Diaz exam 4
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
primary headache
no underlying cause
secondary headache
underlying structural problems (stroke, tumor, meningitis, encephalitis)
tension headache
constant pressure pain (wraps around) and sensitive to light
cluster headache
unilateral pain around the eye
migraines
mood changes, fluid retention, increased urinary output, excessive uncontrolled yawing, food cravings, aura, confusion, exhaustion
headache diagnosis
history and physical. blood tests, lumbar puncture, CT/MRI to identify causes
headache treatment
treat underlying cause! NSAIDs (anti-inflammatories), Analgesics, Muscle relaxants, sedatives, antidepressants
status migrainous
unable to attain headache relief (more than 72 hours). Inpatient treatment needed
Gliomas brain tumor
originate in the cerebrum and are found mainly in the frontal lobes
Meningiomas brain tumor
most common primary brain tumor and presents around 40-70 years of age
Oligodendrogliomas brain tumor
slow growing tumors that do not spread to surrounding tissue
Acoustic neuroma brain tumor
benign, slow growing tumor that compress the cranial nerves
pituitary tumor
benign tumor found in the anterior lobe of the pituitary causing hyper secretion of pituitary hormones
Cushing’s triad
widened pulse pressure, bradycardia, and irregular respirations
brain tumor output
increased urine output may indicate increased ICP
to decrease cerebral edema
give glucocorticoids (dexamethasone)
brain tumor nursing actions
replace fluids, elevate head of bed, administer stool softener, administer antipileptic
seizures manifestations
rhythmic jerking and loss of consciousness to apparent daydreaming (absent)
seizures diagnosis
EEG
Tonicity
stiffening of muscles
clonicity
jerking and twitching
seizures medications
Antiepileptic medications: Levetiracetam (keppra), topiramate (topamax), phenytoin (dilantin), valproate (depilate), and more
acute meningitis
bacterial cause with quick symptom onset
chronic meningitis
onset of weeks to months with duration greater than 4 weeks
meningitis clinical manifestations
over/chills, headache, altered mental status, photophobia, nausea/vommiting, Brudzinski’s and Kernig’s signs
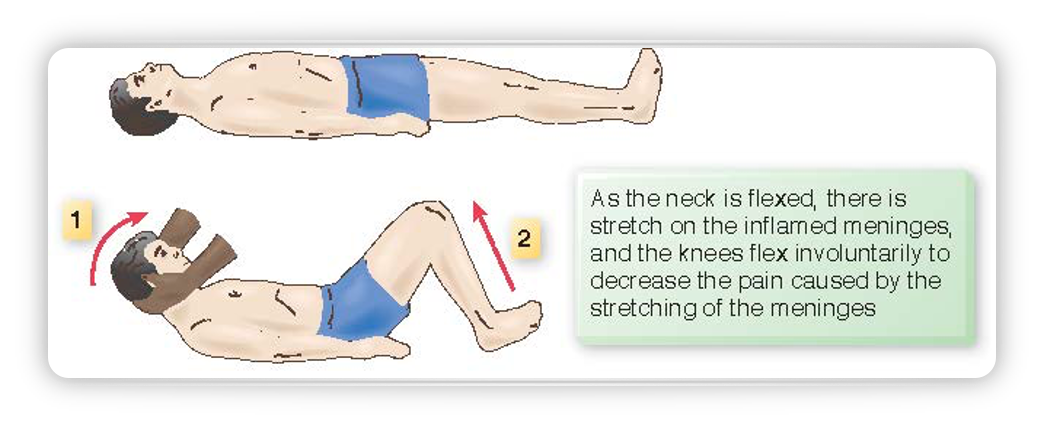
Brudzinski’s sign
as the neck is flexed, there is stretch on the inflamed meninges, and the knees flex involuntarily to decrease the pain caused by the stretching of the meninges
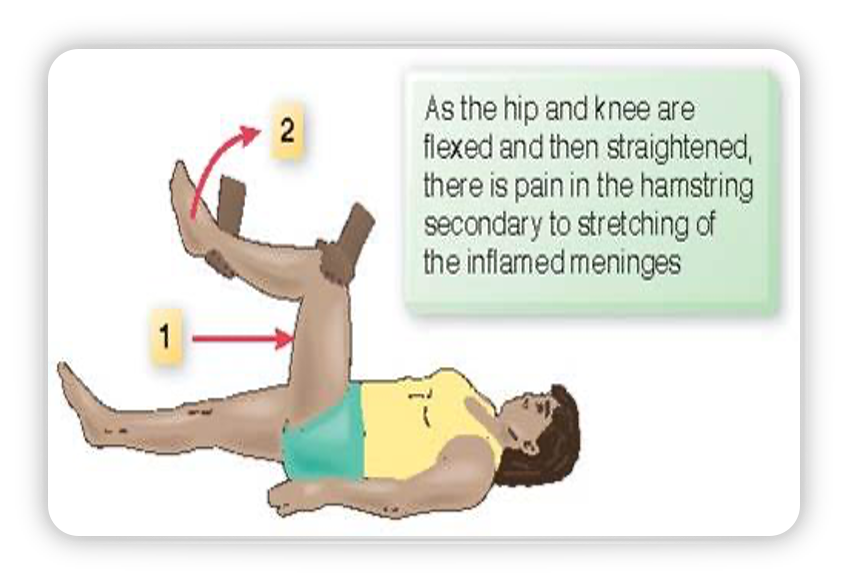
Kernig’s signs
as the hip and knees are flexed and then straightened, there is pain in the hamstring secondary to stretching of the inflamed meninges
Encephalitis
acute inflammation of the brain (in cerebrum, brainstem and cerebellum)
Encephalitis manifestations
fever, neurological deficits, headache, photophobia/phonphobia, nuchal rigidity
Encephalitis diagnosis
lab tests (CBC, electrolytes, inflammation markers)
lumbar puncture (CSF evaluation)
EEG
CT scan/MRI
Encephalitis medications
Antivirals
Acyclovir and Ganciclovir
Encephalitis nursing actions
elevate bed 30-45 degrees to facilitate venous drainage and minimize ICP
Parkinson’s disease
loss of dopamine-producing Bain cells.
decrease dopamine in the brain→ uninhibited acetylcholine → decreased movement, resting tremors
Parkinson’s disease manifestations
resting tremors, muscle rigidity, stooped posture, slowness
Parkinson’s disease medications
Dopamine-receptor agonists: Carbidopa-Levodopa (sinemet)*
Anticholinergics: reduce tremor and drooling
Parkinson’s disease diagnosis
temors, rigidity, bradykineasia
Gag and swallow
Mobility
Bowel and bladder function
Alzheimer’s disease
forgetfulness, loss in the ability to complete tasks
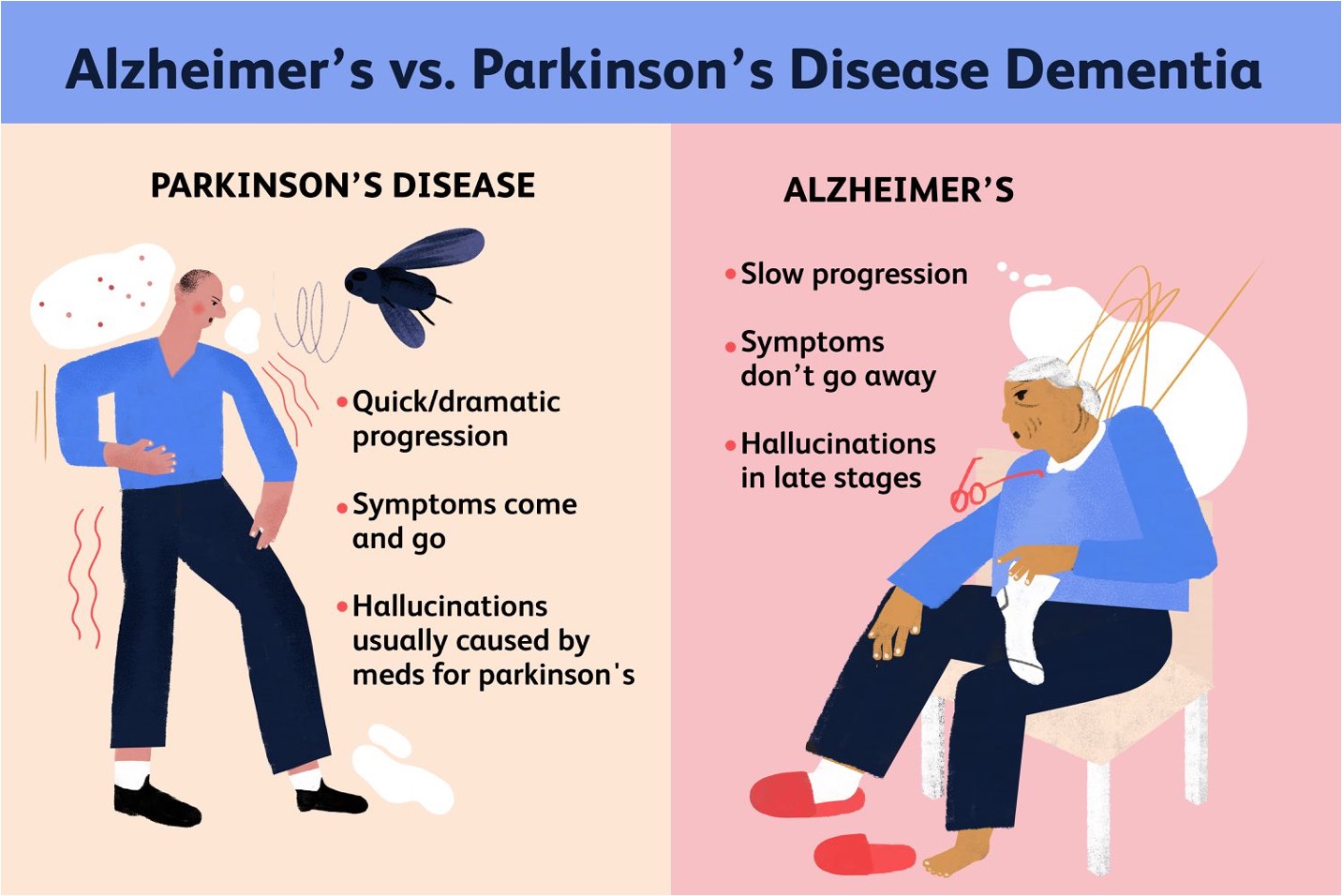
Alzheimer’s disease vs Parkinson’s disease dementia
Monroe-kellie doctrine
the sum of the volumes of brain, CSF, and intracranial blood is constant, so an increase in one should cause a decrease in one, or both, of the remaining two
stroke risk factors
hypertension, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, drug use, older than 55
Ischemic stroke
sudden blockage of cerebral blood vessel. reduce blood supply
left middle cerebral artery syndrome
weakness of the right face, arm, leg
decreased sensation on the right side of the body
right homonymous hemianopia (loss of vision in right temporal field)
Dysphasia (Broca’s vs Wernicke’s)
Broca’s (expressive) aphasia
difficulty expressing thoughts and to make errors in speech that they cannot detect
Wernicke’s (receptive) aphasia
inability to process speech input in the brain, causing errors in speech that patient is unaware of
Right Middle cerebral artery syndrome
weakness of the left face, arm, and leg
decrease sensation of left side
left homonymous hemianopia (loss of vision in left temporal field)
Basilar artery syndrome
dizziness
ataxia
tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
nausea/ vommiting
weakness on one side
Ischemic stroke diagnosis
ct scan, MRI, Carotid duplex, Echocardiogram, laboratory tests
Ischemic stroke medications
recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA)