BIOCHEMISTRY LEC - Carbohydrates
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Carbohydrates
They are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or compounds that yield them upon hydrolysis.
Glucose
Polyhydroxy aldehyde
in carbon 1
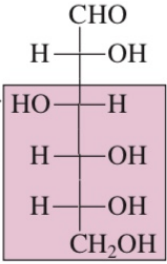
Fructose
Polyhydroxy ketone
in carbon 2
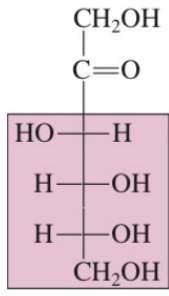
Functions of Carbohydrates
Provides energy
Short-term energy storage (immediate)
Supply carbon atoms for synthesis of other biochemical substances
Part of the structural framework of DNA and RNA molecules
Linked to lipids: Structural components of cell membranes
Linked to proteins: Function in cell-cell and cell-molecule recognition processes
Classification of Carbohydrates (based on how many building blocks you have)
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Oligosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Saccharide
Part of a word that is a giveaway that it is dealing with sugar.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar unit
Building blocks
glucose
fructose
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides linked together
maltose
lactose
sucrose
Oligosaccharides
2-10 monosaccharides linked together
Polysaccharides
Many monosaccharides linked together
starch
glycogen
cellulose
Classification of Carbohydrates by Functional Group
Aldose (ex. glucose)
Ketose (ex. fructose)
Classification of Carbohydrates by Number of Carbon Atoms
Triose (3C) - dihydroxyacetone, glyceraldehyde
Tetrose (4C) - erythrose, threose
Pentose (5C) - ribose, arabinose
Hexose (6C) - glucose, galactose, fructose, mannose
Isomerism
Same molecular formula but differ in the way atoms are arranged.
Sterioisomers
Same molecular and structural formula, but differ in the orientation of atoms in space.
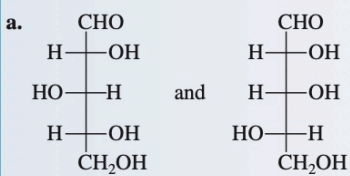
Enantionmers
Non-superimposable mirror images
X - superimposable
/ - mirror image
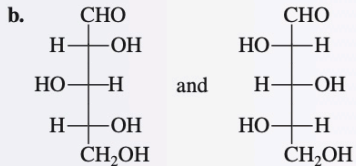
Diastereomers
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images
X - superimposable
X - mirror image
Epimers
Differ in configuration around a single specific carbon
Point reference is glucose
X - superimposable
X - mirror image (only 1 center mirrored)
Dextro Isomers
OH group is on the right side
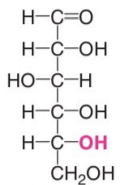
Levo Isomers
OH group is on the left side
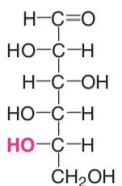
Classification of Carbohydrates by the Haworth Projection Formula
Cyclic Configuration
Pyranose: 6 member ring (ex. glucopyranose)
Furanose: 5 member ring (ex. ribofuranose)
Anomers
Differ at the anomeric carbon in cyclic structures
Alpha = OH down
Beta = OH up (betaas)
Alpha
anomeric OH down
Beta
anomeric OH up
Biochemically Important Monosaccharides
D-Glyceraldehyde and Dihydroxyacetone
D-Glucose
D-Galactose
Fructose
Ribose
D-Glyceraldehyde and Dihydroxyacetone (Biological Importance)
The simplest of the monosaccharides
Trioses
Glucose (Biological Importance)
Grape Sugar
since ripe grapes (20%-30% glucose by mass)
Blood Sugar
since blood contains dissolved glucose (70-100mg/dL)
Dextrose
Main energy source
Galactose (Biological Importance)
Brain Sugar
Milk Sugar
Synthesized from glucose in the mammary glands (in lactating moms) for use in lactose
Present in the chemical markers that distinguish various types of blood:
A
B
AB
O
Each blood type is based on 3-4 monosaccharides
Blood Type O
universal donor
Blood Type AB
universal recipient
Fructose (Biological Importance)
Levulose
Fruit Sugar
used as dietary sugar
used in HFCS (High Fructose Corn Sugar)
Ribose (Biological Importance)
Pentose Sugars
Component of RNA and ATP and DNA molecules
Reactions of Monosaccharides
Oxidation
C1 - weak oxidizing agent
-ose to -onic
Aldonic acid (mild oxidation)
Uronic acid (oxidation of primary alcohol)
Aldaric acid (strong oxidation)
C1 + C6 - strong oxidizing agents
-ose to -aric
Aldaric acid
C6 - enzymes
-ose to uronic
Alduronic acid
Reduction
-itol
Produces sugar alcohols
Sorbitol
Glycoside Formation
Hemiacetal to acetal
Replacement of the hemiacetal carbon -OH group with an -OR group
Glucoside
Galactoside
Phosphate Ester Formation
Attach phosphate to C6
Amino Sugar Formation
Hydroxyl group is replaced with an amino group
Amino sugar is produced
C2
Oxidation (Weak Oxidizing Agents)
C1 - weak oxidizing agent
-ose to -onic
Aldonic acid (mild oxidation)
Uronic acid (oxidation of primary alcohol)
Aldaric acid (strong oxidation)
Oxidation (Strong Oxidizing Agents)
C1 + C6 - strong oxidizing agents
-ose to -aric
Aldaric acid
Oxidation (Enzymes)
C6 - enzymes
-ose to uronic
Alduronic acid
Reduction
-itol
Produces sugar alcohols
Sorbitol
Glycosidic Formation
Hemiacetal to acetal
Replacement of the hemiacetal carbon -OH group with an -OR group
Glucoside
Galactoside
Phosphate Ester Formation
Attach phosphate to C6
Amino Sugar Formation
Hydroxyl group is replaced with an amino group
Amino sugar is produced
C2
Usually found in polysaccharides
Biochemically Important Disaccharides
Maltose
Cellobiose
Lactose
Lactulose
Sucrose
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
Malt Sugar
Beer Sugar
Alpha 1-4 glycosidic linkage
Cellobiose
Formed from intermediate hydrolysis of cellulose
Beta 1-4 glycosidic linkage
Hydrolyzed by cellobiase (enzyme)
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Milk Sugar
Beta 1-4 linkage
Alpha form is sweeter and more soluble in water than Beta form
Lactulose
Neither digested nor absorbed in the intestine
Laxative
Used to relieve/alleviate
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
Table Sugar
sugar cane contains up to 20% by mass
sugar beets contain up to 17% by mass
Alpha, Beta 1-2 glycosidic linkage
Classification of Polysaccharide
Function
Storage Polysaccharide
Structural Polysaccharide
Product of Hydrolysis
Homopolysaccharide
Heteropolysaccharide
Mucopolysaccharide
Storage Polysaccharide
Storage form
Used as an energy source in cell
Starch
Glycogen
Starch
Plant energy storage
AKA glucan, amylum, gluose
Amylose + Amylopectin
Glycogen
Animal energy storage
Animal starch
Stored in liver and muscles
Glycogenesis
Synthesis of glycogen
Excess Blood Glucose
Glycogenolysis
Decomposition of glycogen
Low Blood Glucose
Structural Polysaccharide
Serves as structural element in plant cell walls and animal exoskeletons
Cellulose
Chitin
Cellulose
Plant cell wall component
Most abundant naturally occurring polysaccharide
“Woody” portions of plants
Beta 1-4 glycosidic linkages
5000 glucose units
Humans lack this
Chitin
Gives rigidity
Also occurs in the cell walls of fungi
Exoskeleton of arthropods
Polymer of N-acetylglucosamine
Beta 1-4 glycosidic linkages
Homopolysaccharide
On hydrolysis yield only a single type of monosaccharide
Glucans are polymers of glucose
Fructosans are polymers of fructose
Starch
Glycogen
Chitin
Cellulose
Heteropolysaccharide
On hydrolysis yield a mixture of few monosaccharides
Mucopolysaccharides
Mucopolysaccharides
AKA glycosaminoglycans (GAG)
Made up of repeating units of sugar derivatives
Amino sugars
Uronic acids
Hyaluronic Acid
Chondroitin Sulfate
Dermatan Sulfate
Makes them acidic polysaccharide (negative)
Forms mucoproteins or mucoids or proteoglycans
Hyaluronic Acid
Found in connective tissue and joint lubrication
Indicated for knee pain
Can induce swelling
Chondroitin
Found in cartilage
Dermatan
Found in skin and blood vessels
Keratan
Small amounts of mannose, fructose, sialic acid.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels
Glucagon raises blood glucose levels
Lactose Intolerance
Deficiency in lactase enzyme
Diabetes Mellitus
Impaired glucose metabolism
Dietary Fiber
Provides the digestive tract with “bulk” that helps move food through the intestinal tract and facilitates the excretion of solid waste.