1- Radiation Safety & Physics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Radiation Exposure
• Radiation is harmful to your body! Not only high doses delivered acutely but also low doses over long periods of time.
• Veterinarians/techs/nurses- Skin cancer is the major concern.
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable, defined by NRC, means making every reasonable effort to maintain exposures to ionizing radiation as far below the dose limits as practical, consistent with the purpose for which the licensed activity is undertaken.
How To Accomplish ALARA- Sheilding
Avoid the Primary Beam! PPE is meant to protect from scatter radiation. Can use a Lead Apron, Thyroid Shield, Gloves, Head covering (less popular), and Eye wear. Structural sheilding is also an option in certain situations
How To Accomplish ALARA- Distance
• Doubling distance away from the beam will reduce exposure by a factor of 4.
• Do you need to be right next to the patient when the
radiograph is taken?
• Chemical Restraint
• Sandbags
How To Accomplish ALARA- Time
• How many views are necessary?- Three view thorax vs two view abdomen
• How many retakes are needed?
• Does the same technician take radiographs every single time or can they be rotated to minimize exposure time?
Collimation
• A factor that can help with distance from the primary beam is collimation.
• Collimation is how narrow the machine is set for the primary beam.
Equine X-Rays
• Radiographs outside of a controlled environment.
• Can we increase distance from the primary beam?- Yes, Extenders exist to hold plate.
• Make sure handlers and others are as far away as possible.
• Same PPE applies!
What is the purpose of a dosimeter badge?
To monitor how well the occupational radiation safety program is followed.
Should dosimeter badges be shared between personnel?
No, they should NOT be shared.
Where should a dosimeter badge be worn?
It should be worn on the outside of lead aprons while in the workplace.
Why should a dosimeter badge not be worn outside of the workplace?
Wearing it outside could falsify the institution's data.
What materials are used in a dosimeter badge to trap electrons?
Radiation sensitive aluminum oxide or lithium fluoride crystals.
How are readings obtained from a dosimeter badge?
By measuring trapped electrons relative to the amount of exposure.
What part of the spectrum do x-rays belong to?
Electromagnetic radiation
How are x-rays produced?
By electron interactions outside the nucleus
Do x-rays have a charge?
No charge
Do x-rays have mass?
No mass
At what speed do x-rays travel?
Speed of light
Can x-rays be seen or felt?
Invisible and cannot be felt
In what direction do x-rays travel?
In a straight line
Can x-rays be deflected by magnetic fields?
No, they cannot be deflected
What can x-rays penetrate?
ALL matter to some degree
Can x-rays ionize atoms?
Yes, they can ionize atoms
How are x-rays made?
X-rays are produced when high speed electrons strike metal.
Where does the production of x-rays occur in modern machines?
In today's x-ray machines, this happens inside an x-ray tube.
Why is a vacuum present in the x-ray tube?
The vacuum keeps the electrons from interacting with air.
What starts the process of x-ray production?
An electric current is passed through the filament to start.
What charge does the cathode (filament) have in an x-ray tube?
The cathode (filament) is negatively charged.
What is the role of the anode in x-ray production?
The anode is positively charged and receives electrons from the cathode.
What influences the number of electrons produced in an x-ray machine?
The number of electrons produced is influenced by the amount of electric current passed through the filament.
What controls the electric current in an x-ray machine?
The current is controlled by the milliamperage (mA) of the machine.
What controls the voltage difference between the cathode and anode in an x-ray machine?
The voltage difference is controlled by kilovoltage peak (kVp).
What does adjusting mA control do for x-ray production?
Increasing mA increases the quantity of x-rays produced.
How is adjusting mA analogous to a lightbulb?
Increasing mA is like increasing the wattage of a lightbulb; a higher wattage bulb emits more light rays.
What effect does adjusting kVp have on electron velocity?
Adjusting kVp allows electrons to travel at a higher velocity.
What happens to the voltage difference when kVp is increased?
Increasing kVp increases the voltage difference between the cathode and anode.
What is the result of higher velocity electrons hitting the anode?
Higher velocity electrons release more kinetic energy when they hit the anode.
What is the overall effect of increasing kVp on x-ray production?
Increasing kVp increases both the energy and number of x-rays produced, though less than mAs.
How does our patient influence all of this?
• The x-ray machine to include the kVp and mAs will be set up based on the size of your patient and the part of the body radiographs need to be obtained.
• The measuring caliper seen here will allow you to measure your patient and then compare that number to a chart to know your machine settings.
How is grey scale made?
• Different parts of the body appear differently on a radiograph- Air, Fat, Water (soft tissue), Mineral (bone), Metal
• Why is this the case?- These different parts of the body absorb and reflect x-rays in a particular pattern. Due to this, gray scale appearance is created.
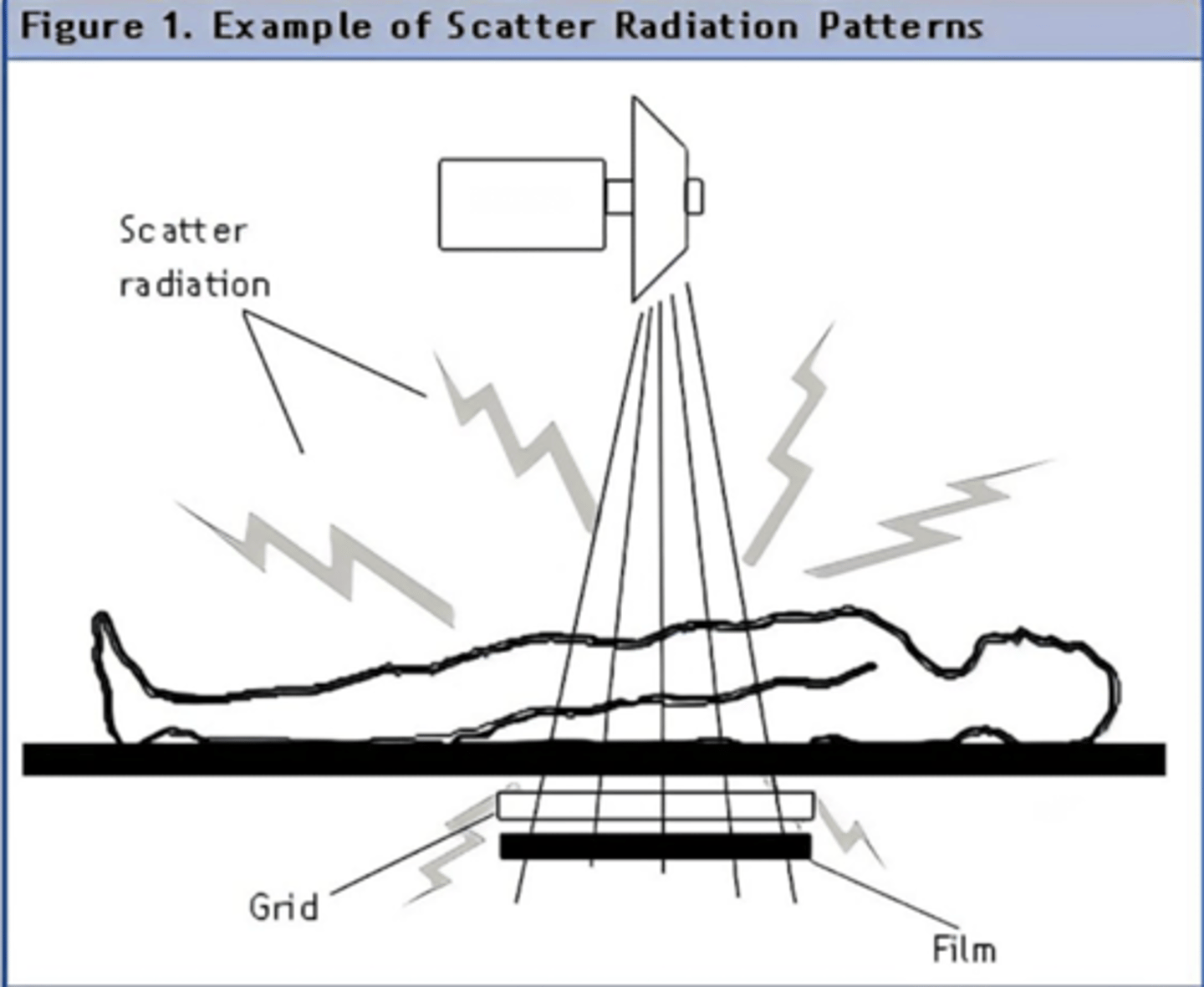
Grid
Grid helps to filter out scatter radiation to allow a better image to be recorded!