
Unmyelinated nervous tissue in the brain.
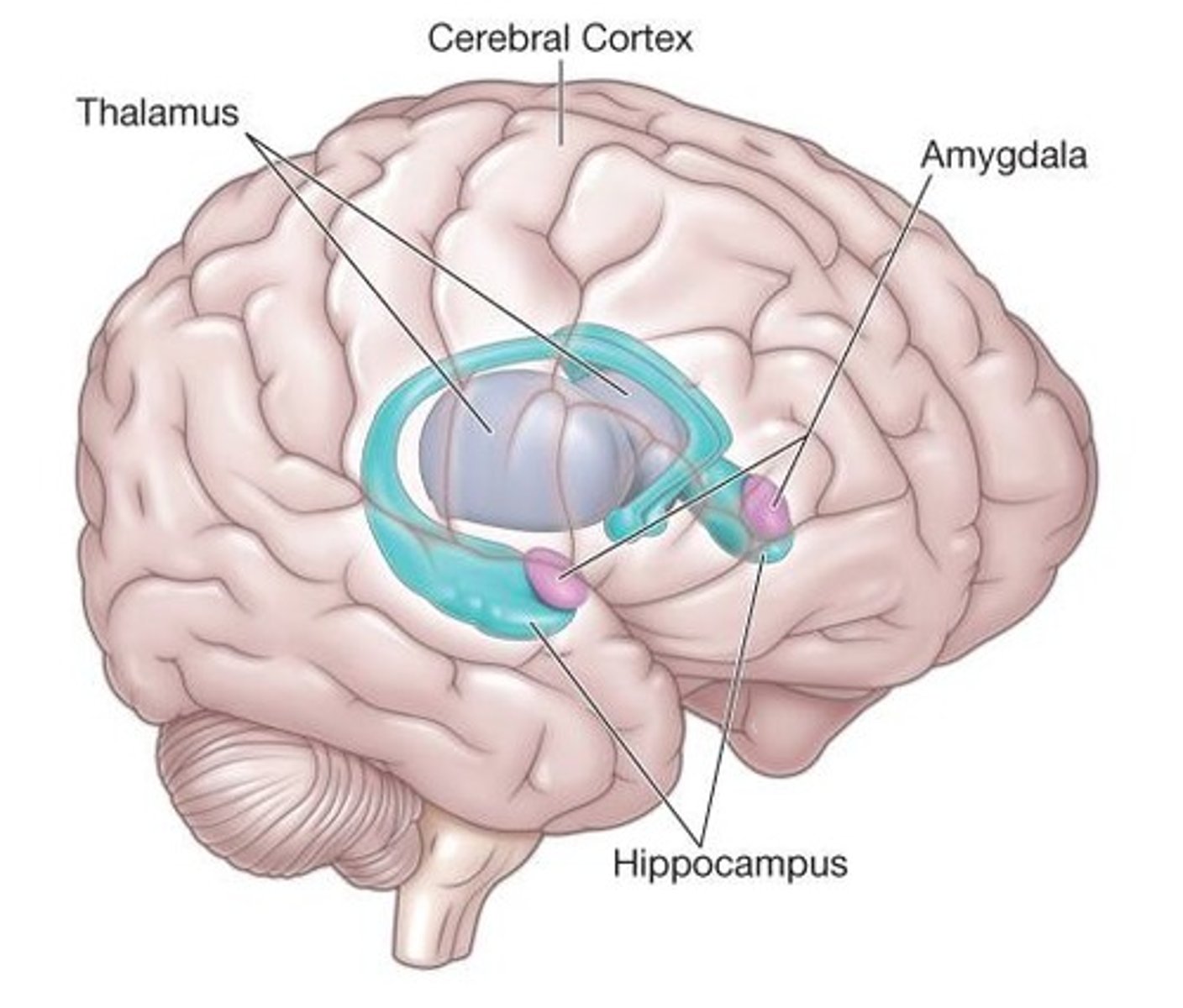
Thalamus
A structure in the diencephalon that relays sensory information.
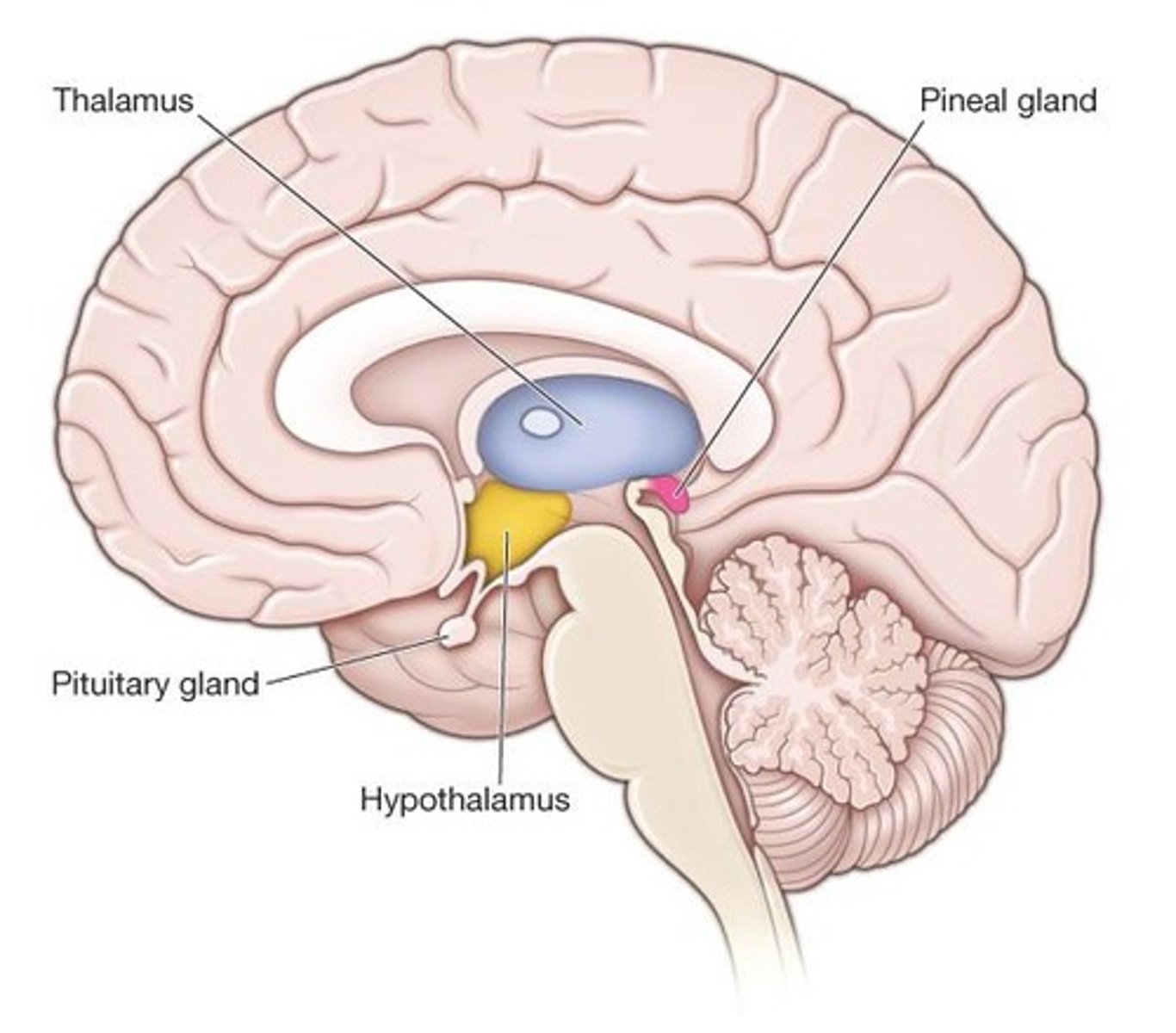
Hypothalamus
A structure in the diencephalon that regulates autonomic and endocrine functions.
Epithalamus
A part of the diencephalon that includes the pineal gland.
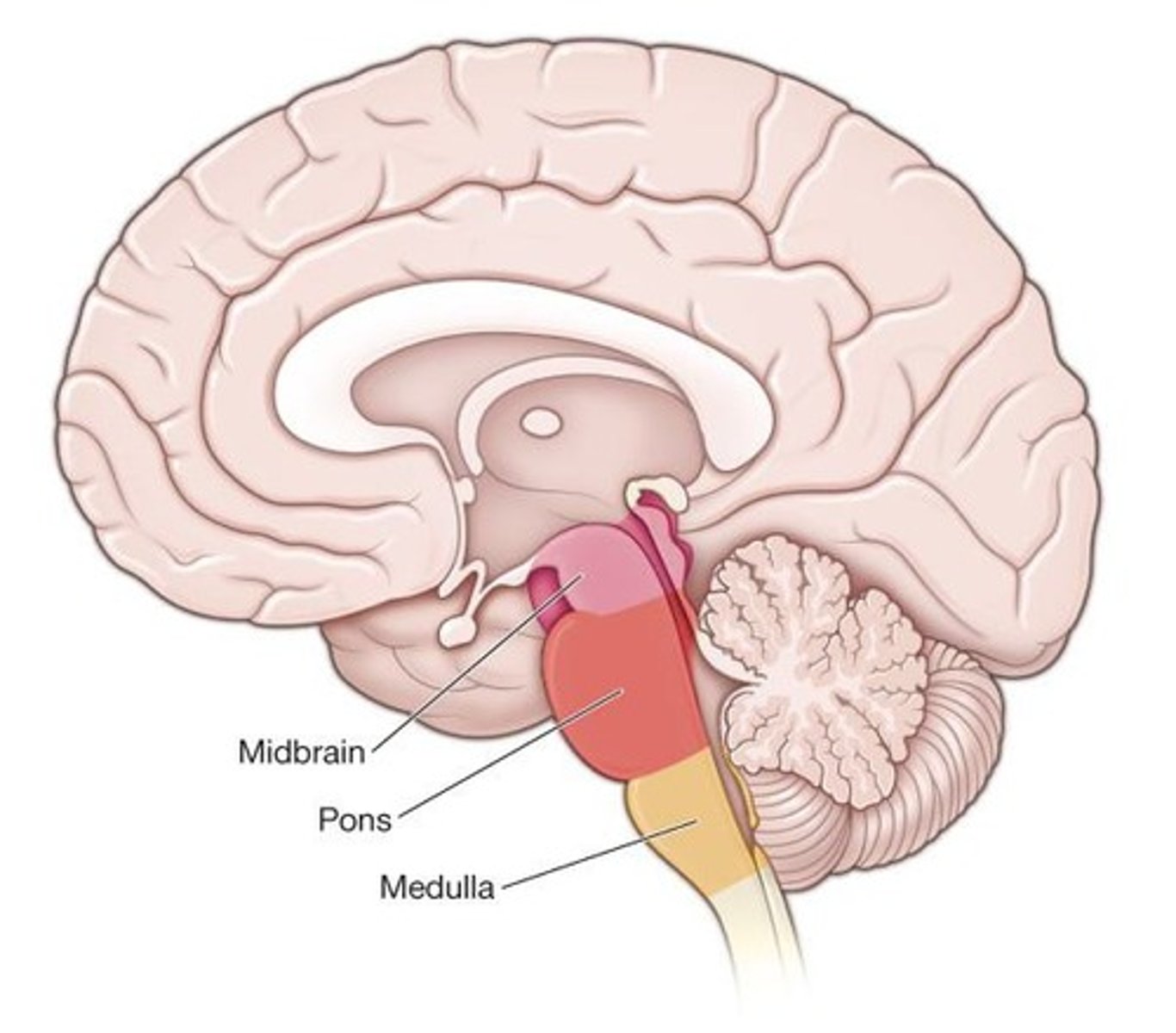
Pons
A part of the brainstem that connects different parts of the brain.
Limbic System
A set of structures in the brain that deal with emotions and memory.
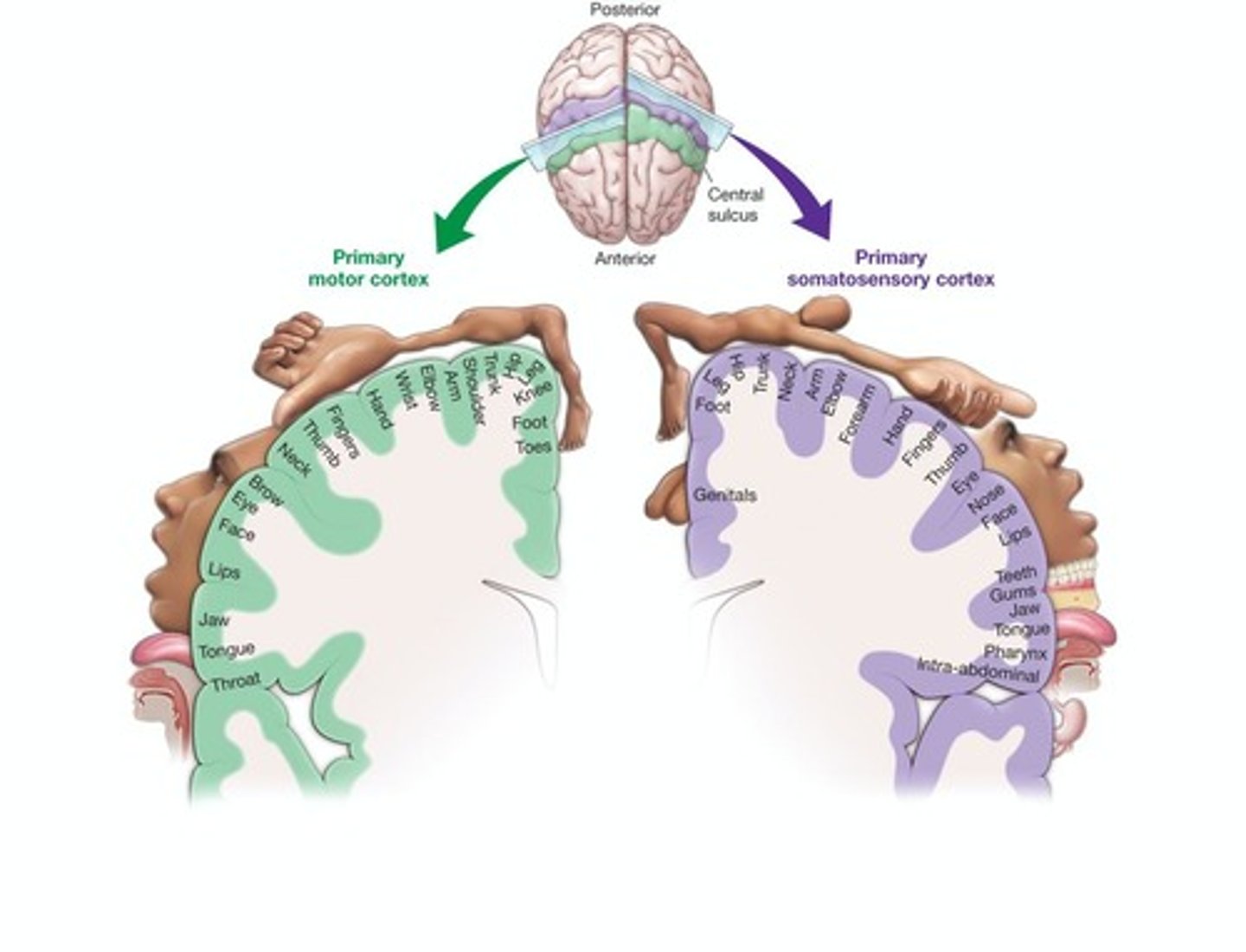
Primary motor cortex
Area of the cerebrum responsible for the physical generation of speech.
Primary somatosensory cortex
Cortical area that processes sensory information from the body.
Primary auditory cortex
Cortical area that processes auditory information.
Primary visual cortex
Cortical area that processes visual information.
Primary olfactory cortex
Cortical area that processes smell.
Primary gustatory cortex
Cortical area that processes taste.
Motor speech area (Broca area)
Cerebral area responsible for the physical generation of speech.

Wernicke area
Cerebral area involved in the construction of language.
Damage to Broca area
Results in lack of speech including inability to repeat words.
Damage to Wernicke area
Leads to fluent aphasia where phrases lack meaning.
Diencephalon
Composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland.
Thalamus
Paired structure that serves as a rest stop for incoming sensory information, editing, amplifying, or diminishing it.
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis center that directly controls endocrine function and influences autonomic function.
Homeostasis
Stable, dynamic internal conditions such as temperature.
Endocrine system
System of hormones that control functions throughout the body.
Autonomic nervous system
Pertaining to involuntary functions of the body.
Pineal gland
Secretes melatonin, a hormone involved in sleep and wake cycles.
Brainstem
Involved in basic life-sustaining activities such as heart rate and breath rate.
Pons
Structure that processes sensory information from one side of the body to the opposite side.
Cerebellum
Controls long-term patterned motor activities such as walking and dancing.
Proprioception
Understanding of where the body is in space.
Limbic system
Collection of deep brain structures that regulate emotions, memories, and emotional responses to sensory stimuli.
Amygdala
Fear center that processes fear and coordinates appropriate nervous system responses.
Hippocampus
Structure that forms, consolidates, and retrieves memories.