Session 2: Energy Production from Carbohydrates
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is stage three of the process of catabolism of carbohydrates?
The TCA cycle
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
matrix of mitochondria
What is stage four of catabolism of carbohydrates?
Oxidative phosphorylation
What is starch an example of?
A polysaccharide
What is glycogen?
A polysaccharide - major store of glucose in mammals
Where is glycogen stored?
In the liver
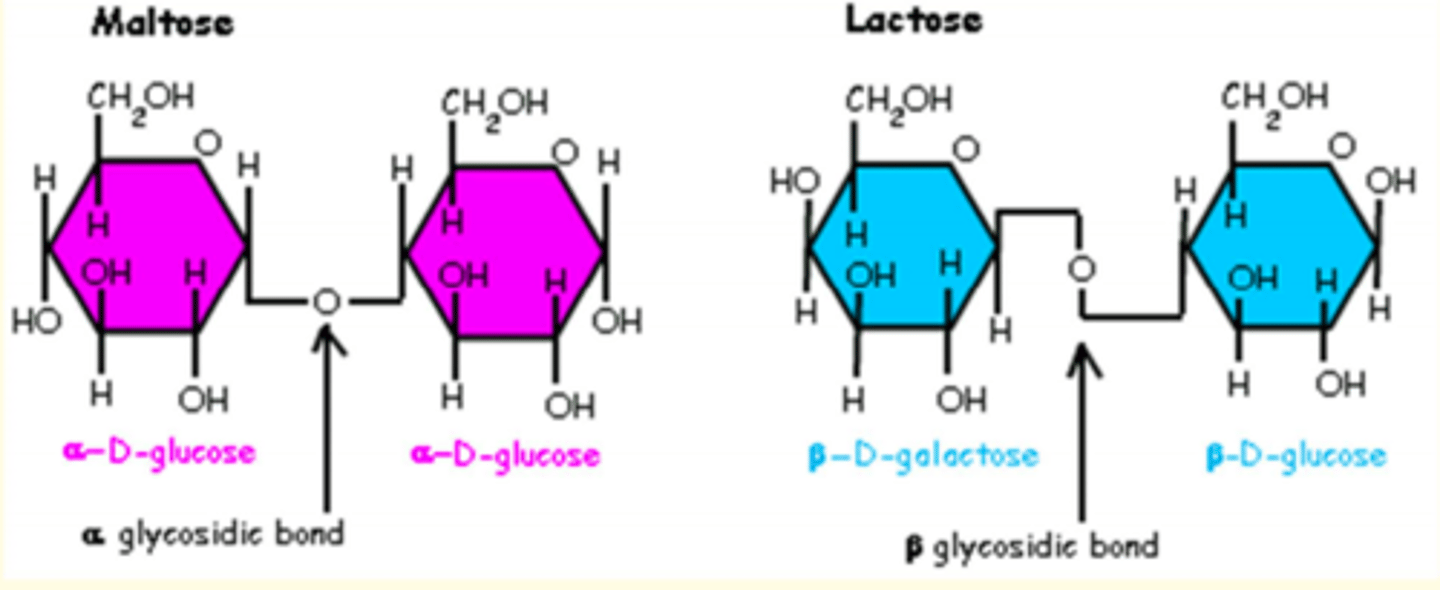
List common disaccharides and their monosaccharide components
Lactose = galactose & glucose
Sucrose = fructose & glucose
Maltose = glucose & glucose
List common monosaccharides
Fructose, glucose, galactose
Give an example of an oligosaccharide made up of glucose monomers (3-10 monosaccharides)
Dextrins
What is the name of the more thermodynamically stable structure of glucose?
Hawthorne projection (ring structures)
List examples of common polysaccharides
Glycogen, starch, cellulose (polymers of glucose)
In the polymerisation of monosaccharides - what is the name of the bond that forms between monosaccharides?
Glycosidic bonds
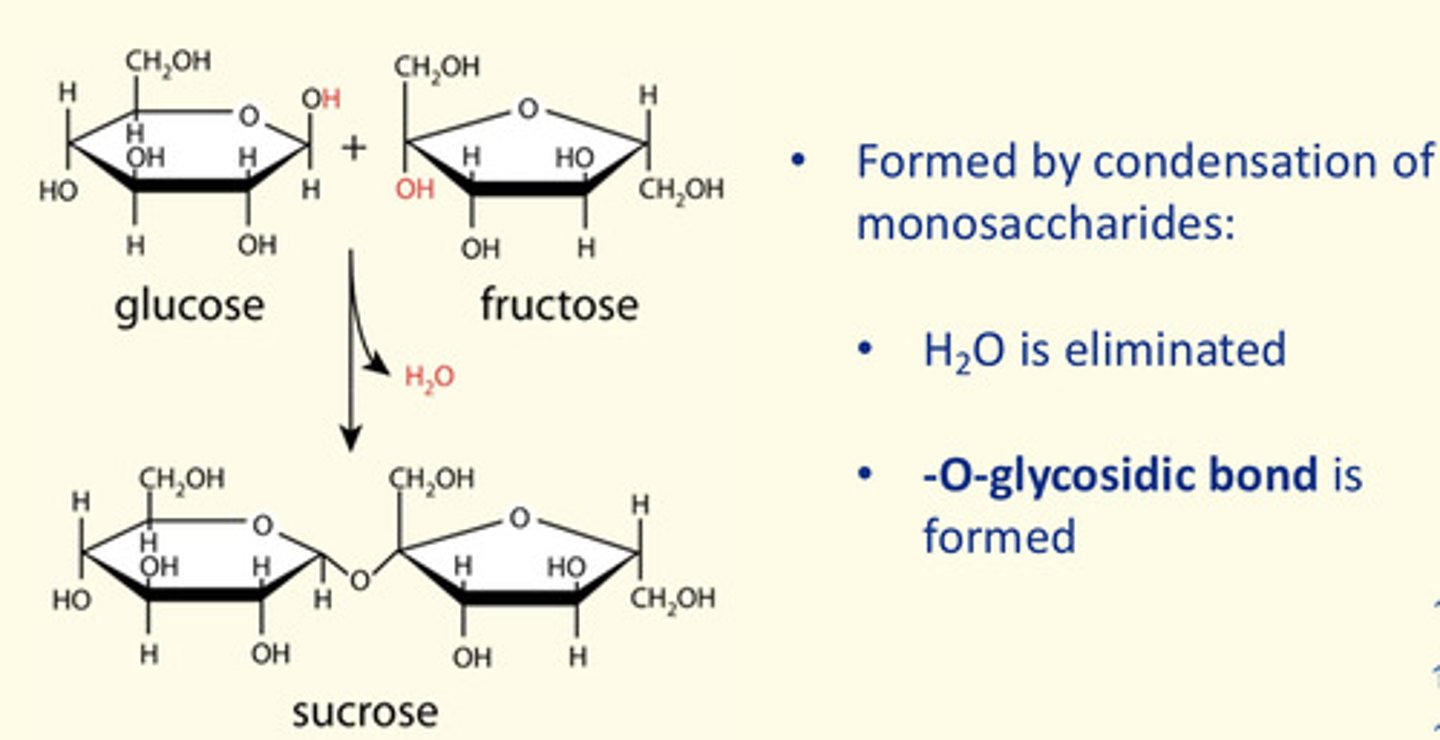
What is an example of a highly branched polysaccharide of glucose?
Glycogen is highly branched
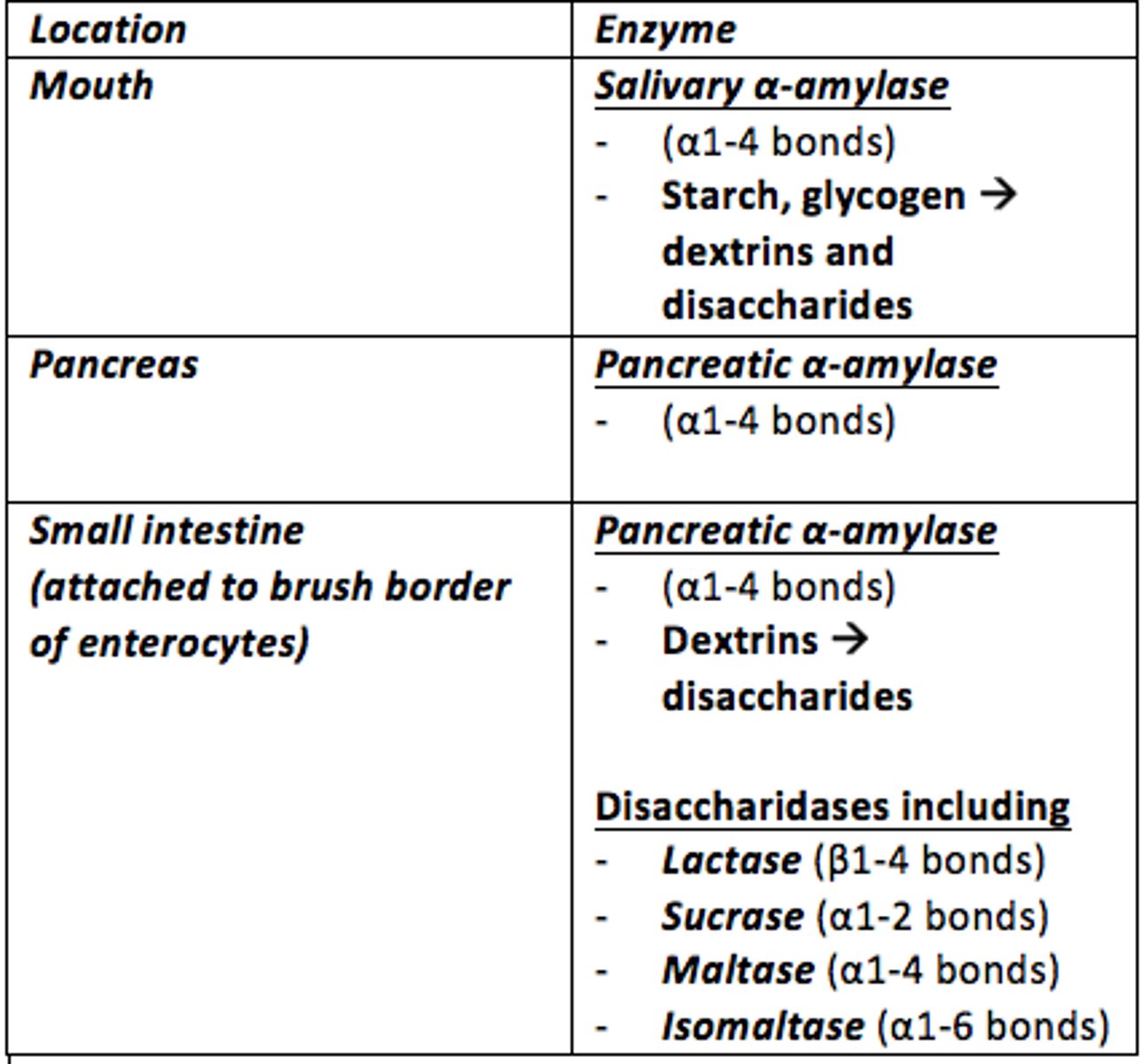
What is one example of an enzyme secreted in the mouth in the digestion of carbohydrates?
Salivary alpha-amylase
Starch/glycogen —> dextrins/disaccharides
What are some enzymes in the small intestine which assist in the digestion of carbohydrates
Disaccharidases - attached to brush border of epithelial cells (enterocytes)
- Lactase
- Sucrase
- Maltase
- Isomaltase
What is isomaltase
An isomer of maltose
What is the name of the adaptation of epithelial cells in the small intestine which facilitates absorption of nutrients?
Microvilli (brush border) - apical membrane extensions of epithelial cells
How are glucose, galactose and fructose transported to enterocytes (epithelial cells)?
By facilitated or active transport
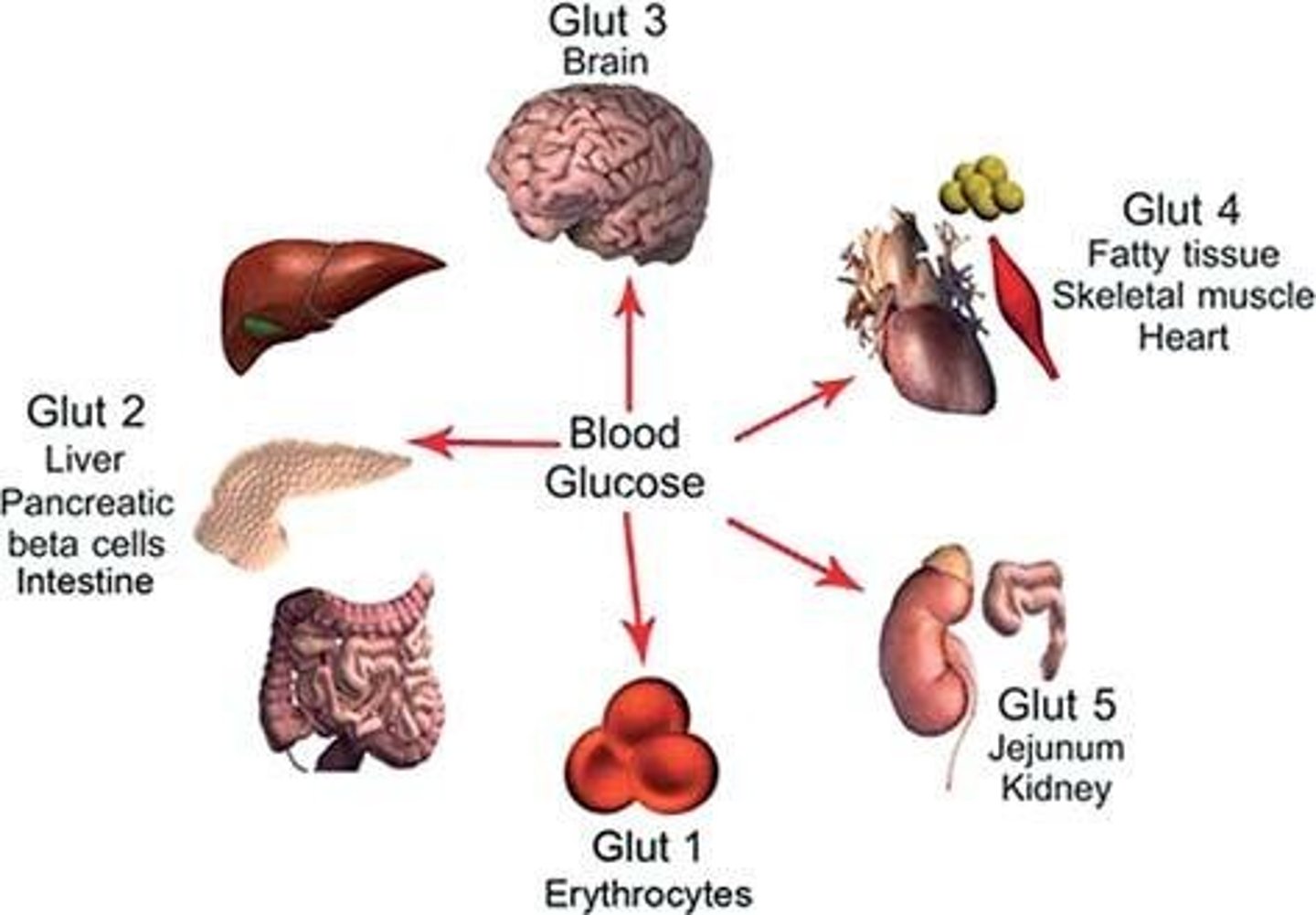
What is the role of GLUT2 (glucose transporter type 2)
Monosaccharides transported from enterocytes into the bloodstream by GLUT2
What is the role of GLUT1-14
Glucose transporters which transport monosaccharides to the target tissues
What is the cause of lactose intolerance?
Loss of reduction of lactase activity = lactose is not hydrolysed to glucose and galactose
What are the symptoms of lactose intolerance?
Diarrhoea, abdominal cramps, bloating, abdominal pain, nausea (appearing 30-120 minutes post-consumption)
How is lactose intolerance diagnosed?
Positive hydrogen breath test, positive stool acidity test
How do you manage lactose intolerance?
Decrease or eliminate amount of lactose (lactose free-diet), consumption of lactase-treated foods or lactase supplementation
What are the glucose requirements of tissues needed per day in grams
Around 180g of glucose is needed per day
Which tissues have an absolute requirement for glucose? How much glucose per day in grams?
RBC, WBC, kidney medulla, testes, lens and cornea of eye
- Around 40g/day
Approximately how much does glucose does CNS (prefer) everyday?
CNS prefers glucose as a fuel (~140g/day)
What is the name of stage two in catabolism of carbohydrates?
Glycolysis
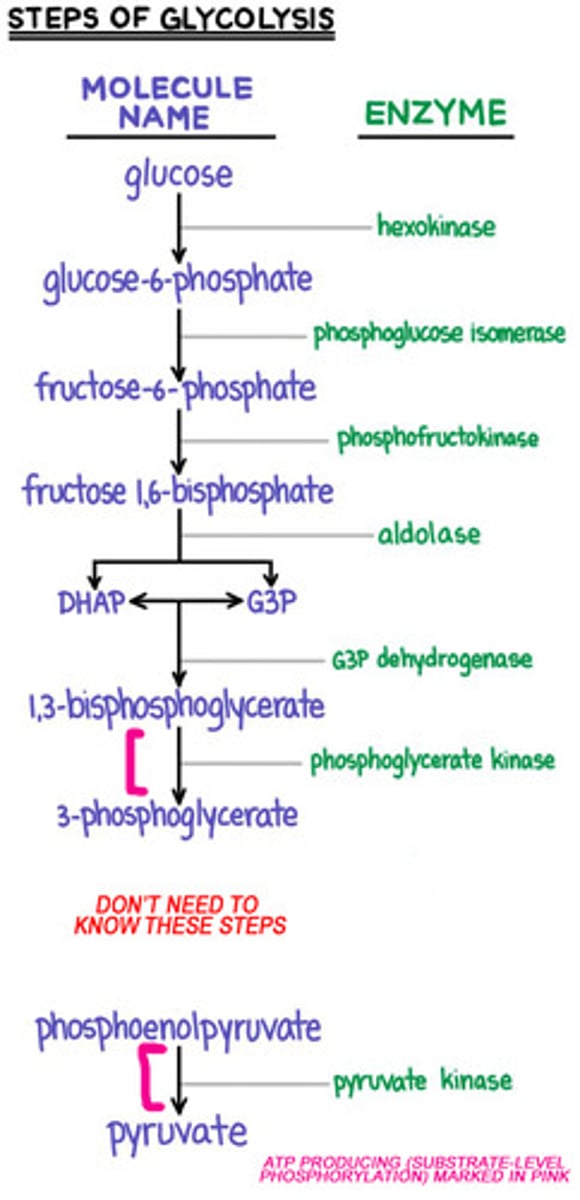
What is the product of glycolysis?
Pyruvate
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytosol of the cell (of all tissues)
What is the only catabolic pathway that can operate anaerobically?
Glycolysis
Is glycolysis an endergonic or exergonic pathway?
Glycolysis is a catabolic process - it is exergonic (releases energy and ATP)
What is the name given to aldehyde-containing sugars? Give an example
Aldoses e.g. glucose, galactose
What is the name given to keto-containing sugars? Give an example
Ketones e.g. fructose
Are carbohydrates hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Simple carbohydrates are small POLAR molecules - contain many (-OH) groups which makes them hydrophilic
Which is the naturally occurring form of stereoisomers?
D-isomers
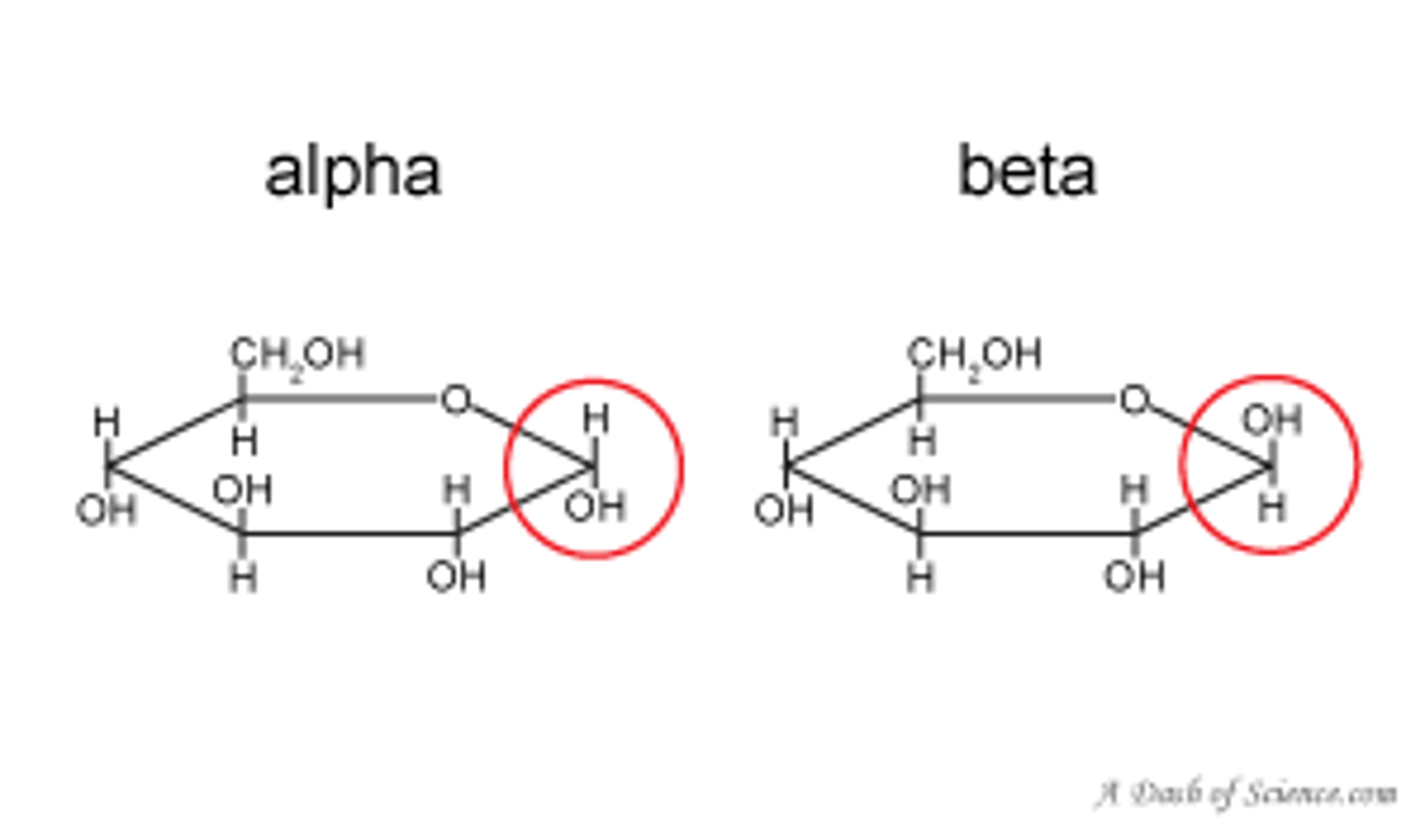
The position of the ______ group on carbon-__ determines whether D-glucose has alpha or beta structure
The position of the OH group on carbon-1 determines whether D-glucose has alpha or beta structure
Roughly how many monosaccharides do oligosaccharides contain e.g., dextrins
3-10 monosaccharides
Roughly how many monosaccharides do polysaccharides contain?
10-1000 monosaccharides
What is Dextrin an example of?
A glucose oligosaccharide
How many (NET) ATP molecules are produced per glucose in glycolysis
2 ATP
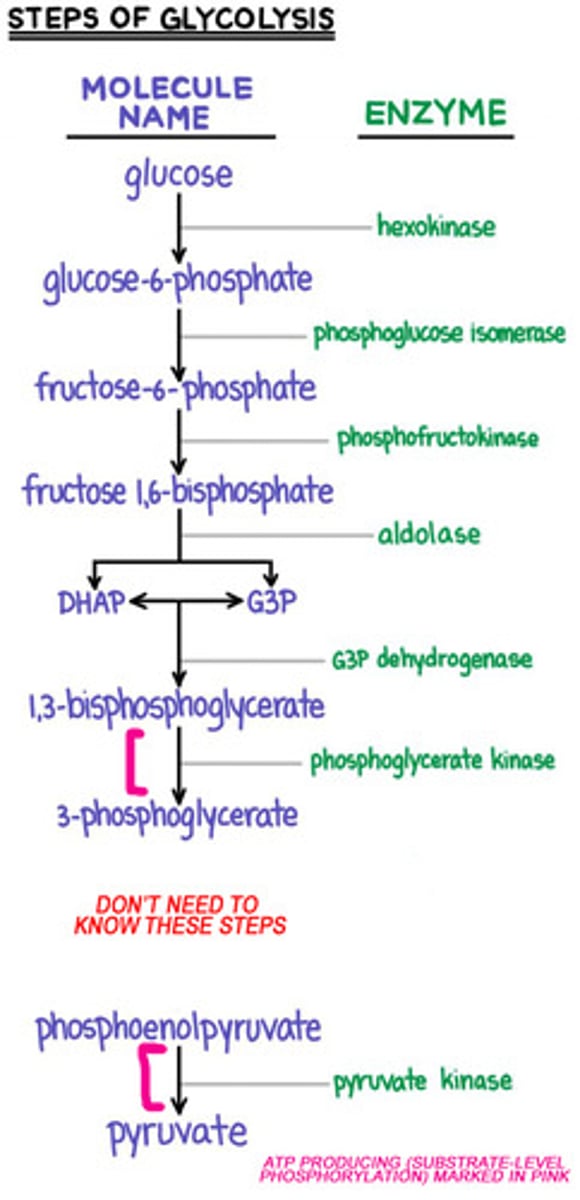
Is glycolysis an exergonic or endergonic reaction
Glycolysis is an exergonic reaction
Glycolysis is the only catabolic pathway that can also operate in the absence of _______
Glycolysis if the only catabolic pathway that can also operate in the absence of oxygen
Is glycolysis an oxidative or reductive reaction?
Glycolysis is oxidative
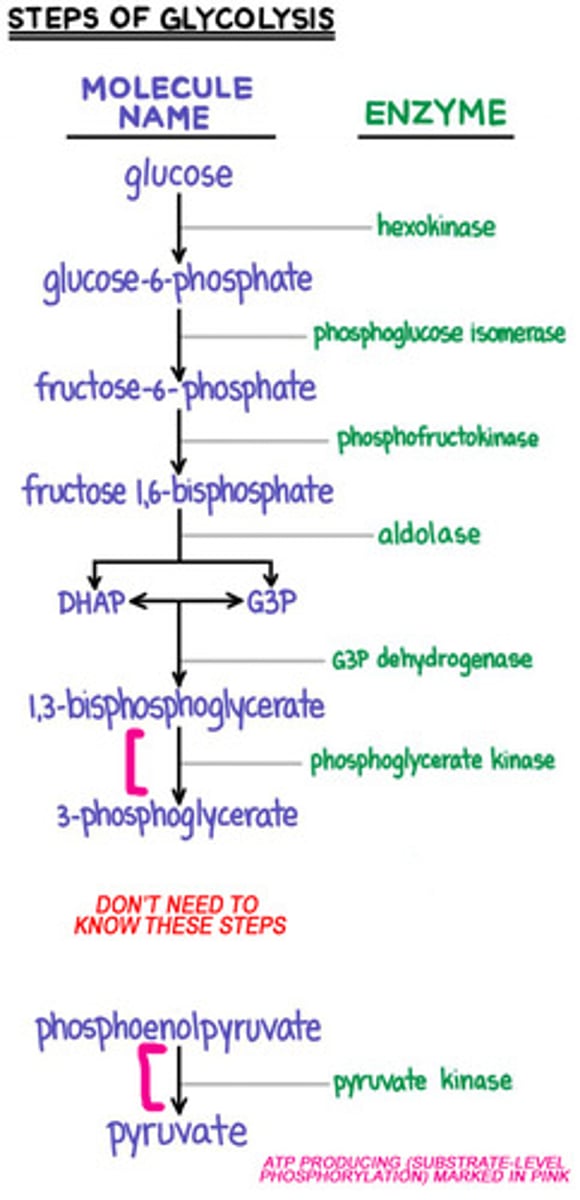
What enzyme catalyses the phosphorylation of glucose in glycolysis to G-6-P?
Hexokinase enzyme
What are the major dietary monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Name the dietary macronutrient which should provide you with the most energy
Lipids
Which polysaccharide cannot be digested in the human body?
Cellulose
β 1-4 linkages cannot be hydrolysed
Which are the three key fuel molecules that undergo oxidation during catabolism?
Fatty acids, glucose and amino acids
The end-product of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions
Lactate
Name the facilitated transporter that transports monosaccharides from enterocytes to the blood
GLUT2
Name the insulin-responsive glucose transporter that occurs in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue
GLUT4
Which cells/tissues have an absolute requirements for glucose as a fuel?
Testes, lens/cornea, kidney medulla, red and white blood cells
What is the net synthesis of ATP from one mole of glucose?
2
Which polysaccharide is highly branched and allows for an efficient way of storing glucose in a small space?
Glycogen
Glycolysis is the only catabolic pathway that can occur in the absence of ______.
Glycolysis is the only catabolic pathway that can occur in the absence of oxygen.
Which of the following metabolic intermediates in glycolysis gives rise to glycerol 3 phosphate?
- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- Glucose 6 phosphate
- 3 phosphoglycerate
- 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
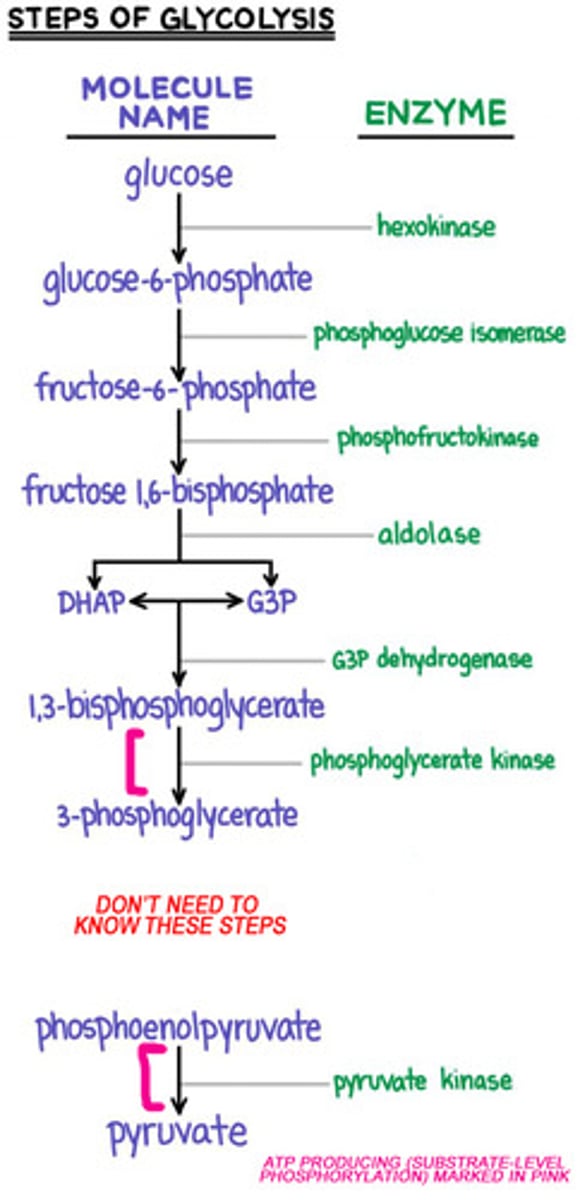
Which of the following control enzymes in glycolysis is activated by insulin through dephosphorylation?
Pyruvate kinase
Name the key enzyme in anaerobic glycolysis?
Lactate dehydrogenase
Where is lactate metabolised?
In the liver, heart and kidney
Name the enzyme of which deficiency causes fructose intolerance
Aldolase
GLUTs
Stage one of carbohydrate metabolism occurs extracellularly (GI tract)
Describe some of the major enzymes involved in this process...
Difference between α- and β-glycosidic bonds
α - H is up
β - H is low
Starch is made up what?
Amylose α1‐4 glycosidic bonds
Amylopectin α1‐6 glycosidic bonds
Genetic cause of lactase deficiency
Lactase activity is high in infants but decreases in childhood in most populations (especially African and Asian)
Nongenetic cause of lactase deficiency
Injury to the small intestine (e.g. inflammatory bowel disease, surgery, infection)
Consequences of lactose intolerance
- Undigested lactose is passed to the large intestine
- Colonic bacteria ferment lactose and produce organic acids and gases
- Lactose and organic acids increase osmotic pressure and draw in water causing = diarrhoea
- Gases cause abdominal cramps and bloating
Blood glucose is regulated at what level in the blood?
~5 mM