L4 - Eukaryotes
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells. How? (3)
Usually bigger, more complex, more organelles
How is DNA packaged in eukaryotic cells?
Into linear chromosomes & kept in double membrane bound nucleus
Eukaryotc cells have membrane-bound organelles including?
Mitochondria (most eukaryotic microorganisms), and sometimes both mitochondria & chloroplasts (e.g. algae)
Secretory pathways/ What are they made up of? (2)p
Series of multiple organelles that directs newly made proteins to their new destinations.
endoplasmic reticulum (ER; rough & smooth)
golgi apparatus
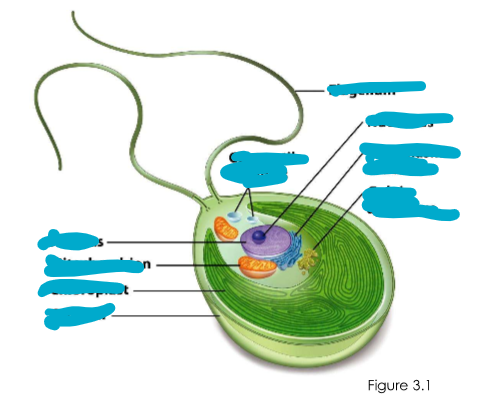
Morphology of typical eukaryotes
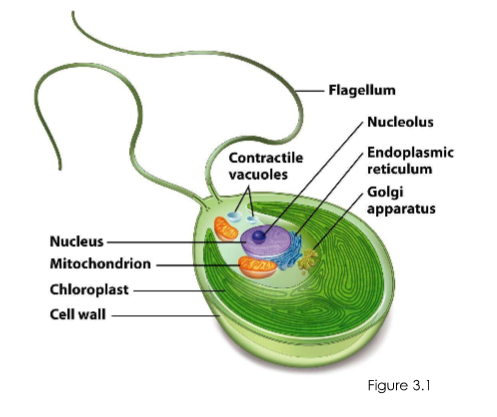
Morphology of typical eukaryotes (4)
membrane bound nucleus
larger than bacterial or archaeal cells
contain organelles
possess a cell wall & complex internal cytoskeleton
Internal organelles of eukarya (9)
Nucleus
mitochondrion
chloroplast
rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Golgi apparatus
vacuole
lysosome
peroxisome
hydrogenosome
Internal organelles of eukarya - nucleus function
Contains most of cell’s DNA, site of transcription
Internal organelles of eukarya - nucleus interesting features (2)
double membrane containing pores
outer membrane continuous w/ endoplasmic reticulum
Internal organelles of eukarya - mitochondrion function
energy production
Internal organelles of eukarya - mitochondrion interesting features (4)
double membrane
contains DNA
Independent replication
not present in amitochondriates
Internal organelles of eukarya - chloroplast function
photosynthesis
Internal organelles of eukarya - mitochondrion interesting features (4)
Double membrane
contains DNA
Independent replication
unique to photosynthetic organisms
Internal organelles of eukarya - Rough endoplsamic reticulum (ER) function
Site of translation & protein folding
Internal organelles of eukarya - Rough endoplsamic reticulum (ER) interesting features
Rough ER has protein-synthesizing ribosomes attached to it
Internal organelles of eukarya - golgi apparatus main function
Modifies, sorts, and transports proteins
Internal organelles of eukarya - golgi apparatus interesting features
Connected to ER thru a series of vesicles
Internal organelles of eukarya - vacuole main function
Storage & structure
Internal organelles of eukarya - vacuole interesting features (2)
Food vacuoles serve as sites of digestion
Contractile vacuoles help maintain water balance
Internal organelles of eukarya - lysosome main function
Digestion of macromolecules
Internal organelles of eukarya - lysosome interesting features
Contains digestive enzymes
Internal organelles of eukarya - peroxisome main function
Breakdown of fatty acids
Internal organelles of eukarya - peroxisome interesting features
Contains various oxidative enzymes, like catalase and oxidase
Internal organelles of eukarya - hydrogenosome main function
Production of H2 & ATP
Internal organelles of eukarya - hydrogenosome interesting features (3)
double membrane
found in some amitochondriates
may be remnant of mitochondrion
Nucleus
what does it do?
what kind of structure?
contains…?
what exists within nucleus?
Plays a role in the storage & expression of info.
Double membrane structure.
Contains linear chromosomes of cell
Non-membrane bound nucleus exists within nucleus (ribosome synthesis)
In the nucleus, there is ___ separation. Discuss (2)
Spatial
transcription occurs in nucleus
translation occurs in cytoplasm
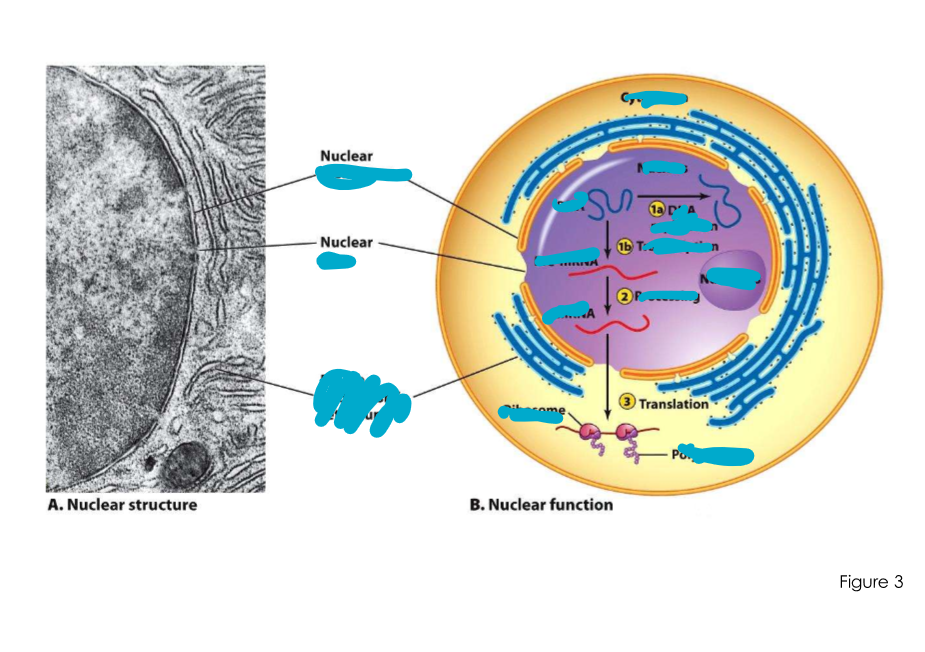
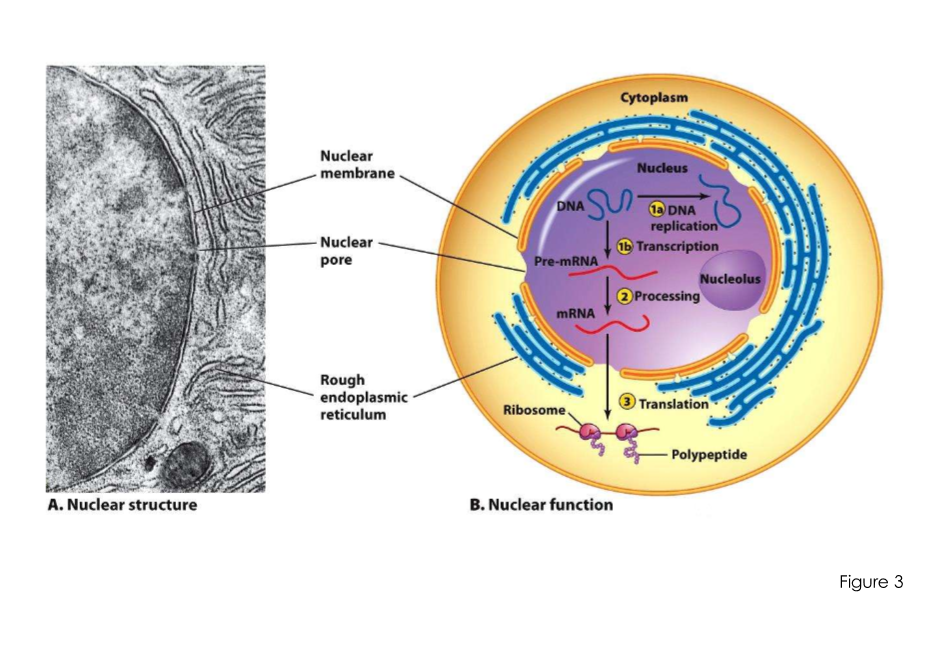
Secretory pathway
what does it use?
what happens to proteins here?
Uses ER/Golgi apparatus. Proteins are often extensively modified in these structures prior to reaching their destinations
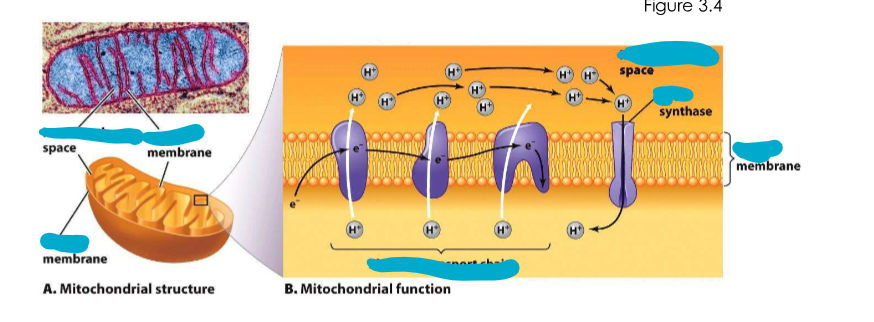
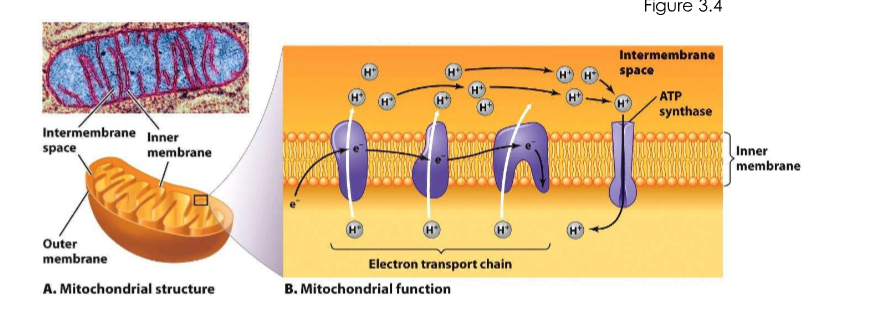
Mitochondria
what does it do?
what does it use to produce ___?
Play a role in cell metabolism - TCA cycle. Use electron transport chains to produce ATP (chemiosmosis via the proton motive force).
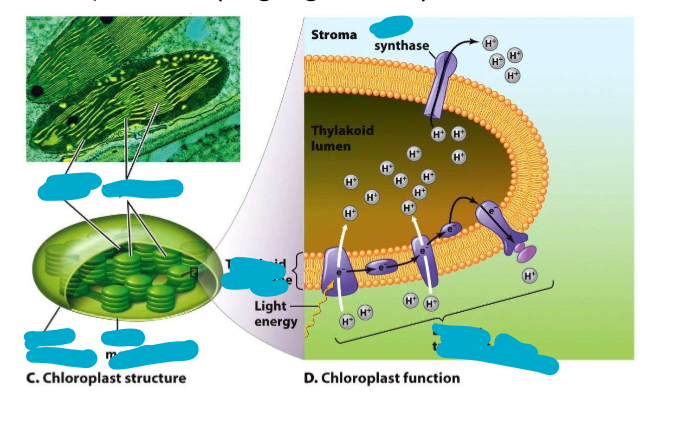
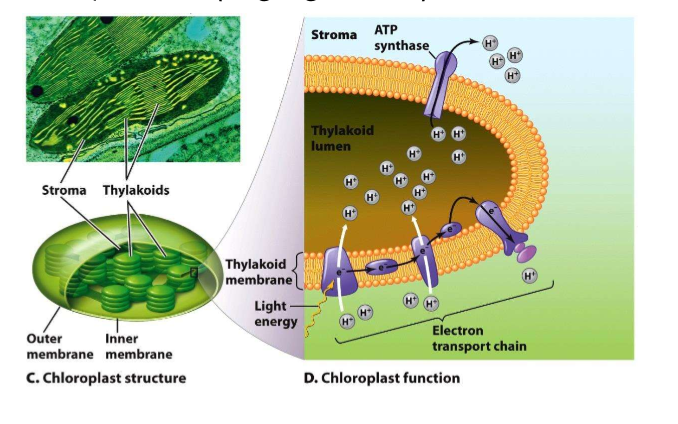
Chloroplasts
what do they do?
what do they leverage
What do they do with ATP?
Play a role in cell metabolism
leverage electron transport chains to produce ATP (chemiosmosis via proton motive force)
Use ATP they produce to fix carbon into organic compounds (e.g., glucose)
Both mitochondria & chloroplasts are ____?
Semi-autonomous
Both mitochondria & chloroplasts are semi-autonomous.
what do they each have?
can they replicate?
where do most of their proteins come from?
each has a DNA genome, ribosomes, and transcription machinery
can replicate independently of the rest of the cell
most of their proteins originate from the DNA in the nucleus of the cell.
Plasma membrane - layer
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that allow molecule transport. Facilitated diffusion (no energy required from cell). Active transport (cell expends energy)
Plasma membrane plays a role in?
Homeostasis - maintaining a constant internal environment
Plasma membrane characteristics (4)
membrane structure
lipid structure
sterols
proteins
Plasma membrane characteristic - membrane structure
function (3)
membrane assembly
hydrophilic surface
hydrophobic core
Plasma membrane characteristic - lipid structure
function
Membrane fluidity
Plasma membrane characteristic - strerols
function
membrane stability
Plasma membrane characteristic - proteins
function
structural
Plasma membrane characteristic - membrane structure
bacteria
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane characteristic - membrane structure
archaeons
bilayer or monolayer
diverse lipid composition (sulfo, glyco, isoprenoid)
Plasma membrane characteristic - membrane structure
eukarya
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane characteristic - lipid structure
bacteria
ester linkage
straight fatty acid chains
Plasma membrane characteristic - lipid structure
archaeons
ether linkage
branched isoprenoid chains
Plasma membrane characteristic - lipid structure
eukarya
ester linkage
straight fatty acid chains
Plasma membrane characteristic - sterols
bacteria
No
Plasma membrane characteristic - sterols
archaeons
No
Plasma membrane characteristic - sterols
eukarya
yes
Plasma membrane characteristic - proteins
eukarya
low abundance
Plasma membrane characteristic - sterols
archaeons
high abundance
Plasma membrane characteristic - sterols
bacteria
high abundance
Cell wall
Plays a role in cell support. Broad separation btwn those w/ & those w/o cell walls. Vary widely btwn domains
Cytoskeleton
Role in cell structure. Each major piece differs in structure/fxn; all contribute to cell shape.
Cytoskeleton is compromised of ___ major pieces. What are they?
3
microtubules (tubulin)
microfilaments (actin)
intermediate filaments (various proteins)
Cytoskeleton is also involved in ____, ___, and ____. Can be observed via ?
Cytoskeleton is also involved in intracellular trafficking, motion, and cell division. Can be observed via fluorescent microscopy
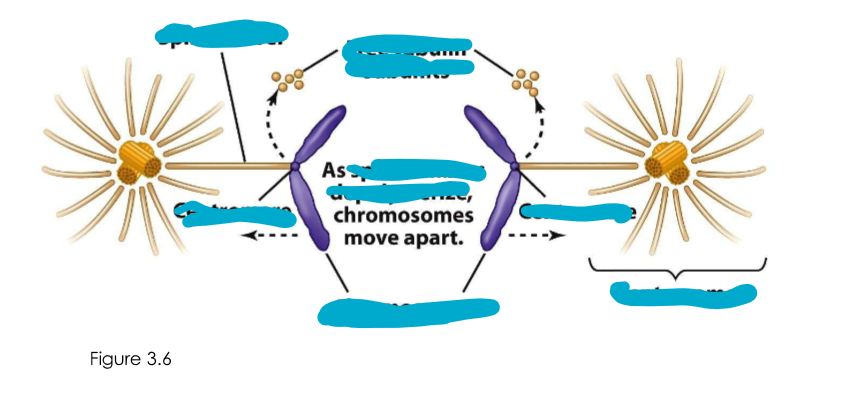
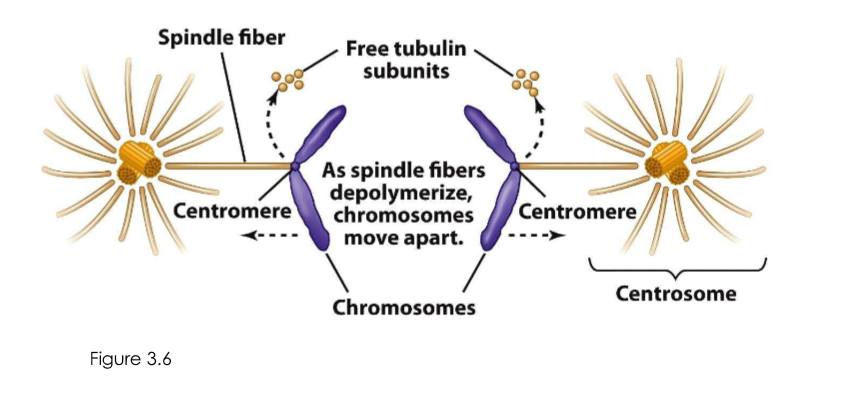
Cell division is assisted by?
Spindle fibers
Motion of eukarya is achieved by?
Cilia/flagella. Very different structure than for bacteria or archaea.
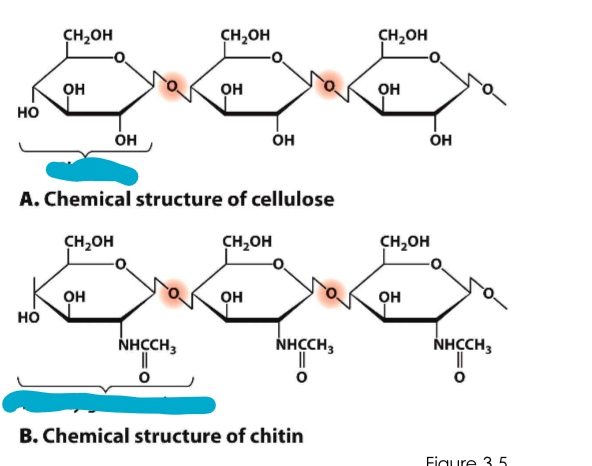
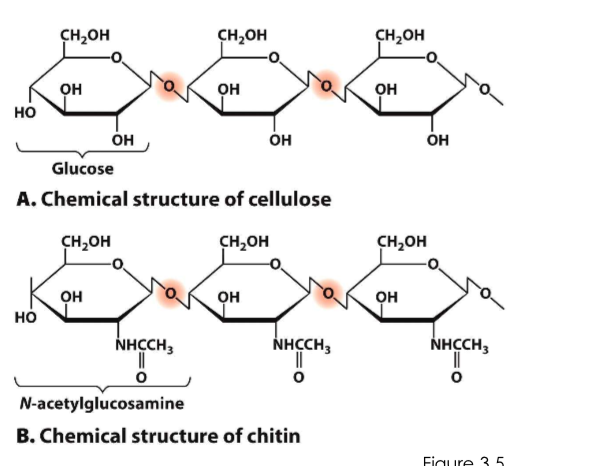
Cellulose and chitin
use…?
provides?
specific b-1,4-glycosidic bonds btwn sugars
provides strength & rigidity
How many microtube doublets are there? What do they form?
9, form a tube around a core pair of microtubules (axoneme)
When does motion occur? (microtubules)
When ATP is burned, helping microtubules in the axoneme slide past each other.
What can pathogens do here? E.g. (2)
Exploit cytoskeleton. E.g., HSV, listeria
Basic structural components for bacteria - gram-positive (2)
thick peptidoglycan layer (~40nm) compromises 40-80% of cell wall dry weight
surface of peptidoglycan layer decorated by teichoic acid.
Basic structural components for bacteria - gram-negative (2)
thin peptidoglycan layer (~2nm) compromises 5% of cell wall dry weight
Outer membrane has phospholipid inner leaflet & lipopolysaccharide outer leaflet
Basic structural components for archaea
Varied
Basic structural components for archaea - methanogens
glycopeptides or pseudopeptidoglycan
Basic structural components for archaea - Halogens & hyperthermophilic
glycopeptides
Basic structural components for eukarya - fungi
chitin
Basic structural components for eukarya - algae
cellulose
Basic structural components for eukarya - protozoa
none
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya (3)
Microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
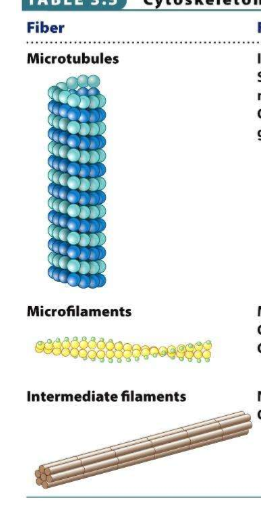
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microtubules
functions (3)
intracellular transport
separation of chromosomes in mitosis & meiosis
cell movement (e.g., cillia & flagella)
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microtubules
structure (2)
25 nm
13 protofilaments that form a hollow tube
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microtubules
building blocks
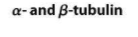
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microtubules
motors (2)
Dyneins, kinesns
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microfilaments
motors
myosins
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microfilaments
building blocks
actin
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microfilaments
structure (2)
7nm diameter
2 protofilaments twisted around each other in helix
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - microfilaments
functions (3)
maintain cell shape
cerate division furrow in cytokinesis
cell movement (e.g., pseudopods)
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - intermediate filaments
building blocks
varied: lamin, keratin, vimentin
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - intermediate filaments
motors
none
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - intermediate filaments
structure
8-11 nm diameter
Cytoskeleton structure & proteins in eukarya - intermediate filaments
functions (2)
nuclear structure, cell-cell interactions
Flagella structure in bacteria (3)
nonflexible hollow helical filament
extends outside of cell membrane & cell wall
composed of flagellin subunits
Flagella assembly in bacteria (2)
at distal tip
flagellin monomers are transported out inside of hollow flagella
Flagella arrangement in bacteria (2)
polar (1 or multiple)
peritrichous (multiple)
Flagella motion in bacteria (2)
motor in membrane turns flagella in a screw-like motion
energy from a proton motive force
Flagella structure in eukarya (3)
flexible
covered by cell membrane
composed of a 9+2 array of microtubules termed the axoneme
Flagella assembly in eukarya (2)
at distal tip
microtubule segments are transported out along the outside of the axoneme via intraflagellar transport system
Flagella arrangement in eukarya
varies by cell type
Flagella motion in eukarya (2)
fynein spokes slide microtubules along each other within axoneme. This bends axoneme & gives a whip-like motion to flagella
energy from hydrolysis of ATP
2 organelles that help with cellular metabolism?
mitochondria, chloroplasts
Mitochondria & chloroplasts contain what to generate ____ through ___ thanks to?
internal membranes, ATP, chemiosmosis, proton motive force
Main structural categories in eukaryotic protein-filament cytoskeletons (3)
microtubules (tubulin)
microfilaments (actin)
intermediate filaments (different proteins)
Phylogeny of eukaryotic microorganisms is typically determined by?
Comparing small subunit (SSU) rRNA genes & other highly conserve genetic sequences
4 general categories of eukaryotic microorganisms
fungi
protozoa (“protists”)
slime moulds
algae
Fungi
Heterotrophic microorganisms with chitin-based cell walls.
Example of fungi, incl scientific name
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast)