biochemistry 30s 👩🔬
5.0(6)Studied by 376 people
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:26 PM on 5/9/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
the study of the chemistry of living organisms
define biochemistry
2
New cards
the building block of matter
what is an atom?
3
New cards
a particular type of atom
what is an element?
4
New cards
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon
which four elements make up 96% of living organisms?
5
New cards
hydrogen-white
oxygen-red
nitrogen-blue
carbon-black
oxygen-red
nitrogen-blue
carbon-black
what are the colours of the HONC elements?
6
New cards
hydrogen-1
oxygen-2
nitrogen-3
carbon-4
oxygen-2
nitrogen-3
carbon-4
how many bonds do each of the HONC elements want?
7
New cards
molecules that contain carbon
what are organic molecules?
8
New cards
organic molecules (molecules with carbon)
what is organic chemistry the study of?
9
New cards
a group of 2 or more atoms joined by covalent bonds
what is a molecule?
10
New cards
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
what are the 4 types of organic molecules in living organisms?
11
New cards
\-molecules containing C,H and O
\-contain a ratio of 2H:1O
\-there are 3 types
\-contain a ratio of 2H:1O
\-there are 3 types
carbohydrates (3)
12
New cards
carbohydrates
what does CHO stand for?
13
New cards
1. monosaccharides
2. disaccharides
3. polysaccharides
what are the 3 types of carbohydrates?
14
New cards
\-also known as simple sugars
\- used as a source of energy by cells
\-ep. fructose, glucose, galactose
\- used as a source of energy by cells
\-ep. fructose, glucose, galactose
monosaccharides (2) and name examples (3)
15
New cards
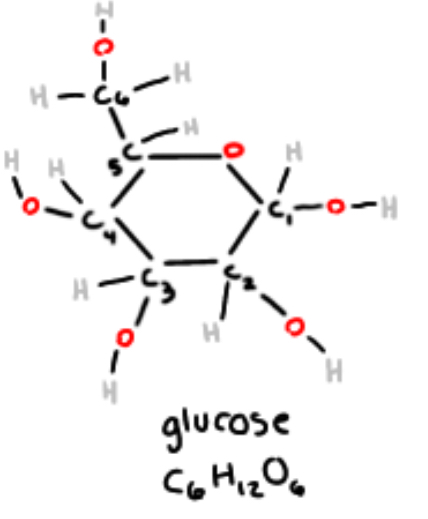
what is the formula for glucose + draw glucose
16
New cards
1. draw a hexagon
2. draw 5 carbon (number them) and one oxygen, attach C6 to C5
3. add a hydroxyl group to each carbon except C5
4. add hydrogen to all carbons that do not have enough bonds
what are the four steps for drawing glucose?
17
New cards
\-O-H
what is a hydroxyl group?
18
New cards
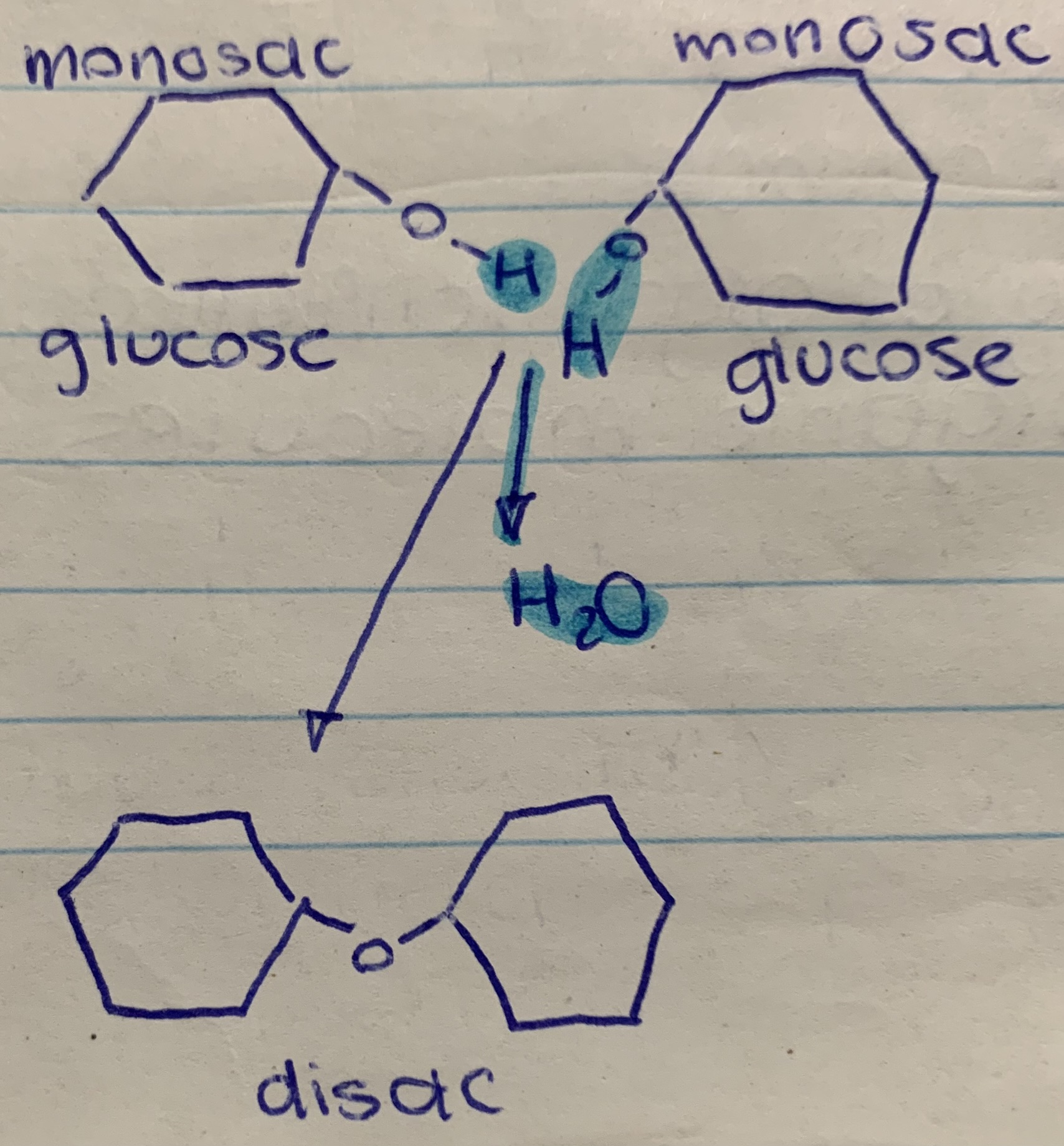
the process by which 2 molecules are joined to one another involving the removal of a water molecule
dehydration synthesis (1) and sketch an example
19
New cards
\-2 monosacs joined together during dehydration synthesis
\-ep. lactose, sucrose, maltose
\-ep. lactose, sucrose, maltose
disaccharides (1) and 3 examples
20
New cards
the process by which a complex molecule is broken down into units when H20 molecules are added
define hydrolysis
21
New cards
greek word meaning many/more than one
define poly
22
New cards
\-a long chain of monosaccharides bonded together through dehydration synthesis
what are polysaccharides? (1)
23
New cards
1. storage of extra sugar
2. structural parts of organisms
what are the two functions of polysaccharides?
24
New cards
\-extra sugar is converted into glycogen which is stored in liver and muscle cells
\-a polysac called chitin makes up exoskeletons in insects
\-a polysac called chitin makes up exoskeletons in insects
polysaccharides in animals (2)
25
New cards
\-plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. when they produce to much, glucose is converted into starch (polysac) for later use
\-cellulose forms rigid cell walls in plants
\-cellulose forms rigid cell walls in plants
polysaccharides in plants (2)
26
New cards
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
name 4 polysaccharides
27
New cards
form rigid, hard parts of organisms (structural parts of organisms)
in addition to storing sugar, what do polysaccharides do?
28
New cards
by moulting the old exoskeleton and forming a larger one
how do organisms with exoskeletons grow?
29
New cards
fats
what are lipids also known as?
30
New cards
glycerol and fatty acids
what are the 2 parts to a lipid molecule?
31
New cards
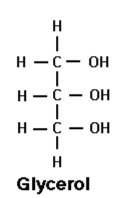
draw glycerol
32
New cards
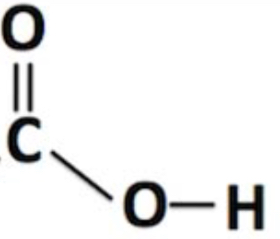
what is a carboxyl group?
33
New cards
a glycerol molecule attached to 1 fatty acid through dehydration synthesis
what is a monoglyceride?
34
New cards
monoglyceride, diglyceride, triglyceride
what are the types of glycerides? (3)
35
New cards
a) diglyceride
b) triglyceride
b) triglyceride
what happens to a monoglyceride if it is attatched to…
a) 1 more fatty acid
b) 2 more fatty acids
a) 1 more fatty acid
b) 2 more fatty acids
36
New cards
saturated and unsaturated
what are the 2 types of fatty acids?
37
New cards
carbons are attached by single bonds only
explain saturated fatty acids
38
New cards
fatty acids with at least 1 double bond between 2 carbons
explain unsaturated fatty acids
39
New cards
monounsaturated and polyunsaturated
what are the two types of unsaturated fatty acids?
40
New cards
monounsaturated fatty acids have only 1 double bond while polyunsaturated have 2 or more
what is the difference between monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids?
41
New cards
\-molecules containing C, H and O
\-NOT in a 2H:1O ratio
\-NOT in a 2H:1O ratio
lipids (2)
42
New cards
liver and muscle cells
where is glycogen found in animals?
43
New cards
adipose/fat tissue
where are triglyceride molecules found?
44
New cards
to store energy in the form of triglycerides in adipose tissue
what is the main function of lipids?
45
New cards
1) glycogen-found in liver and muscle cells
2) triglycerides-found in adipose cells
2) triglycerides-found in adipose cells
where are our 2 “bank accounts” of stored energy and what do they store?
46
New cards
adipose cells (storing triglycerides)
which energy bank is larger?
47
New cards

what is an amino group?
48
New cards
\-a long chain of amino acids
\-contain H,O,N and C, sometimes P and S
\-contain H,O,N and C, sometimes P and S
proteins (2)
49
New cards
20
how many different types of amino acids are there?
50
New cards
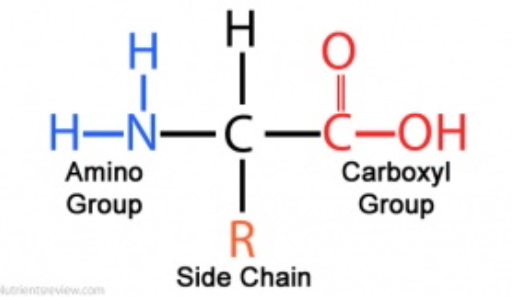
draw an amino acid with an “R” group
51
New cards
the part of an amino acid that makes it different from other amino acids
what is an R group?
52
New cards
polypeptide
what is another name for protein?
53
New cards
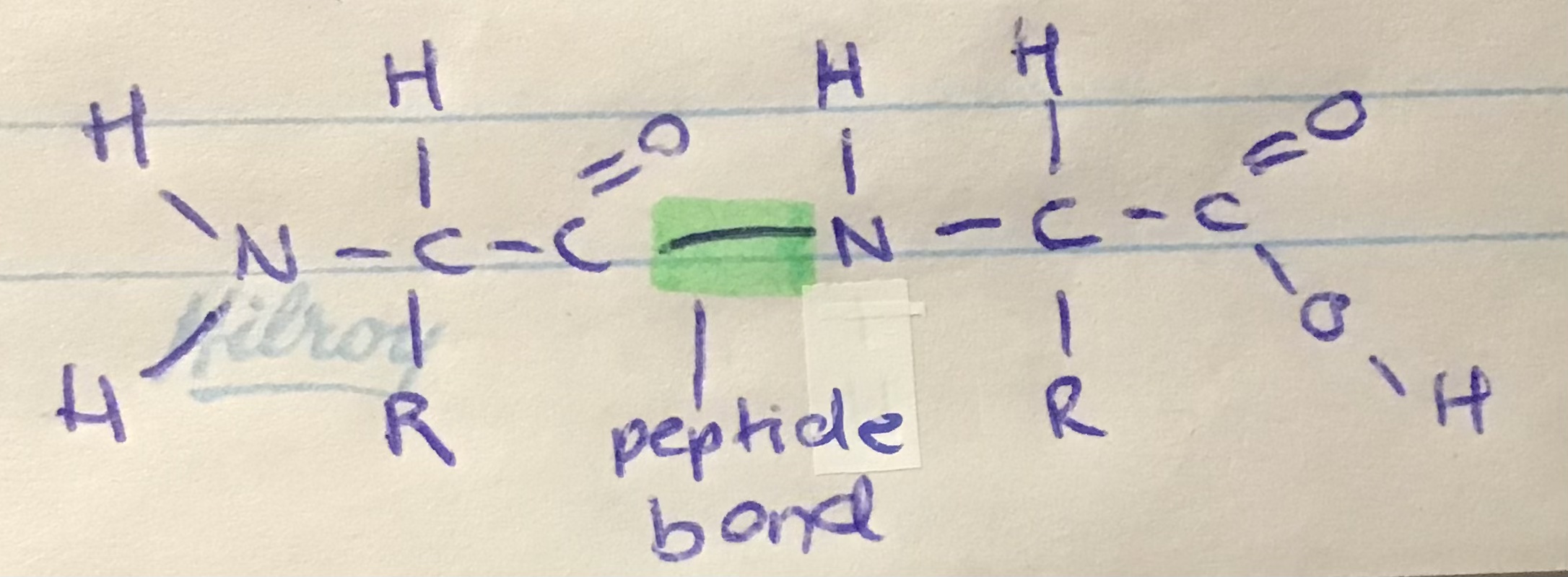
two amino acids joined together through dehydration synthesis
what is a dipeptide? draw a dipeptide
\
\
54
New cards
a bond between amino acids
what is a peptide bond?
55
New cards
ose
what do the chemical names of sugars always end in?
56
New cards
putting together
what does synthesis mean?
57
New cards
enzymes
what causes dehydrations synthesis in living cells?
58
New cards
large molecules that consist of chains of repeating units (amino acids in a protein)
what are polymers and give an example
59
New cards
animal starch
what is glycogen sometimes known as?
60
New cards
maltose
what is the product of 2 glucose molecules joining?
61
New cards
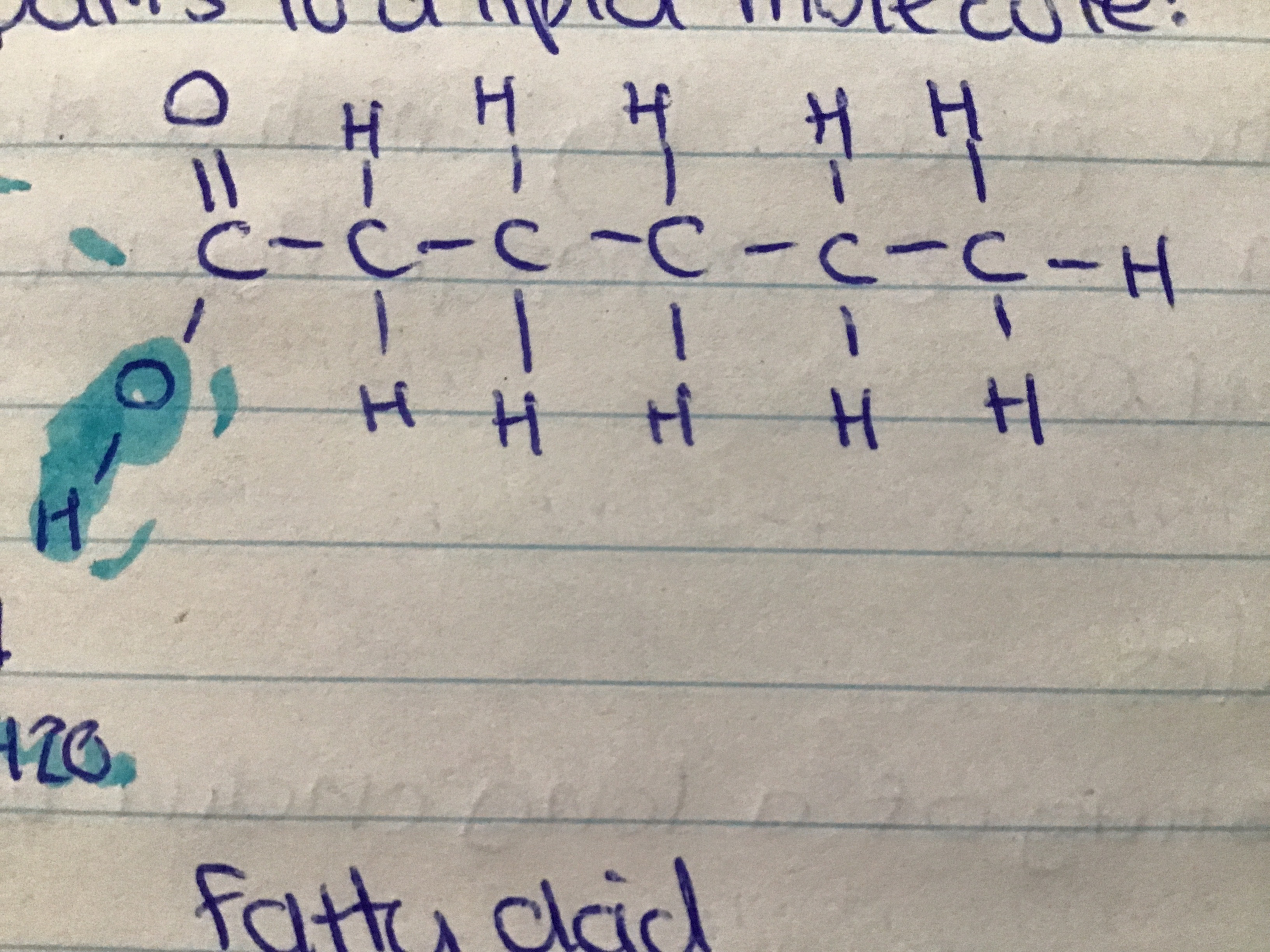
a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms with a carboxyl group at one end
what does a fatty acid consist of? sketch a fatty acid
62
New cards
lipids
which contains less oxygen, lipids or CHOs
63
New cards
yes
do lipids store twice as much energy as CHOs?
64
New cards
under the skin
where do mammals store fat?
65
New cards
the process of changing unsaturated fats into saturated fats by adding hydrogen
what is hydrogenation?
66
New cards
an essential compound found in animal tissues that can buildup in arteries and cause heart attacks and strokes
what is cholesterol?
67
New cards
saturated fat
which type of fat causes the highest cholesterol levels?
68
New cards
unsaturated fats are liquid at room temp, saturated fats are solid at room temp
how can you tell if you are eating saturated or unsaturated fats?
69
New cards
compounds similar to glycerol bond with fatty acids
how are waxes formed?
70
New cards
glycerol bonds with fatty acids
how are fats and oils formed?
71
New cards
variable groups, side chains
what are R groups also known as?
72
New cards
a) the order of amino acids
b) the function of the protein
b) the function of the protein
a) what determines the 3D shape of a protein? b) what does the 3D shape of a protein determine?
73
New cards
a) chemical reactions (through enzymes)
b) defence
c) transportation
b) defence
c) transportation
what are the functions of proteins (3)
74
New cards
breaks sucrose into monosaccharides
what does the enzyme sucrase do?
75
New cards
antibodies
what is a protein that defends?
76
New cards
hemoglobin
what is a protein that transports?
77
New cards
a repeating unit of DNA that has 3 parts
what is a nucleotide? draw a nucleotide
78
New cards
deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
what are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
79
New cards
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
what are the nitrogenous bases?
80
New cards
adenine and thymine, cytosine and guanine
what are the complimentary base pairings?
81
New cards
a 5 carbon sugar
what is deoxyribose?
82
New cards
draw a DNA ladder
83
New cards
C+G=3
A+T=2
A+T=2
how many hydrogen bonds do each complimentary base pairing have?
84
New cards
\-contain H,O,N,C and phosphorous
\-Two types are DNA and RNA
\-Two types are DNA and RNA
nucleic acids (2)
85
New cards
a double helix
what shape is DNA in?
86
New cards
DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA-ribonucleic acid
RNA-ribonucleic acid
what are DNA and RNA short for
87
New cards
acts as an “instruction manual”, the order of nitrogenous bases determines how to make different proteins
what does DNA do?
88
New cards
a region of DNA that codes for a protein
what is a gene?
89
New cards
the nucleus
where are nucleic acids found?
90
New cards
an organic base that contains nitrogen
what is a nitrogenous base?
91
New cards
\-has only 1 strand of bases
\-contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
\-the base uracil instead of thymine
\-contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
\-the base uracil instead of thymine
in what ways does RNA differ from DNA? (3)
92
New cards
3 billion
how many base pairs can 1 strand of DNA have?
93
New cards
50-100 000
how many amino acids are in a chain of polypeptides?
94
New cards
4 centimetres
how long would an uncoiled DNA strand be?
95
New cards
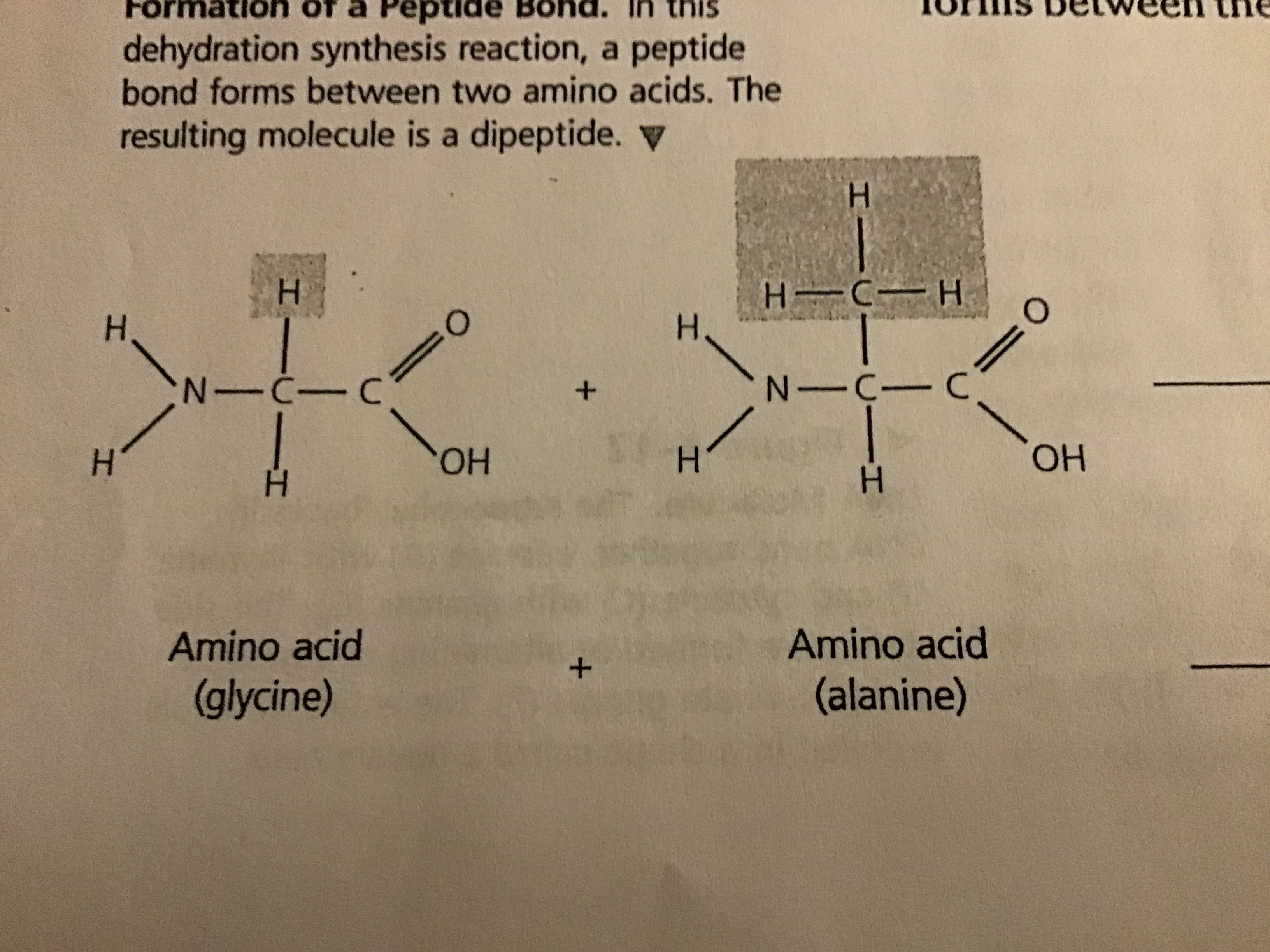
draw glycine and alanine
96
New cards
tissues, structural parts of cells, hormones, antibodies and enzymes
where in the body are proteins found? (5)
97
New cards
bonds that occur between parts of a protein when it folds
what are cross links?
98
New cards
globules, pleated sheets, coils, helixes
what are shapes commonly found in protein molecules? (4)