Structures and Functions of the Eye
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
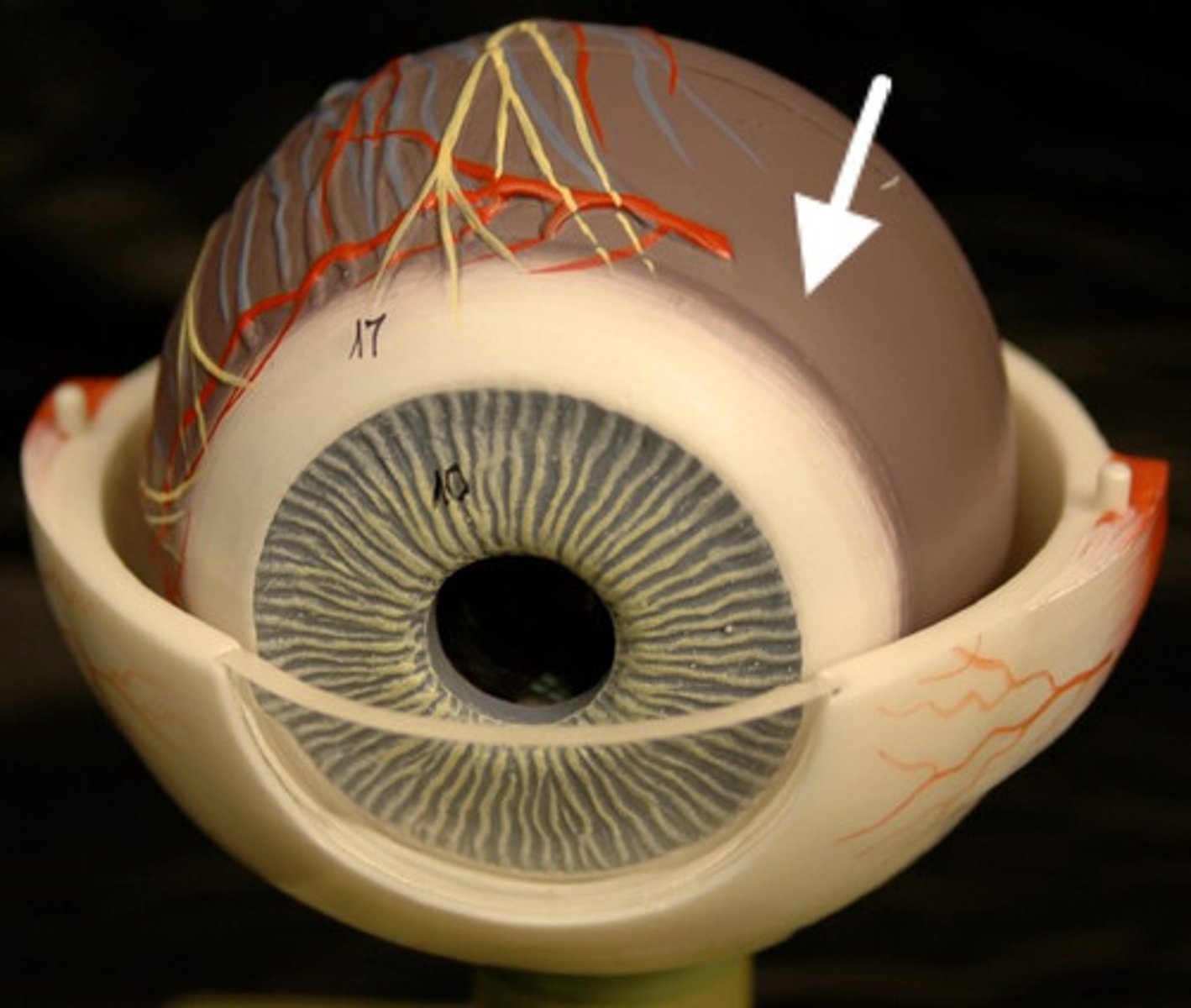
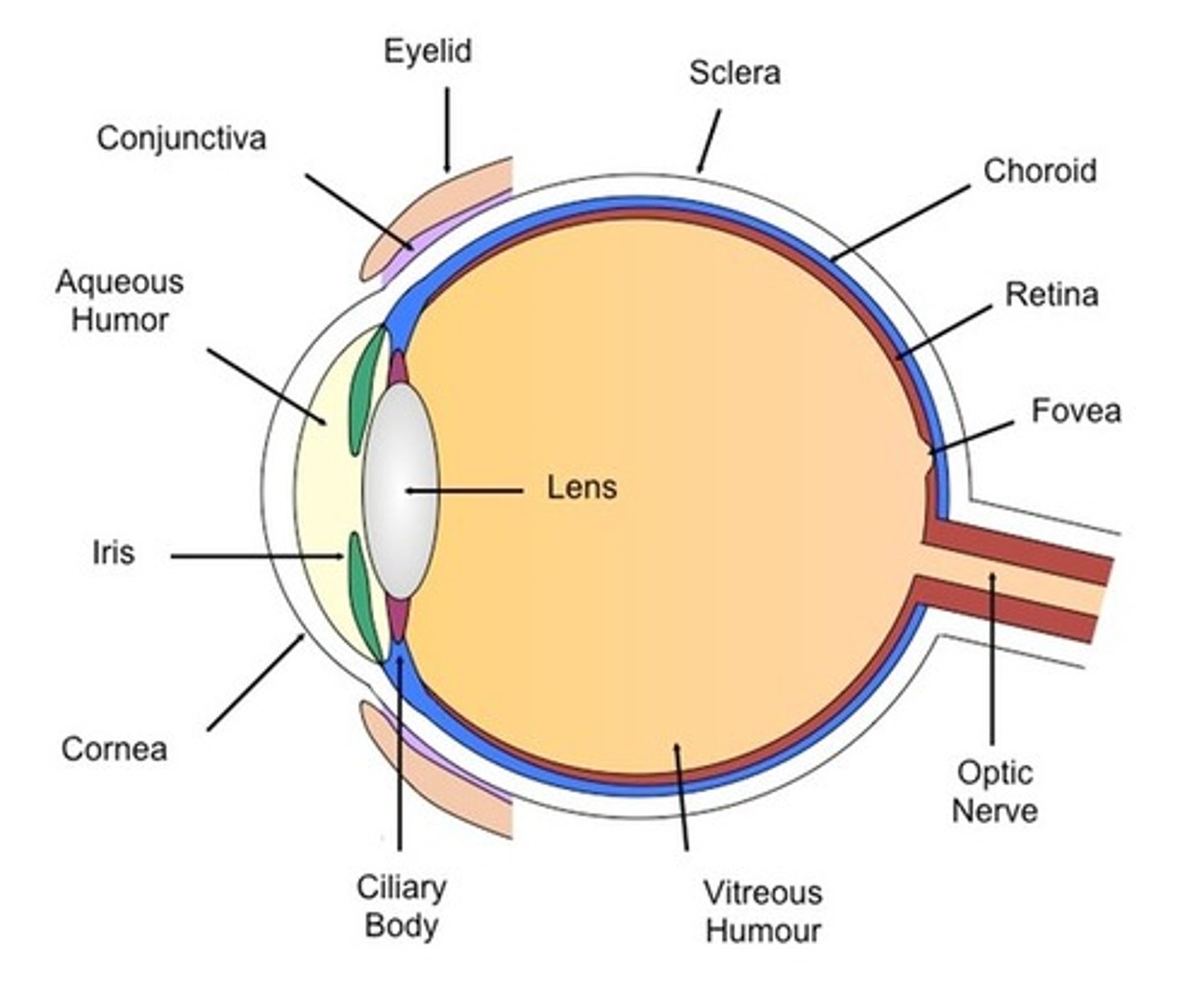
Choroid
Vascular layer providing nutrients to the retina
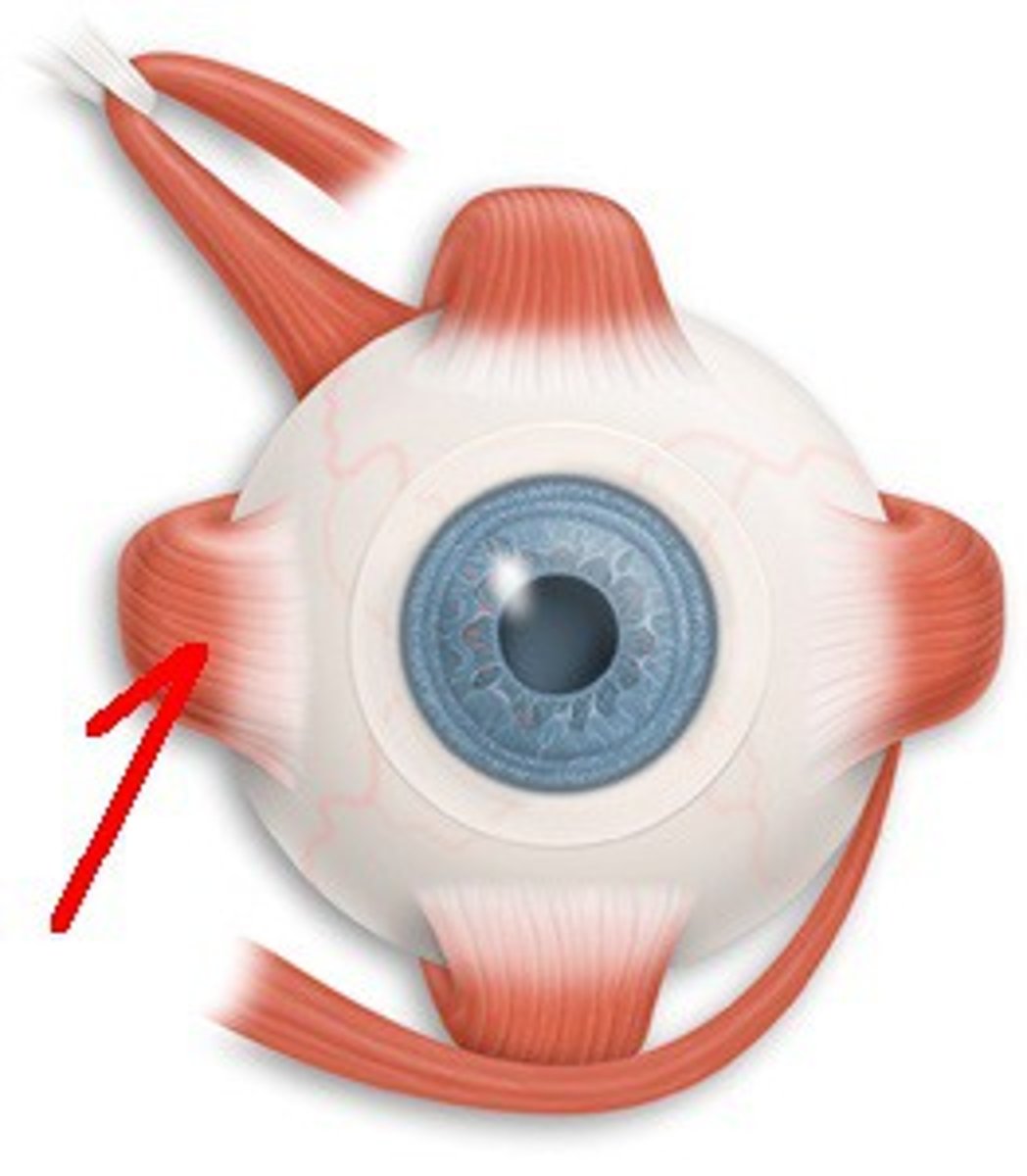
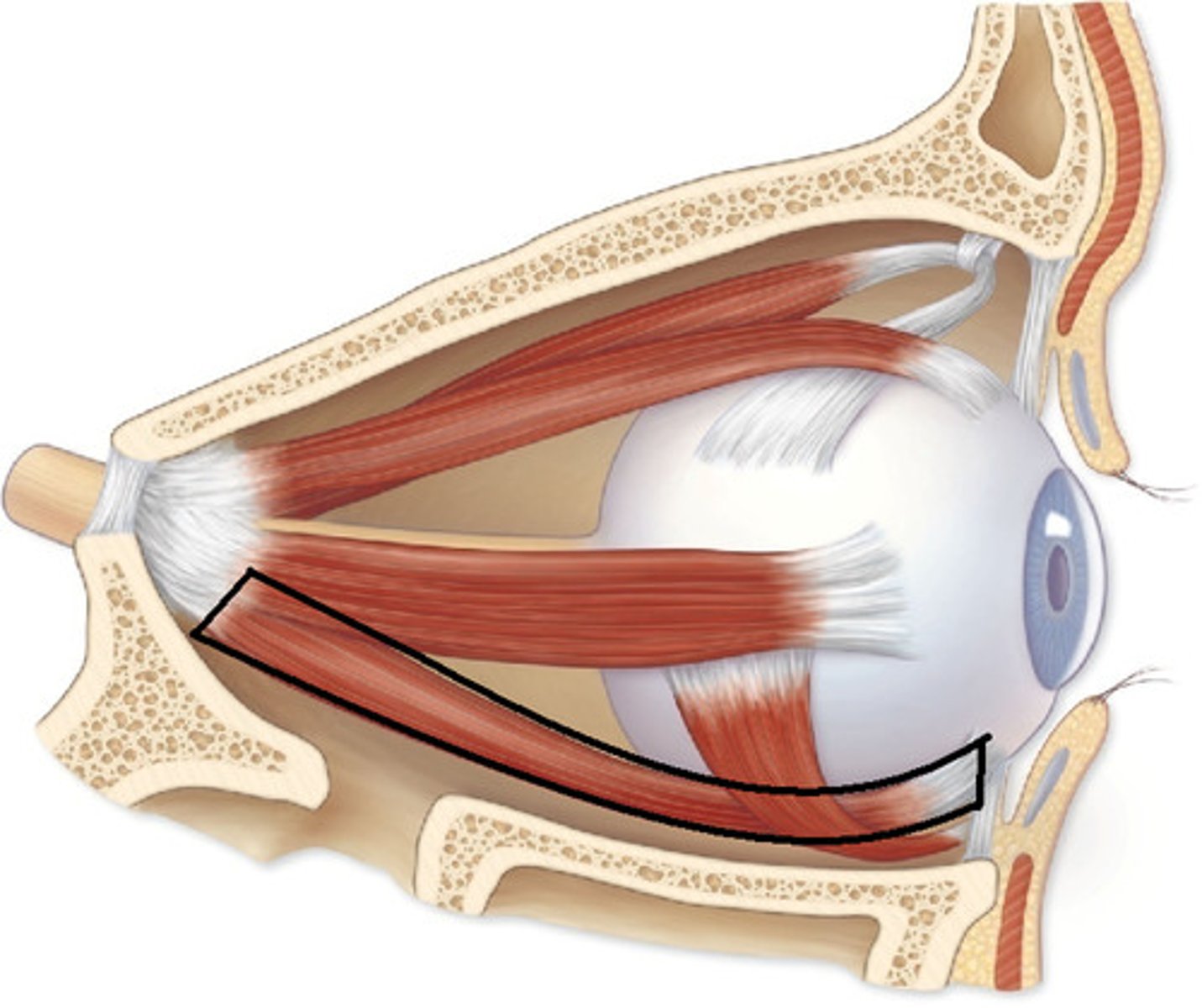
Rectus Muscle
Muscle that moves the eye horizontally
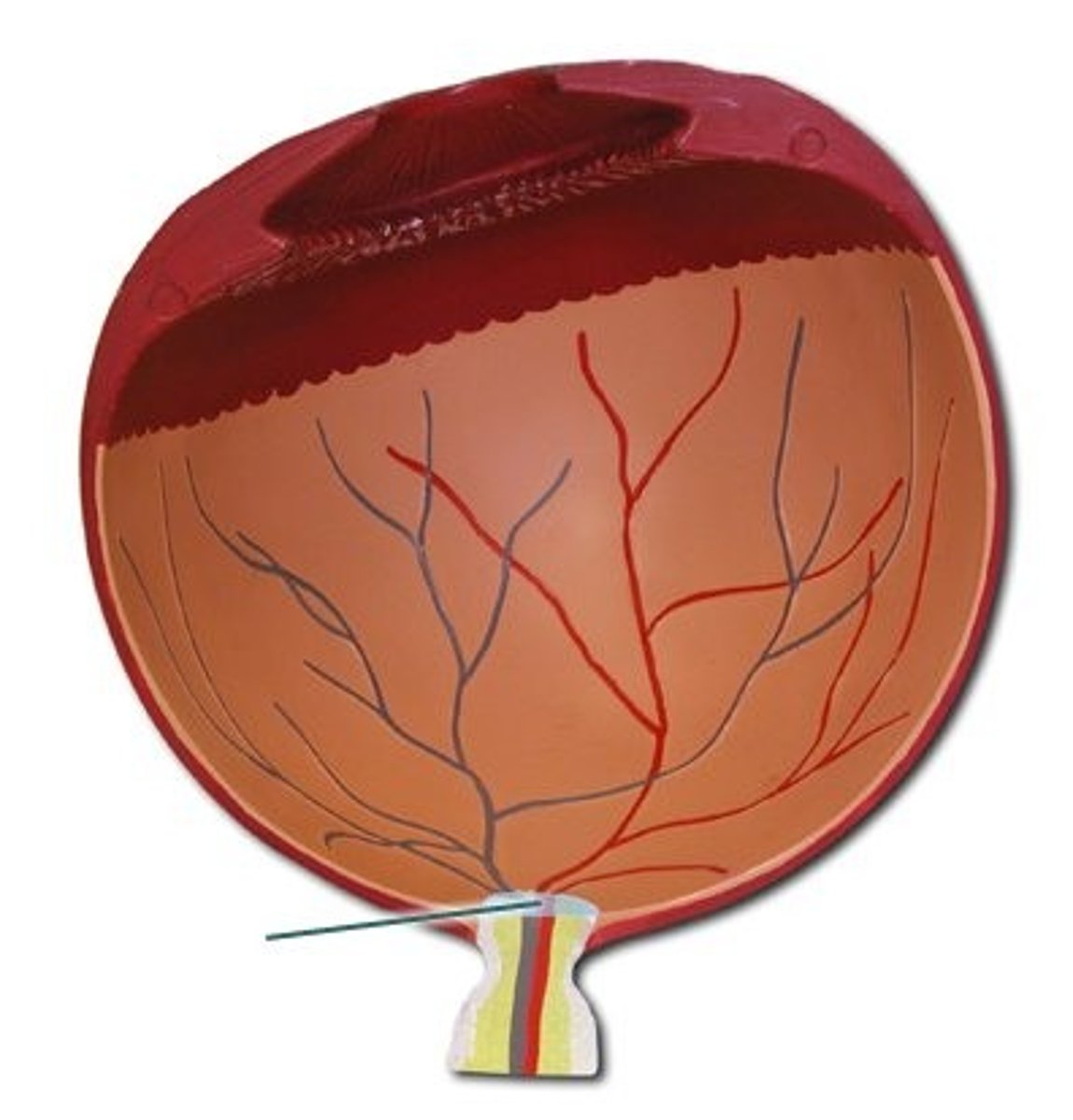
Optic Nerve
Nerve responsible for transmitting visual information to the brain
Superior Oblique
Muscle that turns the eyeball at an angle
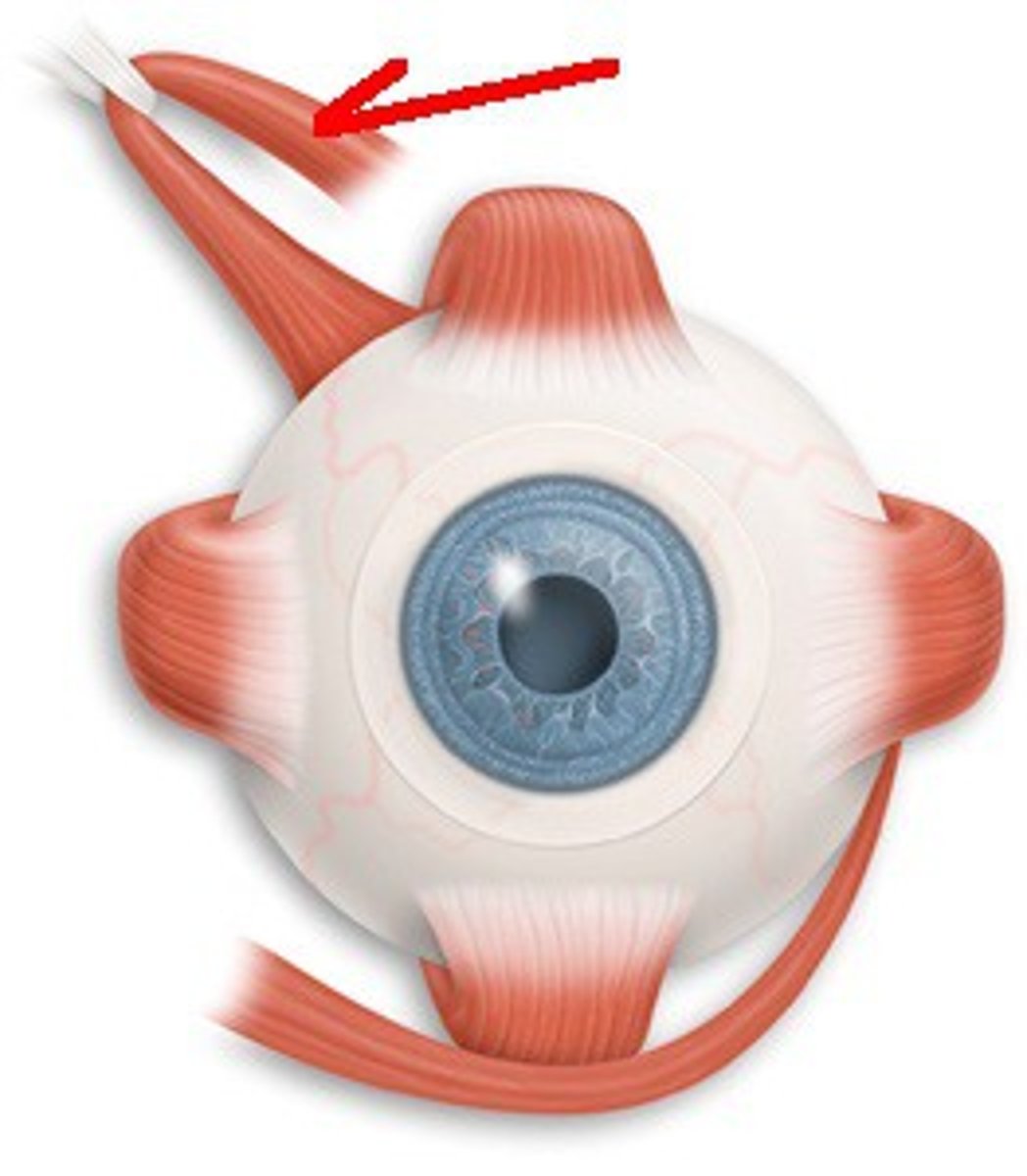
Inferior Rectus Muscle
Muscle that pulls the eye downward
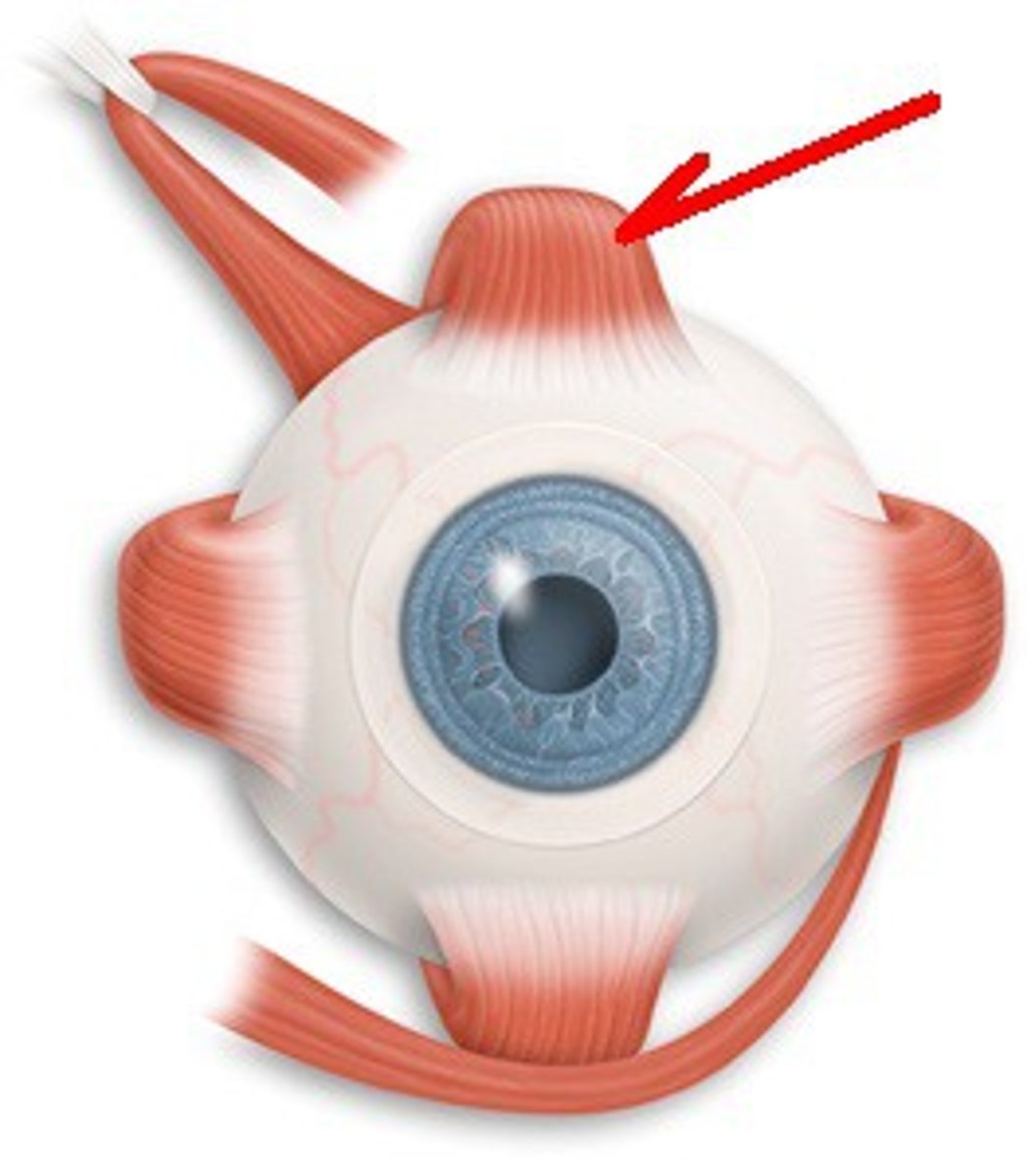
Superior Rectus Muscle
Muscle that turns the eye upward
Strabismus
Disorder causing misalignment due to muscle weakness
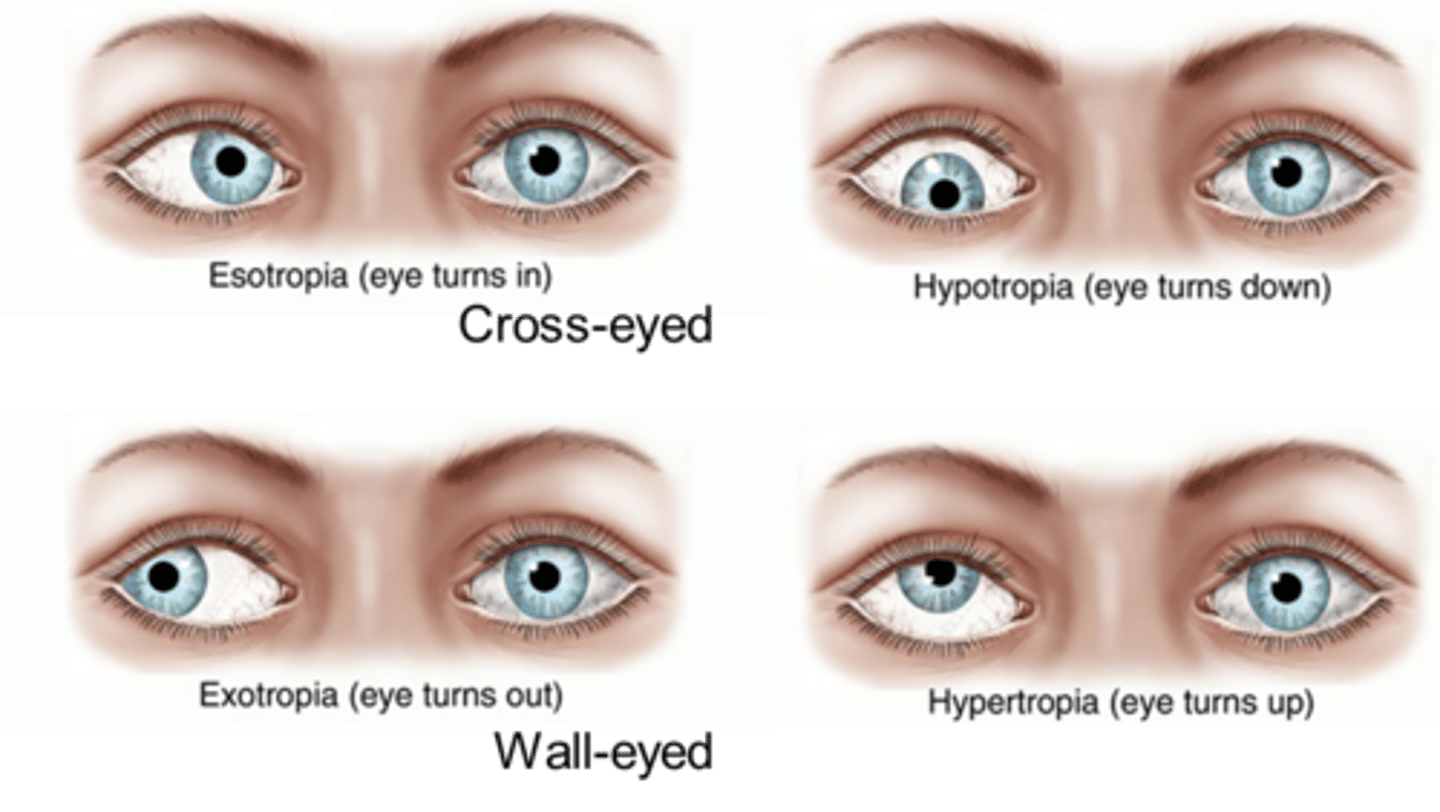
Lazy Eye
Informal term for strabismus resulting in reduced vision
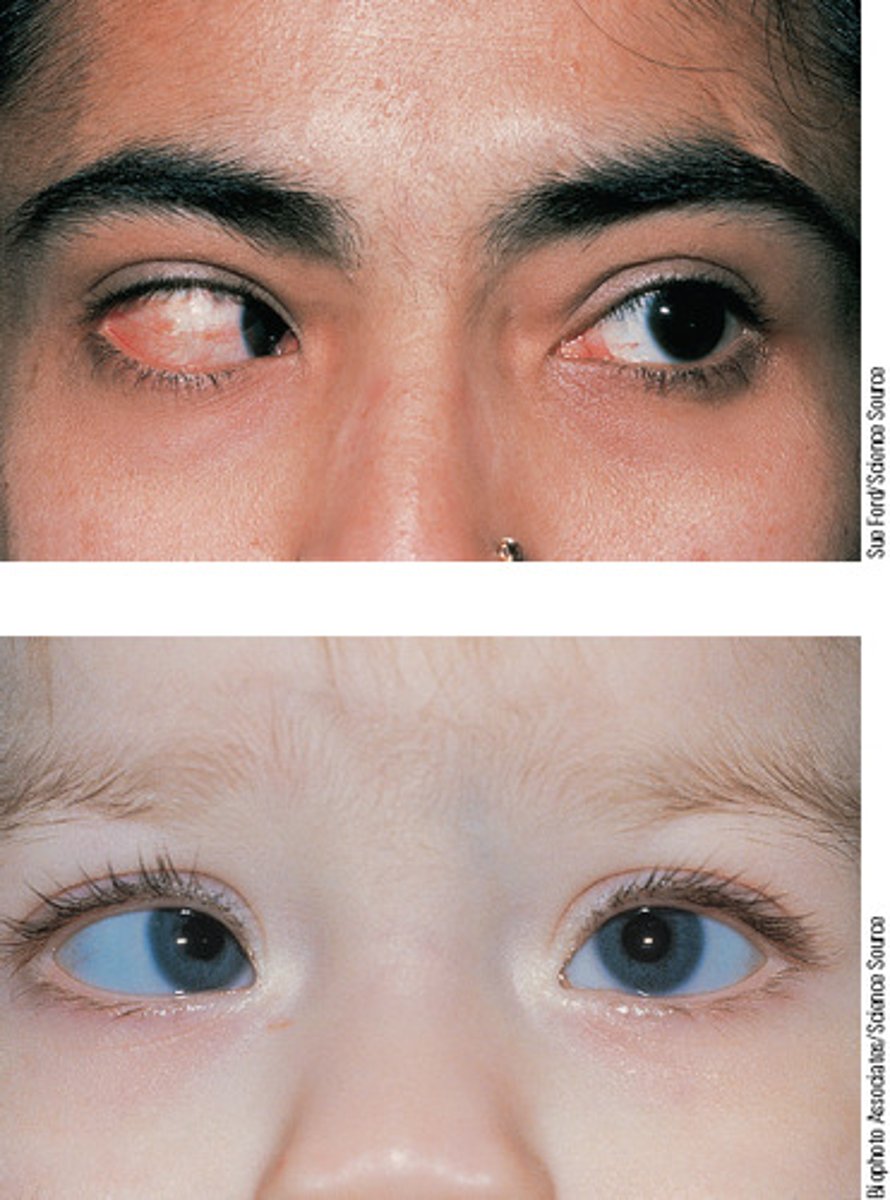
Diplopia
Medical term for double vision

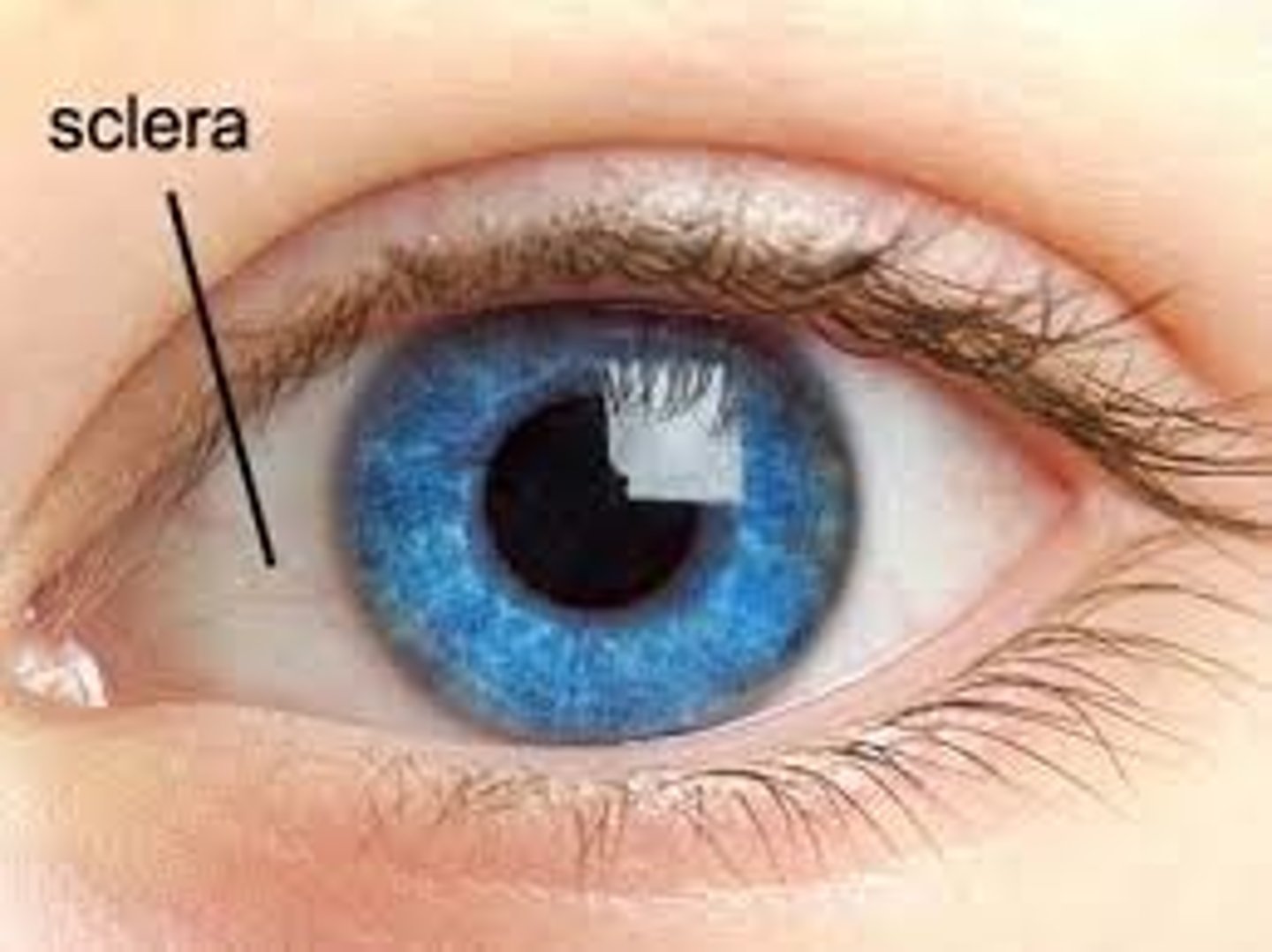
Sclera
White fibrous layer protecting the eye
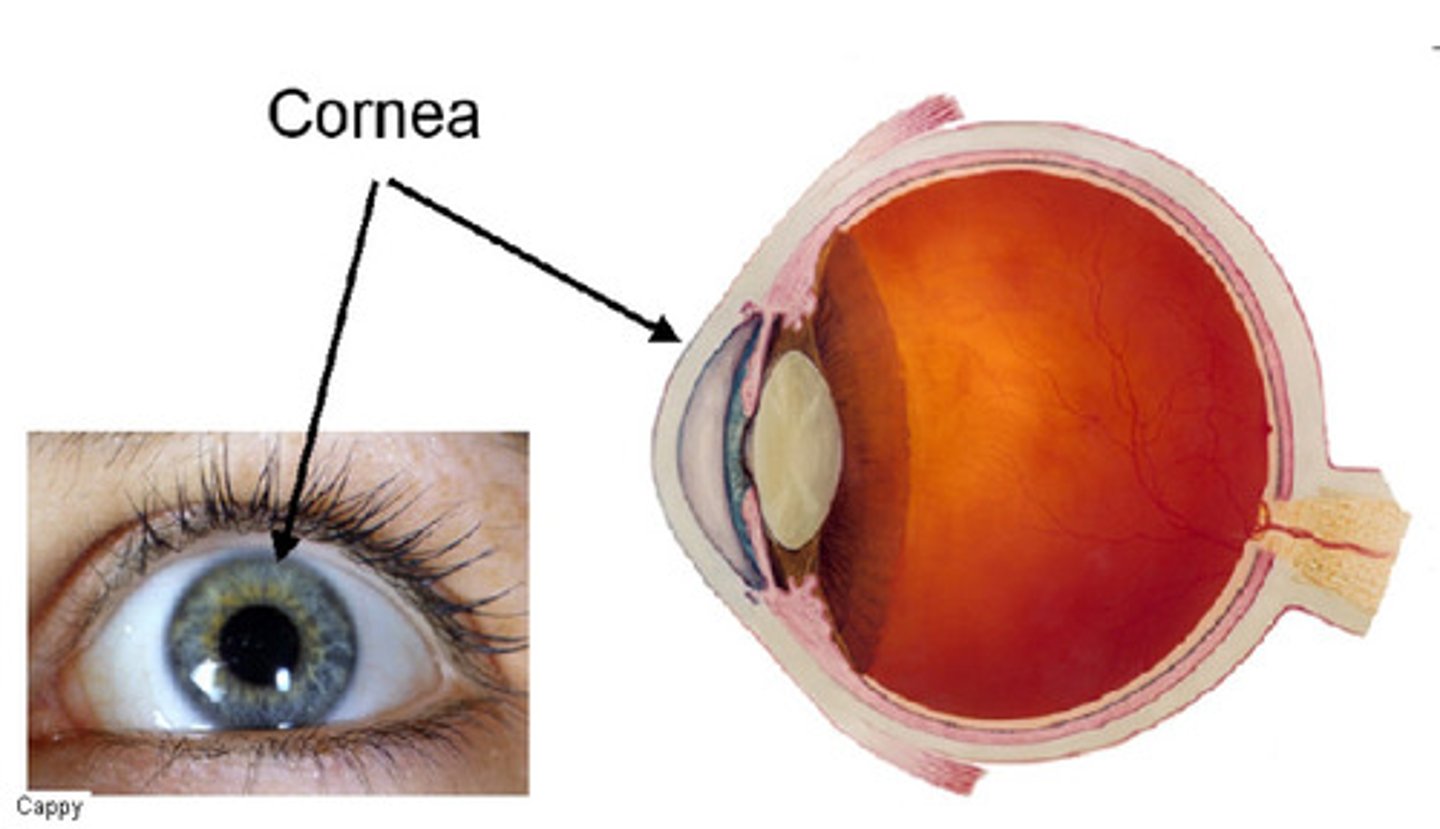
Cornea
Transparent layer covering the front of the eye
Ciliary Bodies
Structure responsible for lens shape changes
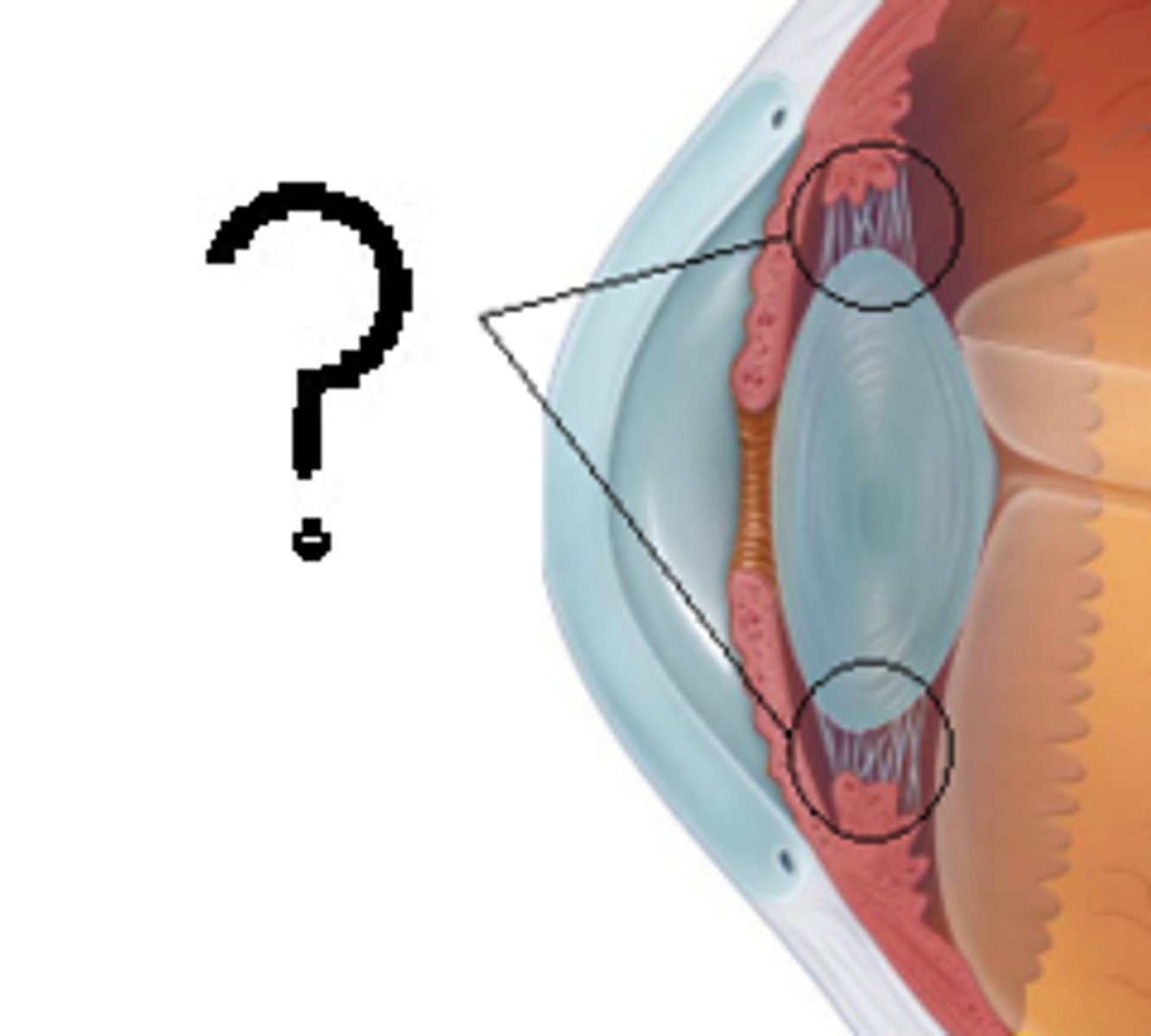
Suspensory Ligaments
Connective tissue attaching the lens to the ciliary body
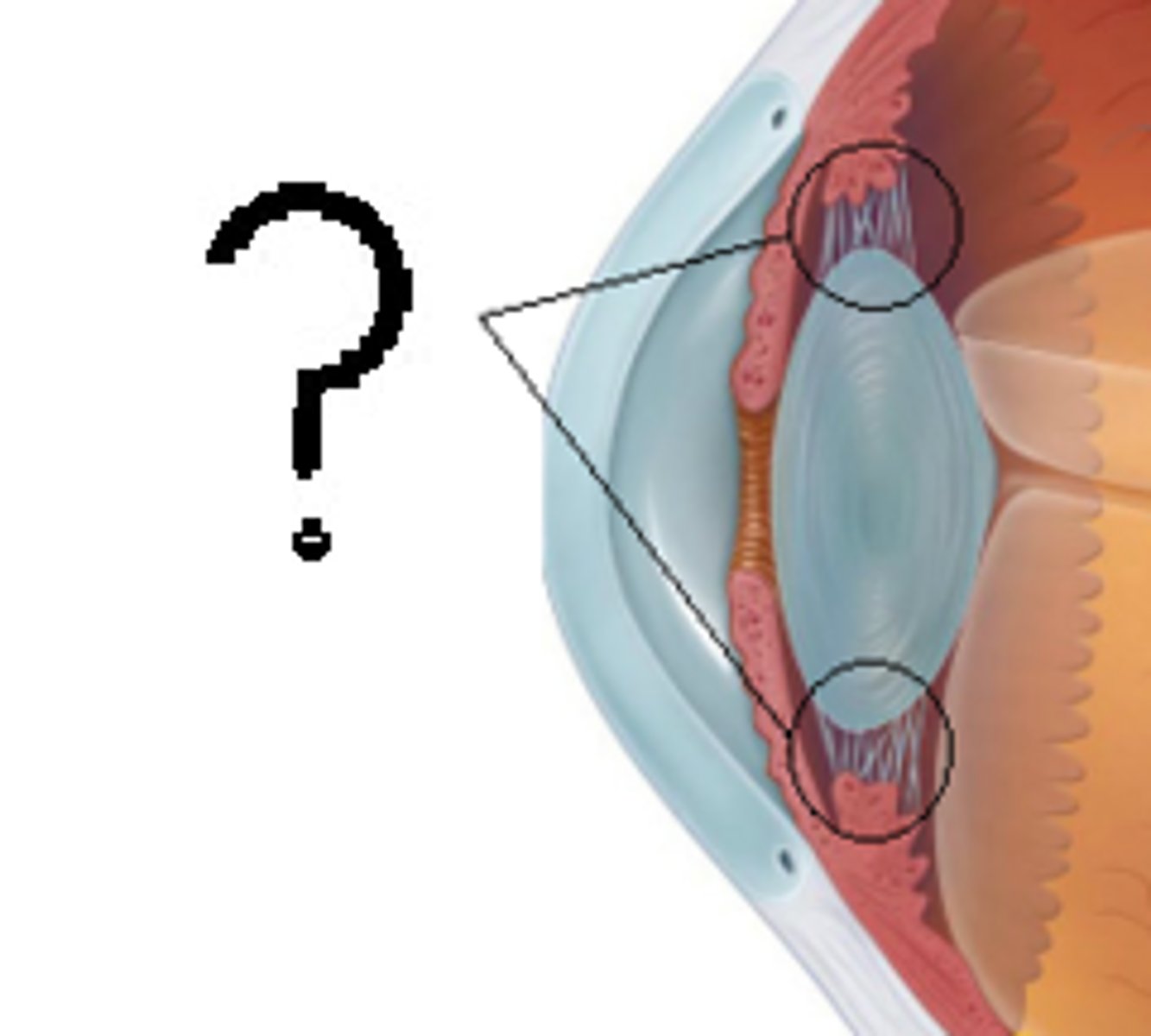
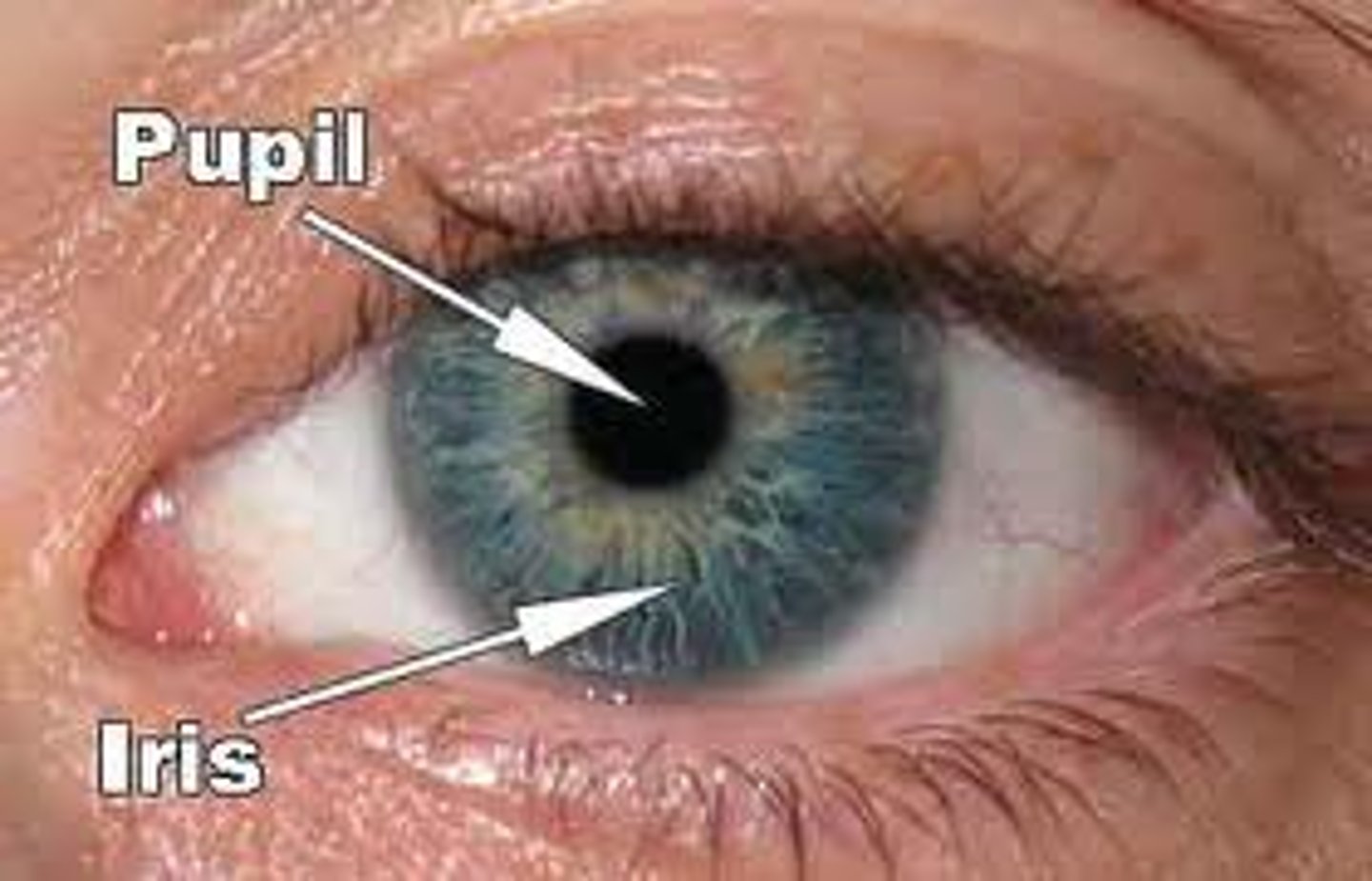
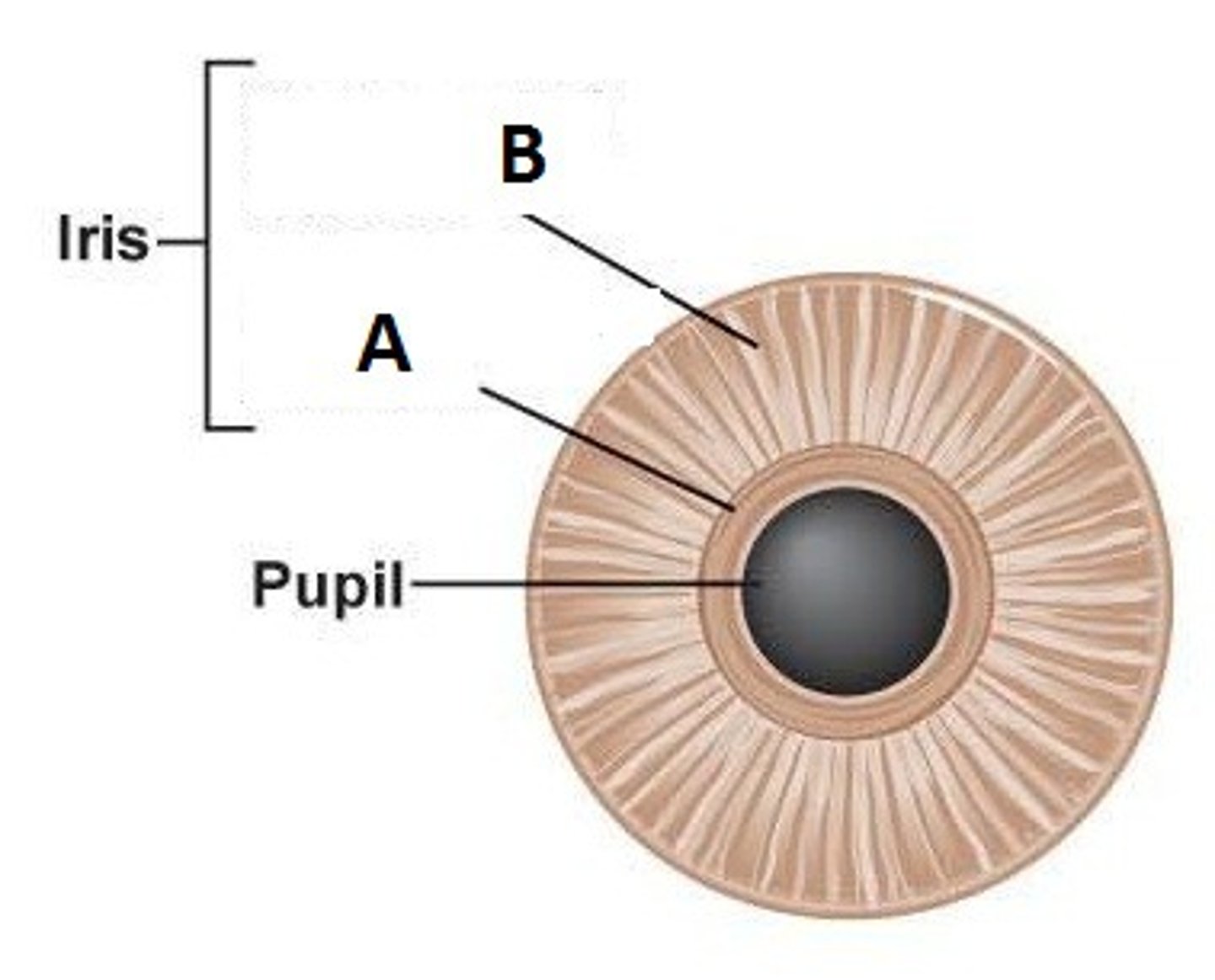
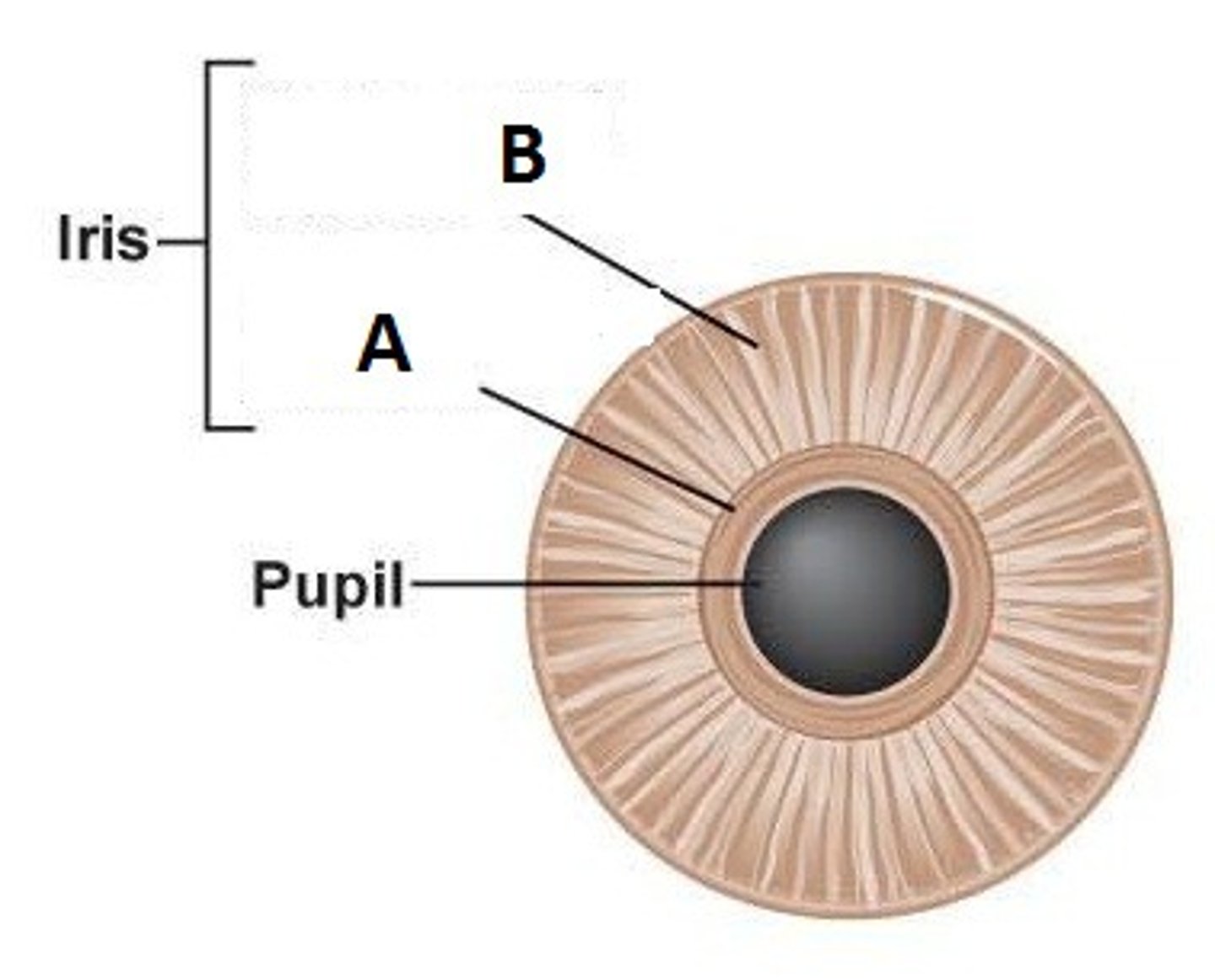
Iris
Colored part of the eye controlling pupil size
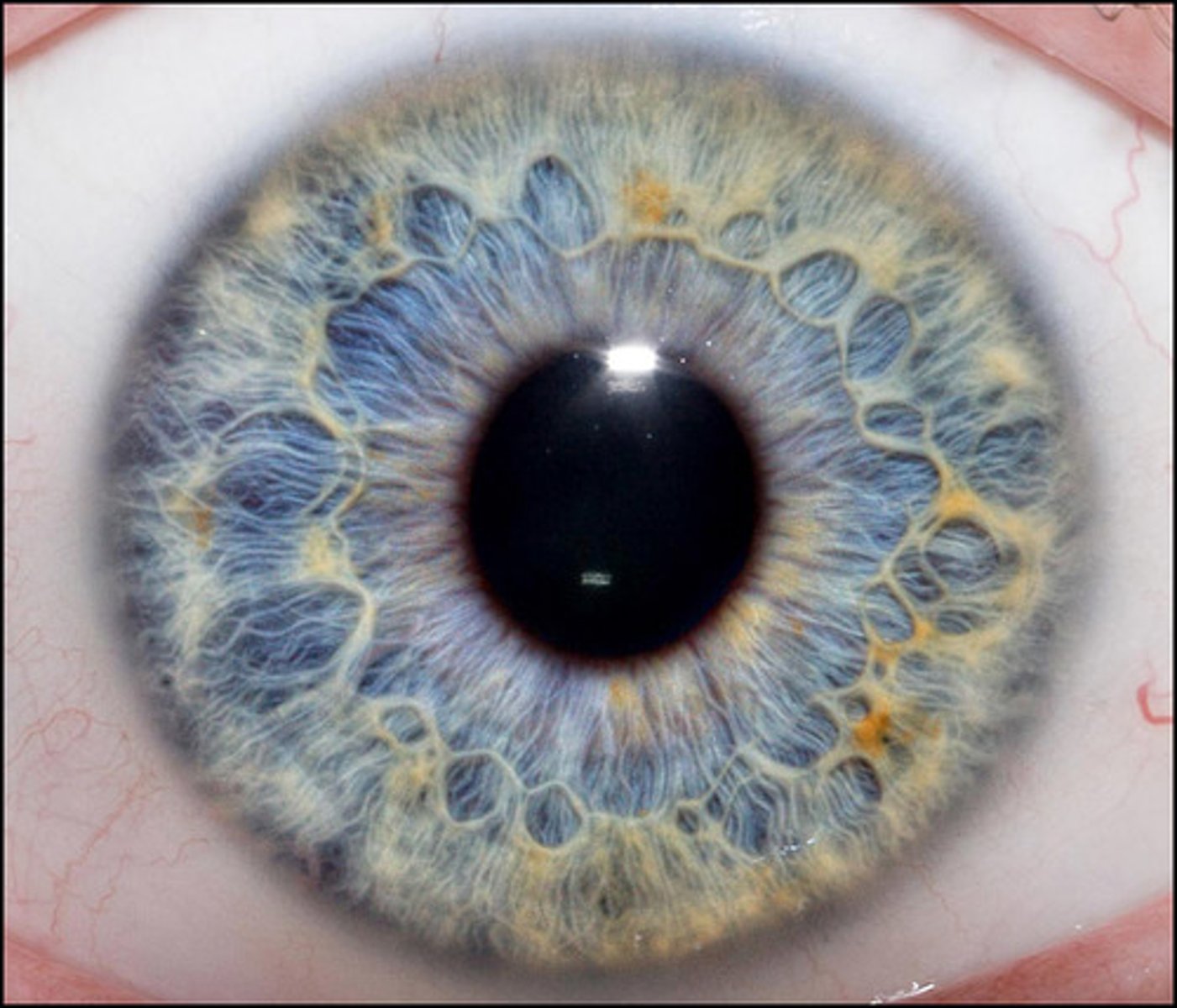
Pupil
Opening allowing light to enter the eye
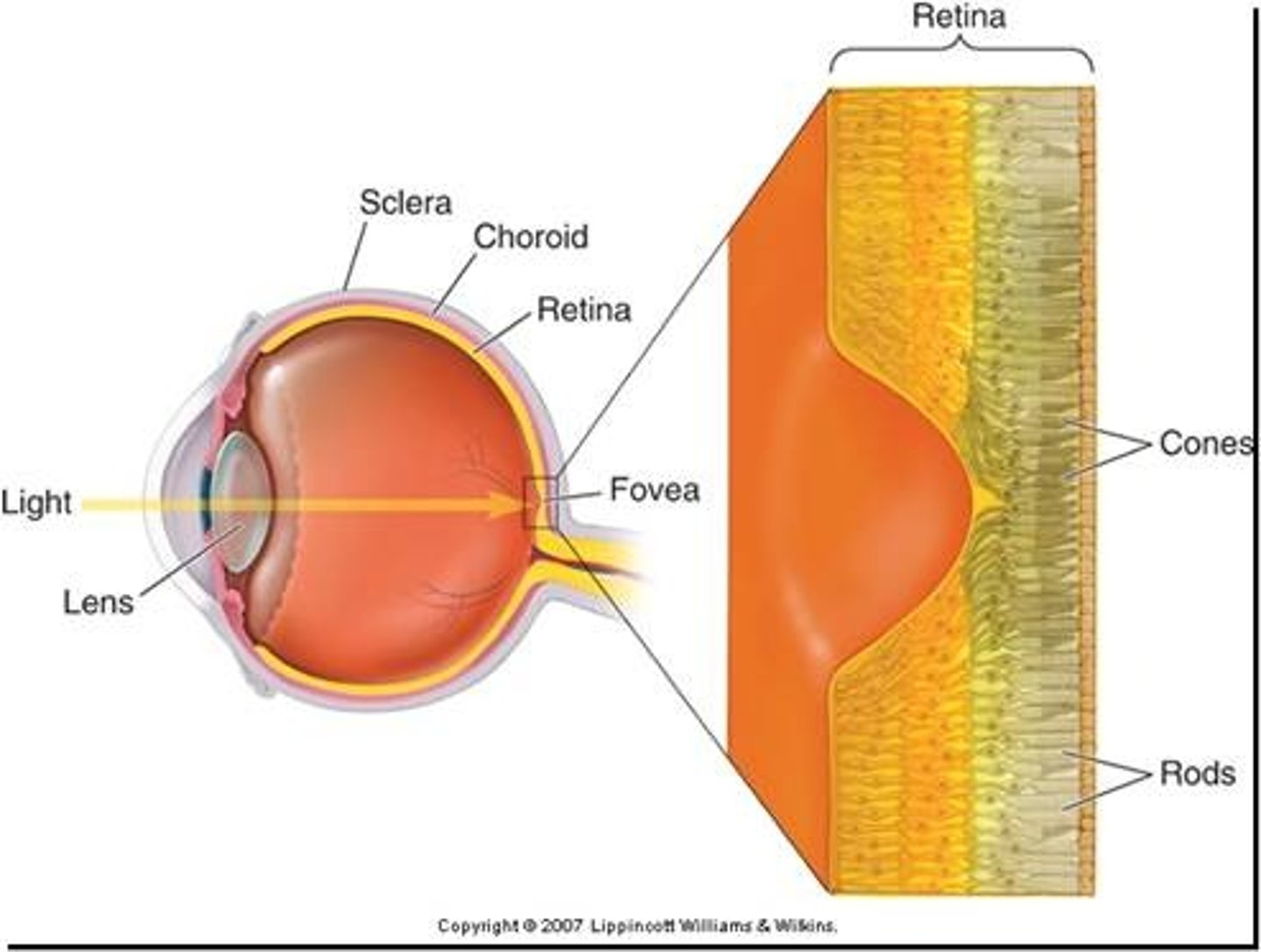
Macula Lutea
Area of high cone cell concentration for visual acuity
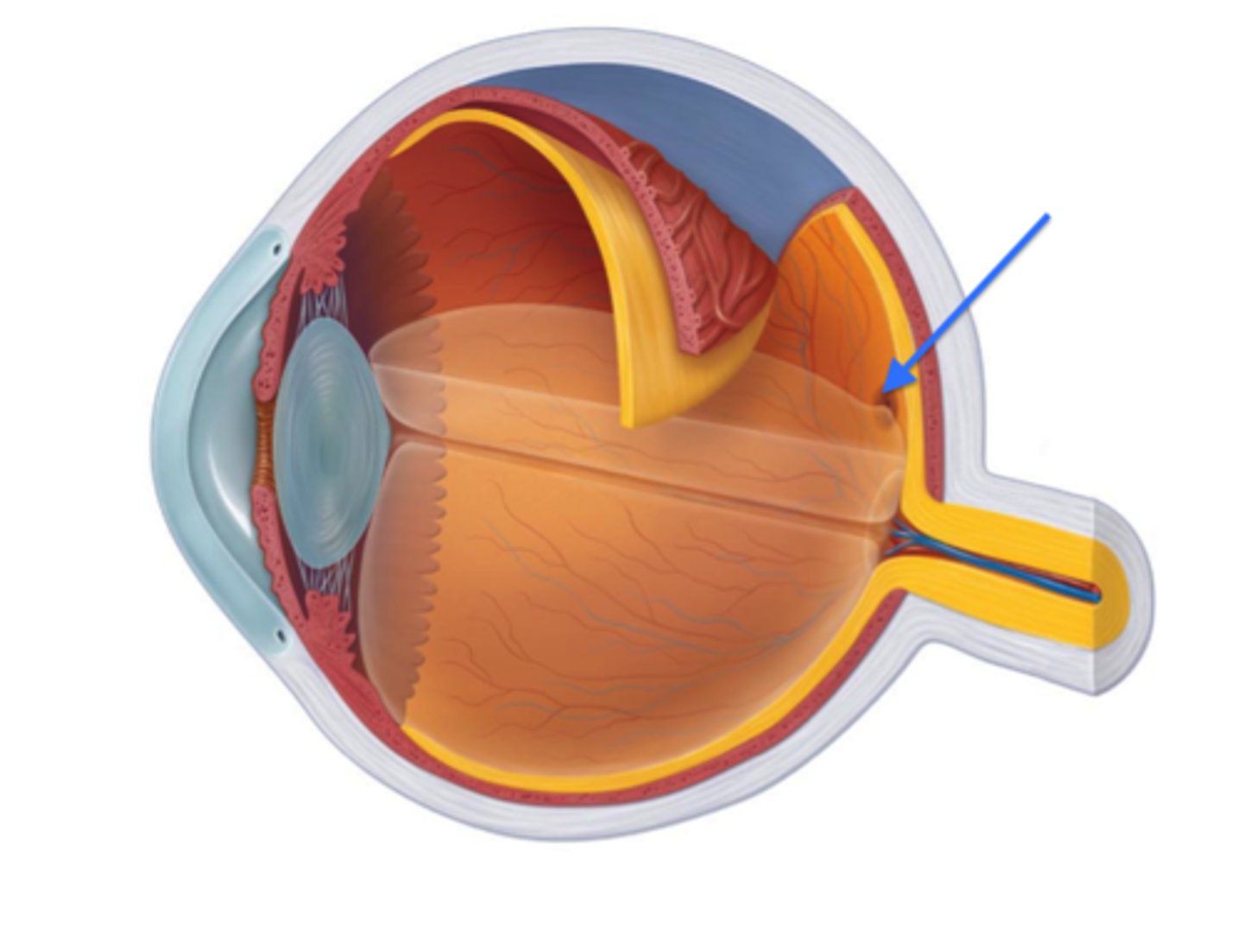
Fovea Centralis
Central area of the macula lutea with the highest visual acuity
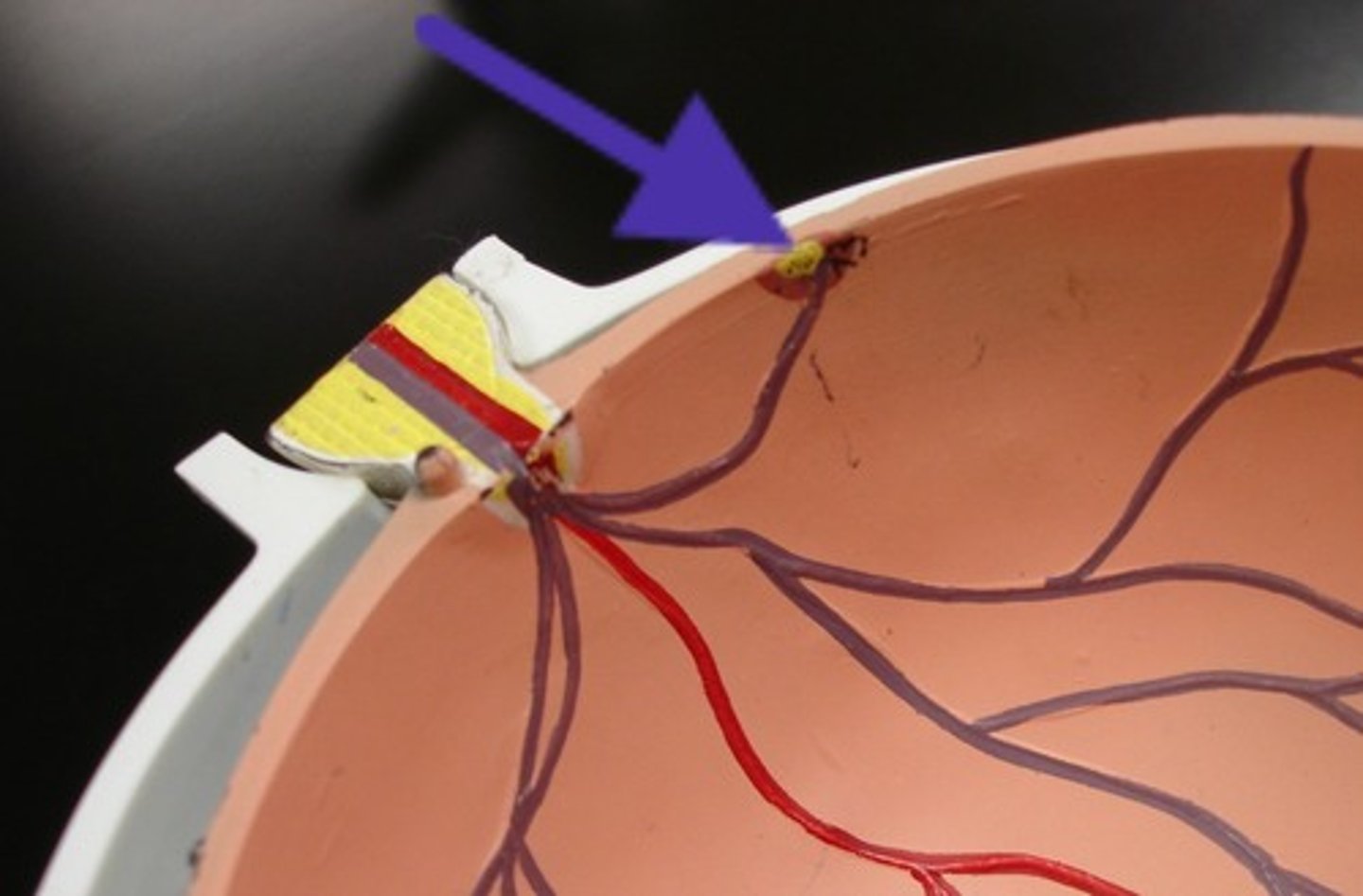
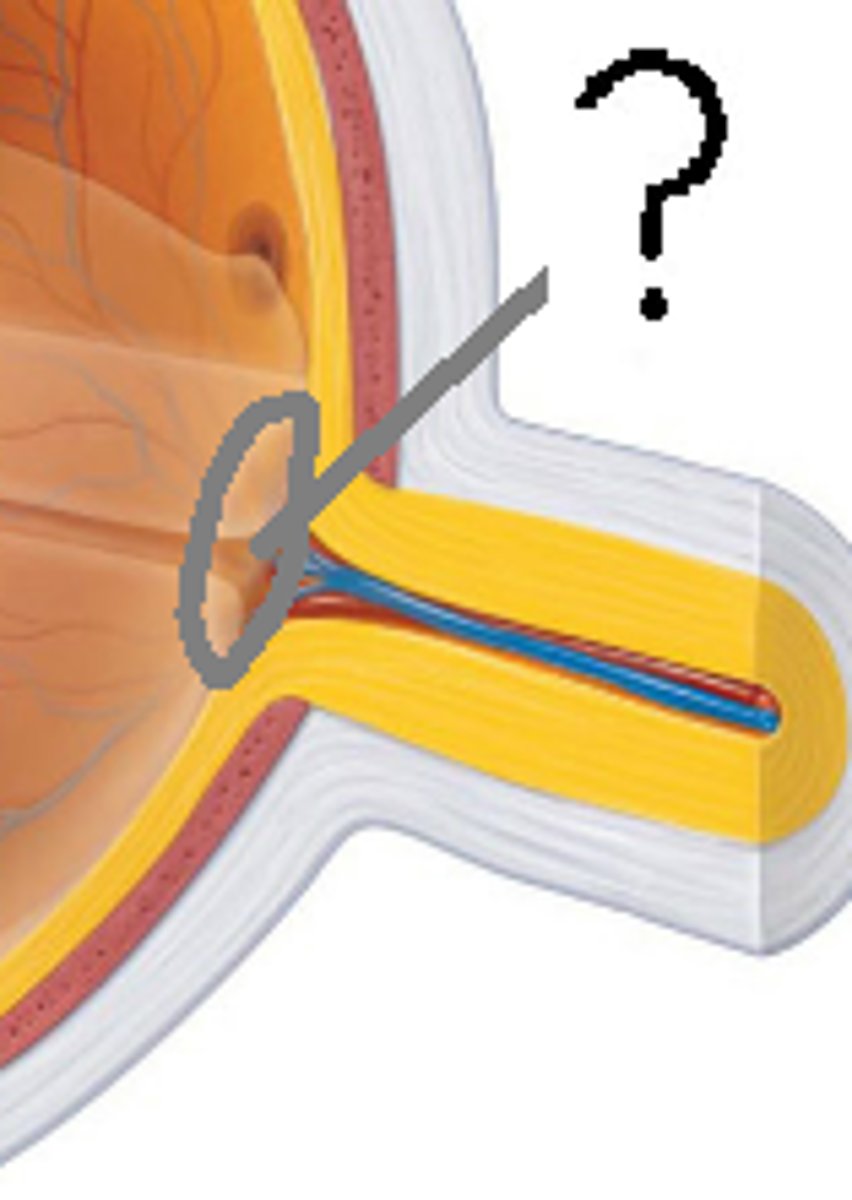
Optic Disc
Blind spot where the optic nerve exits the eye
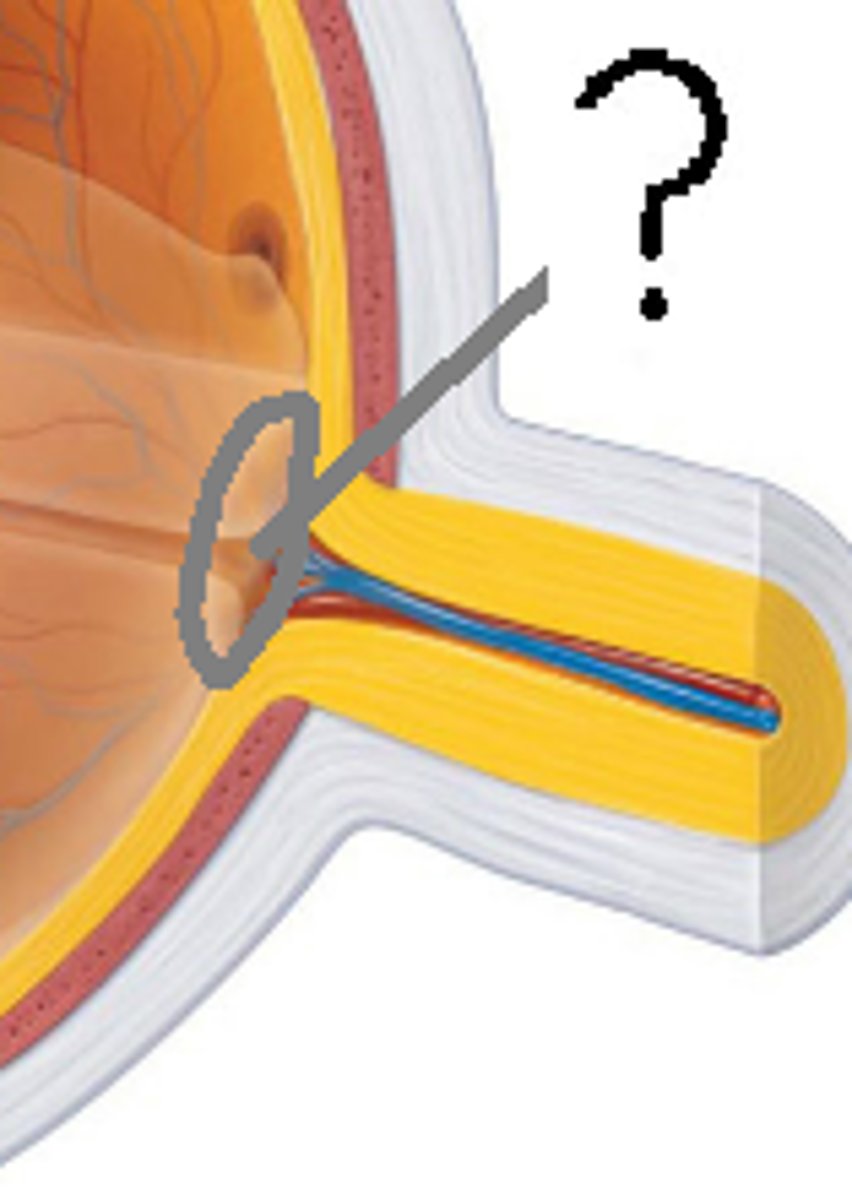
Retina
Innermost layer containing photoreceptor cells
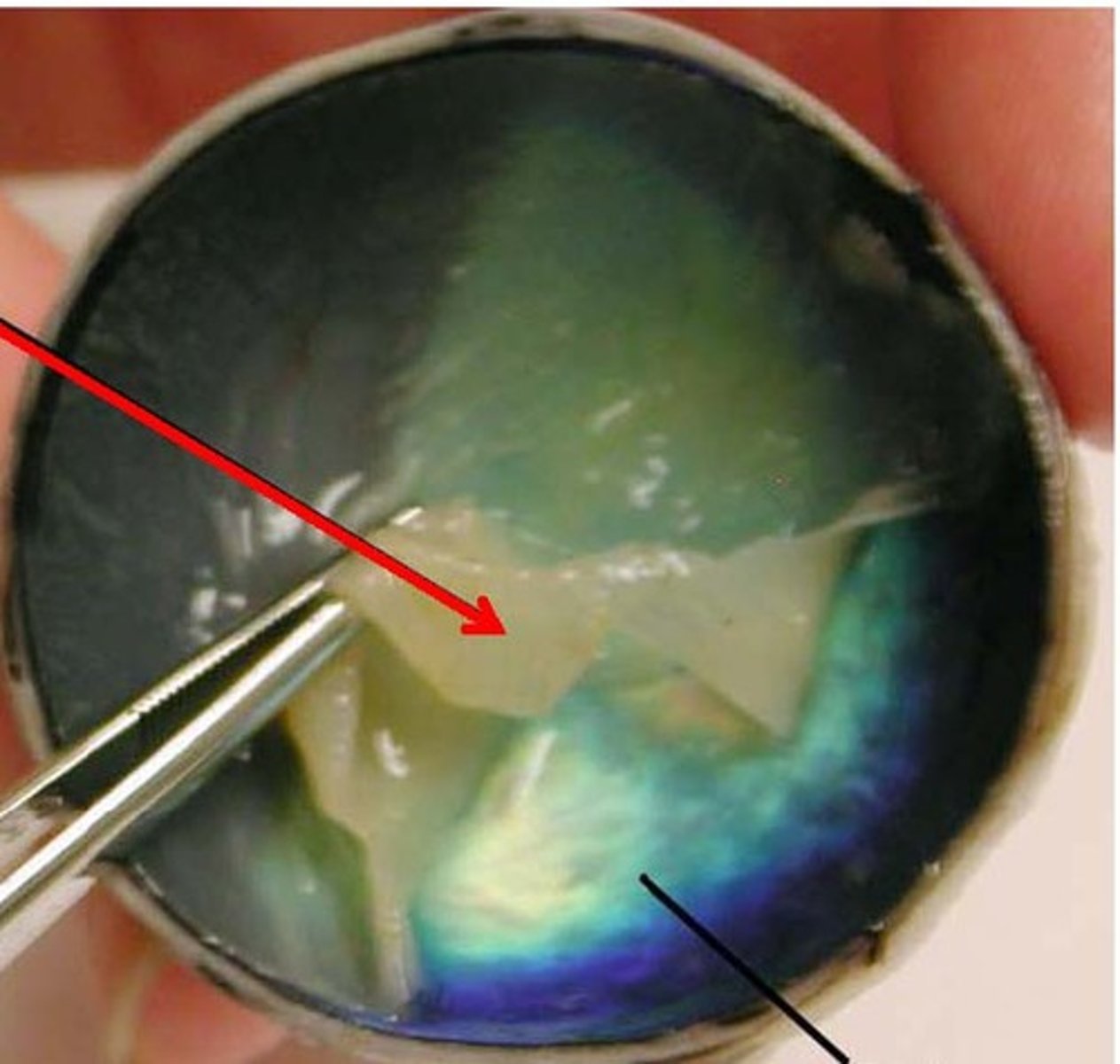
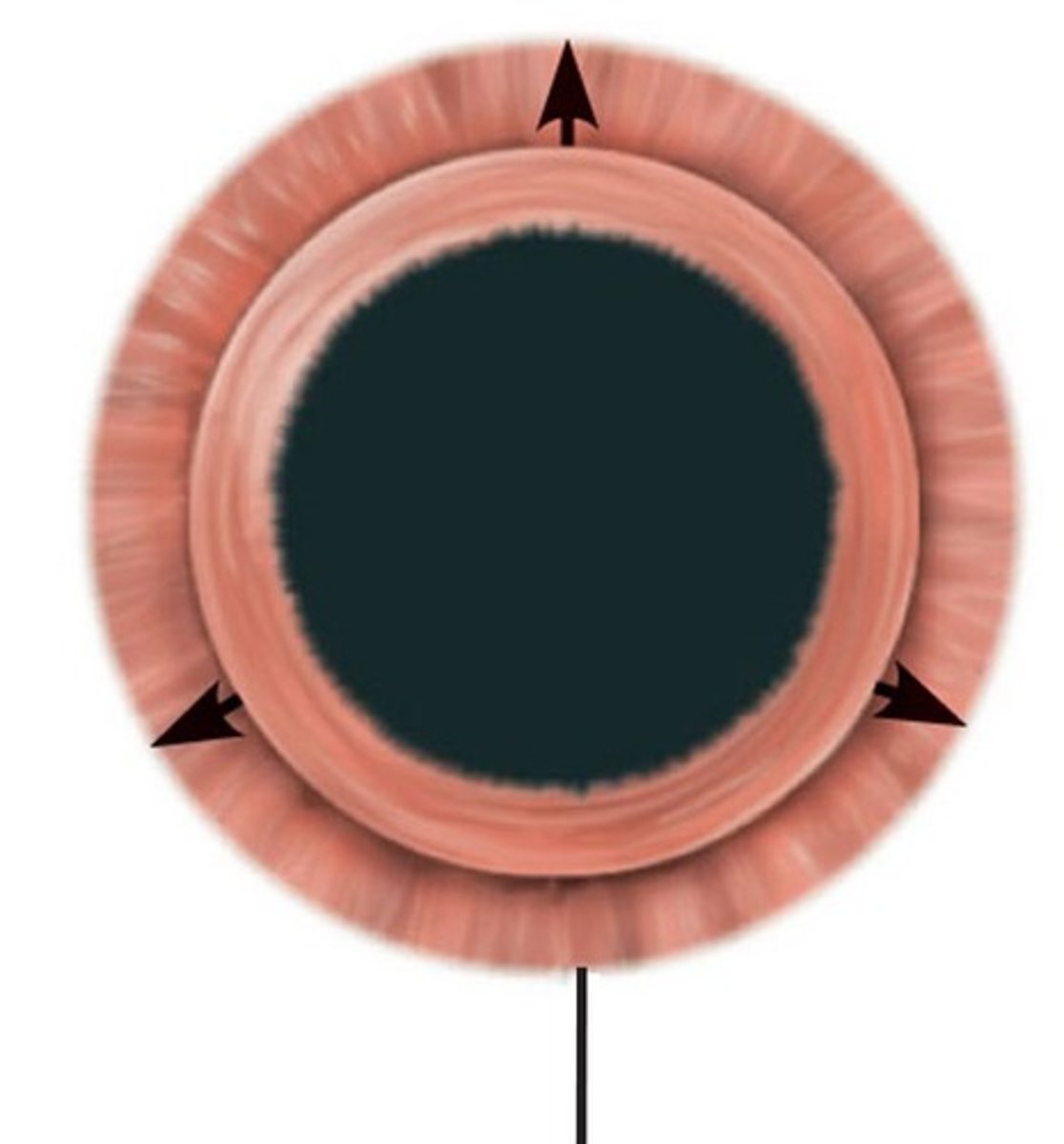
Pupillary Sphincter Muscle
Muscle contracting to constrict the pupil in bright light
Pupillary Dilator Muscle
Muscle contracting to dilate the pupil in low light
Parasympathetic Control
Regulates pupil size based on light intensity
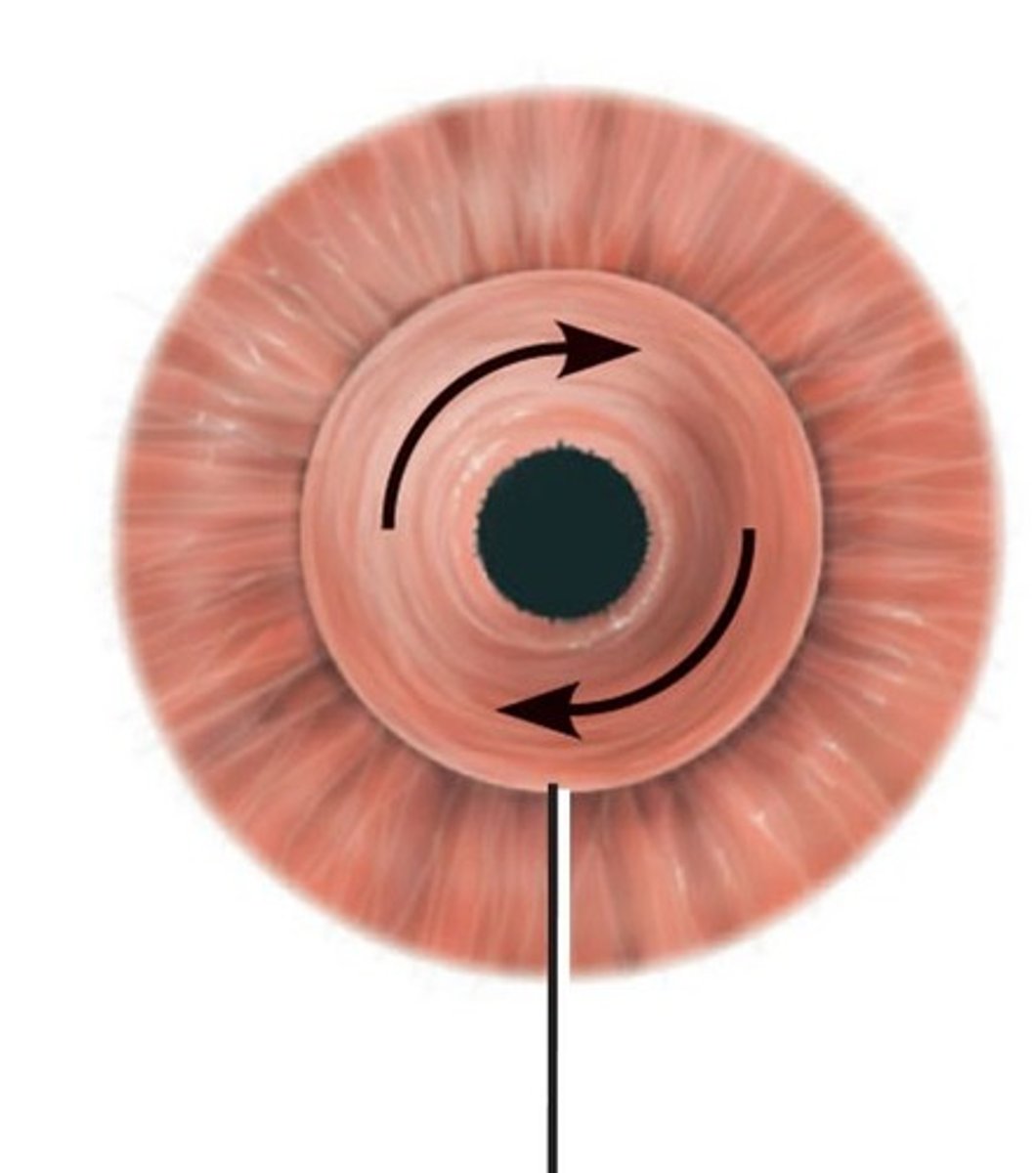

Sympathetic Control
Involved in pupil dilation in response to dark environments
Blind Spot
Area on the retina lacking photoreceptor cells
Lens
Structure responsible for focusing light onto the retina
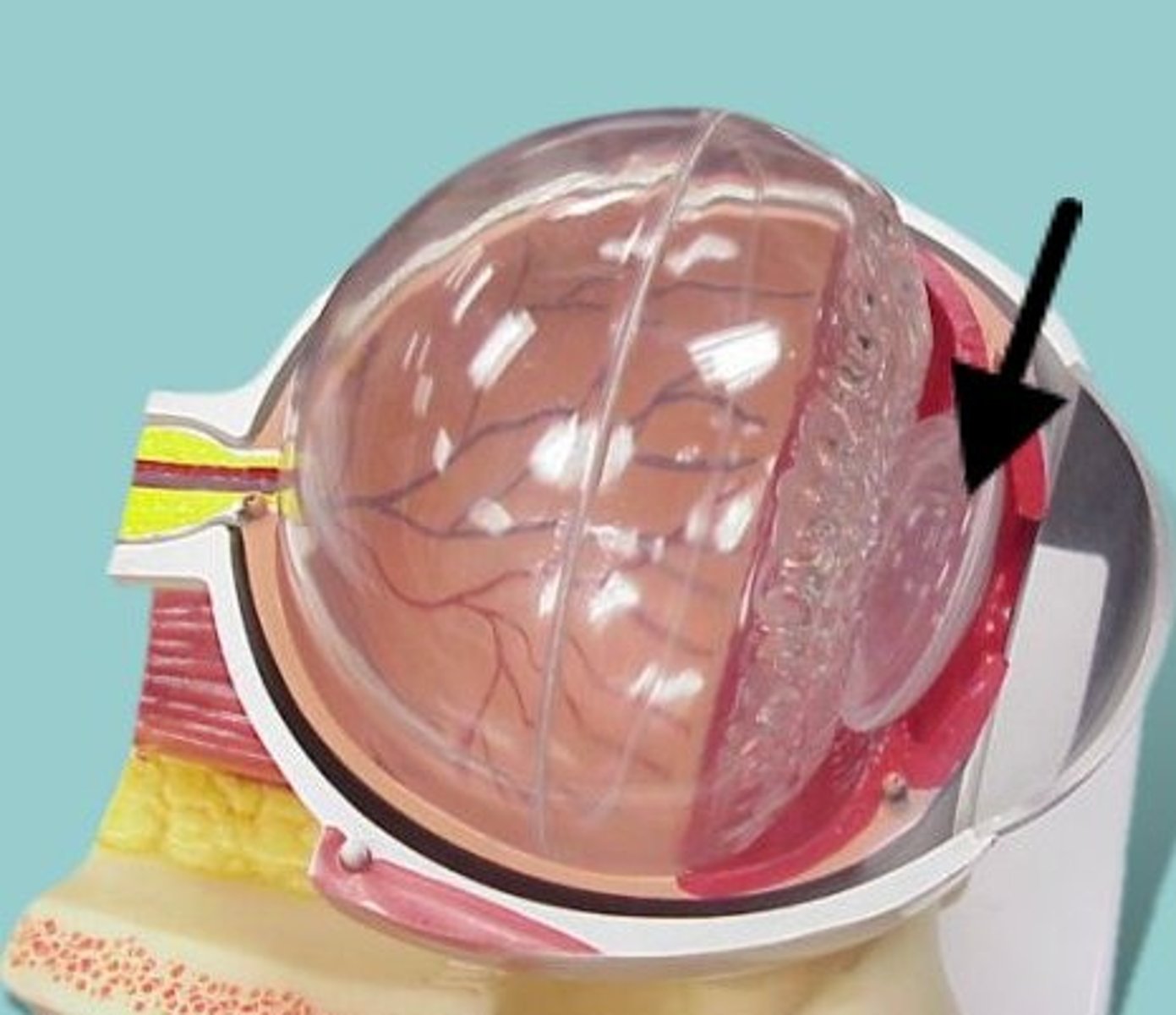
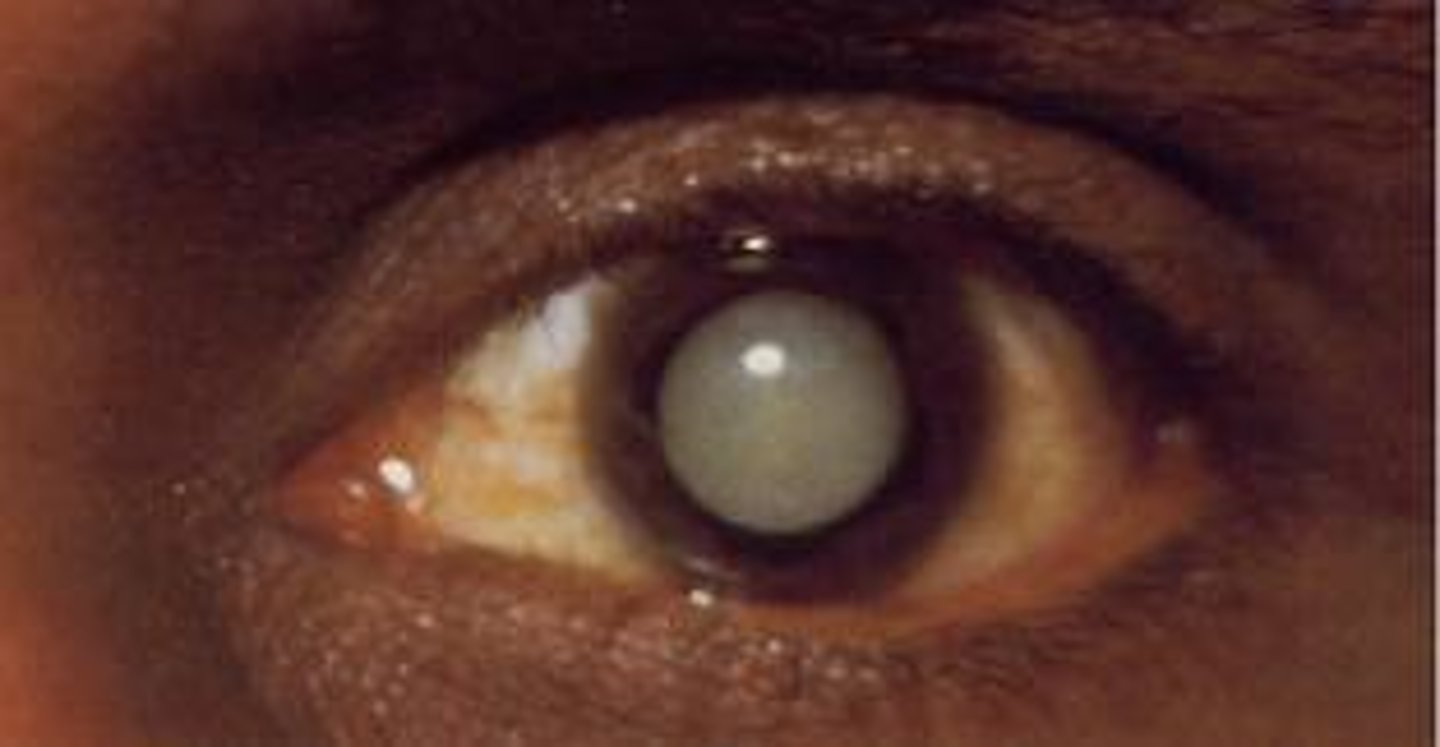
Cataracts
Cloudiness or distortion of the eye's lens
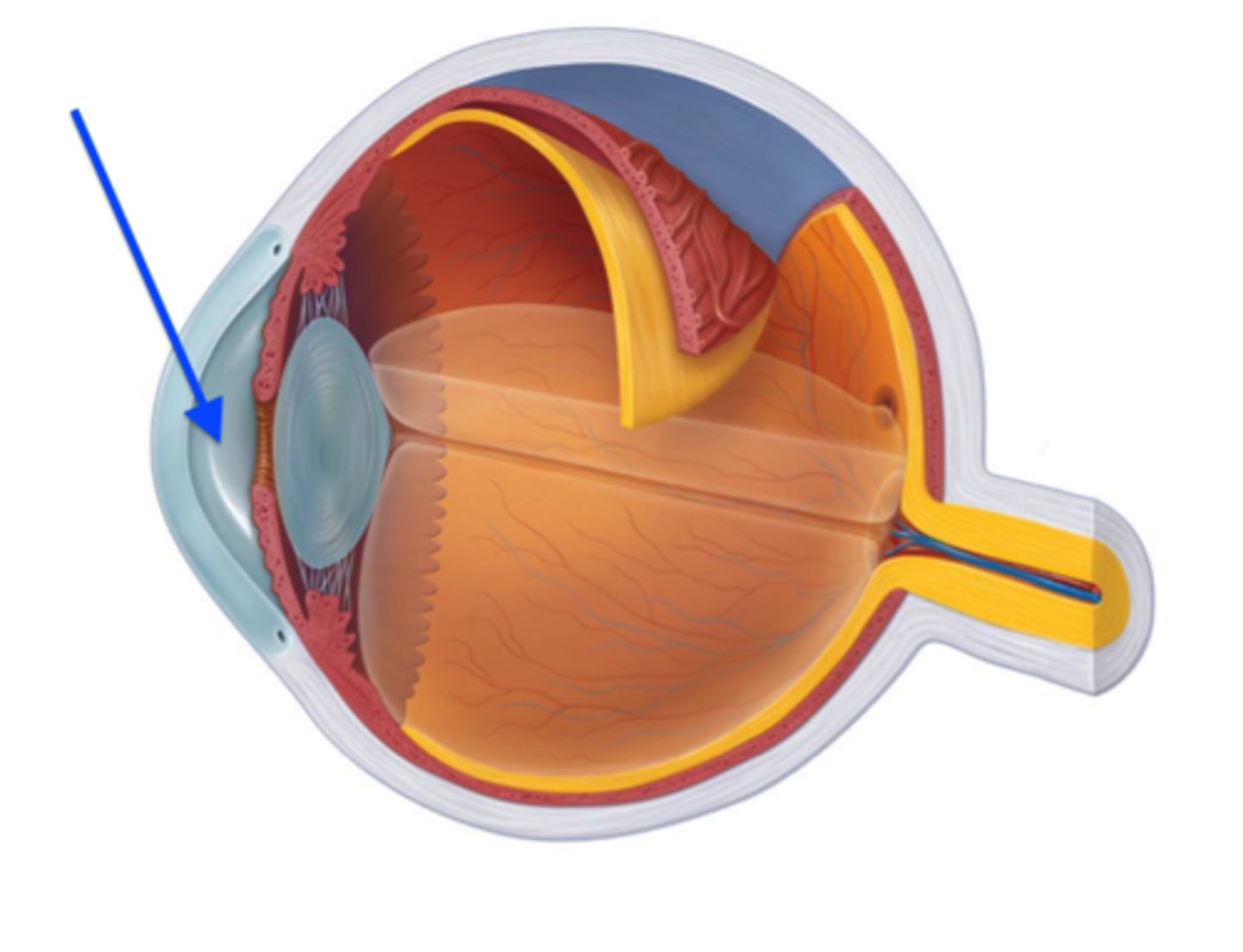
Aqueous Humor
Fluid filling the front and back chambers of the eye
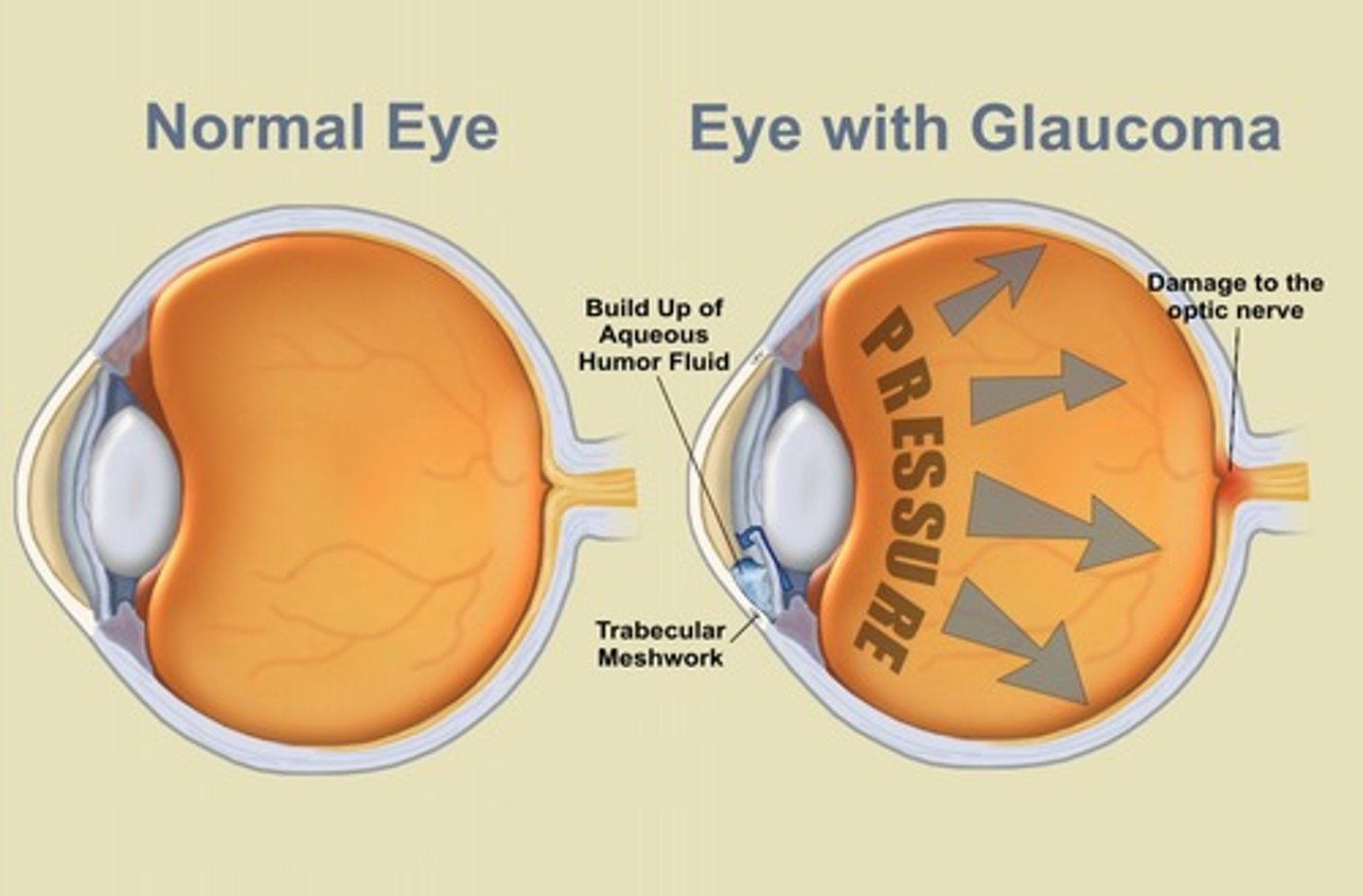
Glaucoma
Condition with increased pressure in the eyeball
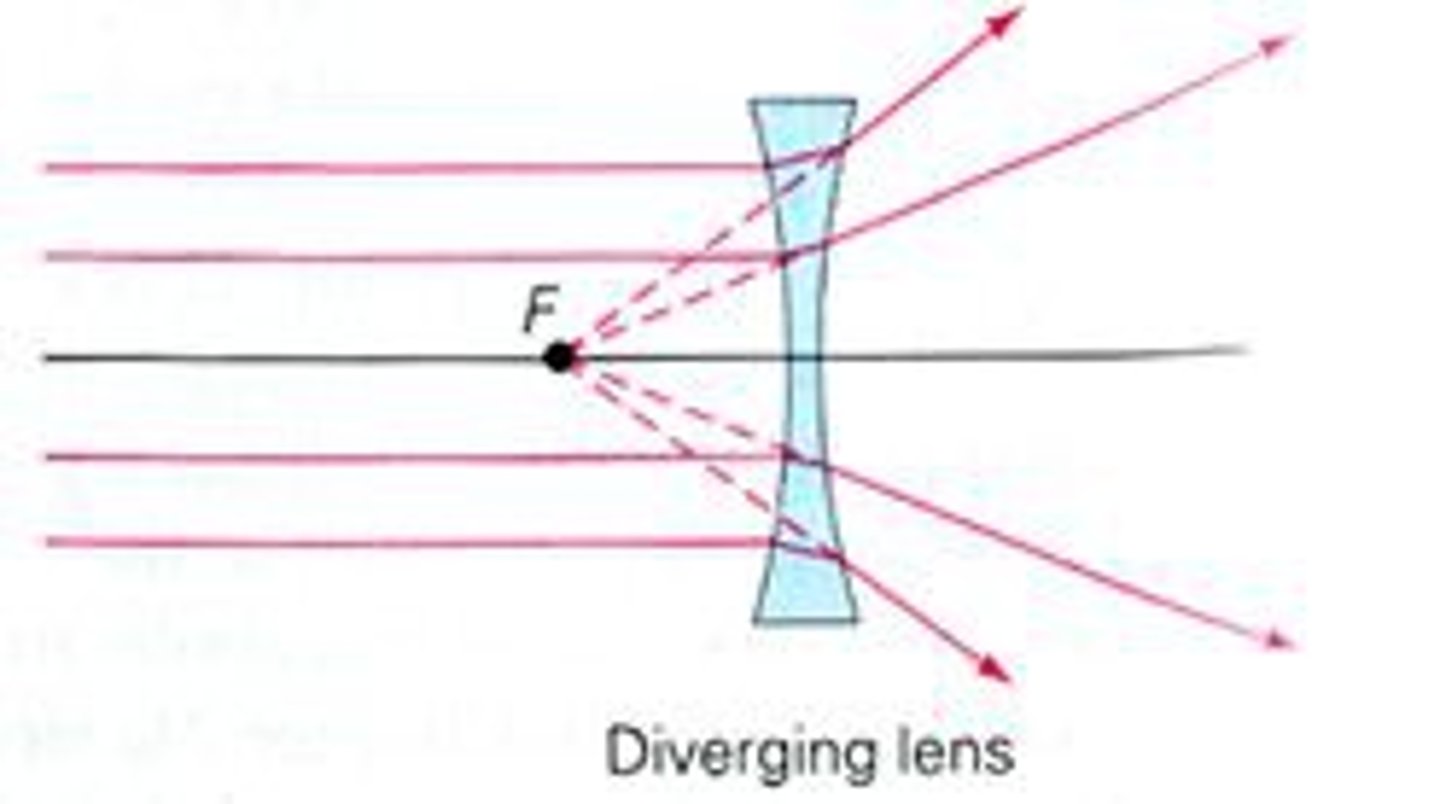
Concave Lens
Lens that diverges light rays outward
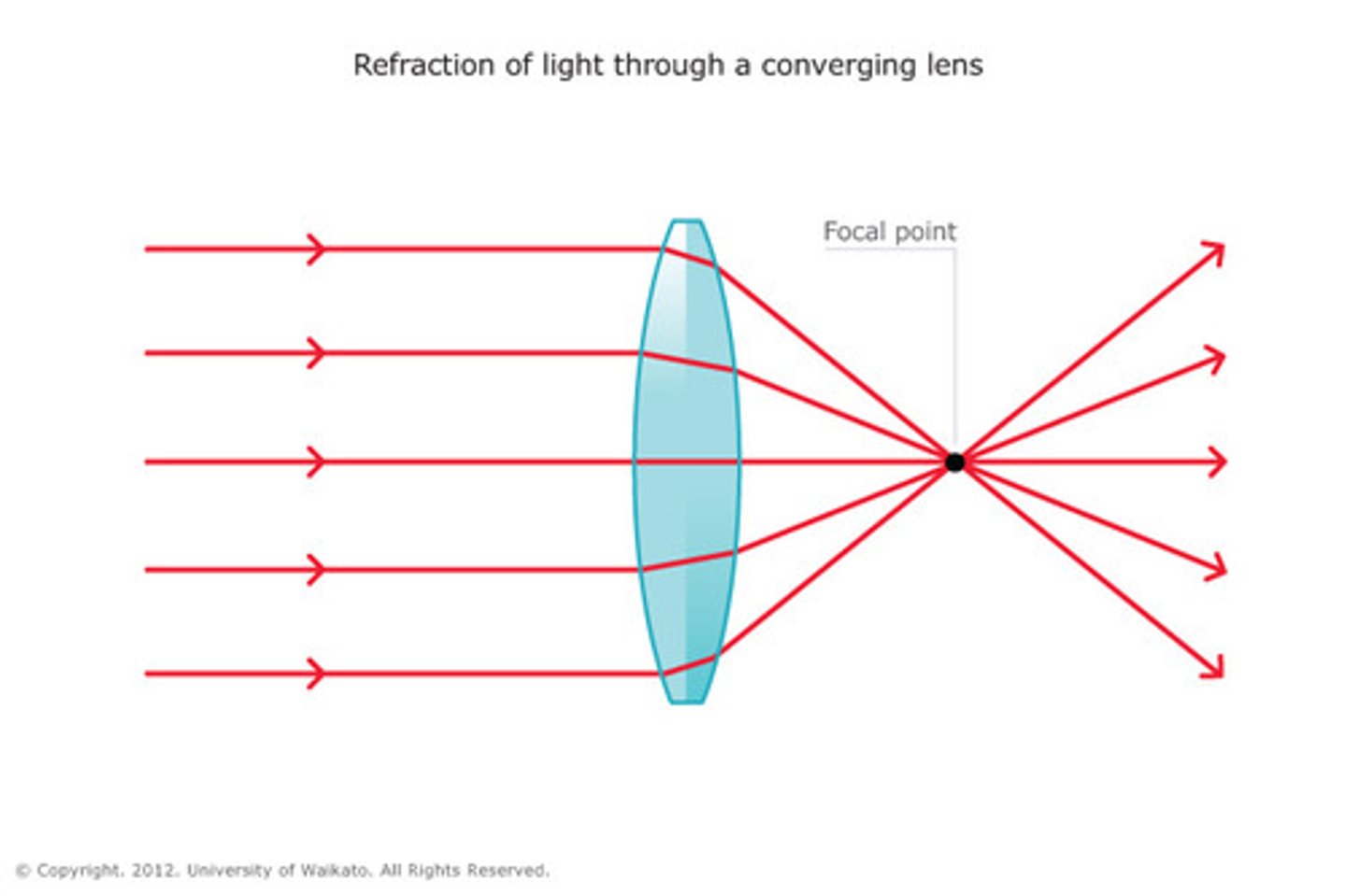
Convex Lens
Lens that converges light rays inward
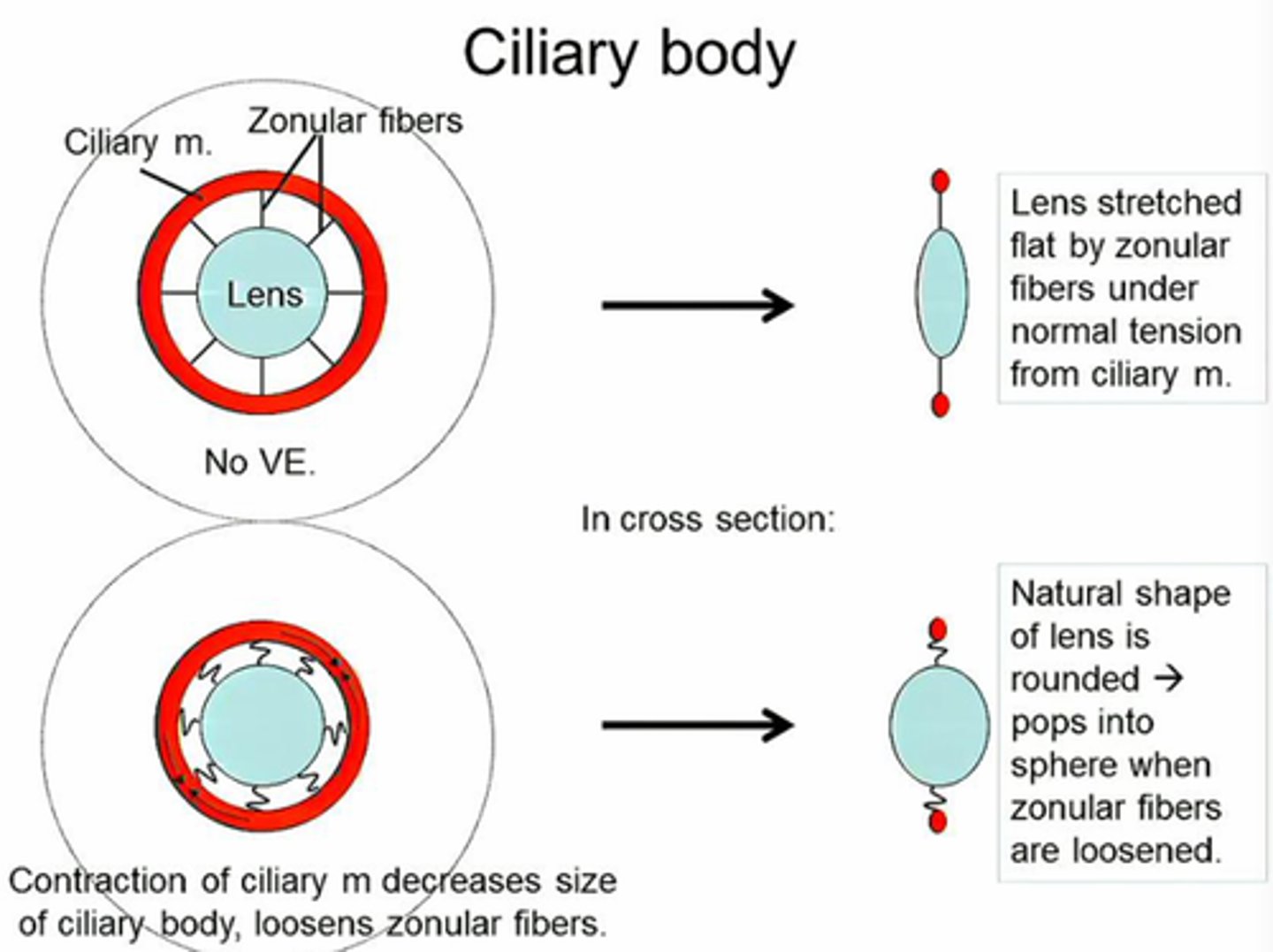
Accommodation
Eye's ability to adjust focus for near or far objects
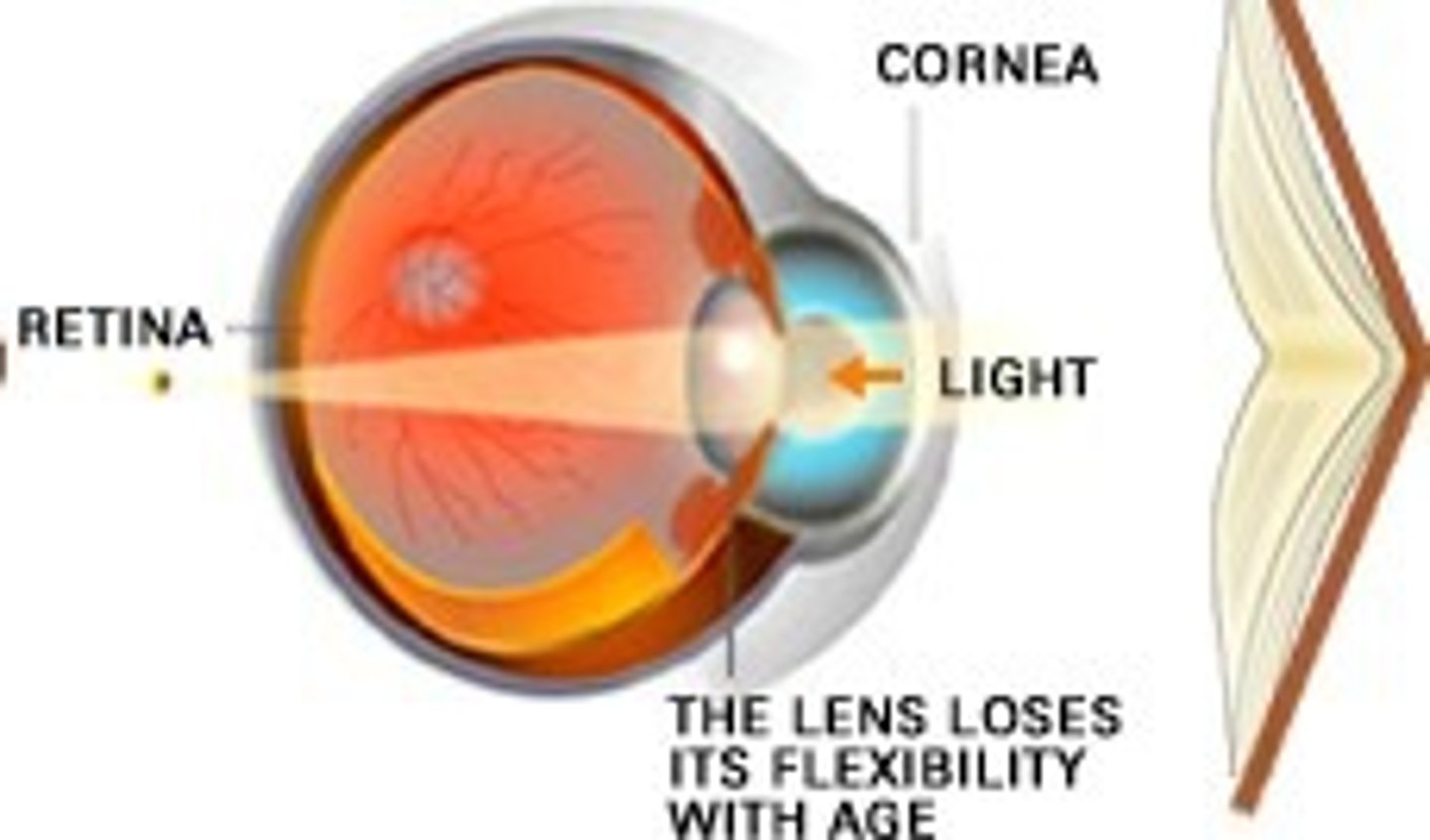
Presbyopia
Age-related loss of near vision
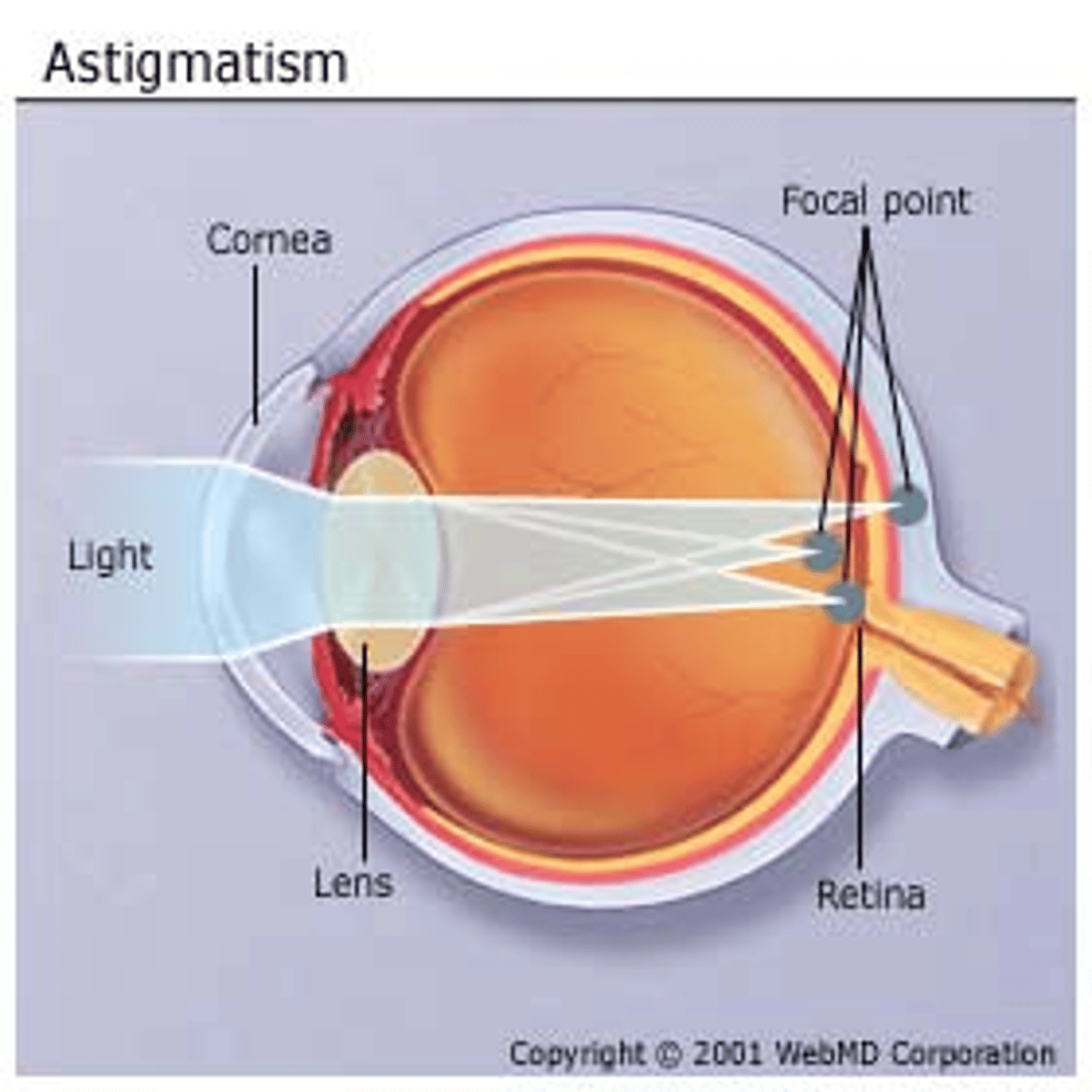
Astigmatism
Irregular curvature of the lens or cornea
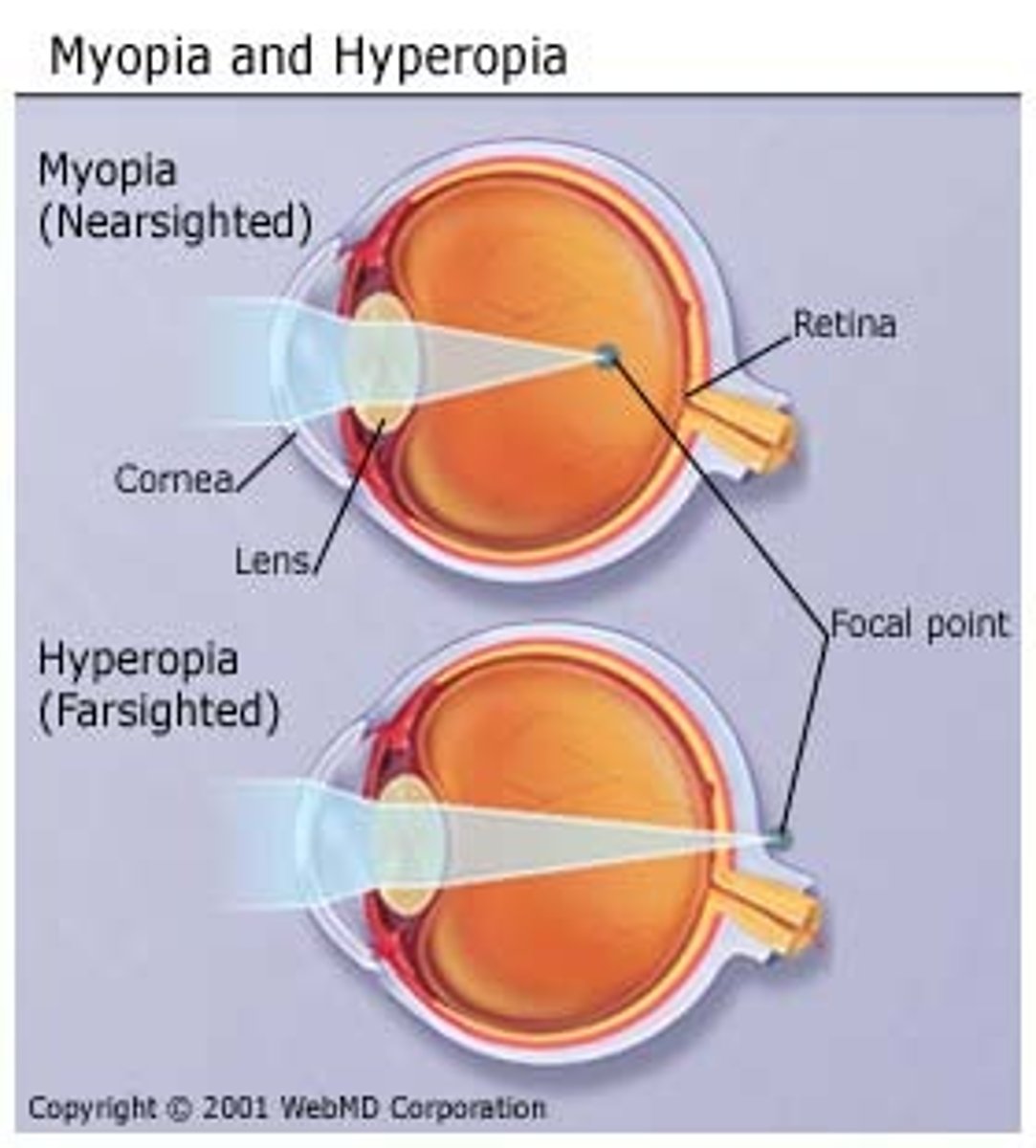
Farsightedness
Condition where light focuses behind the retina

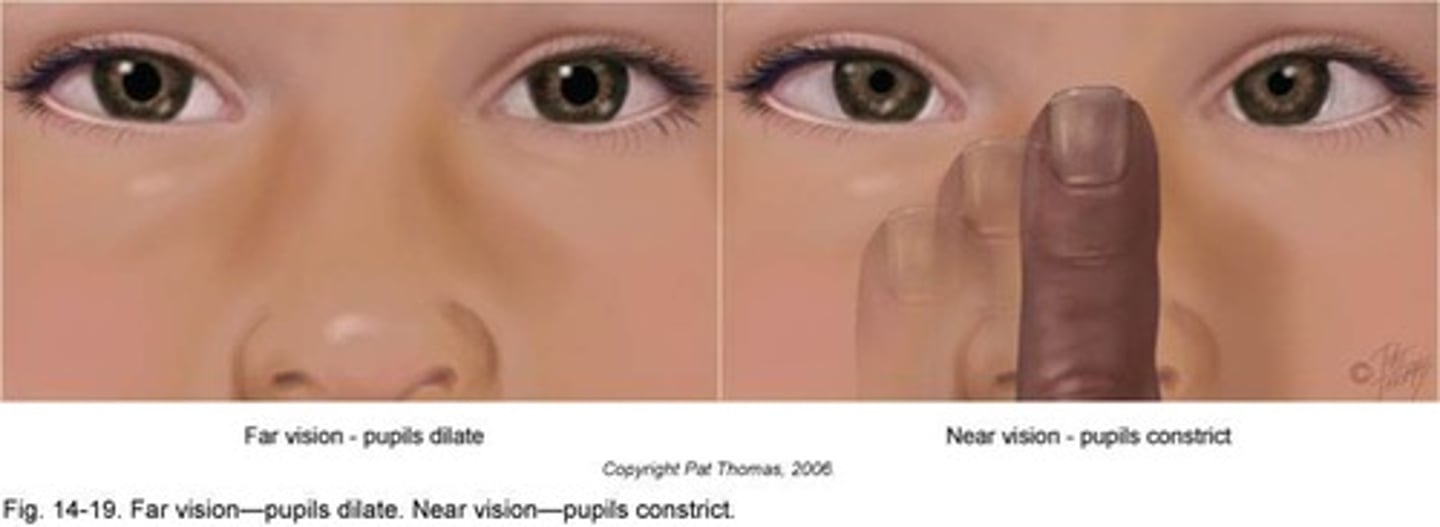
Near Point Accommodation
Ability to focus on objects close to the eye
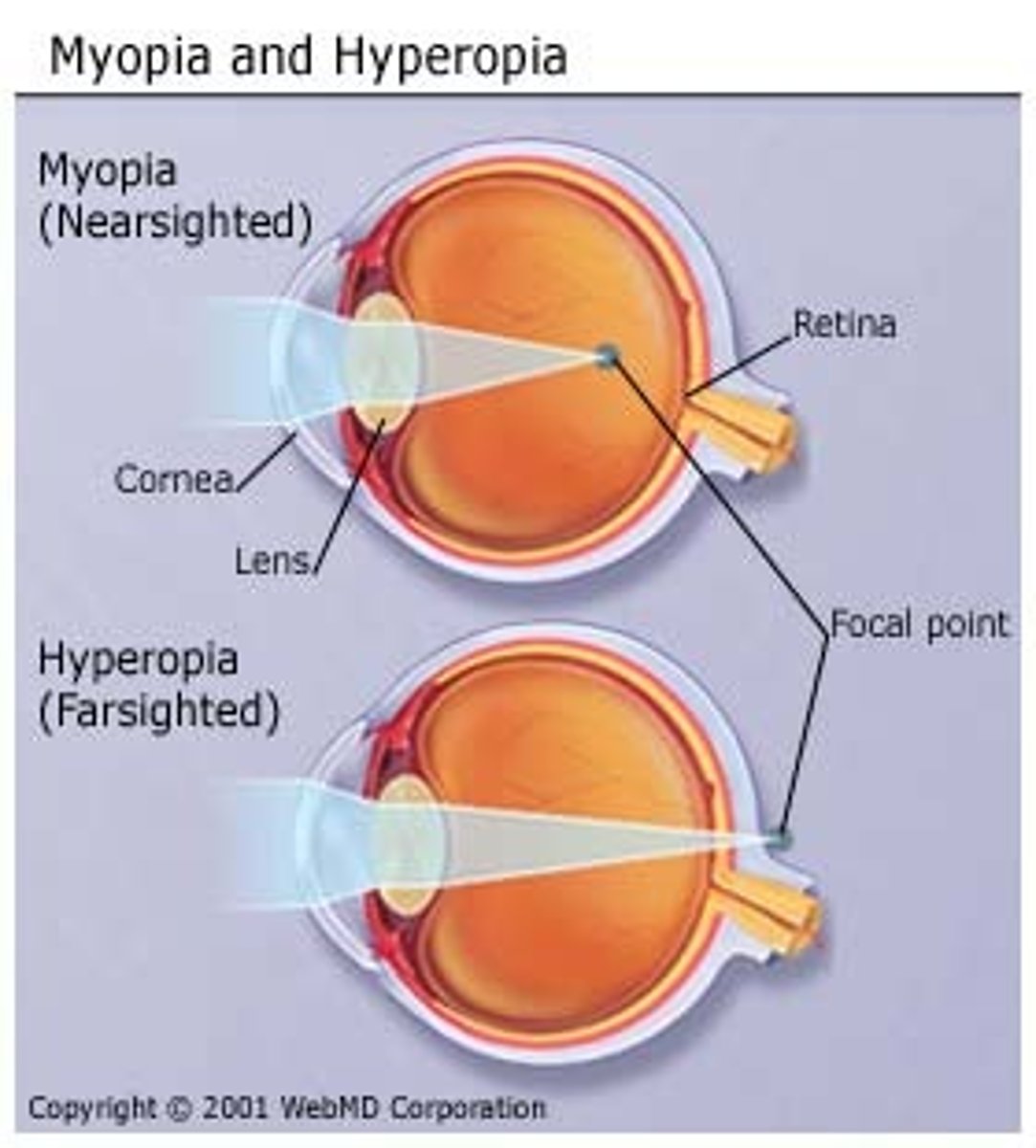
Hyperopia
Farsightedness requiring a convex lens for correction
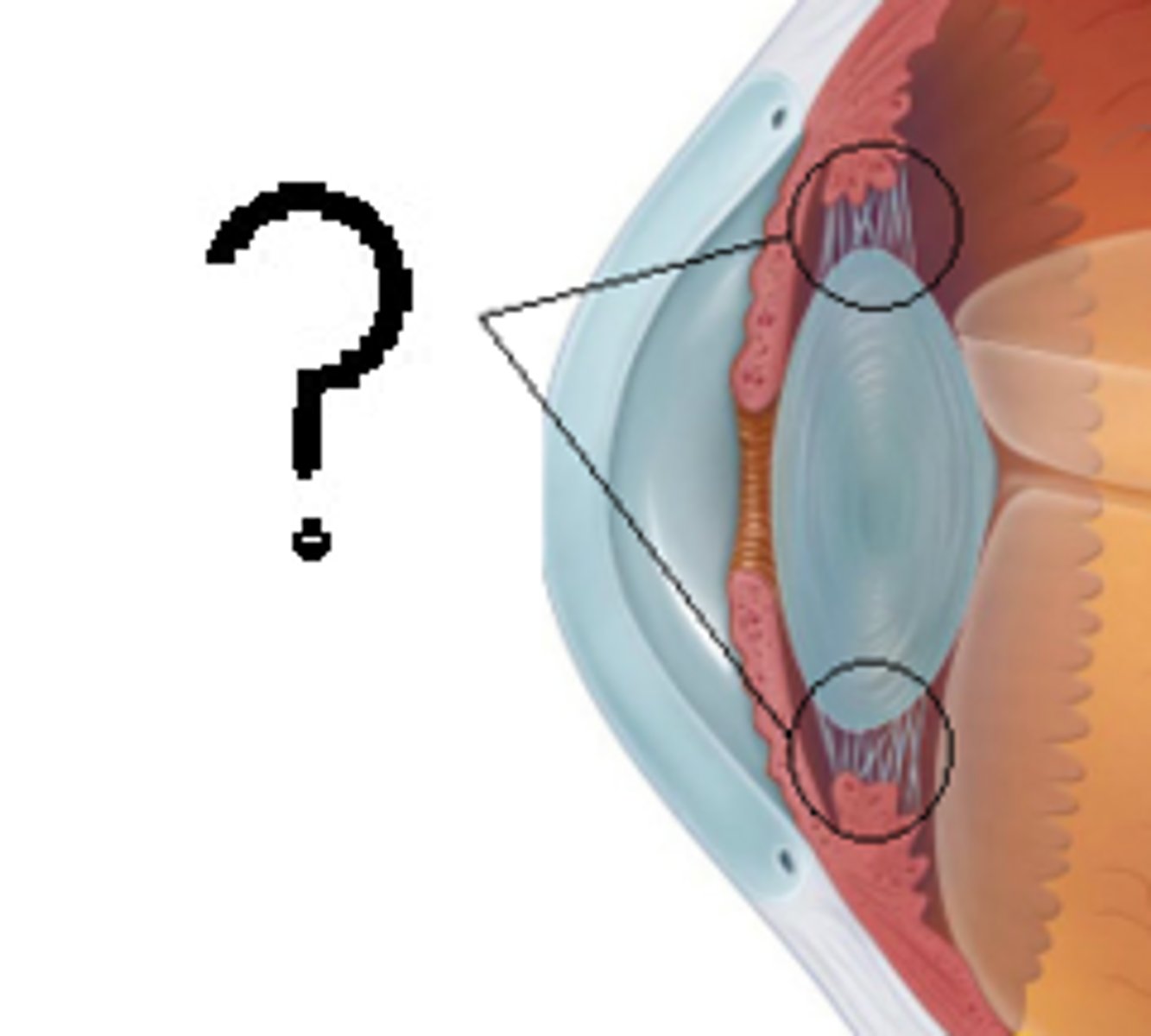
Ciliary Body
Structure containing muscles that control the lens shape
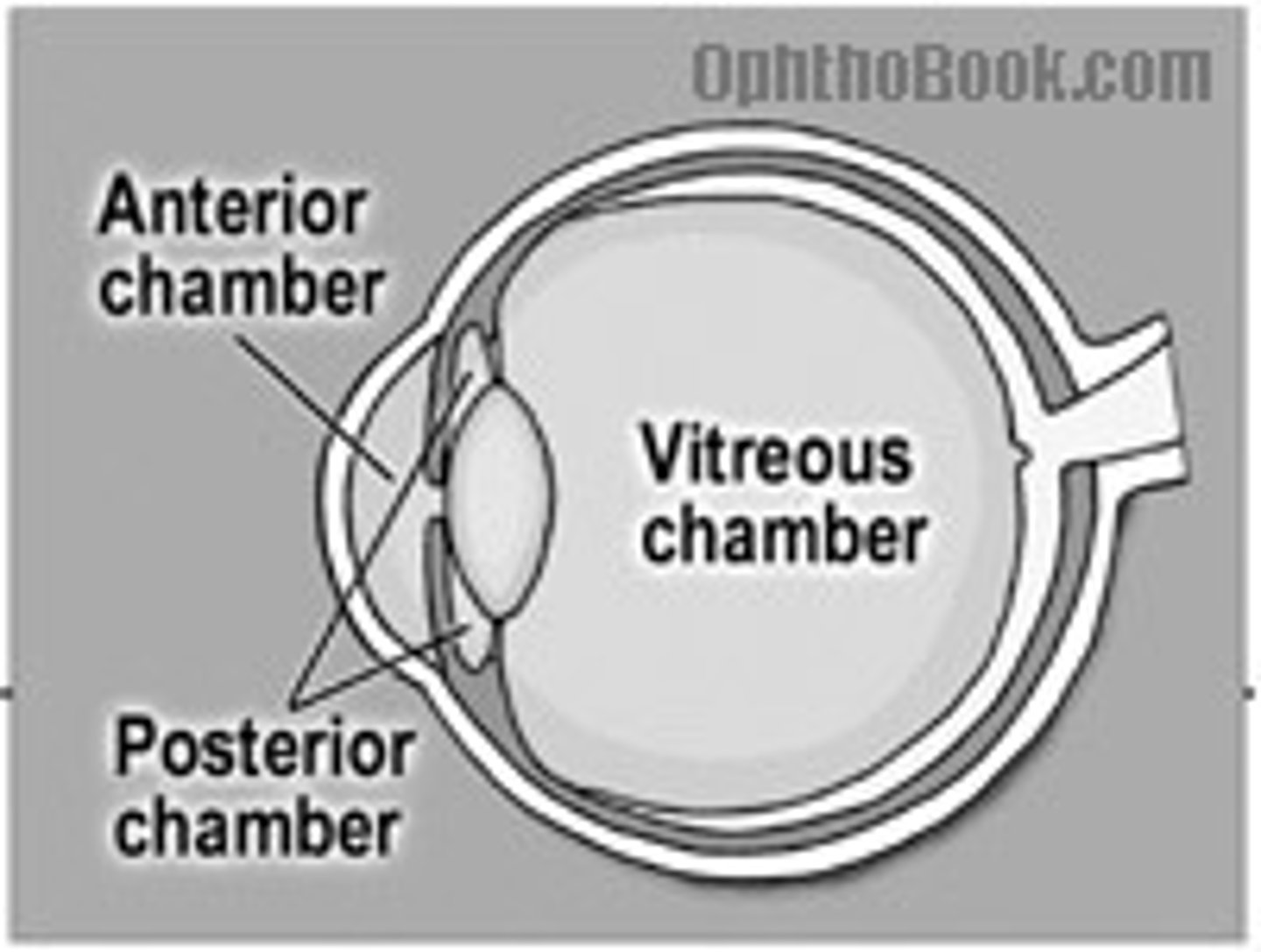
Posterior Chamber
Space filled with aqueous humor behind the iris
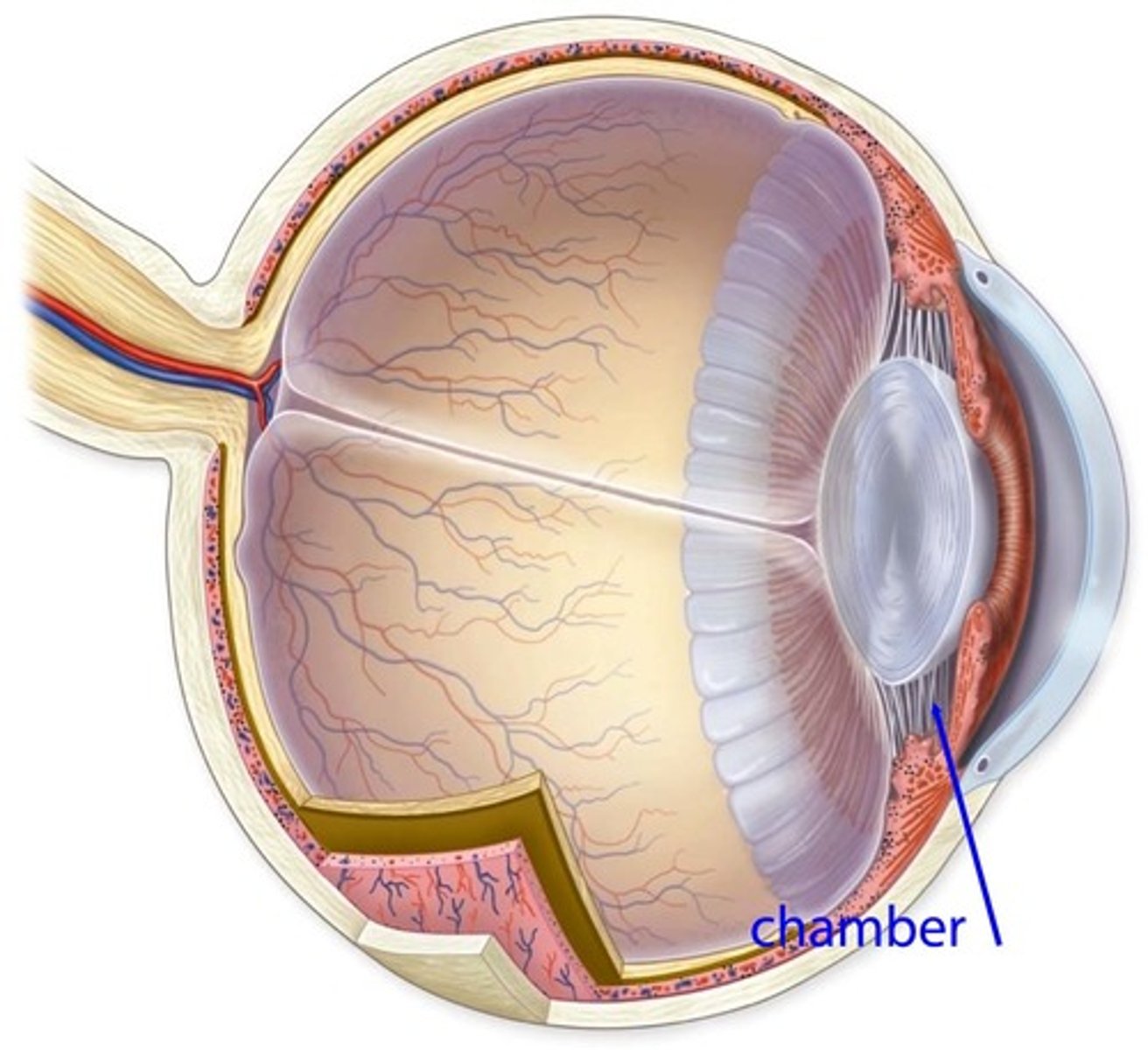
Anterior Chamber
Space filled with aqueous humor in front of the iris
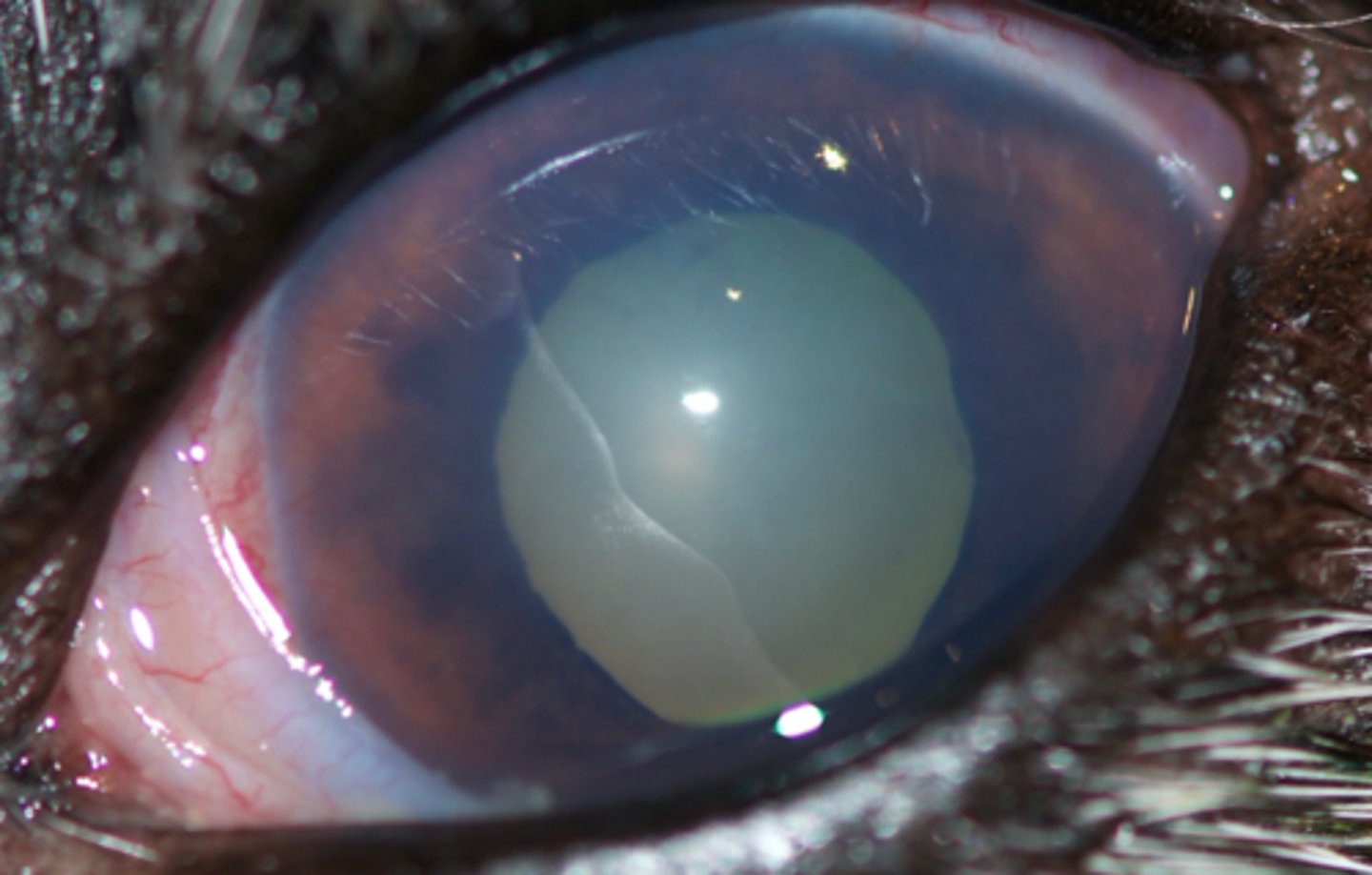
Corneal Cloudiness
Loss of transparency in the cornea leading to vision impairment
eye Lens Adjustment
Process of changing the shape of the lens for focusing
Myopia
Nearsightedness, light rays fall in front of retina
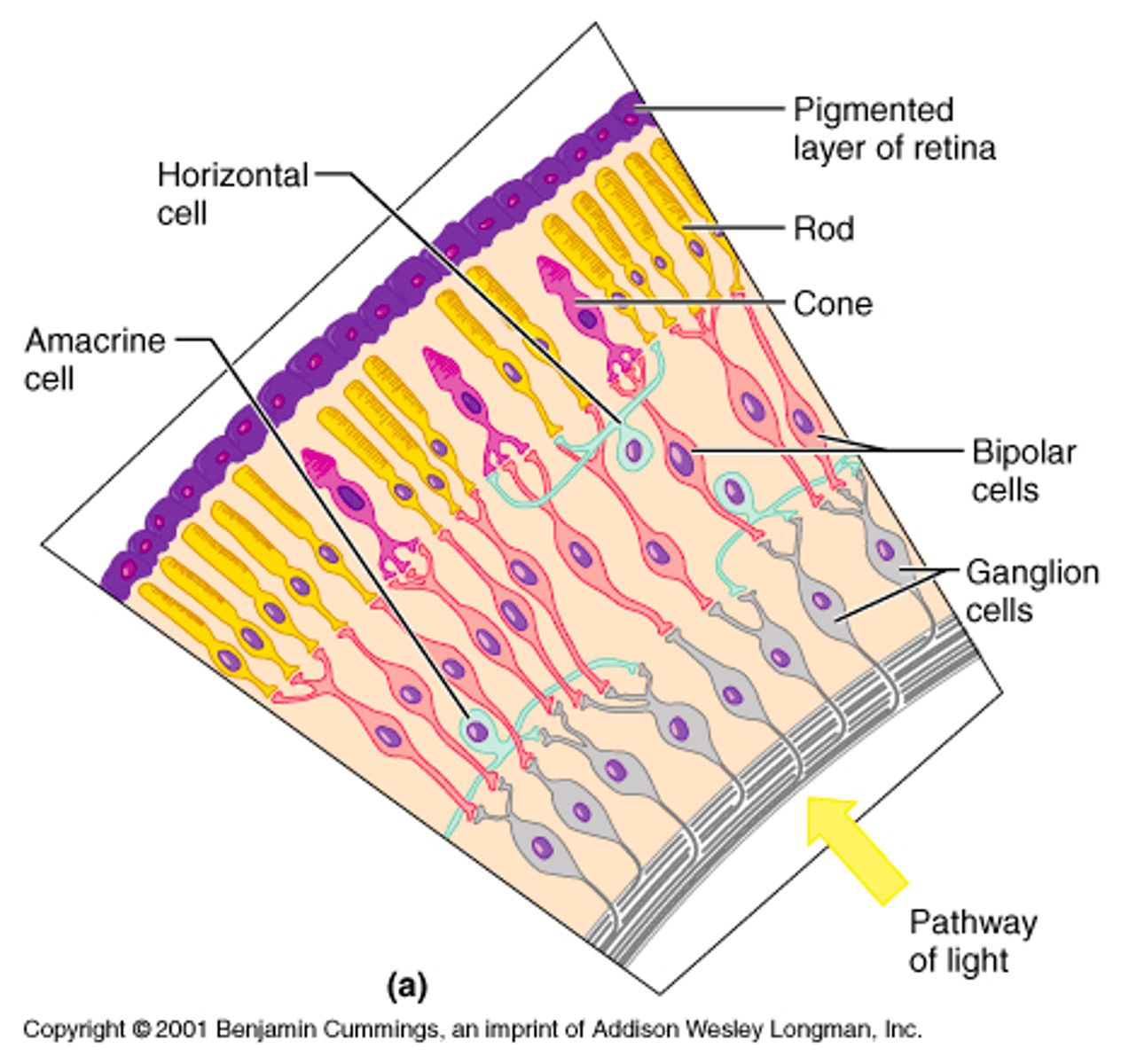
Rod Cells
Detect light, more sensitive in low light
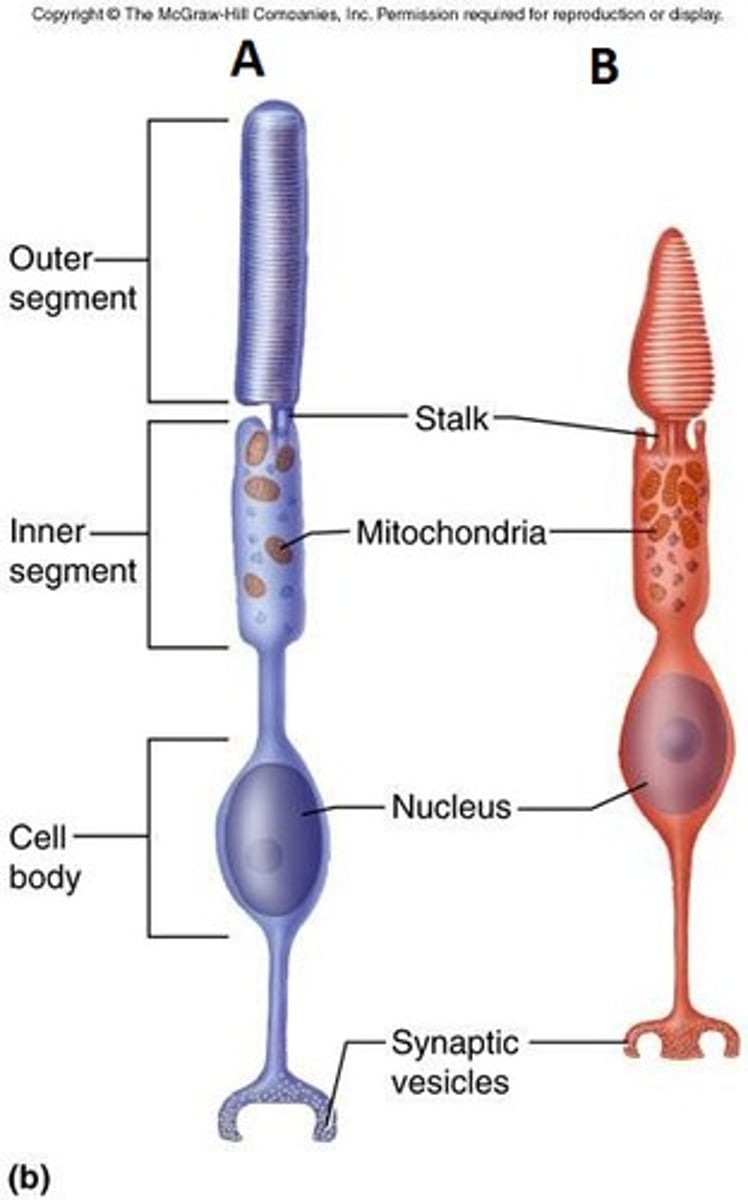
Cone Cells
Detect color, best in bright light
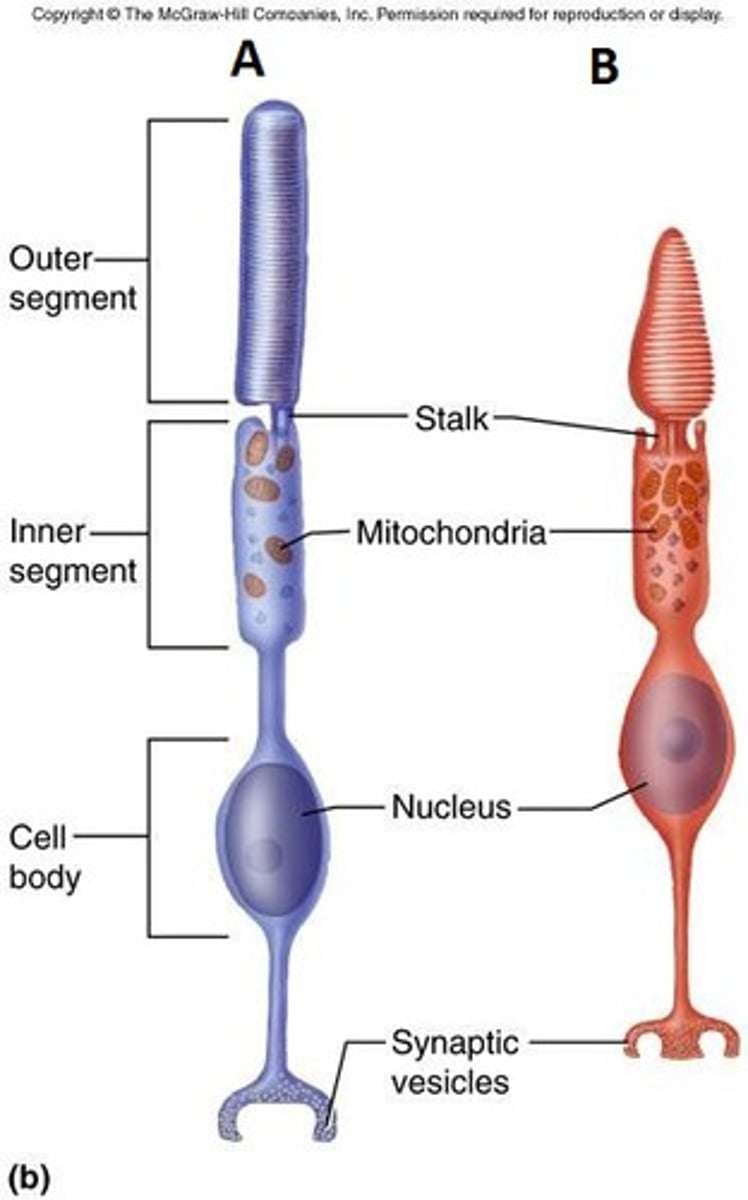
Retinal Ganglion Cells
Part of optic nerve, receive impulses from receptors
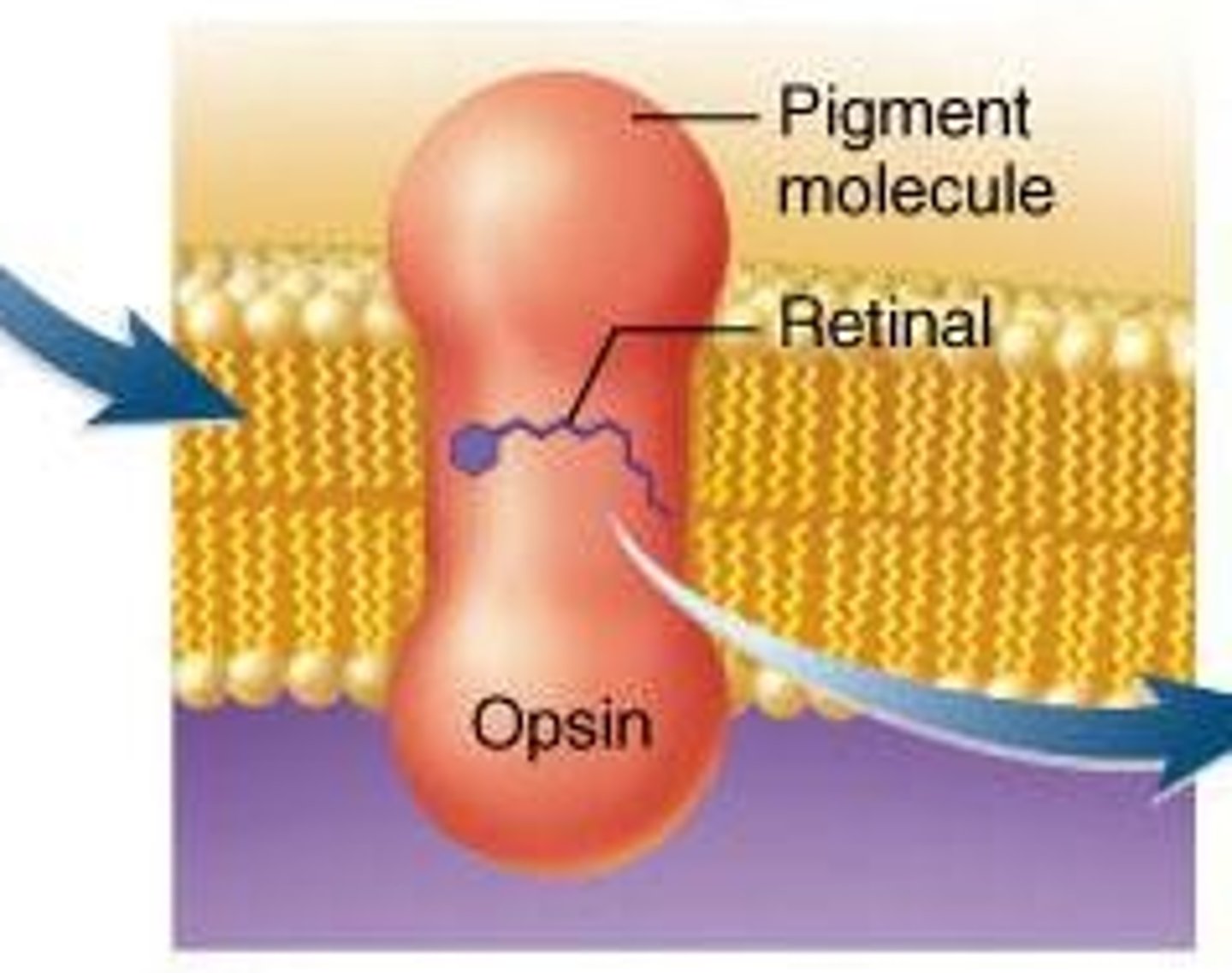
Rhodopsin
In rod cells, composed of opsin and cis retinol
Photoreceptors
Cells in the retina detecting light stimuli
Transducin
Activated by light, triggers signal cascade in rod cells
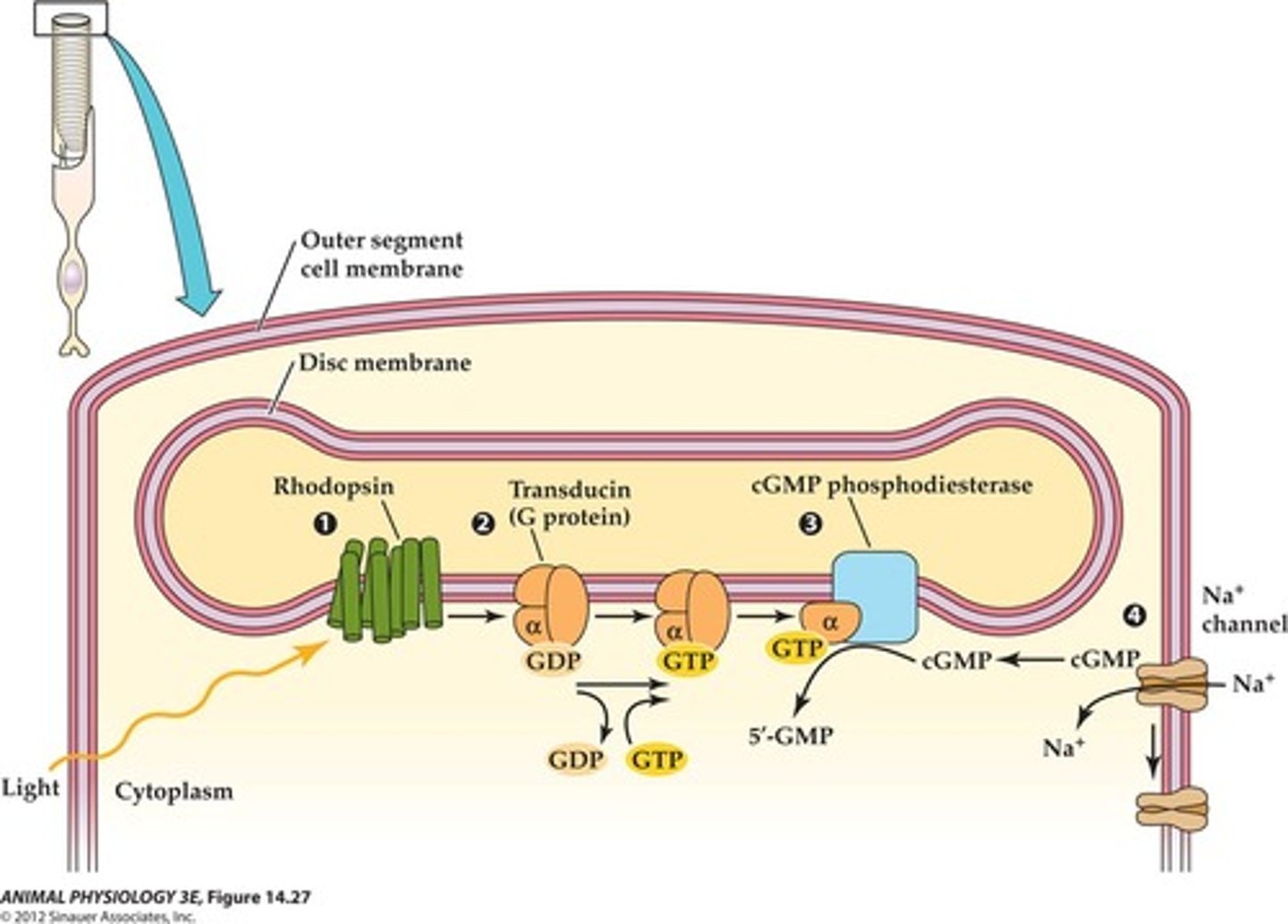
Hyperpolarization
Cell becoming more negative in response to light stimuli
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter released by photoreceptors in absence of light
Bipolar Cell
Cell releasing neurotransmitter onto retinal ganglia
Action Potential
Result of neurotransmitter release along optic nerve
Depolarization
Opening of sodium channels causing cell activation
Opsin
Component of rhodopsin activated by light
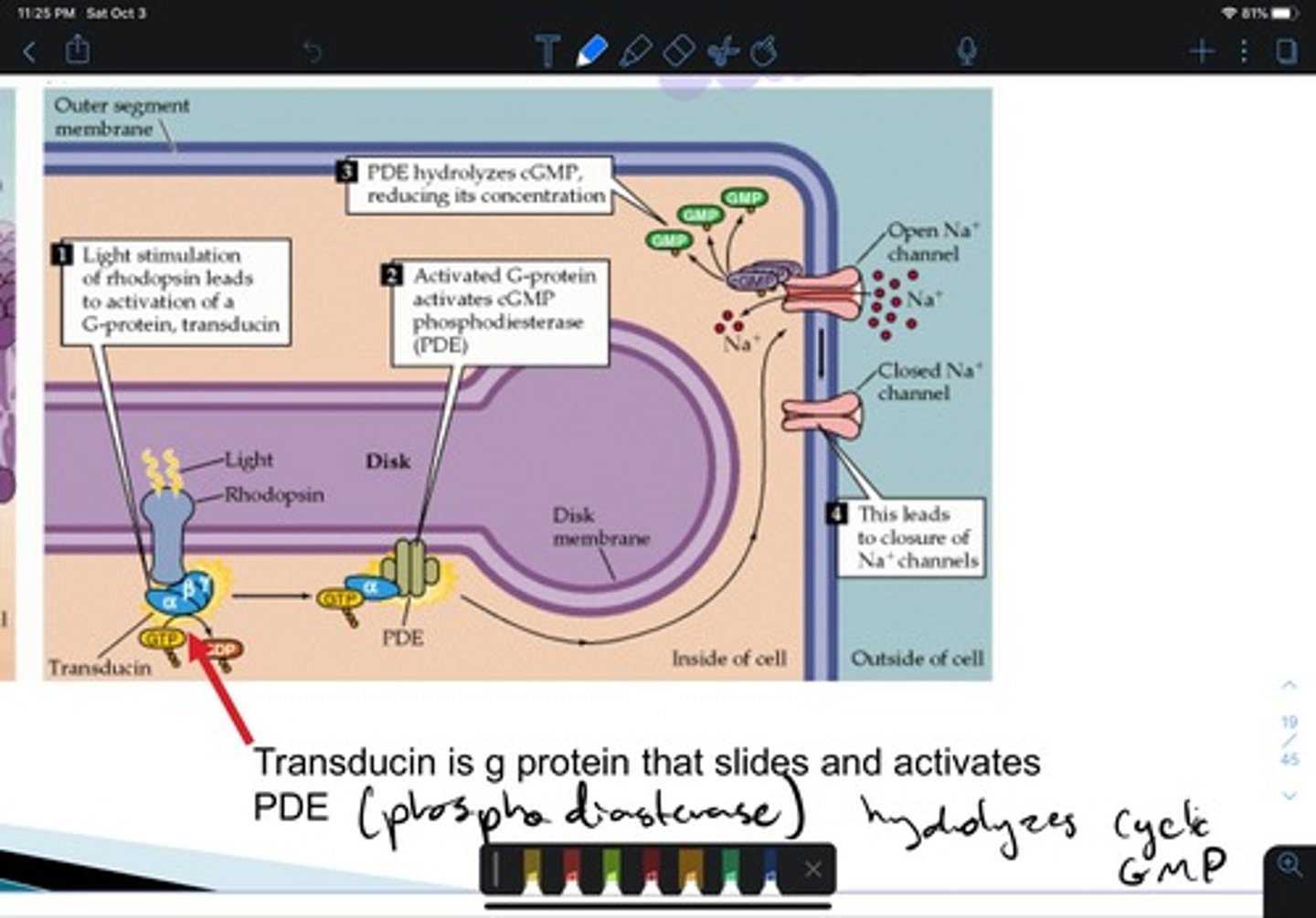
Phosphodiesterase
Enzyme closing sodium channels in photoreceptor cells
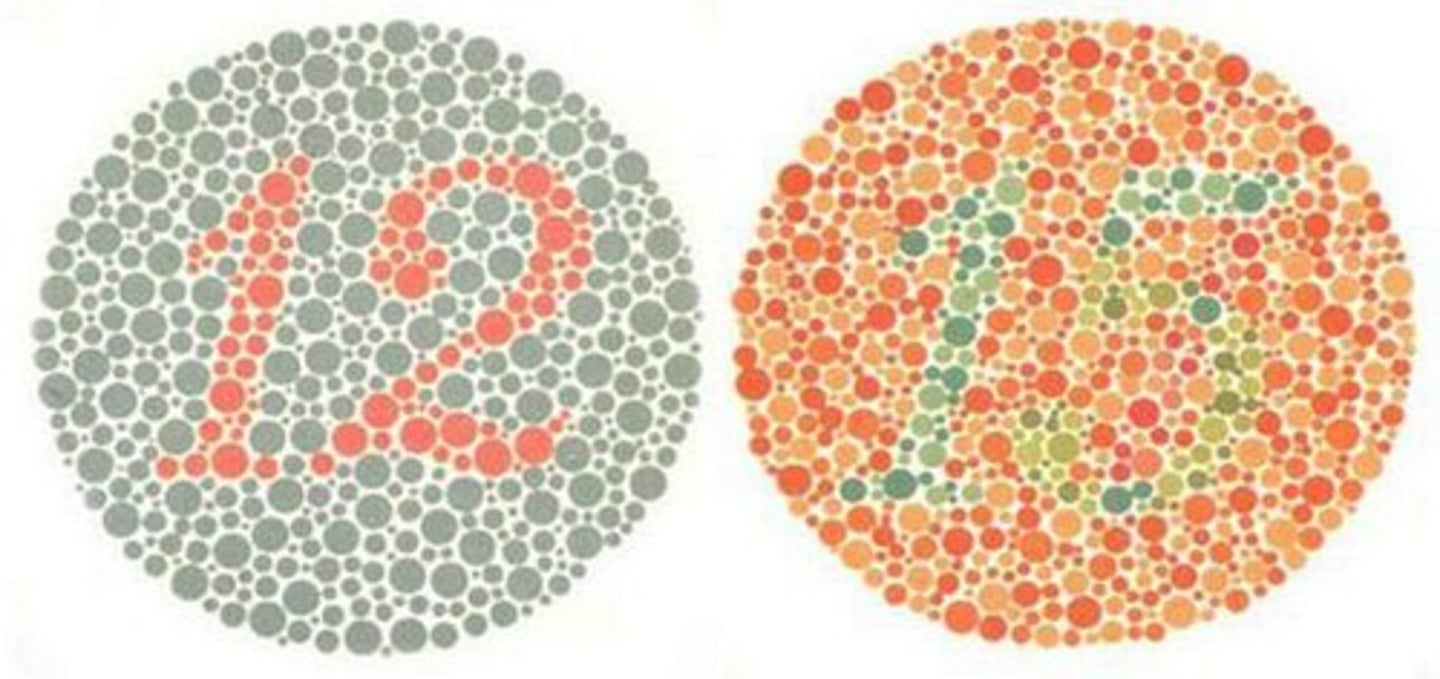
Colorblindness
X chromosome trait affecting color perception
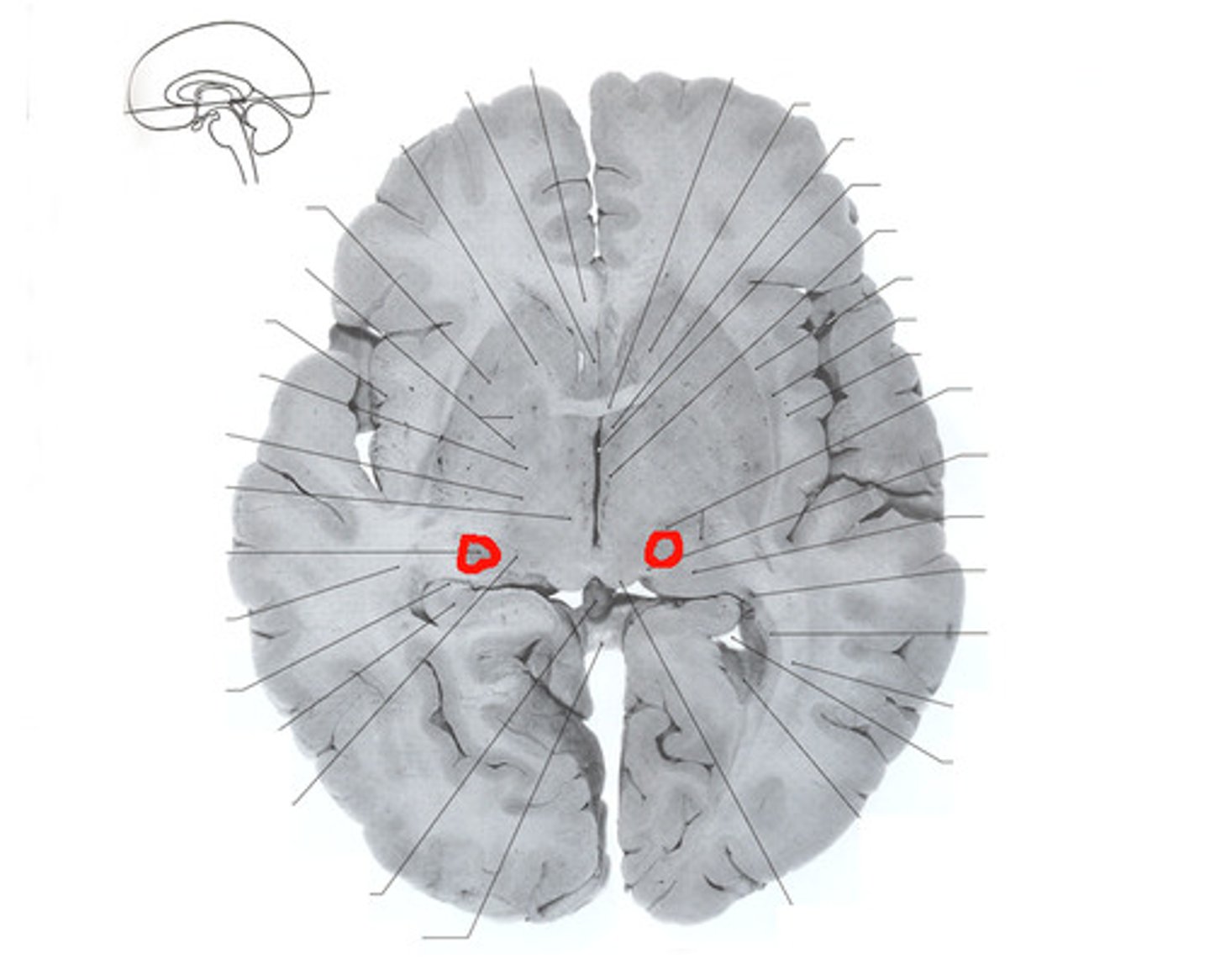
Optic Chiasma
Point where optic nerves partially cross over
Superior Colliculus
Brain structure involved in visual processing
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
Thalamic nucleus relaying visual information
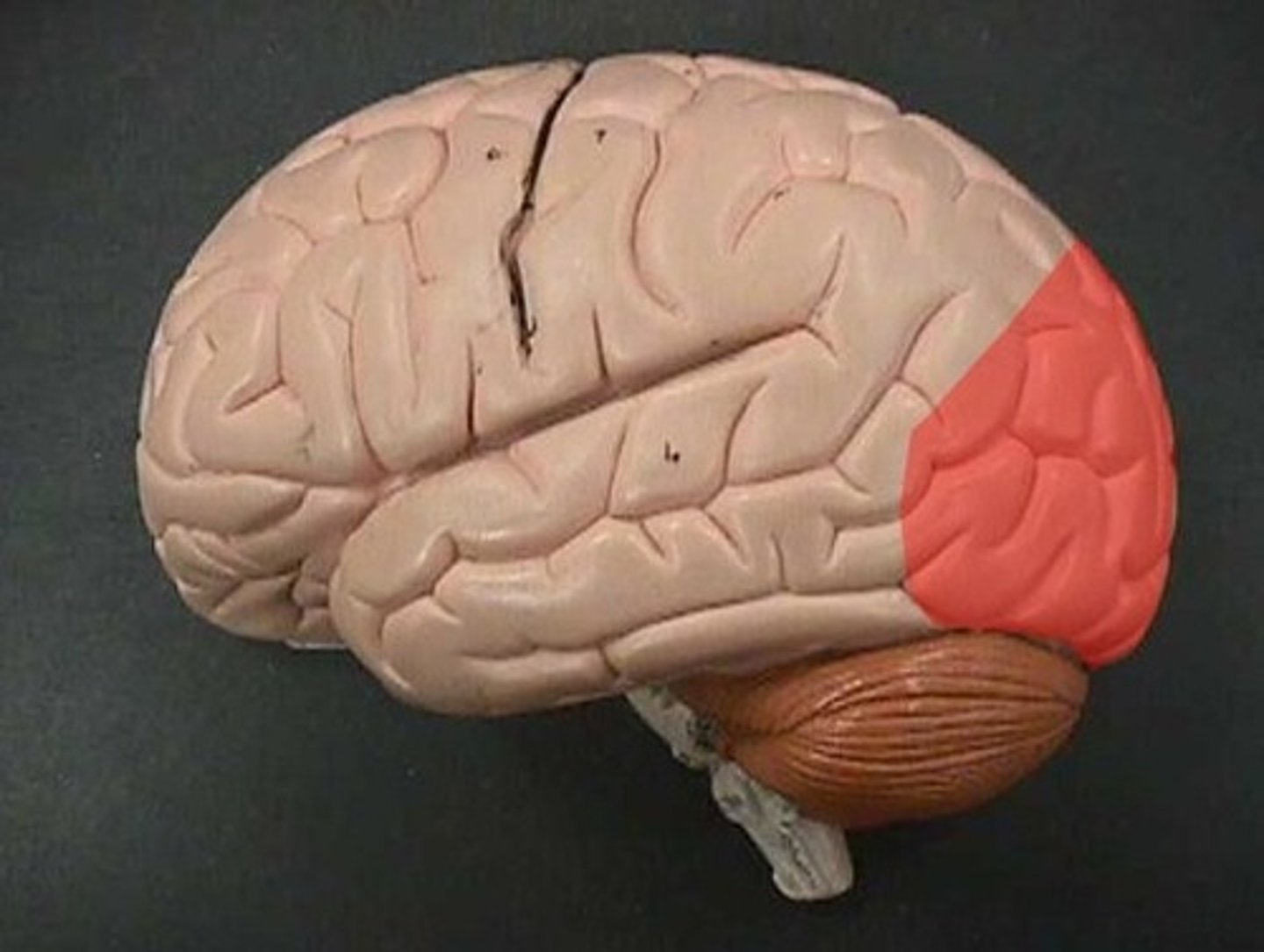
Occipital Lobe
Brain region processing visual stimuli
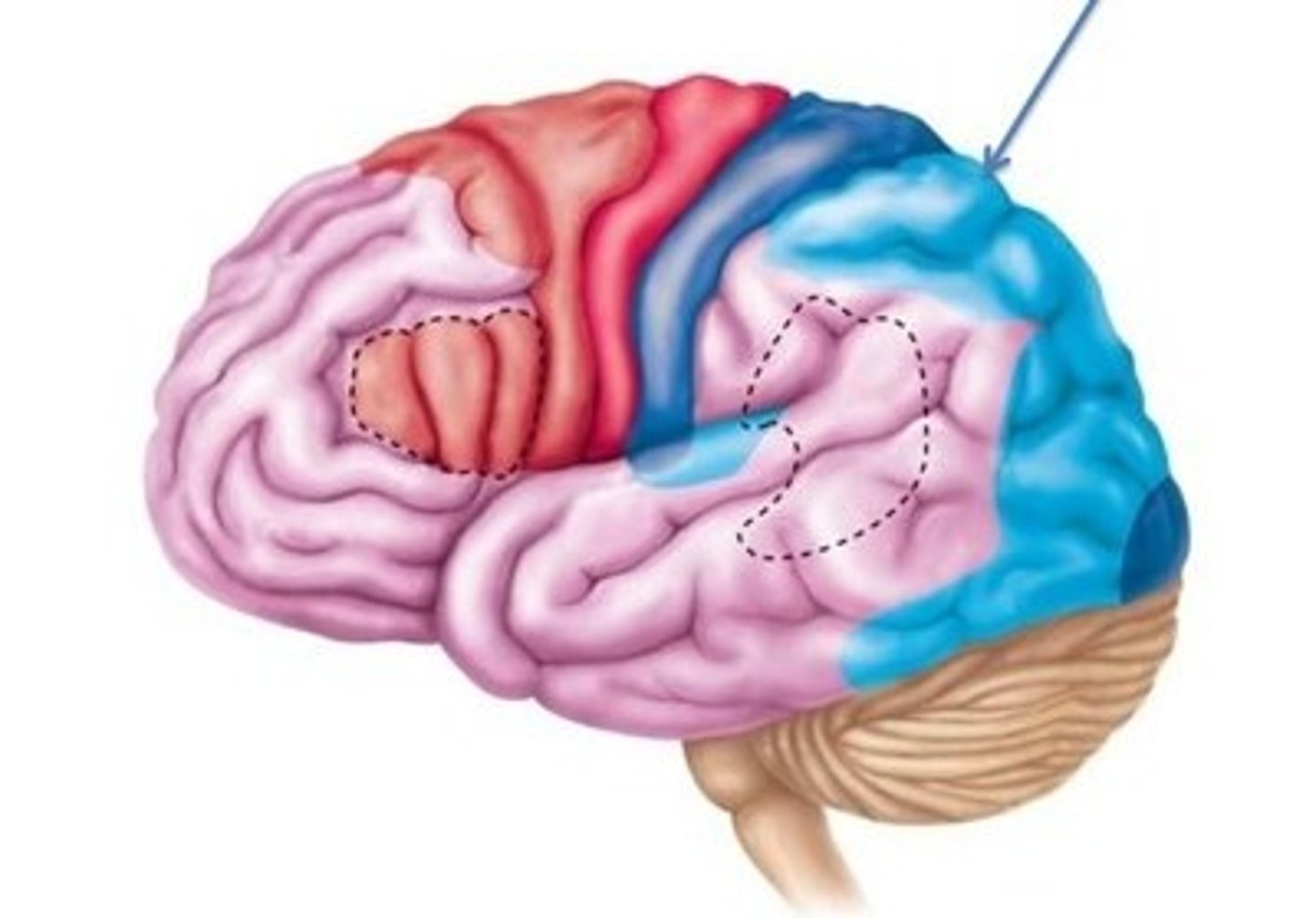
Primary Visual Cortex
Brain area interpreting visual information
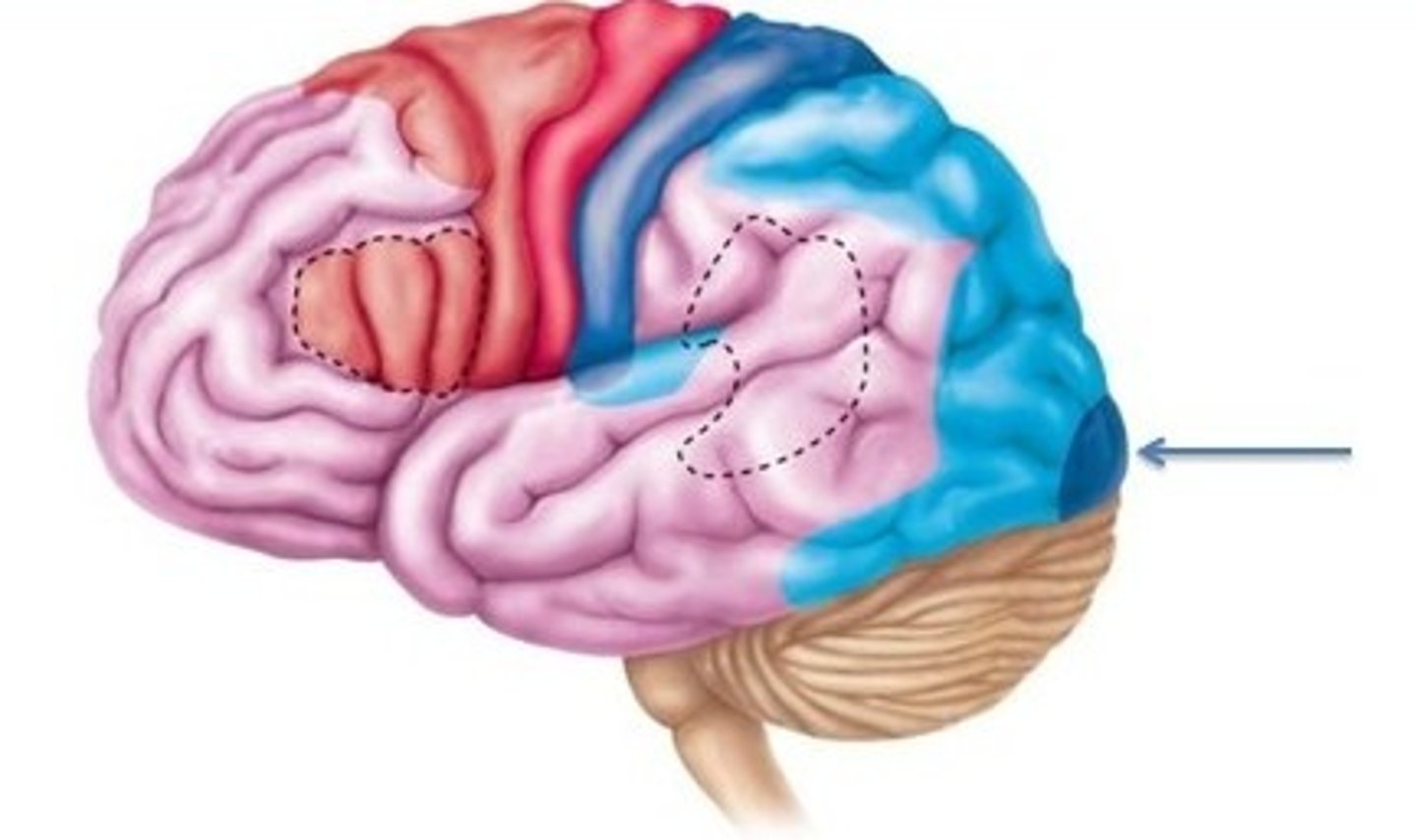
Association Cortex
Brain region integrating sensory information
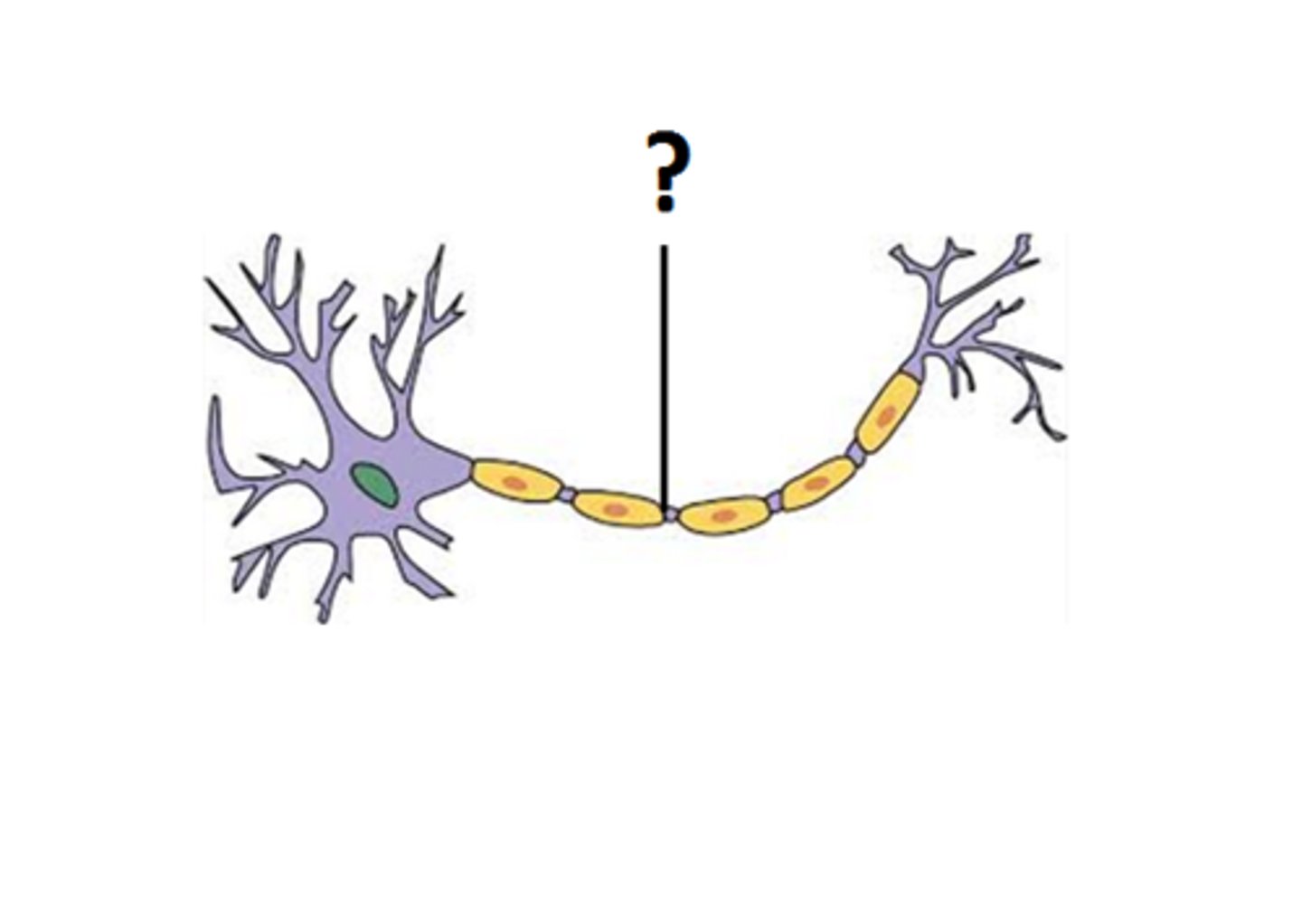
Axons
Nerve fibers transmitting electrical impulses
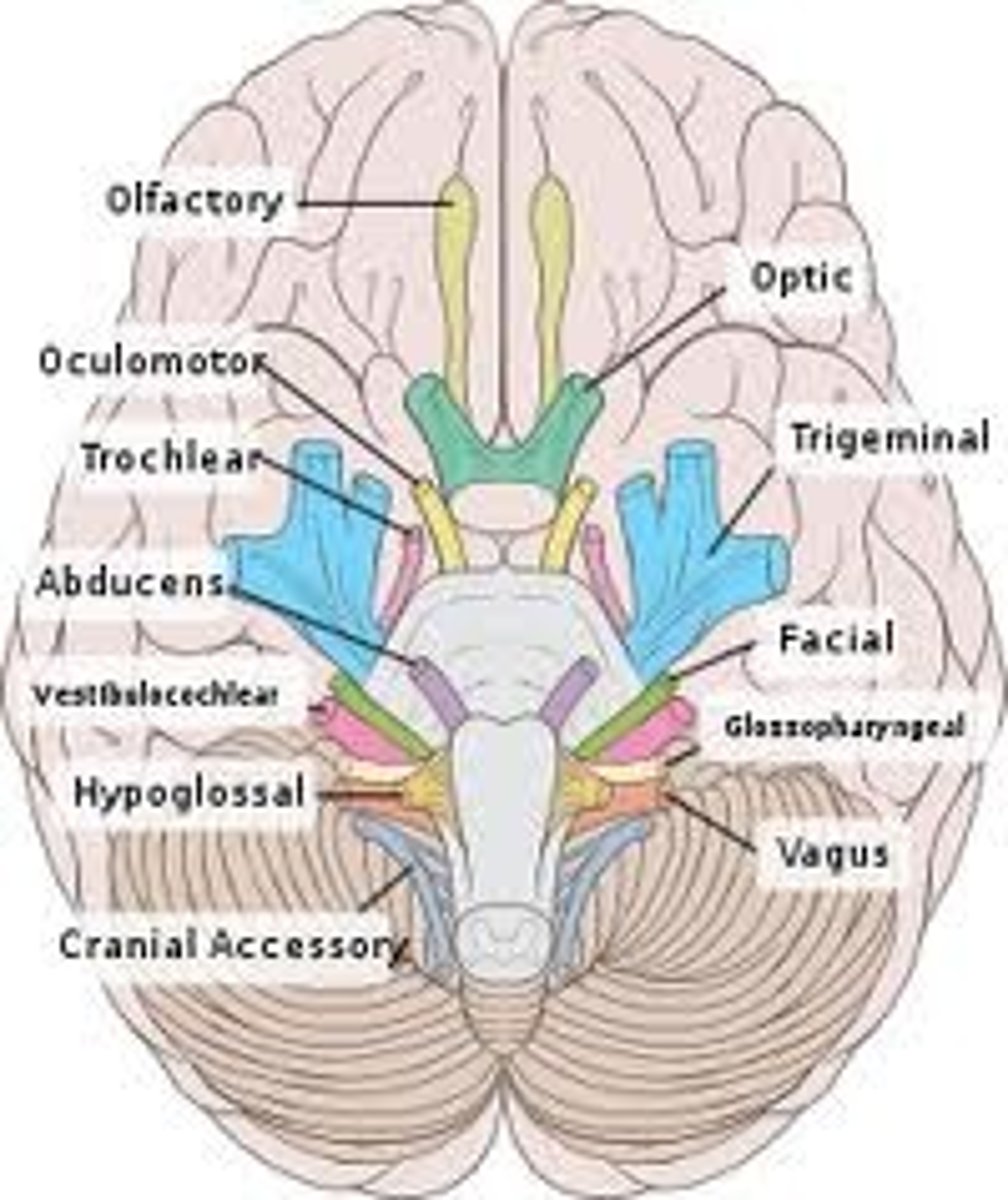
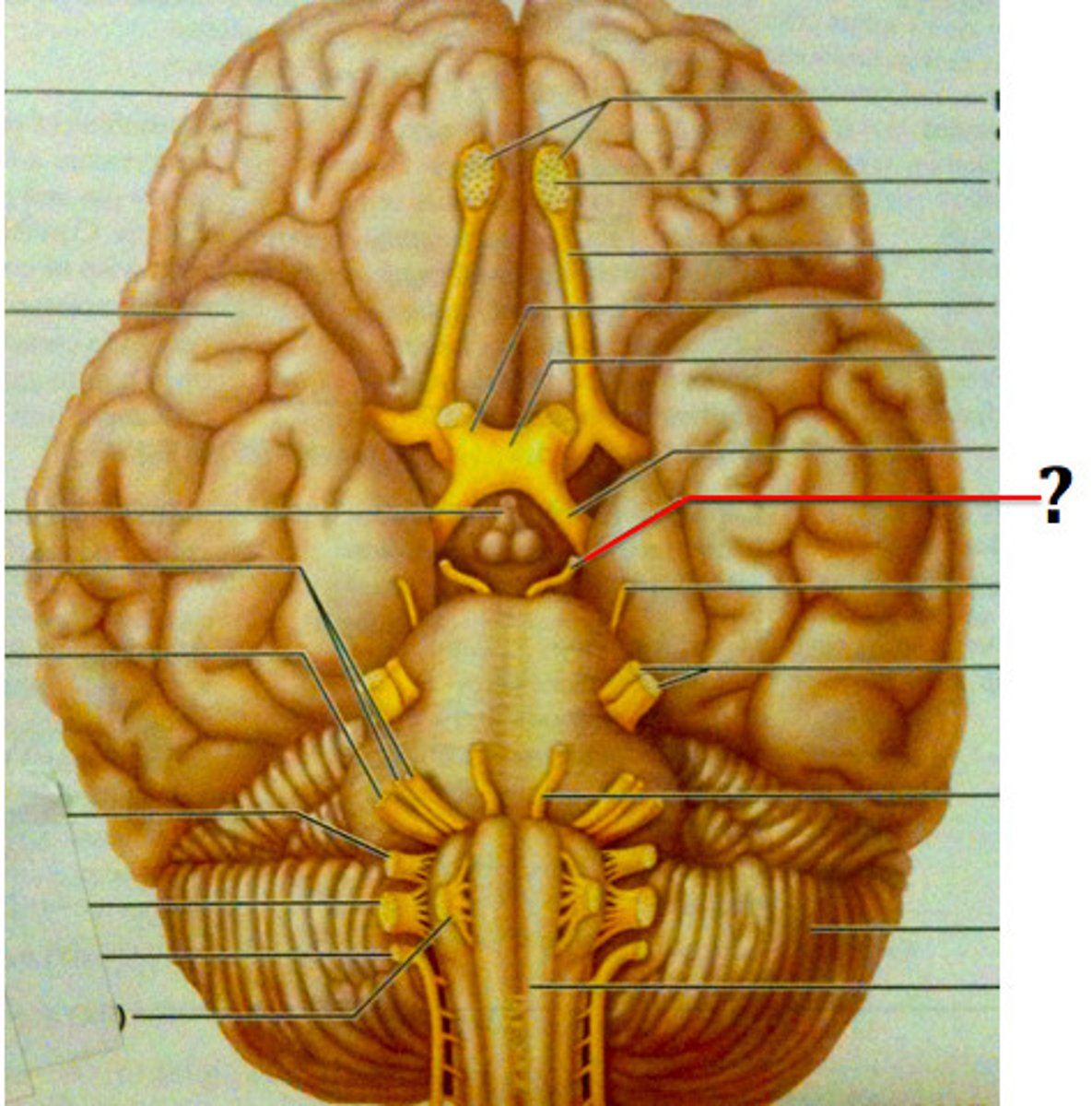
Oculomotor Nerves
Nerves controlling eye movement
Depth Perception
Ability to perceive objects in three dimensions

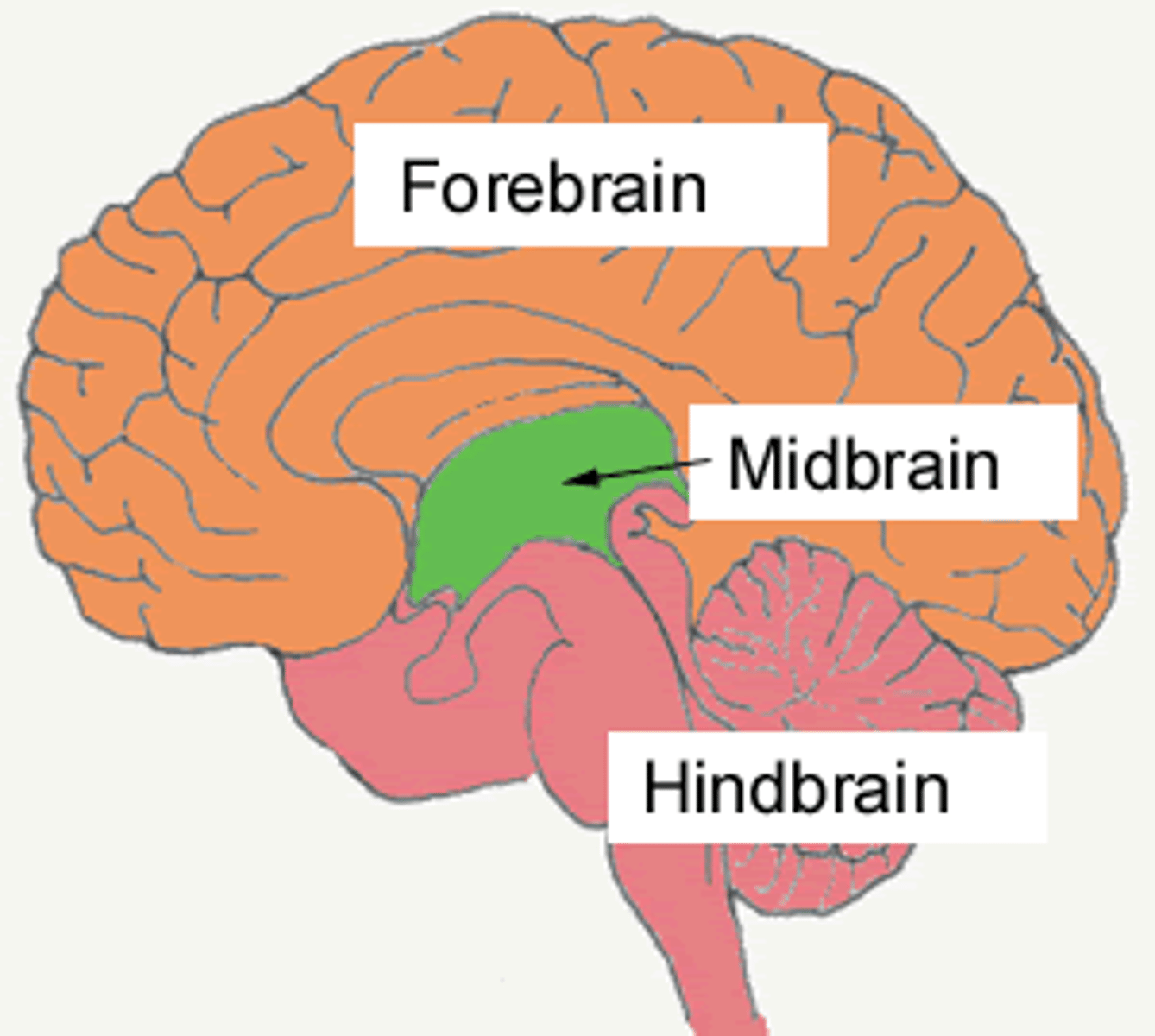
Midbrain
Brain region involved in visual and auditory processing