Chemistry 110 UNIT 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:29 AM on 9/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
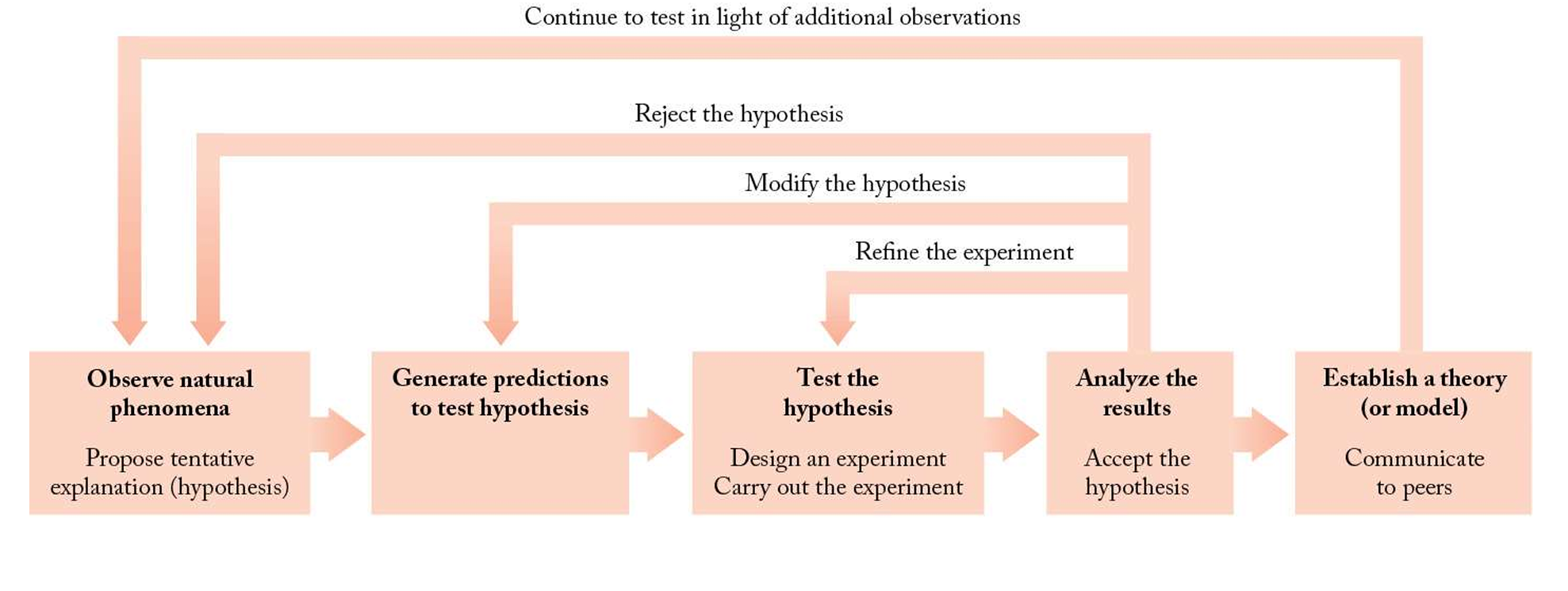
Describe scientific method
2
New cards
Apply the COAST approach to problem solving
* Collect and Organize
* Identify key concepts and skills required to solve a problem; assemble the information needed.
* Analyze
* Evaluate information and relationships or connections; sometimes units will help identify steps needed to solve the problem.
* Solve
* Perform calculations, check units, etc.
* Think About It
* Is the answer reasonable? Are the units correct?
* Identify key concepts and skills required to solve a problem; assemble the information needed.
* Analyze
* Evaluate information and relationships or connections; sometimes units will help identify steps needed to solve the problem.
* Solve
* Perform calculations, check units, etc.
* Think About It
* Is the answer reasonable? Are the units correct?
3
New cards
Distinguish between the classes of matter between the physical and chemical properties of pure substances
**Physical Properties:**
* Intensive property:
* independent of amount of substance
* Example: color, melting point, density
* Extensive property:
* dependent with quantity of substance present
* Example: volume, mass
**Chemical Property:**
* property of substance only observed by reacting it with another substance
* Example: H2 and O2 reacting to create compound water
* Intensive property:
* independent of amount of substance
* Example: color, melting point, density
* Extensive property:
* dependent with quantity of substance present
* Example: volume, mass
**Chemical Property:**
* property of substance only observed by reacting it with another substance
* Example: H2 and O2 reacting to create compound water
4
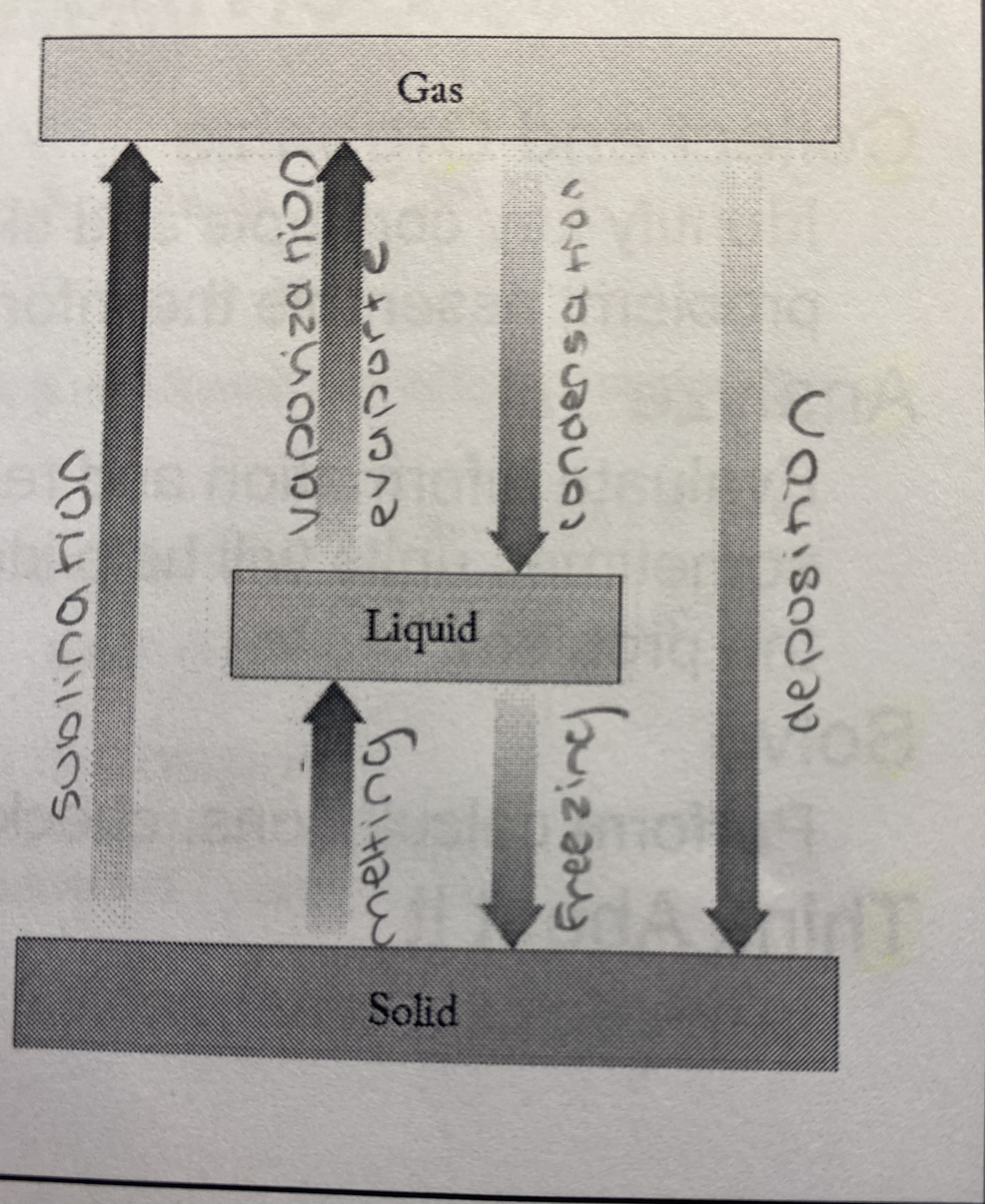
New cards
States of Matter
5
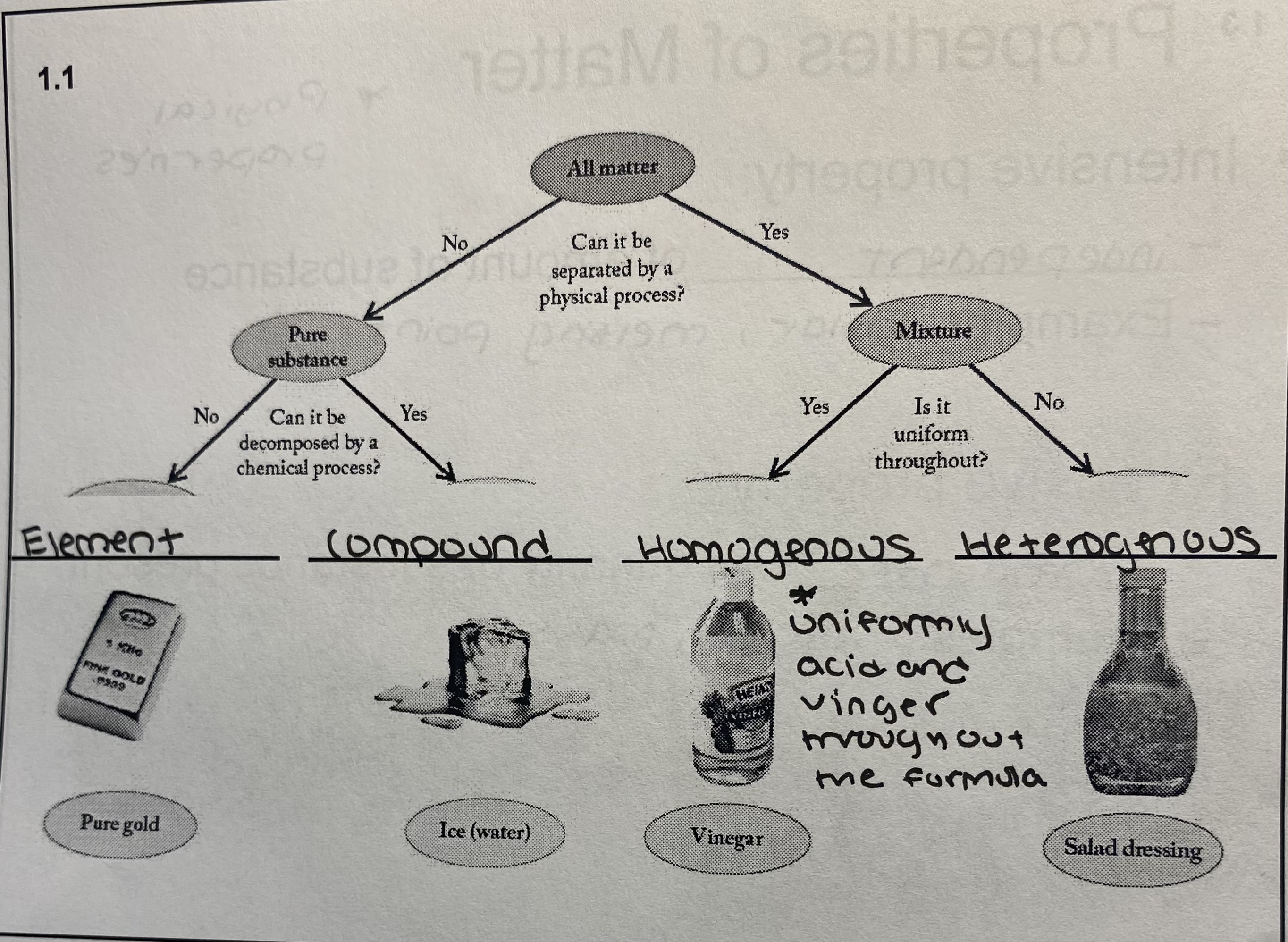
New cards
Pure substance or mixture
6
New cards
Law of conservation
states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another
7
New cards
Prefixes
Tera = 12
Giga = 9
Mega = 6
Kilo = 3
Hecto = 2
Deka = 1
Deci = -1
Centi = -2
Mili = -3
Micro = -6
Nano = -9
Pica = -12
Giga = 9
Mega = 6
Kilo = 3
Hecto = 2
Deka = 1
Deci = -1
Centi = -2
Mili = -3
Micro = -6
Nano = -9
Pica = -12
8
New cards
Convert C to K
K = C + 273.15
9
New cards
Sig Figs
34\.023 = 5
0\.068 = 2
0\.0680 = 3
\*zeros at the end of the number with a decimal point are significant
110 = 2
110. = 3
1\.234 x 10^-5 = 4
1.234 x 10^5 = 4
1\.2340 x 10^5 = 5
0\.068 = 2
0\.0680 = 3
\*zeros at the end of the number with a decimal point are significant
110 = 2
110. = 3
1\.234 x 10^-5 = 4
1.234 x 10^5 = 4
1\.2340 x 10^5 = 5
10
New cards
Precision in Calculation
1. **When adding or subtracting**
1. # of decimal places in the answer = # decimal places in the number with the fewest places
2. least precise determines the answer
2. **When multiplying or dividing**
1. # of sig figs in means = # sig figs in number with the fewest sig figs
3. Precision is based on experimental values
11
New cards
Quantum theory
Energy = hv
* energy = proton energy
* h = plancks contant 6.626 X 10 -34 J
* v = frequncy
* energy = proton energy
* h = plancks contant 6.626 X 10 -34 J
* v = frequncy
12
New cards
Quantized States
* Quantized states: Discrete energy levels (e.g., steps)
\
* Unquantized states: smooth transition between levels (e.g., ramp)
\
* Unquantized states: smooth transition between levels (e.g., ramp)
13
New cards
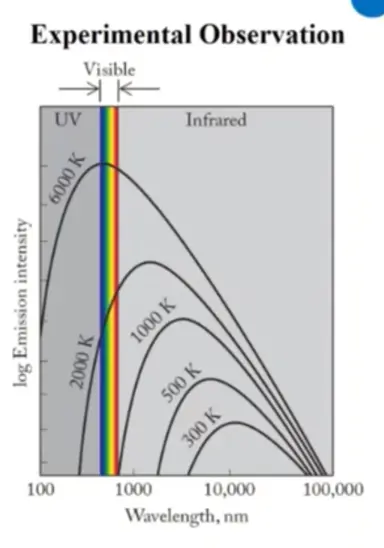
Black Body Radiation
Objects heated > emits radiation
**Key Idea:** Wavelength distribution of the radiation depends on temperature
* Planck introduced concept that energy is released or absorbed in discrete “chunks”
* Quantization of energy required for theory to match
E = hv
E= energy
V = frequency
h= __Planck’s__ constant
* the key overall point is energy is emitted or absorbed in chunks and that is related to temperature
**Key Idea:** Wavelength distribution of the radiation depends on temperature
* Planck introduced concept that energy is released or absorbed in discrete “chunks”
* Quantization of energy required for theory to match
E = hv
E= energy
V = frequency
h= __Planck’s__ constant
* the key overall point is energy is emitted or absorbed in chunks and that is related to temperature
14
New cards
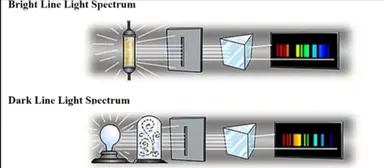
Line Spectrum
Dark lines = Bright lines
* Emitted light (bright line) at the same “energy” as absorbed light (dark line)
* SO… there must be *certain characteristic energy states* in a gas that are reversible (can take in or give off energy)
* Emitted light (bright line) at the same “energy” as absorbed light (dark line)
* SO… there must be *certain characteristic energy states* in a gas that are reversible (can take in or give off energy)
15
New cards
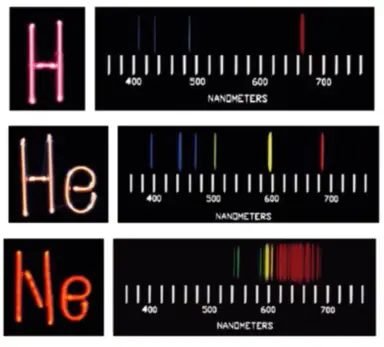
Atomic Emission Spectra
* bright line emission spectra are unique for different elements and therefore a key way to identify unknown elements
* more complex the elements the more lines
* more complex the elements the more lines
16
New cards
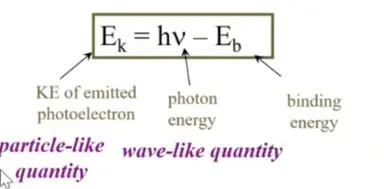
The Photoelectric Effect
**Key Idea:** When a photon hits a metal surface it ejects an electron
\*einstein
\
Experimental Observations:
1. No electrons are ejected unless the light exceeds a threshold frequency ( if not enough or below freq then no ejection of electrons)
2. The kinetic energy of the electrons increases linearly with the frequency of the light
3. But the kinetic energy of the electrons is independent of the light intensity
4. Even at a low light intensity, electrons are ejected immediately
\
Experimental Results: If you triple the number of photons then it triples the electrons
\-higher freq of light increases then velcity increaese
\*einstein
\
Experimental Observations:
1. No electrons are ejected unless the light exceeds a threshold frequency ( if not enough or below freq then no ejection of electrons)
2. The kinetic energy of the electrons increases linearly with the frequency of the light
3. But the kinetic energy of the electrons is independent of the light intensity
4. Even at a low light intensity, electrons are ejected immediately
\
Experimental Results: If you triple the number of photons then it triples the electrons
\-higher freq of light increases then velcity increaese
17
New cards
Photoelectric Effect Overall
* Observation
Electons are emitted by metal only if light has frequnwcy greater than certain minimum value, no mater how intese the light
* When electons are emitted, the number emitted is proportional to tlight intenisty
Electons are emitted by metal only if light has frequnwcy greater than certain minimum value, no mater how intese the light
* When electons are emitted, the number emitted is proportional to tlight intenisty