Unit 2 AP Psych ALL VOCAB
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Intelligence
Mental ability encompassing the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
Reliability
Test consistently produces the same results under the same conditions, ensuring its trustworthiness and stability over time
Test-Retest Reliability
Consistency of a measure when it is administered to the same group of individuals at different points in time
Split-Half Reliability
Measures test’s internal consistency by dividing it into two halves (eg: odd and even questions), administering it once, and then correlating people’s performance
Validity
Degree to which test/measurement accurately assesses what it claims to measure
Construct Validity
Degree test accurately assesses specific, underlying theoretical concept it is designed to measure
Predictive Validity
Extent to which test can accurately forecast future performance or behavior based on its results
Aptitude Tests
Assess person’s potential to succeed in a certain area, even if they haven’t received any education/training in it
Ex: ACT/SAT
Achievement Tests
Evaluates individual’s knowledge or proficiency in certain areas they have been taught/trained in
Standardized Tests
Test given and scored under uniform conditions to compare results against social norms and ensure scores are reliable and valid for assessing knowledge
Fixed Mindset
Belief that one’s abilities, intelligence, and talents are static traits that can not be improved or developed
Growth Mindset
Belief that one’s ability and intelligence can be developed through effort, learning, and perseverance
Spearman’s Intelligence Theory (g factor)
Single, underlying cognitive ability (g) that influences performance across all mental tasks, If you do good on one intelligence test you will likely to good on the other
Gardner’s Intelligence Theory
Intelligence not a single general ability but multiple, distinct capabilities
Linguistic
Logical-Mathematical
Spatial
Bodily-Kinesthetic
Musical
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Naturalistic
Sternberg’s Intelligence Theory
Intelligence composed of three interrelated components
Analytical
Creative
Practical
Standford-Binet IQ Test
Classic, standardized intelligence test that measures cognitive abilities across five factors to produce an IQ score
Mental Age
Person’s level of mental development relative to others
Chronological Age
Actual amount of time person had been alive
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
Score derived by standardized intelligence tests. (Mental age/Chronological Age) x 100
Wechsler Intelligence Scales (WAIS ) and (WISC)
IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability to provide a comprehensive IQ score
Normal Distribution
Frequency distribution where most measurements are centered around the equal mean/median/mode and two sides of curve are symmetrical
Percentile Rank
Percent of test takers you did better than. Compares your score in relation to others who took the test.
Heritability
Proportion of observed differences on a trait among individual of a population that are due to genetic differences. Higher heritability score means more due to genetic
Factor Analysis
Statistical technique used to identify underlying groups (factors) among many correlated test items or variables
Stereotype Threat
Fear one’s behavior will confirm an existing stereotype a group has. It actually may impair performance on tasks related to that stereotype.
Stereotype Lift
Performance improvement experienced by non-stereotyped group when compared to weaker group leading to increased self esteem
Sociocultural Responsiveness
Understanding and integrating a person’s cultural background, social context, and experiences into psychological services to make them more relevant
Flynn Effect
Observed, long term rise in IQ over generations likely because of better nutrition, education, and healthcare
Memory
Learning that has continued over time
Three-Box/Information Processing Model
Three Step Processing Model
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Levels of Processing Model
Suggests that depth of processing affects encoding and subsequent retrieval of information. Three main levels of processing:
Structural Encoding
Phonemic Encoding
Semantic Encoding
Sensory Memory
Process everything we sense. Info will leave brain in a few seconds if not encoded. Two types:
Echoic Memory
Iconic Memory
Selective Attention
Focus on one thing while ignoring the other competing things
Encoding
Way info is transformed and placed in the memory
Automatic Processing
Info processing of much-related or well-learned activities that occurs without conscious effort. May require some attention when first performed but with practice becomes automatic
Effortful Processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Deep Processing- Semantic
More long-lasting memory. Involved elaborate rehearsal, along with a meaningful analysis of the ideas and words being learned.
Intermediate (Phonemic) Processing
Focuses on sound of Information. Deeper than shallow processing but not as deep as semantic processing
Shallow Processing
Memorize something without attaching meaning to it. Less durable memory, tend to forget it quickly,
Structural Encoding
Encoding using basic visual qualities of word/concept. Shallowest level. Ex: Physical characteristics: appearance, shape, or sound
Phonemic Encoding
Processing the sound or pronunciation of stimulus. Deeper than structural but shallower than semantic. Ex: rhythm pattern, syllable structure to phonemic components.
Semantic Encoding
Processing meaning of stimulus and its relationship to other concepts and info already stored in memory. Deepest form of encoding.
Short-Term/Working Memory
Without active processing, memories have limited life-15-30 sec duration/ Can store ± 7 concepts.
Central Executive
Main component of working memory, responsible for coordinating cognitive processes. Doesn’t store info but controls attention and coordinates activity with other subsystems.
Phonological Loop
Auditory and verbal info. Two parts:
Phonological Store (Inner ear)
Holds auditory info from speech for two seconds
Articulatory Control Process (inner voice)
Rehearsal of verbal info- refreshes and maintain it in phonological store
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Processes visual and spatial info. Ex: mental imagery, spatial reasoning, and navigation
Chunking
Organizing items into familiar and manageable units. Increases amount of info stored in STM.
Mnemonic Devices
Link new info to existing knowledge or experiences through association. Makes info more memorable. Ex: Acronyms or visual imagery.
Method of Loci
Associate items with imagery of places
Ex: counting windows in your house by visualizing house
Rehearsal
Conscious repetition of info to encode it into memory
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repeating info so not forgotten immediately, helps hold in short-term but doesn't process in long term
Elaborative Rehearsal
Linking new concepts to old ones to help move them to long-term memory
Spacing Effect
Information better retained and recalled when it is studied or rehearsed over multiple spaced intervals of time
Storage
Process of retaining encoded information over time
Iconic Memory
Fleeting visual images in sensory memory
Echoic Memory
Auditory signals in sensory memory
Long-Term Memory
Can store info indefinitely, but must be encoded.
Episodic Memory
Stories of our lives and experiences that we can recall (like episodes of a television show) and tell to someone else
Semantic Memory
Impersonal memories not drawn from personal experiences but rather from common, everyday kinds of knowledge, such as names of color and names of states
Procedural Memory
Memories of how to do something, like ride a bike, bake cookies, create code for a computer
Prospective Memory
Person recalls or remembers to do something in the future
Explicit Memory
Past knowledge that is consciously brought to mind. Conscious, intentional recall of facts and personal experiences.
Implicit Memories
Memories retained without conscious effort and often without our awareness. Unconsciously retrieved.
Retrieval
Recalling stored memories
Retrieval Clues
Stimuli or hints that help you access stored info in your memory
Metacognition
The process of thinking about thinking. Helps identify which strategies are most effective in helping retrieve memories.
Recognition
Memory retrieval where identify info as familiar, or previously encountered, from a set of options
Recall
Process of retrieving info without any cues or prompts
Primacy Effect
Tendency to remember first piece of info
Recency Effect
Remember info that came last more than earlier info
Serial Position Effect
Tend to remember info presented at beginning or end of a list better than that presented in middle
Autobiographical Effect (memory)
Memory system that has info about ourselves including personal experiences, events, and facts from our lives. Includes episodic and semantic memories.
State-Dependent Effect
Memory retrieval most effect when in same state of consciousness as when memory formed
Mood Congruent Effect
More likely to recall info when in a mood similar when it was acquired
Context-Dependent Memory
Recall of info while in same context or environment in which it was acquired
Constructive Memory
Process where memories are actively reconstructed, elaborated on or modified when recalling event. Illustrates how memories can be influenced by external factors and previously held ideas
Memory Consolidation
Newly formed memories are stabilized and integrated into LTM. Takes place when learn a new skill.
Imagination Inflation
Repeatedly imagining or elaborating on an event can lead to an increased confidence in the event’s occurrence, even if it actually never happened.
Testing Effect
Retrieving info from memory enhances long-term retention of that info.
Ex: taking a test on the material lead to better retention than studying instead
Relearning Effect
Previously learned material is learned more quickly second time around. Information was not previously forgotten but remained stored in memory
Encoding Failure
Inability to store or retrieve information in long-term memory due to failure in the initial encoding process
Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon
Can’t recall a specific word or term, but feel certain that you know it. It’s on the “tip of my tongue”
Retroactive Interference
New info disrupts recall of previously learned info. New memory overshadows old one.
Ex: Remembering new phone number makes you forget old one
Proactive Interference
Older, previously learned info hinders recall of newer info
Ex: can’t remember new phone number, because have old one stored already
Repression
Unconscious defense mechanism that blocks distressing thoughts, memories, or impulses from their conscious mind to protect themselves from emotional pain
Misinformation Effect
Person’s memory of an event is altered by misleading info received after event occurred Leads to false memories
Ex: Shown a pic of a man’s face then asked about a mustached man. Will recall man having mustache even if he had none
Framing
People’s decisions influenced by how info is presented rather than just the info itself
Source Amnesia (misattribution)
Attributing an event, fact, or idea to the wrong source, while forgetting where you actually learned it
Alzheimer’s Disease
Neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a significant and irreversible decline in cognitive and functional abilities leading to dementia
Infantile Amnesia
Inability of most adults to retrieve episodic memories from first few years of life, generally before age of 2-4
Anterograde Amnesia
Psychological condition where an individual is unable to form long-term memories after illness. Can recall memories before illness, but not after
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memory for events and info that occurred before specific event. Often caused by brain trauma after injury or disease
Long-Term Potentiation
Persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent activity. Allows synapse to become more effective at transmitting signals. Ex: repeatedly practicing to learn how to ride a bike
Rosy Retrospection
People recall past events more positively than they actually experienced them
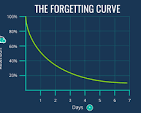
Forgetting Curve
Model that shows how we lose retention of new info overtime without reinforcement
Cognition
Mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Metacognition
Thinking about how you think
Concepts
Mental representations of categories of items or ideas, based on experiences
Prototypes
Mental image or best example of category/concept
Schemas
Generalizations and mental representations about persons, places and things which provide automatic thought patterns and opinions