AP PSYCH UNIT 6 - Development
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Last updated 11:13 PM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
Developmental Psychology
Changes (physical, cognitive, social, emotional) across the lifespan.
2
New cards
The Prenatal Development (pre-birth)
1. Germinal Stage (conception → 2 weeks)
2. Embryonic Stage (2 → 8 weeks)
3. Fetal Stage (9 weeks → birth)
3
New cards
Germinal Stage
(conception → 2 weeks)
* Zygote
* DNA is assembled
* Zygote
* DNA is assembled
4
New cards
Embryonic Stage
(2 → 8 weeks)
* Embryo
* Organ __development__ & cells __differentiate__ into different functions (e.g. eyes, ears, etc.)
** highest risk of miscarriage.*
* Embryo
* Organ __development__ & cells __differentiate__ into different functions (e.g. eyes, ears, etc.)
** highest risk of miscarriage.*
5
New cards
Fetal Stage
(9 weeks → birth)
* Fetus
* Organs continue to grow/function more efficiently
* Can kick, make a fist, etc.
* Fetus
* Organs continue to grow/function more efficiently
* Can kick, make a fist, etc.
6
New cards
Critical Period
A __sensitive__ __time__ period when certain developmental __milestones__ need to occur.
*ex~* __*Prenatal development = Embryonic stage*__
*ex~* __*Prenatal development = Embryonic stage*__
7
New cards
Placenta
Provides __nutrients__ to the baby.
8
New cards
Teratogens
__Harmful__ substances that can cause birth __defects__.
9
New cards
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
…
10
New cards
Motor Development
Muscle development & coordination
11
New cards
Cephalocaudal trend
Development that occurs form __head to toe__.
12
New cards
Proximodistal trend:
Development occurs from __center to outward__.
\
*ex~ muscular control of the arms relative to the hands and fingers. (trying to pick up food)*
\
*ex~ muscular control of the arms relative to the hands and fingers. (trying to pick up food)*
13
New cards
Maturation
__Genetically__ predetermined __sequence__ of development (natural viewpoint).
\
*ex~ like if the parent always gets/does stuff for the baby too much w/o giving the baby independance, they will be used to it & may develop later.*
\
*ex~ like if the parent always gets/does stuff for the baby too much w/o giving the baby independance, they will be used to it & may develop later.*
14
New cards
Understanding Developmental Norms
__Age ranges__ where “__typical__” behaviors & abilities develop.
15
New cards
Reflexes *(involuntary movements)*
* As motor development progresses, reflexes disappear
* Rooting = baby turns face towards cheek being touched
* Moro = baby sprawls out when they feel like they are falling
* Babinski = fanning of feet when tickled
* Rooting = baby turns face towards cheek being touched
* Moro = baby sprawls out when they feel like they are falling
* Babinski = fanning of feet when tickled
16
New cards
Newborn Senses
* Vision = __worst__ sense; prefer __larger__ objects, objects with __contrast__, prefer human __faces__
* Hearing = prefer __high-pitched__, exaggerated, __expressive__ human voices
* Taste = prefer __sweet__-tasting things
* Smell = prefer smell of own mother's breast milk
* Hearing = prefer __high-pitched__, exaggerated, __expressive__ human voices
* Taste = prefer __sweet__-tasting things
* Smell = prefer smell of own mother's breast milk
17
New cards
__Long__itudinal Design
__One group__ of participants studied over a __long period of time__.
\
*ex~ Researchers compare curiosity ratings of a group of toddlers with that* __*same group’*__*s scores 15 years later.*
\
*ex~ Researchers compare curiosity ratings of a group of toddlers with that* __*same group’*__*s scores 15 years later.*
18
New cards
Cross-sectional Design
__Different age groups__ tested at __one time__ *(could be a consistent, short window of time).*
\
*ex~ same survey to 9th graders, 10th graders, etc. and ask how they liked their experience. Looking at different age groups and seeing how they experience things differently. Freshman experience v senior experience.*
\
*ex~ same survey to 9th graders, 10th graders, etc. and ask how they liked their experience. Looking at different age groups and seeing how they experience things differently. Freshman experience v senior experience.*
19
New cards
Cohort Effects
Occurs when differences among groups (cohorts) are due to life experiences, historical events, etc. Sometimes referred to a “generational gap”.
\
*ex~ grandparents might hoard more than younger generations now since they experienced the great depression.*
\
*ex~ grandparents might hoard more than younger generations now since they experienced the great depression.*
20
New cards
Cross-sequential Design
Starts with __diff. Age groups__ & then following each group __over a period of time (incremental check-ins)__.
\
*ex~ to study depth perception in newborns & infants, researchers test babies ranging in age from 1month to 15 months* __*once a month*__ *for a total of 10 months.*
\
*ex~ to study depth perception in newborns & infants, researchers test babies ranging in age from 1month to 15 months* __*once a month*__ *for a total of 10 months.*
21
New cards
Temperament: Category Type 1
1. **Easy~**
* Not overly fussy
* Predictable
* Adjusts to new situations well
\
2. **Difficult~**
* More fussy/irritable
* Unpredictable
* Hard time adjusting to new situations
\
3. **Slow-to-warm-up~**
* Start off wary and then adjust well when comfortable.
22
New cards
Temperament: Category 2
1. **Inhibited temperament~**
“Guarded” - shy, timid.
\
2. **Uninhibited temperament~**
Lets guard down easily, open to new experiences.
23
New cards
Attachment
Emotional bond between a child & their caregiver.
24
New cards
Imprinting (on AP exam only)
The process where certain animals form strong attachments during an early-life critical period (research by **Konrad Lorenz** & ducklings) (doesn’t occur w/ humans).
25
New cards
Harlow’s Theory of Attachment
**Finding of Harlow’s research:** there is a biological need for contact comfort (monkeys spent majority of the time w/ the cloth mother).
26
New cards
Separation Anxiety
Feelings of distress that young children may experience when the caregiver leaves.
27
New cards
Patterns of Attachment (definition)
Observed child’s behavior when mom was present, when mom left, when “stranger” enters, & when mom returns (__the “reunion” was the most important__)
1. Secure Attachment\~
2. Anxious-Ambivalent (AKA resistant)\~
3. Anxious-Avoidant\~
4. Anxious-disorganized\~
1. Secure Attachment\~
2. Anxious-Ambivalent (AKA resistant)\~
3. Anxious-Avoidant\~
4. Anxious-disorganized\~
28
New cards
Secure Attachment
Uses mom as a __home base__ while playing; when their mom leaves, the baby is upset, but can calm down easily; when mom returns = happy
29
New cards
Anxious-Ambivalent (AKA resistant)
__Clingy__ to mom; when mom leaves, the baby is __inconsolable__; when mom returns= still __upset__.
30
New cards
Anxious-Avoidant
__minimal__/__no__ __interaction__ w/ mom at any of the 3 stages.
31
New cards
Anxious-Disorganized
__Inconsistent__ behavior throughout the 3 stages.
32
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Trust v. Mistrust
\
\
(Infant)
*Can I trust the world? Are my needs being met?*
*Can I trust the world? Are my needs being met?*
33
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Autonomy v. Shame & Doubt
(toddler)
__Physical independence__; directing own behaviors. *Can I do this myself?*
\
*ex~ potty training. If you punish them for having an accident, they will doubt their abilities.*
__Physical independence__; directing own behaviors. *Can I do this myself?*
\
*ex~ potty training. If you punish them for having an accident, they will doubt their abilities.*
34
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Initiative v. Guilt
(preschool age)
Using imagination; asking lots of questions (__curiosity__); freedom of __choice__; capable of taking on some responsibility. __Creativity__. *Why?*
Using imagination; asking lots of questions (__curiosity__); freedom of __choice__; capable of taking on some responsibility. __Creativity__. *Why?*
35
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Industry v. Inferiority
(elementary school age)
Learning __social__ & academic skills; feeling __competent__ & developing self-__esteem__; making __comparisons__. *How do I compare w/ others?*
Learning __social__ & academic skills; feeling __competent__ & developing self-__esteem__; making __comparisons__. *How do I compare w/ others?*
36
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Identity v. Role Confusion
(adolescence)
Deciding who or what you want to be. (in terms of occupation, beliefs, attitudes, behavioral patterns, etc.) *Who am I?*
Deciding who or what you want to be. (in terms of occupation, beliefs, attitudes, behavioral patterns, etc.) *Who am I?*
37
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Intimacy v. Isolation
(early adulthood)
Searching for committed relationships. *Shall I find another or live alone?*
Searching for committed relationships. *Shall I find another or live alone?*
38
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Generativity v. Stagnation
(middle adulthood)
Being creative, productive, & nurturing of the next generation; giving back. *Am I making an impact on the world?*
Being creative, productive, & nurturing of the next generation; giving back. *Am I making an impact on the world?*
39
New cards
**Erikson’s Stages of** __**Psychosocial**__ **Development:** Integrity v. Despair
(late adulthood)
Wisdom, spiritual tranquility, a sense of wholeness & acceptance. *Have I lived a good life? Do I have any regrets?*
Wisdom, spiritual tranquility, a sense of wholeness & acceptance. *Have I lived a good life? Do I have any regrets?*
40
New cards
Schemas
Mental rep. Of objects, events, etc. created through experience.
41
New cards
Assimilation *“fitting in”*
__adding__ info to __an existing__ schema (“as is”; exactly as we have in the past).
\
*Ex~ babies’ schema of a cup is where they suck on it, so when they see a regular cup, they use it in the same way as using a sippy cup; but it’s not the same so not successful.* \n
\
*Ex~ babies’ schema of a cup is where they suck on it, so when they see a regular cup, they use it in the same way as using a sippy cup; but it’s not the same so not successful.* \n
42
New cards
Accommodation
If new info doesn’t fit, we have to __modify__ an existing schema or __create a new__ schema.
43
New cards
**Sensorimotor Stage (1- 2 yrs)**
Mental activity is confined to sensory & motor functions.
44
New cards
**Sensorimotor Stage:** Object permanence (lacking)
The ability to recognize that objects continue to exist even when they are no longer visible. *(According to Piaget, once child develops this they are no longer in the sensorimotor stage)*
45
New cards
**Preoperational Stage (2-7 yrs) (1st & 2nd halves)**
* First-half (2-4 yrs)\~
\*play pretend imaginative; display animism & egocentrism.
\*begin to represent things w/ words & images (symbolic thinking).
\
* The second half (4-7 yrs)\~
Use intuition (instead of reasoning); ask a lot of “why?” questions; egocentrism & animism begin to lessen.
\*play pretend imaginative; display animism & egocentrism.
\*begin to represent things w/ words & images (symbolic thinking).
\
* The second half (4-7 yrs)\~
Use intuition (instead of reasoning); ask a lot of “why?” questions; egocentrism & animism begin to lessen.
46
New cards
Animism (displayed)
Believing inanimate objects are real & have feelings.
47
New cards
Ecocentrism (displayed)
When a child believes that others see the world as they do (they can’t put themselves in someone else’s shoes).
\
*Ex~ child sees there are m&m’s in a crayon box instead of crayons, but the child still thinks that if her friend came in, that friend would also know there are m&m’s in the crayon box.*
\
*Ex~ child sees there are m&m’s in a crayon box instead of crayons, but the child still thinks that if her friend came in, that friend would also know there are m&m’s in the crayon box.*
48
New cards
**Preoperational Stage:** Theory of Mind (lacking)\~
The ability to understand their own & others’ mental states, & that they may differ; (feelings, perceptions & thoughts & the behaviors these might predict)
49
New cards
**Preoperational Stage:** Conservation (lacking)
The awareness that physical quantities remain the same despite changes in shape/appearance. *(According to Paiget, once children develop conservation they are no longer in the preop stage.)*
\
*Ex~ two glasses of the same amount of juice, however when one was poured into a taller glass, the child thought the tall glass had more juice.*
\
*Ex~ two glasses of the same amount of juice, however when one was poured into a taller glass, the child thought the tall glass had more juice.*
50
New cards
**Preoperational Stage:** Centration (displayed)
The tendency to focus on just one feature of a problem, neglecting other important aspects.
51
New cards
**Preoperational Stage:** Irreversibility (displayed)
The inability to envision reversing an action.
52
New cards
**Concrete Operational Stage (7-11 yrs)~**
\*developed conservation
\* lacked egocentrism & animism
\*can use simple logic (adding/subtracting, can sort, etc.)
\*CANNOT use higher-level through/abstract reasoning.
\* lacked egocentrism & animism
\*can use simple logic (adding/subtracting, can sort, etc.)
\*CANNOT use higher-level through/abstract reasoning.
53
New cards
**Formal Operational Stage (11+ yrs)**
\*Can use higher-level thought
\*Can think abstractly
\*Can use reason to hypothesize.
\*Can think abstractly
\*Can use reason to hypothesize.
54
New cards
Evaluating Piaget’s Theory
\*Stages are not as fixed as he thought; more continuous more like “waves”
\*Timing of stages likely diff.
\*Timing of stages likely diff.
55
New cards
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory of Cognitive Development
\
*Social interaction/culture/language development influences* cognitive development.
\*Children benefit from “mentors” who scaffold.
*(ZPD is a part of this)*
*Social interaction/culture/language development influences* cognitive development.
\*Children benefit from “mentors” who scaffold.
*(ZPD is a part of this)*
56
New cards
Zone of proximal development (ZPD)
\
Range of tasks that are too difficult to do alone, but can be accomplished w/ guidance from someone w/ experience in the task.
Range of tasks that are too difficult to do alone, but can be accomplished w/ guidance from someone w/ experience in the task.
57
New cards
Kohlberg’s Moral Development Theory (list the 3 types)
\*Kohlbery was interested in the __*reasoning*__ behind decision-making.
1. Preconventional
2. Conventional
3. Postconventional
1. Preconventional
2. Conventional
3. Postconventional
58
New cards
Preconventional
__Gaining__ rewards/__avoiding__ punishments
59
New cards
Conventional
Following the __rules__/__law__, gaining others’ __approval__
60
New cards
Postconventional
Equality, justice, ethical principles, human rights.
61
New cards
Gilligan *(AP Exam only)*
Gender differences in moral development/reasoning.
62
New cards
Authoritarian Parenting Style
\*Parents: strict, unsympathetic, not open for discussion.
\*Children: somewhat unfriendly, withdrawn, distrustful, & possibly aggressive.
\*Children: somewhat unfriendly, withdrawn, distrustful, & possibly aggressive.
63
New cards
Permissive Parenting Style
\*Parents: lack discipline/boundaries, give complete freedom, more like a friend.
\*Children: dependent, somewhat immature, lacks self-regulation.
\*Children: dependent, somewhat immature, lacks self-regulation.
64
New cards
Authoritative Parenting Style
\*Parents: uses reasoning, encourages dialogue w/children, increases child’s responsibility over time.
\*Children: more friendly, cooperative, & well-adjusted.
\*Children: more friendly, cooperative, & well-adjusted.
65
New cards
Empathy v Sympathy
\*Empathy: the ability to relate to what someone else is going through.
\*Sympathy: just feeling bad for someone.
\*Sympathy: just feeling bad for someone.
66
New cards
Self-regulation
Ability to control own emotions & behaviors.
67
New cards
Socialization
Learning appropriate behaviors/norms in society (not gender related).
68
New cards
Sex v. Gender
\*Sex: genetics/biology
\*Gender: society defines gender (i.e. masculine v feminine)
\*Gender: society defines gender (i.e. masculine v feminine)
69
New cards
Gender Schemas, Roles, & Stereotypes
\*Schema of “appropriate” behaviors, emotions, attitudes, occupations, etc. for each gender.
\
\*Roles are a particular part of the schema that relates specifically to culturally defines “appropriate” behaviors for each gender.
\
\*Stereotypes are a particular part of the schema that is related specifically to the culturally influences beliefs about each gender.
\
\*Roles are a particular part of the schema that relates specifically to culturally defines “appropriate” behaviors for each gender.
\
\*Stereotypes are a particular part of the schema that is related specifically to the culturally influences beliefs about each gender.
70
New cards
How are Gender Schemas Developed & Socialization Learned? (4 things)
1. **Operant Conditioning**
2. **Observational Learning**
3. **Self-socialization**
4. **Family, schools, media**
71
New cards
Puberty
Biological & physical changes that occur during adolescence in preparation for reproduction.
72
New cards
Primary v. Secondary sex Characteristics
Primary: necessary for reproduction.
Secondary: changes that are NOT necessary for reproduction.
Secondary: changes that are NOT necessary for reproduction.
73
New cards
Synaptic Pruning
Getting rid of inefficient/unnecessary synaptic connections.
74
New cards
Still developing __prefrontal cortex__ = increases risk-taking
* Continues to develop until \~25 yrs old
(in charge of higher-level thought, decision-making, planning, etc.)
* Due to prefrontal cortex not being fully developed, risk-taking is increased
(in charge of higher-level thought, decision-making, planning, etc.)
* Due to prefrontal cortex not being fully developed, risk-taking is increased
75
New cards
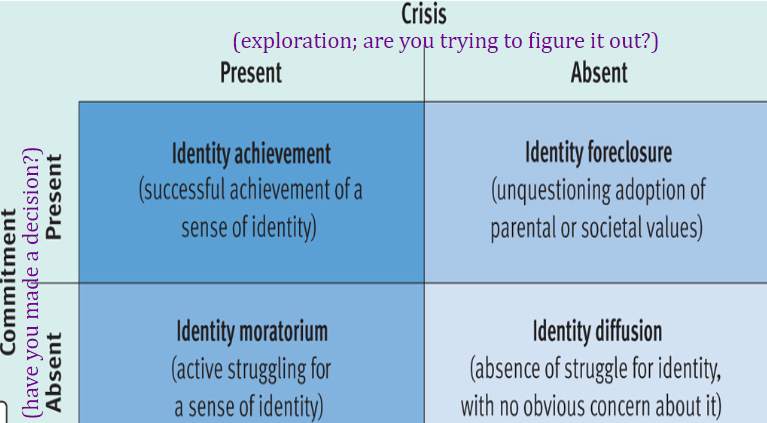
Marcia’s four identity statuses
**Crisis** ***(exploration; are you trying to figure it out?)***
**Commitment** ***(have you made a decision?)***
\
**Identity Achievement~**
* __Successful achievement__ of a sense of identity.
I**dentity Foreclosure~**
* __Unquestioning adoption__ of parental or societal values.
**Identity Moratorium~**
* __Active struggling__ for a sense of identity.
**Identity Diffusion~**
__Absence of struggle__ for identity, w/ no obvious concern about it.
**Commitment** ***(have you made a decision?)***
\
**Identity Achievement~**
* __Successful achievement__ of a sense of identity.
I**dentity Foreclosure~**
* __Unquestioning adoption__ of parental or societal values.
**Identity Moratorium~**
* __Active struggling__ for a sense of identity.
**Identity Diffusion~**
__Absence of struggle__ for identity, w/ no obvious concern about it.
76
New cards
Forming an Identity: Social & Ethnic Identity
To what extent do the groups one belongs to influence one’s identity?
77
New cards
Racial Identity Theory
Development of a group or collective identity based on one's perception that one shares a common heritage with a particular racial group.
78
New cards
Emerging Adulthood
Transition between adolescence and adulthood
(some classify themselves as "adults," some don't see themselves as an adult yet).
(some classify themselves as "adults," some don't see themselves as an adult yet).
79
New cards
“Early” Adulthood (\~20-40+ yrs)
\*physical & cognitive growth continues.
\*social focus: Intimacy v. Isolation (Erikson); establishing self (career).
\*social focus: Intimacy v. Isolation (Erikson); establishing self (career).
80
New cards
“Middle” Adulthood (\~40-65+ yrs)
\*social focus: Generativity v. Stagnation (Erkison)
\*cognition is still good, overall
\*slight physical deterioration
*(decline in eyesight, hearing, soreness, etc.)*
\*cognition is still good, overall
\*slight physical deterioration
*(decline in eyesight, hearing, soreness, etc.)*
81
New cards
“Late” Adulthood (\~65+ yrs)
\*social focus: Integrity v. Despair (Erikson)
\*cognition: slower processing, fluid intell. Starts to decline, etc.
\*physical: continues deterioration of body & blood flow to the brain.
\*cognition: slower processing, fluid intell. Starts to decline, etc.
\*physical: continues deterioration of body & blood flow to the brain.
82
New cards
Dementia
Significant changes in cognitive processing
*ex~ memory problems due to Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s*
*ex~ memory problems due to Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s*
83
New cards
Longevity
Female tend to live longer.
84
New cards
Terminal Drop
Sharp decline in cognitive abilities (usually just before death).