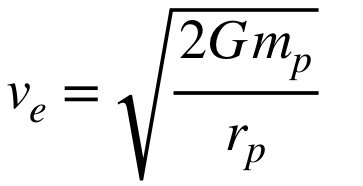Rotational Motion
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
angle of rotation
the measurement of the amount that an object is rotate about a fixed point (angular equivalent to linear distance)
divide distance traveled along the circular path (arc length) by the radius of curvature of the path
Units: radians (1 rad= 180/pi degrees)
I revolution= 2pi rad
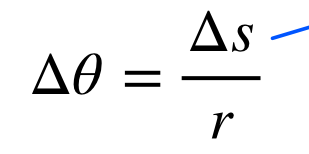
angular velocity
the rate of change of the angle of rotation around a fixed point
agular velocity is the angular equivalent to linear velocity
units: rad/s
positive direction: counter clockwise
negative direction: clockwise
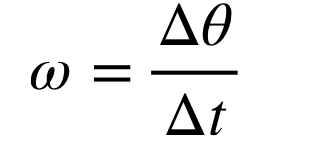
tangential velocity
instantaneous linear velocity of an object during its motion
angular velocity multplied bu the radius
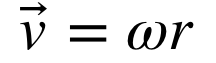
angular acceleration
rate at which angular velocity is changing over time
units: rads/s2
positive: increase in angular velocity
negative: decrease in angular velocity
rotational kinematics equations
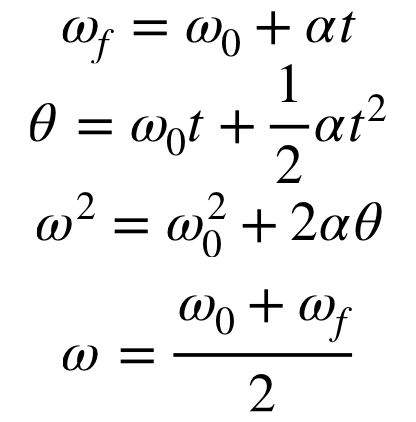
how are linear and angular variables related
linear vairables are just their angular variable equivalent multiplied by r (radius of path curvature)
angular momentum
tendency of a rotating object to keep rotating about its axis
conserved when the net external torque is equal to zero
L= angular momentum
I= moment of intertia
greater I = more torque needed to change an object’s angular momentum
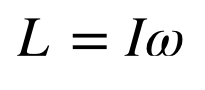
moment of inertia
tendency of an object to resist rotational motion
dependent on mass and the distribution of that mass around the axis of rotation
larger value= more difficult to change the rotational velocity of the object
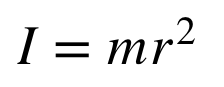
rotational kinetic energy
the kinetic energy that an object posseses due to its rotation
work is equal to the change in kinetic enrgy
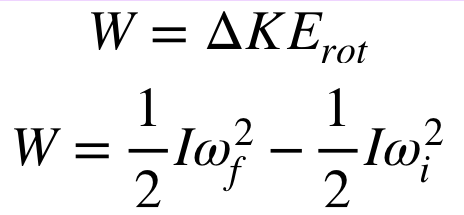
torque on rotational masses
F=ma equivalent for rotational motion
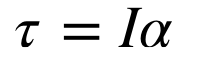
uniform circular motion
object is moving in a circle at constant speed
centripetal acceleration
acceleration radially towards the center of the circle
tangential velocity squared divided by radius
an increase means the direction of velocity is changing more rapidly
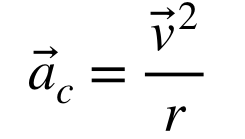
centripetal force
any force that causes an object to move in circular motion
points radially towards the center of the circle
newton’s law of motion
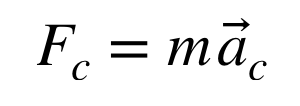
acceleration due to gravity on a planet:
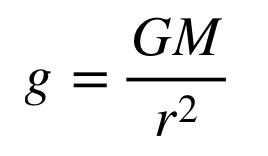
escape velocity
minimum speed an object must achieve to break free from the gravitational pull of a celestial body and move into space
velocity at which the object’s kinetic energy equals the gravitational potential energy