Biology - Genetic Diversity
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I want to end my life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a mutation?
a random change to the base sequence of DNA
Name the four different type of mutations
Substitution, Insertion, deletion and non disjunction mutation
What is an insertion mutation ? Does it cause frameshift?
where a base gets added to the base sequence of DNA. It causes a frameshift.
What is a substitution mutation? Does it cause a frameshift?
where a base gets replaced with another base in the base sequence of DNA. It does not cause a frameshift.
What is a deletion mutation? Does it cause a frameshift?
where a base in the base sequence of DNA gets deleted. It causes a frameshift.
What is a non disjunction mutation? Does it cause a frameshift?
Its the failure of the chromosomes to spereate properly. In humans, non disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis can lead to down syndrome. No it does not cause a frameshift.
What is meiosis? Where does it take place? What are the cells beforehand and what are the cells afterwards
a type of cell division which takes place in the reproductive organs. Cells that divide by meiosis are diploid to start with, but the cells that are formed are haploid.
What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis?
The chromosome number halves.
What happens before meiosis?
DNA unravels and replicates so there are two copies of eachjchromosomes called chromatids.
The DNA condenses to form double armed chromsomes, each made from two sister chromatids. The sister chromatids are joined in the middle by a centromere.
Meiosis I - what happens?
The chromosomes arrange themselves into homologous pairs and align at the equator
When theyu align at the equator the non sister chromatids can become tangled and exchange alleles which results in new combinations of alleles. (This is how meiosis produces gametes that are NOT genetically identical to each other)
These homologous pairs then seperate, halving the chromosome number
What is a homologous pair of chromosome?
A homologous pair of chromosomes is a pair consisting of one maternal chromosome and one paternal chromosome. They carry the same genes but can have different alleles.
What happens in Meiosis II?
the sister chromatids seperate.
What is genetic diversity?
Genetic diversity is the number of different alleles in a population/species. This is what causes natural selection to take place.
What is a genetic bottleneck?
A genetic bottle neck is an event that causes a big reduction in a population for example a massive volcanic eruption.
What is the founder effect?
The founder effect describes what happens when just a few organisms from a population start a new colony and there are only a small number of different alleles in the initial gene pool.
What is natural selection?
Within a population there is genetic variation due to random mutations in DNA
This means that some individuals will have an advantageous allele for their environment/ the selection pressures.
These individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass on the advantageous allele to their offspring.
Over many generations the frequency of the advantageous allele in the population incereases.
Name the three type of adaptations
Behavioural, physiological and anatomical adaptations,
What is a behavioural adaptation?
Ways an organism acts that increases its chance of survival and reproduction .
What is a physiological adaptation?
Processes inside an organisms body that increases its chance of survival.
What is an anatomical adaptation?
Structural features of an organisms body that increase its chance of survival.
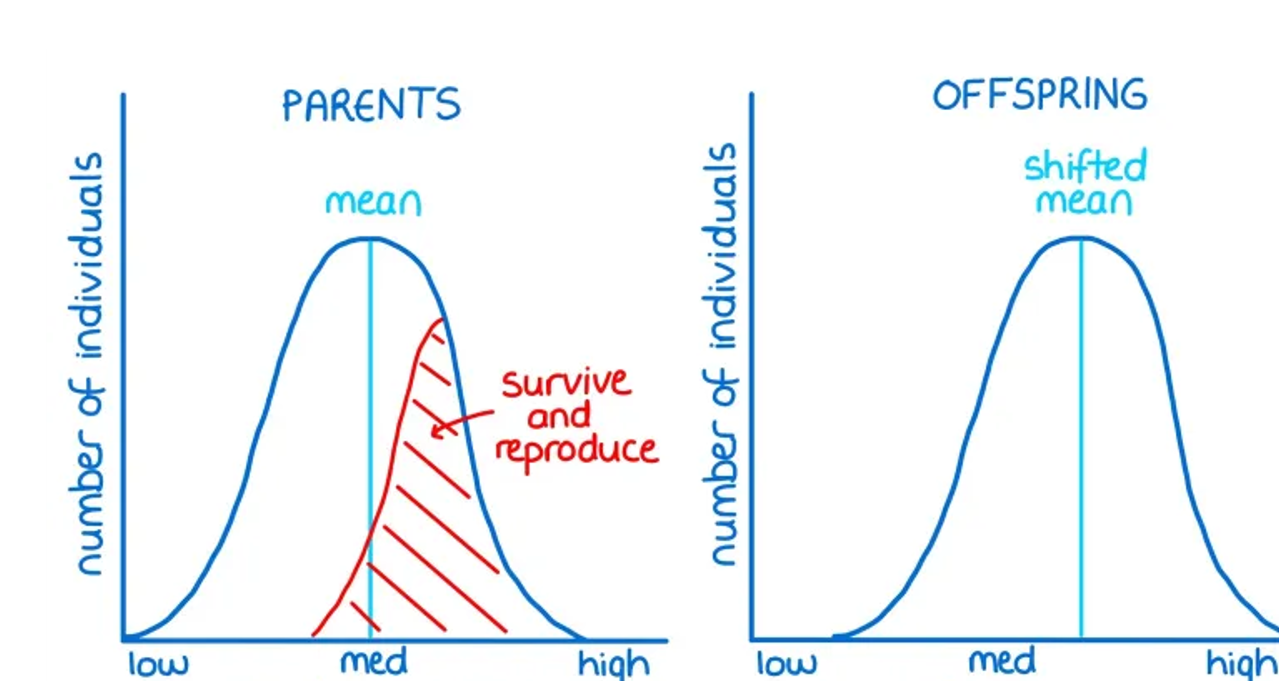
What is directional selection?
where individuals with alleles for characteristics of an extreme type are more likely to survive and reproduice. - eg. antibiotic resistance
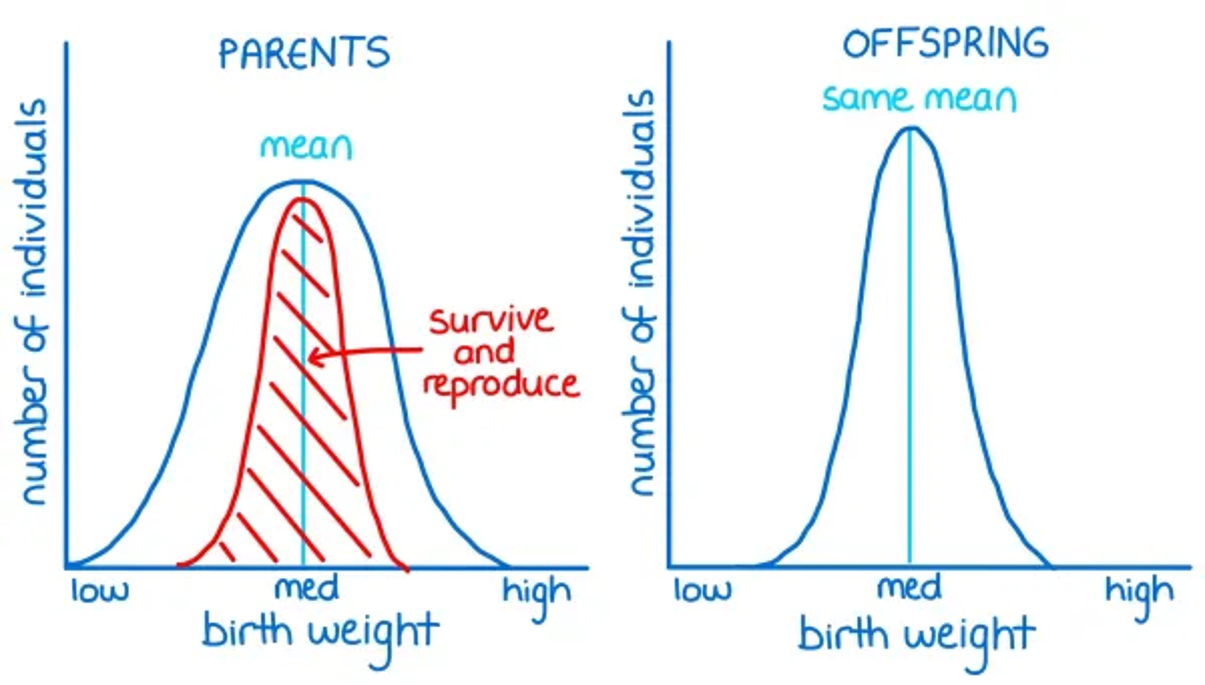
What is stabilising selection?
where individuals with alleles for characteristics towards the middle of the range are more likely to survive and reproduce- eg birth weight
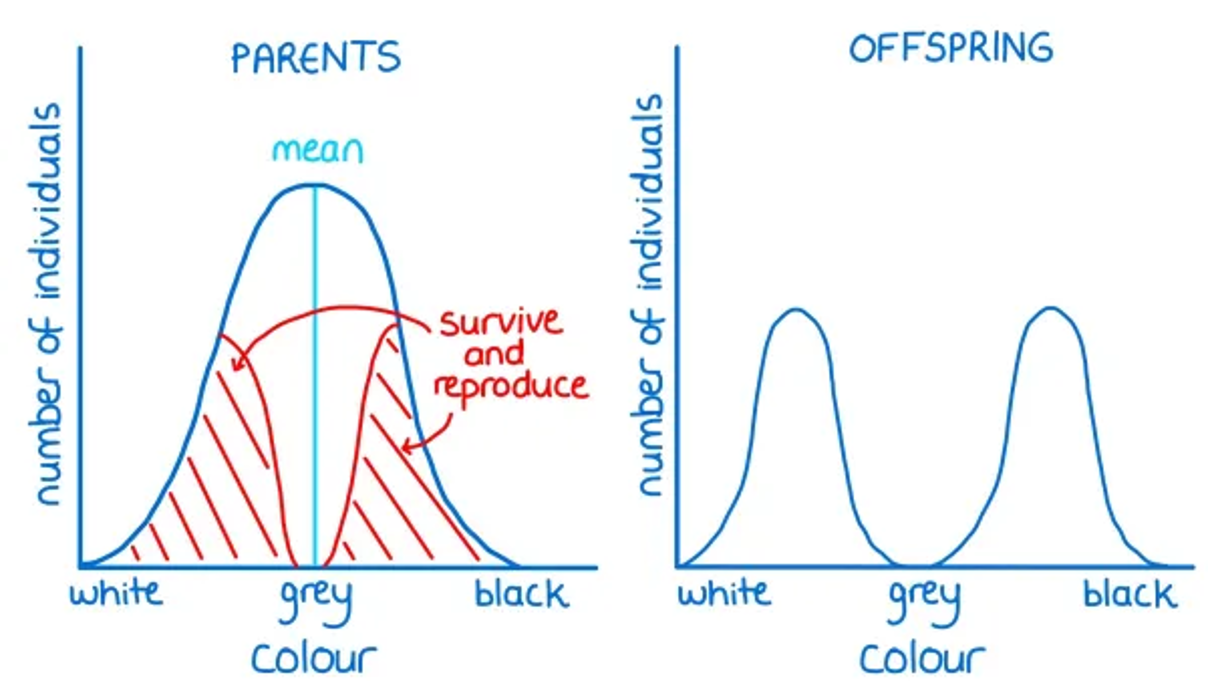
What is disruptive selection?
where phenotypes at both extremes can be an advantage.
Name the steps of transcription
RNA polymerase attatches to the DNA double-helix at the beginning of the gene. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs in DNA#
One strand acts as a template strand
Free floating RNA nucleotides align with exposed bases on the template strand using complementary base pairing
Uracil replaces Thymine
RNA polymerase joins adjacent RNA nucleotides forming phosphodiester bonds. This creates pre-MRNA
Pre-MRNA undergoes splicing, which removes introns, leaving the final mRNA molecule
Name the steps of translation
mRNA leaves the nucles and attatches to a ribosome
A tRNA molecule with a complementary anticodon binds to the first codon on mRNA using complementary base pairing
The tRNA molecule brings a specific amino acid
A second tRNA molecule binds to the second codon on mRNA bringing a second specific amino acid.
The two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond in a condensation reaction using energy from ATP hydrolysis.
The first tRNA molecule detatches and leaves the ribosome.
The ribosome moves along the mRNA and process continuies until a STOP codon is reached forming a polypeptide.
What is a gene?
Short section of DNA bases that codes for a specific polypeptide or functional RNA
Allele
Different version of the same gene
Genome
All the DNA in a cell/ organism
Proteome
The proteome is the full range of different proteins that a cell is able to produce
Loucs
fixed position of a gene on a chromosome
Genetic diversity
the number of different alleles of genes in a population
Gene pool
All of the alleles in a population
Genotype
the genetic constitution of an organism
Phenotype
the expression of this genetic constituition and its interaction wiuth the environment
Species
Organisms with similar characteristics that can interbeed to produce fertile off spring.
Population
A group of organsims of the same species occupying a particular space/habitat/area at the same time that can potentially interbreed.
Codon
Three bases on mRNA that code for a specific amino acid
Anticodon
Three bases on tRNA that are complementary to a specifc codon
Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
homologous chromosomes pair up at the equator of the cell with the maternal and paternal chromosomes re-shuffled in any combination
Crossing over between homologous chromosomes/ non-sister chromatids
Alleles are exchanged between homologous chromosomes creating new combinations of alleles