ANS 220 Exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/290
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
291 Terms
1
New cards
Fetus
What does the inner cell mass in an embryo become?
2
New cards
placenta
What does the trophoblast in a embryo become?
3
New cards
glycoprotein
What type of hormone is Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)?
4
New cards
primates
What species is human Chorionic Gonadotropin found in?
5
New cards
the placenta
Majority of the embryonic hormones are produced by…
6
New cards
the gonads
What does hCG and eCG stimulate?
7
New cards
in the trophoblastic cells of the blastocyst (placenta)
Where is the human chorionic gonadotropin hormone produced?
8
New cards
Human chorionic gonadotropin
What hormone does pregnancy tests test for in urine?
9
New cards
Stimulates P4 production from CL
Indirectly blocks luteolysis
Causes ovulation in non-primate females
Increases fetal growth
Indirectly blocks luteolysis
Causes ovulation in non-primate females
Increases fetal growth
What are the roles of human chorionic gonadotropin?
10
New cards
as early as 8 days of gestation
How early can human chorionic gonadotropin be detected?
11
New cards
Pregnant Mare’s Serum Gonadotropin (PMSG)
What is another name for Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin (eCG)?
12
New cards
glycoprotein
What type of hormone is equine chorionic gonadotropin?
13
New cards
endometrial cups of the placenta
What produces eCG?
14
New cards
chorionic girdle
What specific cell produces eCG?
15
New cards
formation of CLs which increase P4 production
indirectly blocks luteolysis
==acts like FSH in other species==
indirectly blocks luteolysis
==acts like FSH in other species==
What are the function of eCG?
16
New cards
no (maternal recognition in mares is shown on day 14-16, which is before the peak of eCG)
Is eCG the signal of maternal pregnancy?
17
New cards
35 days
What day does eCG peak at?
18
New cards
Glycoprotein
What type of hormone is Interferon Tau (IFNT)?
19
New cards
Only ruminants
What type of animals is INFT found in?
20
New cards
trophoblastic cells of the blastocyte
What produces IFNT?
21
New cards
inhibits oxytocin receptors in the endometrium (blocks smooth muscle contractions)
prevents PGF2a synthesis (allows for the survival of CL and decreases P4)
==Promotes protein production to nourish concepts (embryo)==
\
prevents PGF2a synthesis (allows for the survival of CL and decreases P4)
==Promotes protein production to nourish concepts (embryo)==
\
What is the functions of IFNT?
22
New cards
LH and FSH would increase
==ovulation/rupture of the follicle would occur==
==ovulation/rupture of the follicle would occur==
What would happen if you increase GnRH levels?
23
New cards
No changes to GnRH levels since GnRH is released from the anterior pituitary and not the posterior pituitary like oxytocin
What would happen if you give a single injection of oxytocin?
24
New cards
GnRH levels would increase, which would cause LH levels to increase
The follicle on the ovary could also rupture
The follicle on the ovary could also rupture
What would happen if you gave a single injection of estrogen?
25
New cards
LH, FSH, and testosterone levels would decrease, and GnRH levels would increase
What would happen if you disconnect the hypothalamic portal system?
26
New cards
There would be an increase in LH because of the decrease in testosterone
What would happen to hormones if you castrate bulls at birth?
27
New cards
there would be an increase in LH levels because of a decrease in estrogen
What would happen to hormones in a postmenopausal female?
28
New cards
GnRH, LH, and FSH would decrease, and testes would shrink because of feedback to the hypothalamus
What would happen to hormones if there was continuous testosterone injections?
29
New cards
GnRH and LH levels would decrease and ==ovulation would be blocked==
What would happen to hormones if progestin supplement is given?
30
New cards
GnRH and LH would increase and P4 would decrease, which would lead to the loss of pregnancy
What would happen to hormones if PGF2a is given?
31
New cards
Would cause masculinity in females and a reduction in sperm production
What would happen to hormones if an aromatase inhibitor was given?
32
New cards
No progesterone would be produced and there would be a reduction in pregnancies
What would happen to hormones if a 3-b HSD inhibitor was given?
33
New cards
ectoderm, mesoderm , and endoderm
What are the three layers of the reproductive tract?
34
New cards
ectoderm
What is the outermost layer of the repro tract?
35
New cards
mesoderm
What is the muscular layer of the repro tract?
36
New cards
endoderm
What is the innermost layer of the repro tract?
37
New cards
hypothalamus, nervous system, skin, hair
What does the ectoderm consists of?
38
New cards
muscle, skeletal, cardiovascular, and reproductive system
What does the mesoderm consists of?
39
New cards
digestive system, lungs, endocrine system
What does the endoderm consists of?
40
New cards
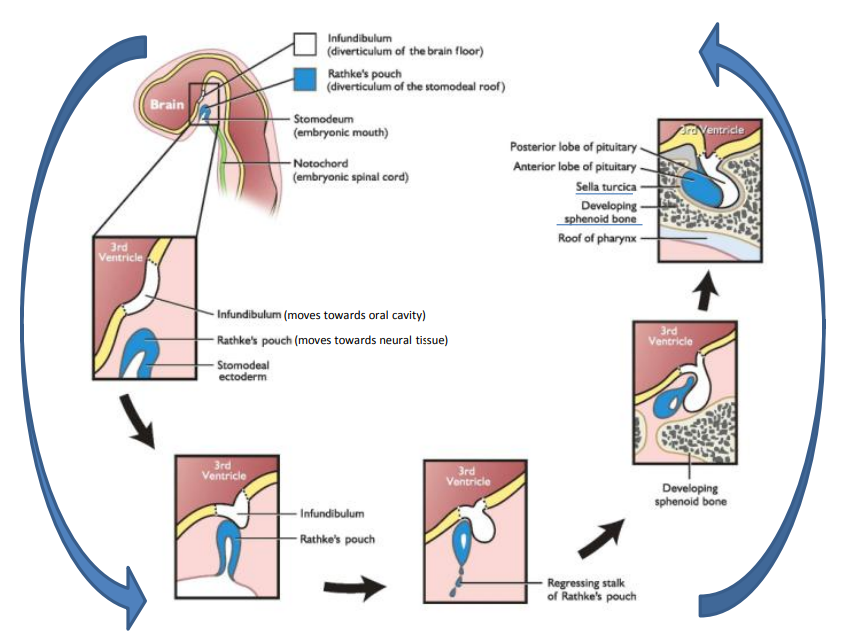
1. The oral portion of the mouth starts to reach for the infundibulum
2. Infundibulum and Rathke’s pouch touch
3. Stalk of Rathke’s pouch regresses
4. Rathke’s pouch wraps around the posterior pituitary
5. Bone encloses the anterior pituitary
How is the anterior and posterior sections of the pituitary developed?
41
New cards
infundibulum
What turns into the posterior pituitary?
42
New cards
Rathke’s pouch
What turns into the anterior pituitary?
43
New cards
there would be no growth hormones or gonadotropins
What would happen if you cut out Rathke’s pouch?
44
New cards
somatic cells and germ cells
What are the two cell types?
45
New cards
all cells in the body except germ cells
autosomes
sex chromosomes
autosomes
sex chromosomes
What are somatic cells?
46
New cards
mitosis
Do somatic cells undergo mitosis or meiosis?
47
New cards
diploid
Are somatic cells diploid or halploid?
48
New cards
60
How many chromosomes do cattle have?
49
New cards
64
How many chromosomes do horses have?
50
New cards
38
How many chromosomes do swine have?
51
New cards
46
How many chromosomes do humans have?
52
New cards
56
How many chromosomes do sheep have?
53
New cards
==oogonia and spermatogonia== formed from primordial germ cells
What are germ cells?
54
New cards
haploid
Are germ cells diploid or halploid?
55
New cards
both
Do germ cells undergo mitosis or meiosis?
56
New cards
produces two identical daughter cells
only 1 phase
only 1 phase
Overview of mitosis…
57
New cards
2 phases
only in germ cells
Meiosis 1: exchange or alteration of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
Meiosis 2: just like mitosis
only in germ cells
Meiosis 1: exchange or alteration of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
Meiosis 2: just like mitosis
Overview of meiosis…
58
New cards
epithelial lining of the gut
What cells have a high rate of mitosis?
59
New cards
brain cells
What cells have a low rate of mitosis?
60
New cards
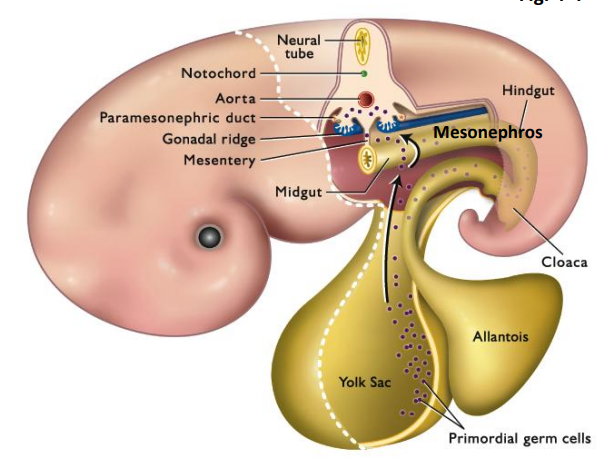
Germ Cell Migration (Know the labels)
61
New cards
nutrient source of fetus
origin of the primordial germ cells
origin of the primordial germ cells
What is the purpose of the yolk sac?
62
New cards
waste holder
What is the purpose of the allantois?
63
New cards
where the primary sex cords are formed
What is the purpose of the gonadal ridge?
64
New cards
Duct that will become kindey
What is the nephros?
65
New cards
1. germ cells start at the yolk sac
2. They migrate through or pass the hindgut
3. they enter the gonadal ridge and start to undergo mitosis
4. ==primordial germ cells are sealed off by the tunica albuginea forming an indifferent gonad==
What is the germ cell migration?
66
New cards
neither a female or a male (sex determination has not been determined)
What is an indifferent gonad?
67
New cards
mesonephros or wolfian duct
What are the names for the male duct?
68
New cards
Paramesonephros or Mullerian duct
What are the names for the female duct?
69
New cards
You get a female adult
What happens if you remove the ovaries from a female fetus?
70
New cards
You get a female adult
What happens if you remove the testes from a male fetus?
71
New cards
SRY (sex determining region)
What is the determining factor of a Y chromosome?
72
New cards
==synthesized by developing sex cords==
causes differentiation of sertoli cells
causes differentiation of sertoli cells
What is testis determining factor?
73
New cards
==anti-mullerian hormone== and testosterone
What do male Sertoli cells produce?
74
New cards
rete testes
==efferent ducts==
epididymis
==vas deferens==
==efferent ducts==
epididymis
==vas deferens==
What does the mesonephros duct form?
75
New cards
Yes
Does the mesonephros contain AMH and androgens?
76
New cards
No
Does the paramesonephros contain AMH and androgens?
77
New cards
male tract
Which tract develops first?
78
New cards
a hormone that causes regression of the mullerian tract
What is anti-mullerian hormone (AMH)?
79
New cards
==oviducts==
==uterus==
==anterior vagina==
==uterus==
==anterior vagina==
What does the paramesonephros tract form?
80
New cards
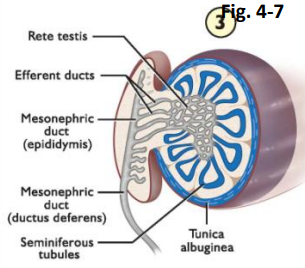
rete testis (ADD FUNCTIONS)
efferent duct
epididymis
vas deferens
seminiferous tubules
tunica albuginea
efferent duct
epididymis
vas deferens
seminiferous tubules
tunica albuginea
Wolfian tract development (know the labels)
81
New cards
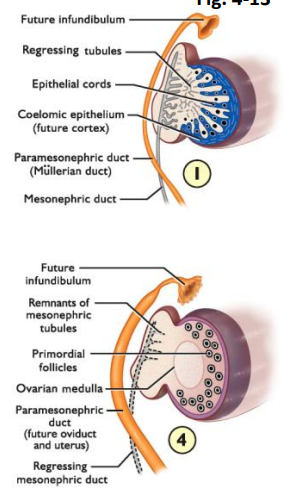
infundibulum (ADD FUNCTIONS)
primordial follicles
ovarian medulla
future oviduct and uterus
primordial follicles
ovarian medulla
future oviduct and uterus
Mullerian tract development (Know the labels)
82
New cards
it regresses
What happens to the mullerian duct in the wolfian duct formation?
83
New cards
it regresses
What happens to the wolfian duct in the mullerian duct formation?
84
New cards
==primary proliferation in the medullary region==
==Primordial germ cells in the medulla is lost==
==Primordial germ cells in the medulla is lost==
What happens in ovary development?
85
New cards
Secondary proliferation only occurs in the inner hollow of the cortex
Why is there a fixed number of cells in the ovary?
86
New cards
1. Female egg cells contain an X chromosome
2. Half of the male’s sperm cells have an X chromosome and half of them have a Y chromosome
3. An egg cell fertilized by a sperm cell containing a Y chromosome develops into a boy
4. An egg cell fertilized by a sperm cell containing an X chromosome develops into a girl
How is sex determined?
87
New cards
ectoderm
What does external genitalia developed from?
88
New cards
sex hormones
What is external genitalia regulated by?
89
New cards
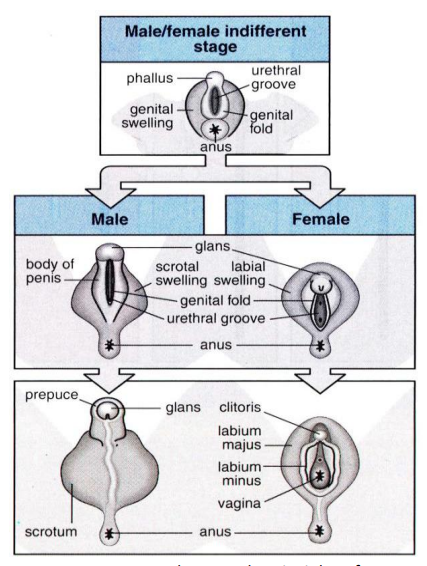
External Genitalia (picture)
90
New cards
==growth rates==
==body size==
==muscle vs adipose (fat storage)==
==hair growth==
==body size==
==muscle vs adipose (fat storage)==
==hair growth==
What are some sexual dimorphisms?
91
New cards
Can cause behavioral changes (masculine vs. feminine)
Steroids can impact (high stress can increase cortisol which can increase masculinity)
intrauterine environment (male fetus in between two females will see more estrogen and vise versa)
Steroids can impact (high stress can increase cortisol which can increase masculinity)
intrauterine environment (male fetus in between two females will see more estrogen and vise versa)
How does sex influence the brain?
92
New cards
estrogen
What does alpha-fetoprotein bind to?
93
New cards
estrogen would be able to enter the hypothalamus and knock out the surge center
What would happen if there was a lack of alpha-fetoprotein in a female brain?
94
New cards
1. the gonads release testosterone and it travels to the hypothalamus
2. testosterone is lipophilic and can transport through the cell membrane
3. testosterone is converted to estrogen due to an increase in aromatase
4. Estrogen regresses surge center
What is the process to knock out the surge center in males?
95
New cards
1. the gonads release estrogen and it travels to the hypothalamus
2. estrogen binds to alpha-fetoprotein which causes them to be rejected from passing through the blood brain barrier
1. Both the surge center and the tonic center can develop
What is the process for the tonic and surge center in the female?
96
New cards
in both males and females
Where is alpha-fetoprotein present?
97
New cards
since males do not have a surge center, there is more room for development of the pre-optic area
Why is there an increase of the pre-optic area in males only?
98
New cards
freemartins
true hermaphrodite
pseudo-hermaphrodite
true hermaphrodite
pseudo-hermaphrodite
What are the three types of intersexuality?
99
New cards
only cattle
What animal can be a freemartin?
100
New cards
some fish
What animals can be a true hermaphrodite?