Board study guide #2
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
While in the sleep lab, a patient has to do all of the following EXCEPT
remain supine for the entire study.
In what age range does narcolepsy normally present?
16-25
Criteria required to score alternating leg muscle activations (ALMAs) include all of the following EXCEPT
It cannot occur in REM sleep
Stage 3 delta waves must have an amplitude of greater than 75 microvolts. On which region of the brain must that requirement be measured?
Frontal region
All of the following tasks must be completed before beginning the PSG EXCEPT
the patient is given a beverage, which is put on the bedside table.
Which of the following is an accurate rule for scoring periodic leg movements?
There is a minimum of four consecutive leg movements in a chain. At least 5 seconds between each leg movement are required. No more than 90 seconds between each leg movement are required.
what types of patients should average volume-assured pressure support be used as treatment?
Patients with obesity hypoventilation syndrome.
What can be done to improve sweat sway artifacts on the EEG and EOG channels?
Decrease the temperature in the room, and turn on a fan.
Which of the following is NOT part of scoring pediatric obstructive sleep apneas?
Missed respirations associated with arousal, awakening, or desaturation of 3% or more.
Which kind of apneic events are characterized by a complete absence of effort in the respiratory monitoring belts?
Central.
Which of the following is FALSE with regard to the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT)?
The MSLT includes seven nap periods.
Which PSG channels of observation are required for a multiple sleep latency test?
BEG, EOG, EKG, and chin EMG.
Completely blind individuals are more likely to experience which sleep disorder?
Free-running sleep disorder
If a patient has issues with mouth breathing while using a nasal-only mask, in which order should the technologist work to alleviate the problem?
Increase heated humidity settings, offer a nasal spray for congestion, apply a chin strap, attempt to flex the comfort settings, and then switch to a full-face mask.
At what age does the American Academy of Sleep Medicine begin considering a patient under the adult scoring guidelines?
13 years of age
To score a hypopneic event for an adult, all of the following criteria are necessary EXCEPT
the entire event must meet the 50% reduction from baseline.
Sleepwalking and night terrors are common in the ages of
3-12
The technologist should document all of the following activities of the patient EXCEPT for
switching from stage N1 sleep to stage N2.
Which is best for cleaning leads?
Bleach
Which region of the brain will show the majority of alpha rhythms during the PSG?
Occipital
The technician notes should include
times of "lights off" and "lights on." changes in the CPAP/BIPAP pressures. patient complaints.
Which of the following EEG frequencies can be seen during an arousal from sleep
Alpha. Theta. Any frequency over 16, excluding sleep spindles.
What is the most important aspect of fielding a patients questions in the morning following
To be positive and and avoid alarming the patient
Which of the following is NOT a therapeutic intervention for narcolepsy?
Diet and exercise
Which of the following is true with regard to electrode impedances?
Impedance levels for each individual electrode should be less than or equal to 5 kg.
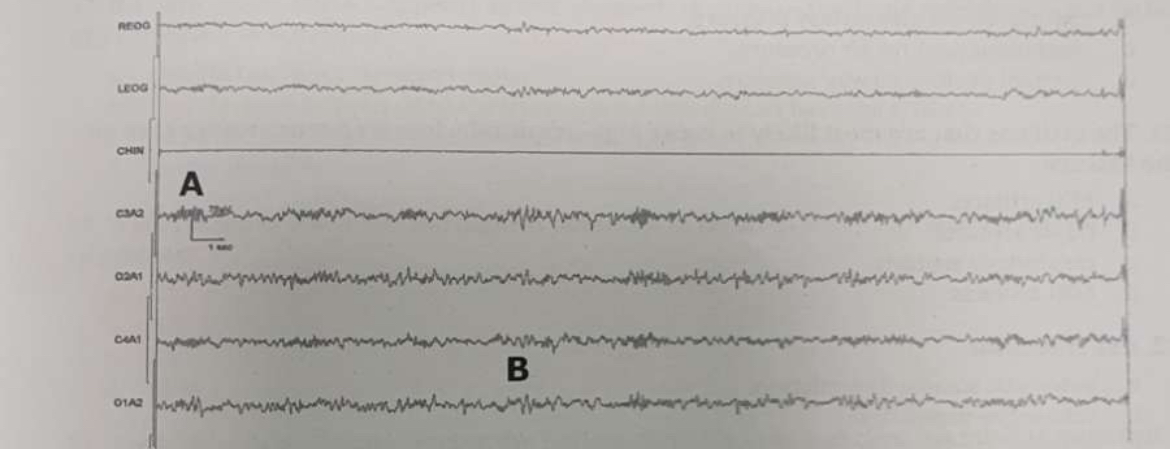
What stage of sleep is shown here?
Stage 2
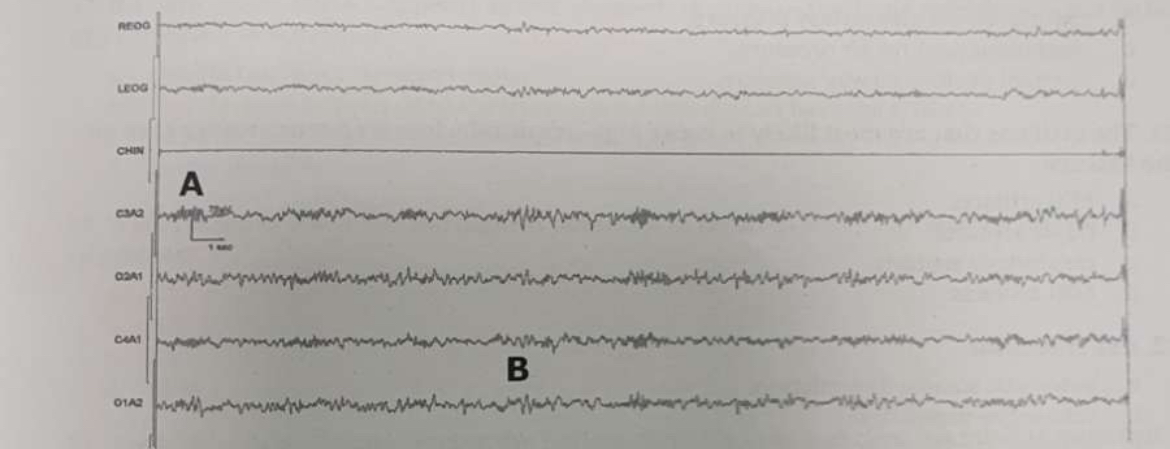
What waveform is seen at the b mark
K- complex
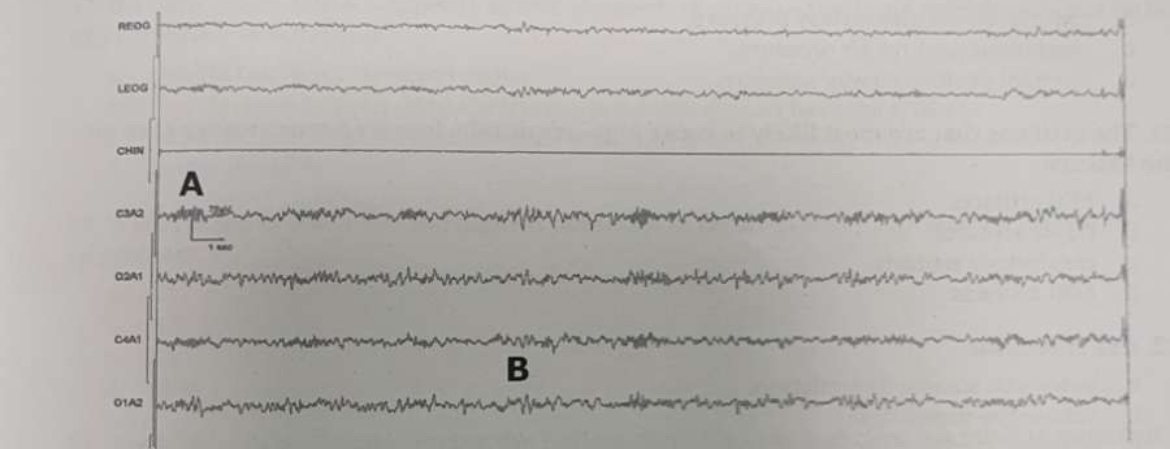
What waveform is seen at the A mark?
Sleep spindle
Correct statements about acceptable PAP titration results include all of the following EXCEPT
It does not reduce the RDI to 10 or less but reduces the RDI by 50% from baseline in severe patients.
CPAP stands for
continuous positive airway pressure
The artifacts that are most likely to cause high-amplitude, low-frequency waves seen on the EEG are
Respiratory artifacts
ASV stands for what?
adaptive servo-ventilation.
How is sleep apnea normally treated in pediatries and pre-adolescent children?
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy.
When should technologists test their equipment for accuracy and function?
Immediately on arriving at the lab before the patients arrive
A patient is fully hooked up and sitting on the side of the bed while the technologist verifies that the data are accurate; the technologist notes that the Sp02 channel reading is 101%. What should the technologist do next?
Remove the pulse oximeter probe from the patient, and verify that it is functioning by placing it on the technologist's finger.
The minimum required biocalibrations before "lights out" and following "lights on" should include which of the following?
Eyes open, eyes closed, look left, look right, look up, look down, blink eyes five times slowly, grit teeth or clench jaw, inhale, exhale, hold breath 10 seconds, flex left foot, flex right foot, and documentation of each action.
if a slow-wave artifact appears in two channels that share the same reference, what is the BEST solution to correct it?
Re-reference both leads to a reference point that doesn't have the artifact.
Which stage of sleep has the highest potential to result in long-lasting sleep inertia symptoms?
N3
During bio-calibrations, having the patient close his eyes and clear his mind is intended to produce which sort of wave?
Alpha waves
Ifa patient has an epoch that has K-complexes and sleep spindles throughout the EEG but has rolling eyes in the EOG, which stage of sleep is scored?
Stage N2
According to the guidelines of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, how long must loud or unambiguous snoring continue in patients 12 years or older before the technologist increases the IPAP settings to treat it
At least 3 minuets
Which of the following is a reason to start a CPAP study higher than 4 cm?
The patient is returning to the lab for re-titration or has an elevated BMI.
Arrhythmias on the EKG that require an immediate response and emergency protocols include all of the following EXCEPT
Atrial flutter
Which channels are necessary in the software montage for a multiple sleep latency test?
1. Leg EMG HI. Chin EMG III. EOG monitors
IV. EEG leads
V. EKG monitors
VI. Sp02
11, II, IV, and V
What do the scoring guidelines of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) say about stage transitions as they pertain to arousal scoring criteria?
Transitions from one stage of sleep to another are not sufficient of themselves to be scored as EEG arousals unless they meet the arousal criteria.
Electrical safety requires all of the following actions from a technologist EXCEPT
the application of a ground placed with the pulse oximetry probe.
During a PAP titration, the pressure should be increased until which of the following combinations of events are eliminated?
Apneas, hypopneas, RERAs, and snoring.
What percentage drop in the SpO, data must be seen to score an obstructive apnea event?
No required drop in the SpOz channel.
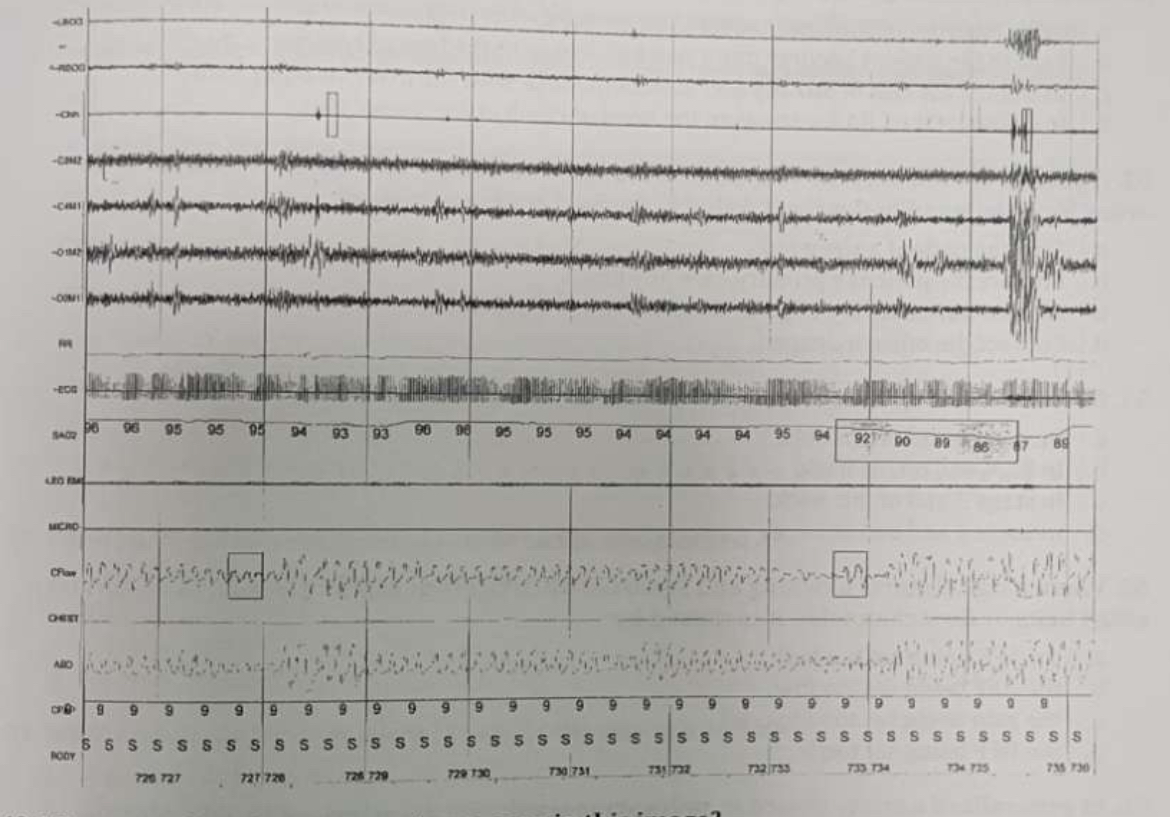
What sort of respiratory events are seen in this image?
Obstructive hypopneas.
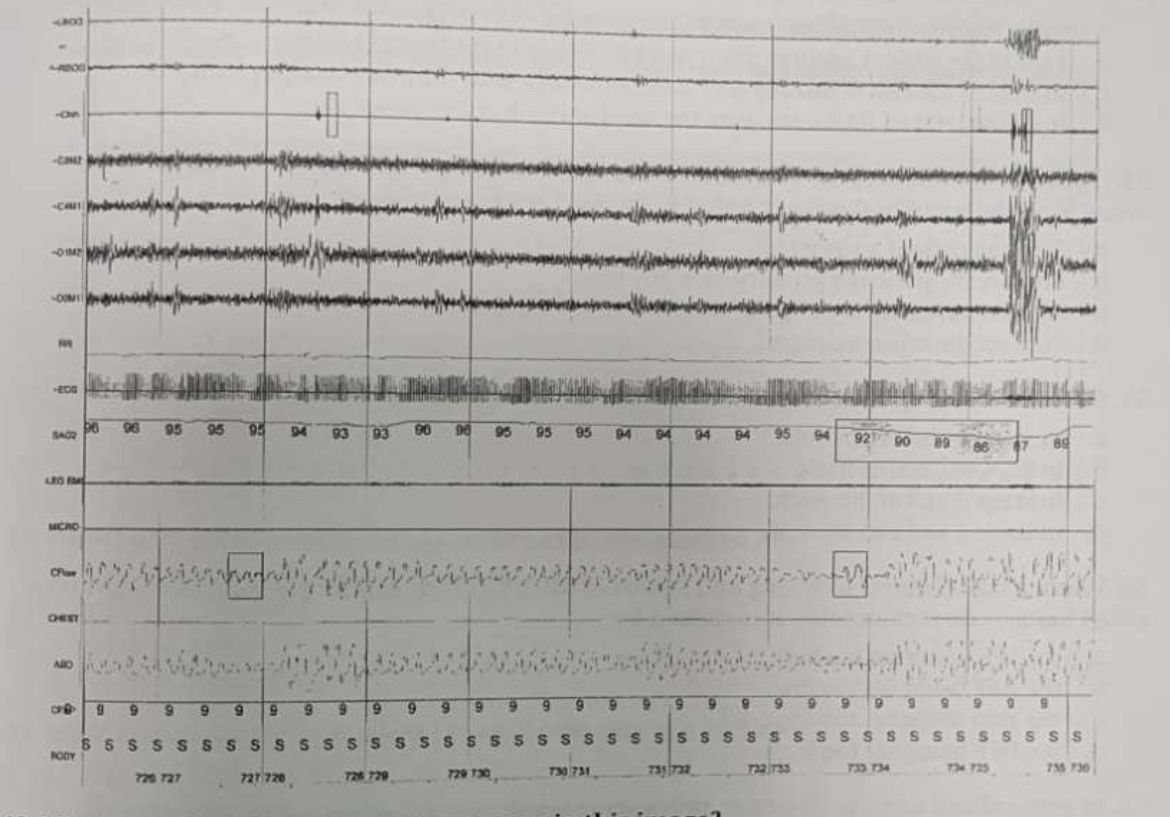
How should the technician treat these respiratory events?
Raise the CPAP to 10 cm.
A mixed apnea is characterized by which of the following?
A lack of respiratory effort at the start of the event where respiratory effort returns before the event ends.
All of the following are purposes of CPAP interface desensitization EXCEPT
to calibrate the CPAP settings to the level of comfort for the patient.
A patient complains that he is not able to sleep and requests a sleep aid. There is no order for a sleep aid in the chart. What is the best course of action?
Ask the patient to try to go to sleep without a sleep aid.
Obstructive sleep apnea is normally at its worst when the patient is
In REM on his back
When a signal starts blocking and squaring off at the top (especially seen in respiratory effort belts or flow channels), it is caused by
The gain being set too high.
In generalized anxiety disorder, polysomnography is characterized by which of the following?
Increased stage 1 non-REM sleep.
Is it possible to designate a patient as having hypoventilation without PaCO, data?
No, persistent SpO, desaturations are not sufficient.
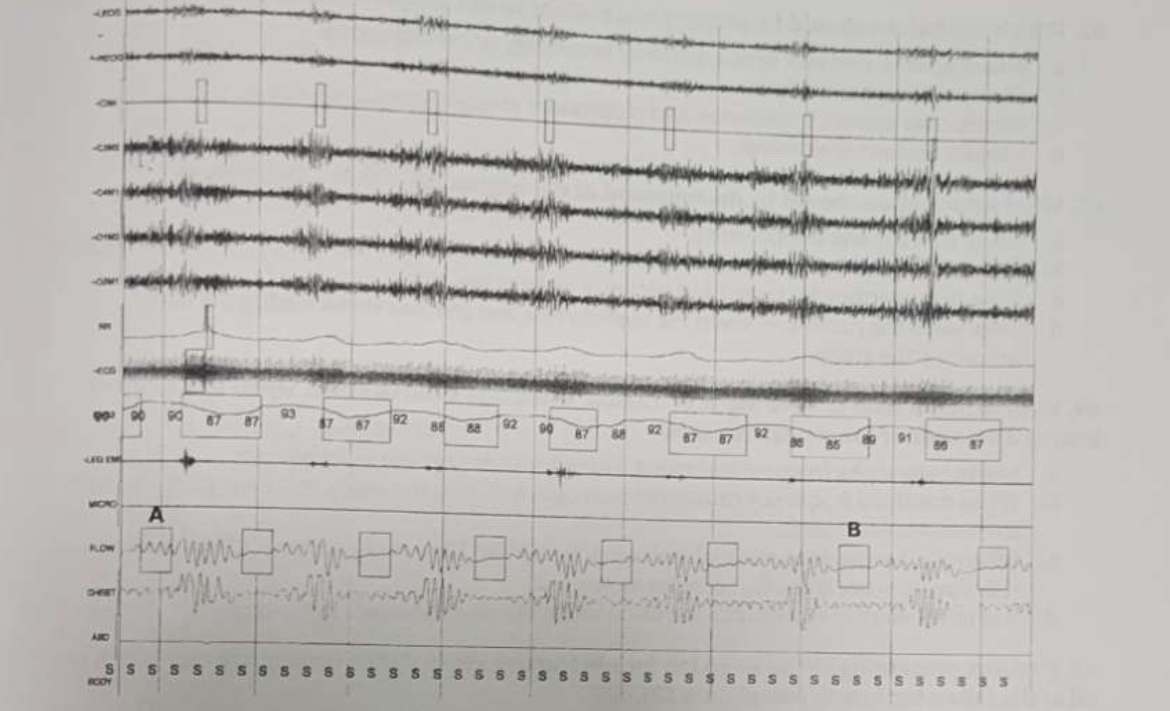
What sort of respiratory event is seen in the box marked A?
Obstructive hypopnea
What sort of respiratory event is seen in the box marked B?
Obstructive apnea
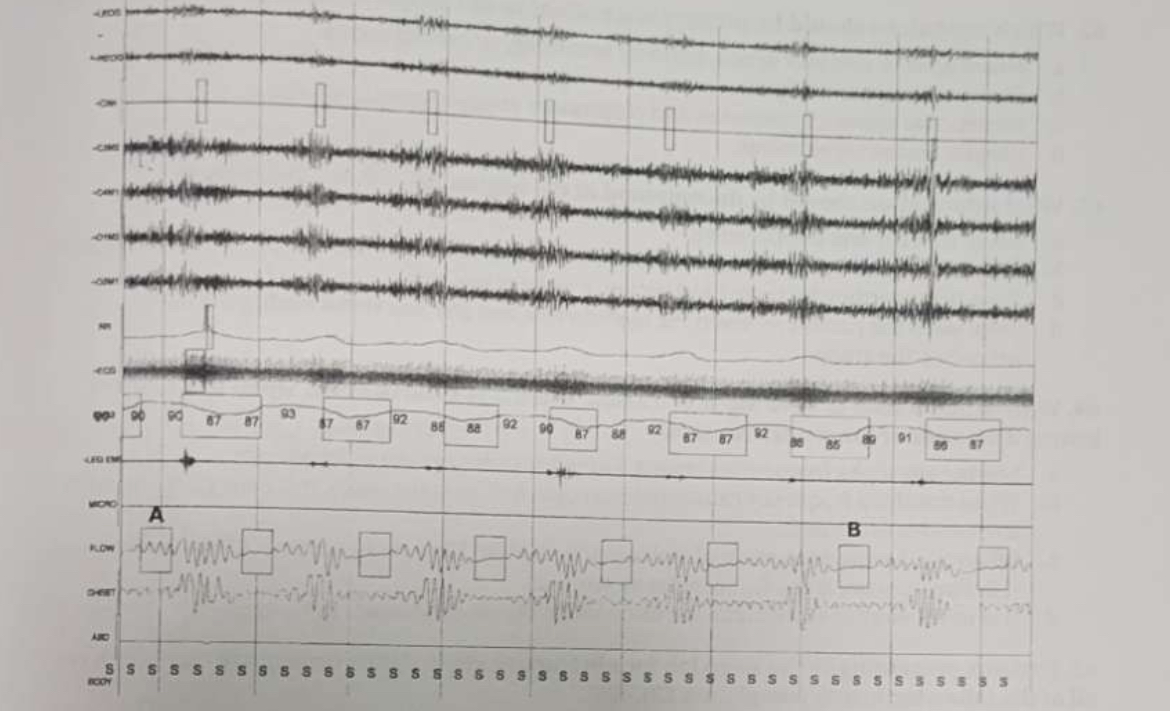
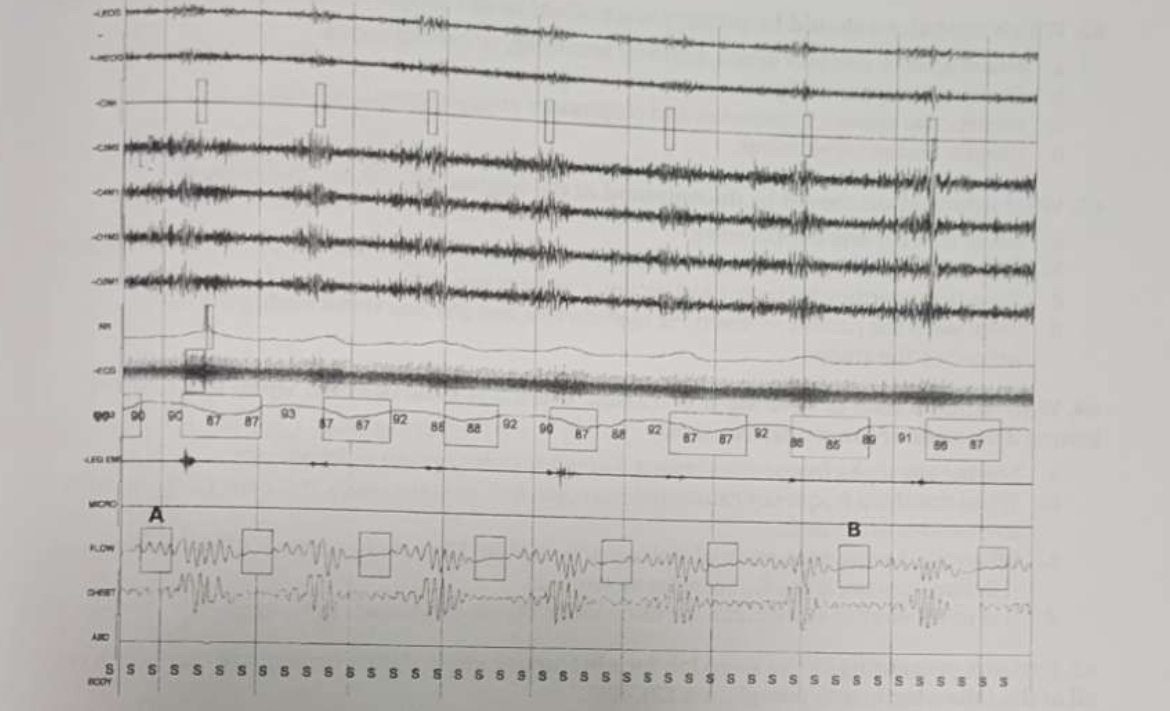
The limb movements in this screen shot can be scored as
respiratory limb movements.
Gloves should be used by the technologist when in contact with all of the following EXCEPT the
Hair
Which conditions should be present in a patient to use adaptive servoventilation?
Mixed apneas, complex apnea, periodic breathing, or central apnea.
What information should be documented at the beginning of every sleep study?
Time the recording is started and patient's current position
With patients seen to have alpha intrusion, when is it valid to score alpha frequencies lasting 3 seconds or longer as arousals?
When the 3 seconds or more of alpha is preceded by 10 or more seconds of alpha-free sleep, it is okay to score alpha frequencies as arousals.
Patients presenting to the sleep lab for obstructive sleep apnea testing are likely to have all of the following health complaints EXCEPT
Increased appetite
Acceptable ways to ensure that the morning paperwork is filled out before the patient leaves the lab include all of the following EXCEPT
ask the the patient fil out the paperwork while the technologist Watches
type 2 sleep study must include all of the following EXCEPT
Testing at a sleep center
Which of the following is NOT a way to decrease the amount of condensation in humidifier tubing?
Decreasing room temperature at night.

What is the apnea index (AI)?
5 / hr

What is the hypopnea index (HI)?
4/ hr

What is the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI)?
9 / hr
Required criteria to score hypnagogic foot tremors (HFT) include all of the following ЕХСЕРТ
It is only scored in rem sleep
Which of the following events would meet the criteria for hypopnea?
A 37% reduction in airflow lasting 12 seconds followed by a 4% O2 desaturation.
What is the clinical conclusion for a patient who has alpha activity in the occipital channels while their eyes are both opened or closed?
Patient has severe sleep deprivation
Following proper prep swabbing, the skin at the prep site should be in which of the following conditions?
Abraded and clear of debris
Which of the following EEG waveforms are in the correct order from the highest to the lowest frequency?
Beta, alpha, theta, and delta.
Criteria necessary to score an arousal in NREM sleep include all of the following EXCEPT
concurrent increase in chin EMG.
One criterion for scoring pediatric respiratory effort-related arousals (RERAs) is that nasal pressure is reduced by what percentage, compared to baseline?
30%
What are some possible causes for secondary PLMS?
Blood iron deficiency
What is hypnagogic jerk?
A muscle spasm during the transition from wakefulness to sleep.
communicating with deaf patients, the interviewer should
Face the patient when talking to them
____ is measured in Hertz (Hz) and _____microvolts
Frequency, amplitude
REM behavior disorder is primarily characterized
Lack of atonia
If the exploring and reference electrodes are close to one another, the amplitude will be
Low
Periodic limb movements in sleep (PLMS) are defined as
at least 4 movements, between 5 and 90 seconds apart, and between 0.5 and 10 seconds in duration for each movement
Which time data are needed to calculate a patient's sleep latency?
Lights out/ sleep onset
During a BiPAP titration, acceptable changes to the settings when a patient begins having complex sleep apnea include which of the following?
Change to a spontaneous-timed mode with a backup rate or reduce IPAP settings.
Ketonuria, Kussmaul respirations, hyperglycemia, and fluid imbalance are characteristic
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
In children, most common parasomnias such as night terrors and sleepwalking present in what stage of sleep?
Stage 3
Which of the following actions by the sleep technician violates the principles of proper body mechanics?
Bending at the waist to reach items
Which accurately describes the placement location of left eye lead?
1 cm lateral and 1 cm below the left outer canthus.
Muscle artifact can be corrected by
Decreasing the HFF and moving the electrode that the artifact is appearing on.
Key things to look for in REM behavior disorder montage are
muscle movements and increased chin EMG activity in REM.

What is the mean sleep latency for this MSLT?
5 minutes

What is the mode sleep latency for this MSLT?
4 minuets

What is the median sleep latency for this MSLT?
4 minuets
What causes EKG artifacts in the EEG and EOG channels?
M1 and M2 being placed directly on the auricular branch of the posterior auricular artery.
To qualify as a sleep spindle, a short burst of EEG activity must be at which of the following frequencies?
12-14 Hz
Why is precise measurement of the head important for a PSG?
Artifacts can be caused by improper placement of electrodes. Observation of important waveforms require precise electrode placement. It is important for the identification of sleep onset and specific sleep stages.
Mixed apnea
starts with a central component that then becomes obstructive.