Lecture 2 Linear Alg
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
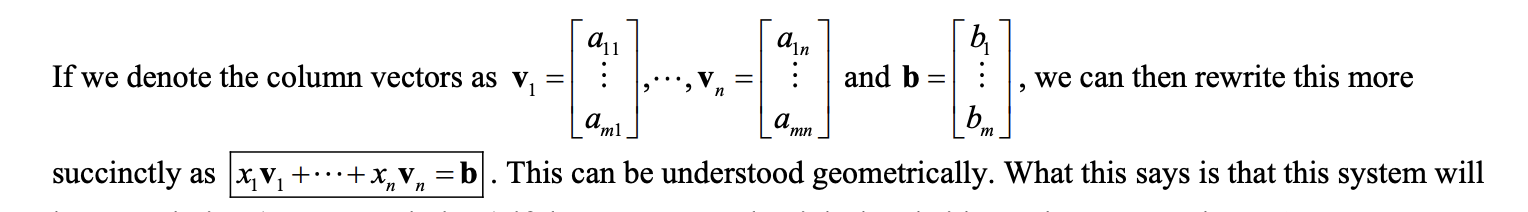
vector form of linear system:
can be written more succintly as:
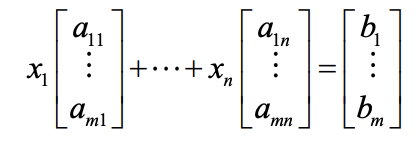
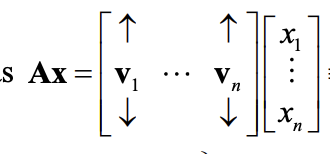
Matrix form of a linear system
Ax=b
A function T: Rn —> Rm is a linear transformation if T satisfies the linearity property T(x) = T(c1v1 + c2v2) = _____
Or if there exists an nxm matrix A such that T(x) = ___
any function of the form L(x) =ax + b is not linear unless b = __
A(x)
0
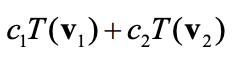
standard or elementary basis vectors e1, e2, … en
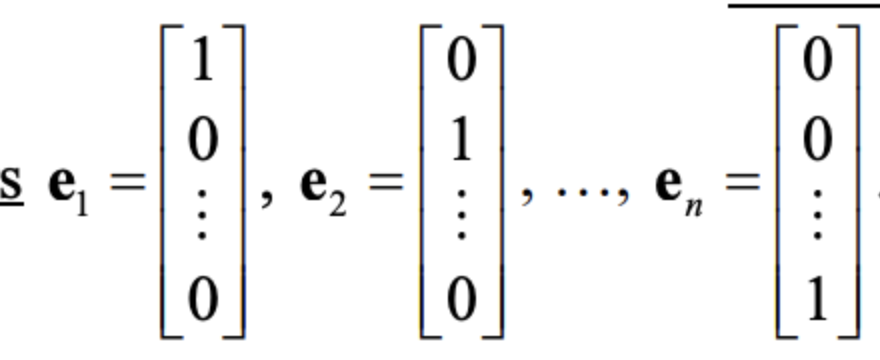
Aen =
vn
nth column of matrix A
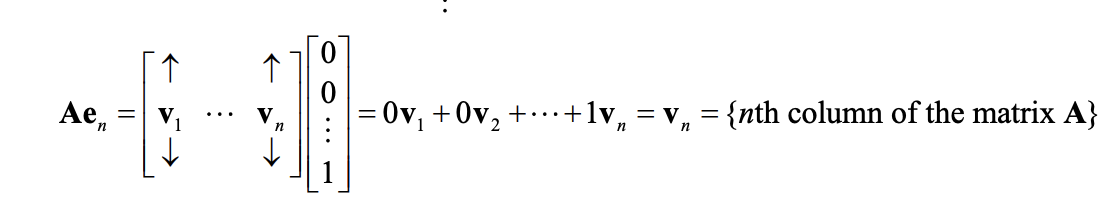
Identity function Id Rn → Rn is simply Id(x)=x
Identity matrix In
This matrix has 0’s everywhere except on the main diagonal, and all of the diagonal entries are equal to 1.
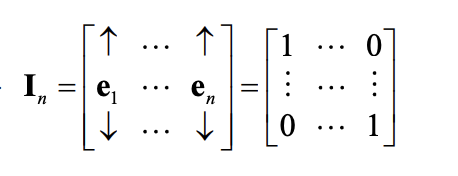
Dilation (scaling) is a transformation of the form T (x) = rx for r>0
Matrix A:
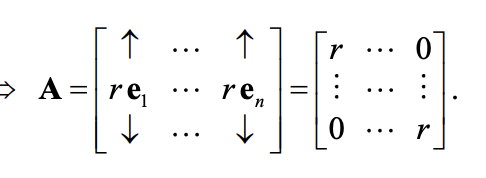
Counterclockwise rotation in R2 Matrix Rθ
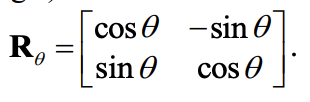
Rotation-dilation in R2 Matrix A:
If we let a =rcosθ and b =r sinθ we see any matrix of form _____
will represent a rotation-dilation where the scaling is by r= ____ and the angle of rotation is determined by θ =___
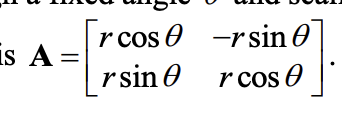
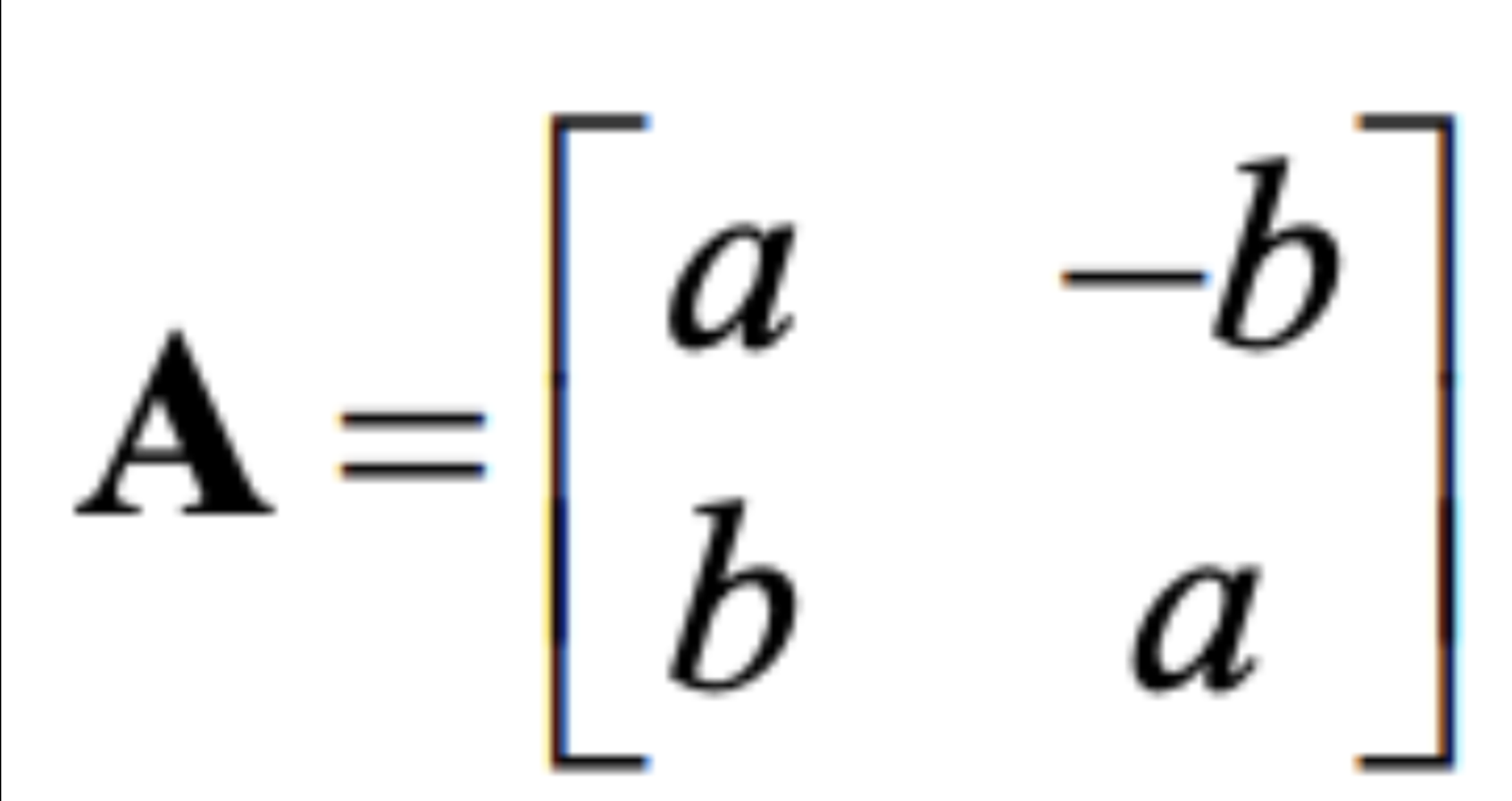
√(a²+b²), tan-1(b/a) in appropriate quadrant
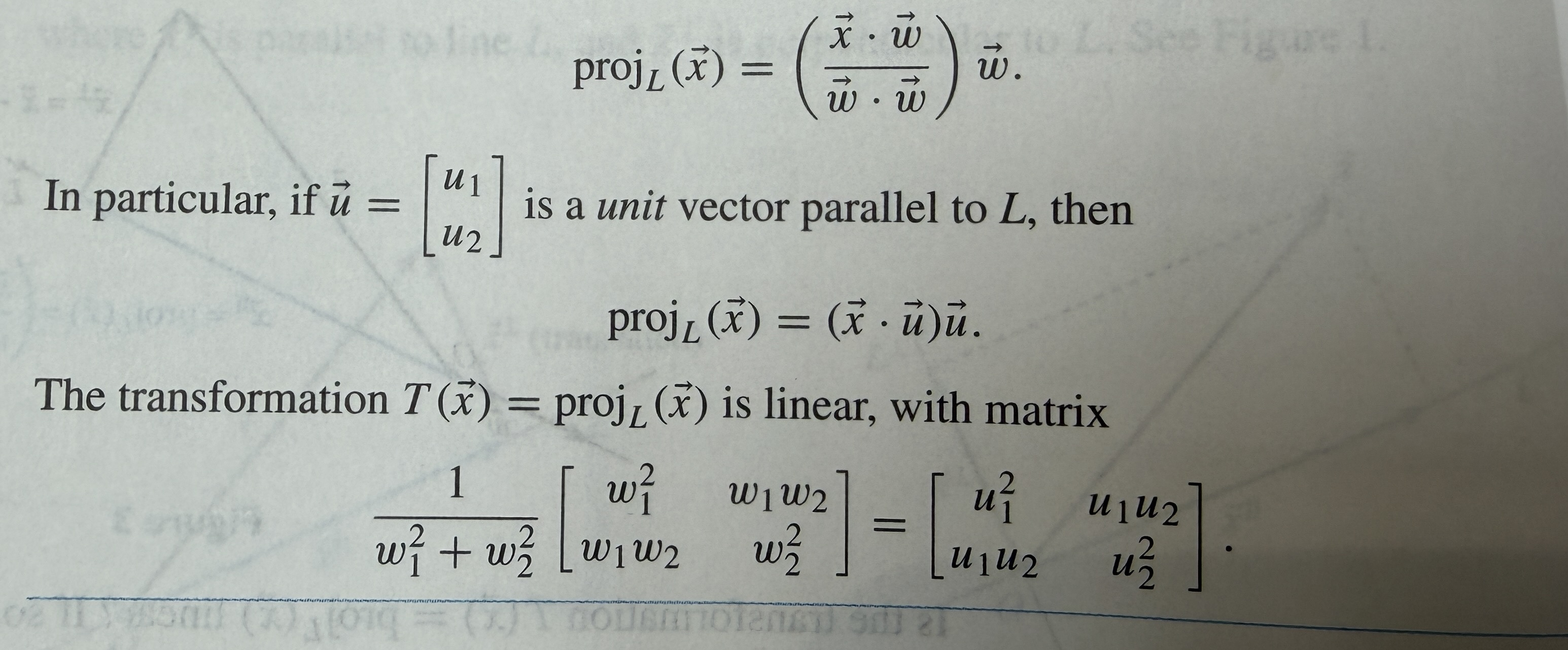
Orthogonal projection of x onto L if u is a unit vector parallel to L:
T(x) = projL(x) is linear, how to create matrix:
do T(e1), T(e2) for each en
Reflection of vector x through a line L:
Matrix of reflection:
2projL(x) - x
2A-I
A respresents matrix of orthogonal proj
Horizontal Shear w/ dilation matrix A3
Vertical Shear w/ dilation matrix A4
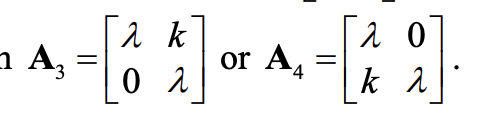
Solving for inverse matrix A-1, going from y -> x
Represent the two equations as a matrix:
Do row reduction rref [ A | In| to see if u can get:
If left half fails to be In, then A is not invertible
If the matrix A has full rank __, then we will be able to solve uniquely for x in terms of y
[A | In]
[In | A-1]
n

if det(A) is not 0, or else A will not have full rank and will not be invertible
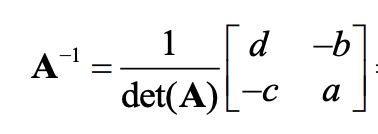
refLx matrix is of form
where a²+b²=1
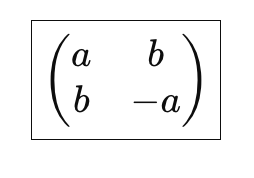
how to do dot product of two vectors
multiply the values of the same row, then add up all the sums of the rows
how to multiply matrixes: ___
If A is mxn and B is nxp (n must be same for both, meaning ___ of A must equal ___ of B), AB is ___
Row of the first × column of the second
columns, rows
mxp
a linear transformation from Rn to Rm is represented by an __ x _ matrix
Build the matrix by doing T(___) for how ever many ___ you need
mxn matrix
e1, e2, etc. columns/previous n dimensions