Polymers intro
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the meaning and derivation of the word plastic?
It means ‘easily shaped or moulded’ and is derived from the Greek ‘plastikos’.
What is the meaning and origin of the word polymer?
It is a Greek word meaning many parts:
poly = many
mer = parts
What are plastics derived from?
Oil or petroleum.
Why are plastics likely the most widely used materials in manufacturing today?
Because of the huge variety available and their different properties.
What are the two types of plastics?
Natural and synthetic.
What are three sources of natural polymers?
Plants (cellulose)
Trees
Animals
What are three sources of synthetic polymers?
Crude oil
Coal
Natural gas
What are three types of plastic that exist?
Natural plastics (made from rubber or latex)
Bio-plastics (made from vegetable starches or algae)
Synthetic plastics (made from petrochemical sources)
What plastics can be derived from plants? (and example products)
Cellulose - tennis balls
Cellulose acetate - films
Cellophane - wrapping
What plastics can be derived from trees? (and example products)
Latex - rubber gloves
Bitumen - roads + rooves
Resin - paints
Amber
What plastics can be derived from animals?
Plastics from their horns, nails or claws which are used for decoration.
What are two examples of naturally occurring plastics?
Amber (fossilised tree resin)
Latex (a form of rubber)
What is the process of acquiring natural latex?
It is harvested form the rubber tree
The bark is scored
The milky sap is then allowed to spill out into a container
What are bioplastics mostly made from?
Corn or vegetable starches.
Why are bioplastics good for the environment?
They are fully biodegradable if composted
Bacteria in the soil breaks down the plastic quickly
Why can’t bioplastics be recycled in a traditional way?
They decompose, and therefore do not have the ability to be recycled in the same way. They can contaminate recycled material as they are organic material.
Where do synthetic plastics come from?
They come from polymers
These come from finite petrochemical resources such as crude oil
Plastics can also be derived from natural gas and coal
What is the main process used to produce polymers called?
Refining.
How is crude oil acquired for processing?
It is extracted from underground
This could be at sea using an oil rig or on land
It is then transported to a plant for conversion
Why do we need to refine crude oil?
Crude oil is naturally heavy, sticky and black
It is virtually unusable in this unrefined state
It has to be converted and refined into other more useable products such as fuels
What is fractional distillation?
A method used to separate the different hydrocarbons found in crude oil.
Fractional distillation:
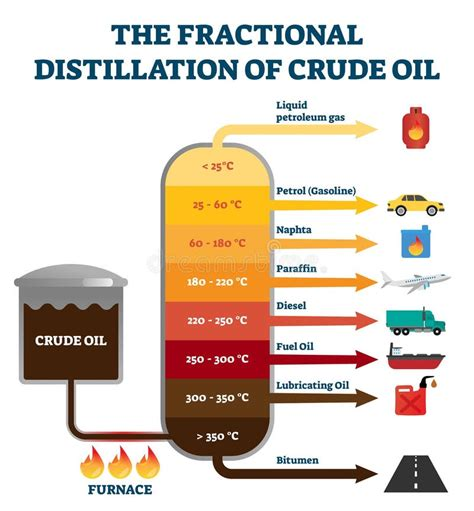
How does fractional distillation work?
Each of the hydrocarbon products produced has different sized molecules with different boiling points
So, each one is separated by heating up the mixture and cooling off each component at a certain temperature
What is the base unit of a polymer?
A monomer.
What are the stages of the fractional distillation process?
• Crude oil is heated to 350°C
• Hot oil is pumped into the base of the distillation tower
• The crude oil vaporises and rises up the tower
• As the crude oil cools, the molecules condense
• Heavier molecules stay at the bottom and lighter molecules
rise to the top
• The fractions (hydrocarbons) are siphoned off for cracking