test 4 Anatomy of the Head, Neck, and Central Nervous System, Contrast Media and Imaging Modalities in Radiation Therapy
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What makes the head and neck one of the most difficult regions to study?
The large amount of structures in a small area.
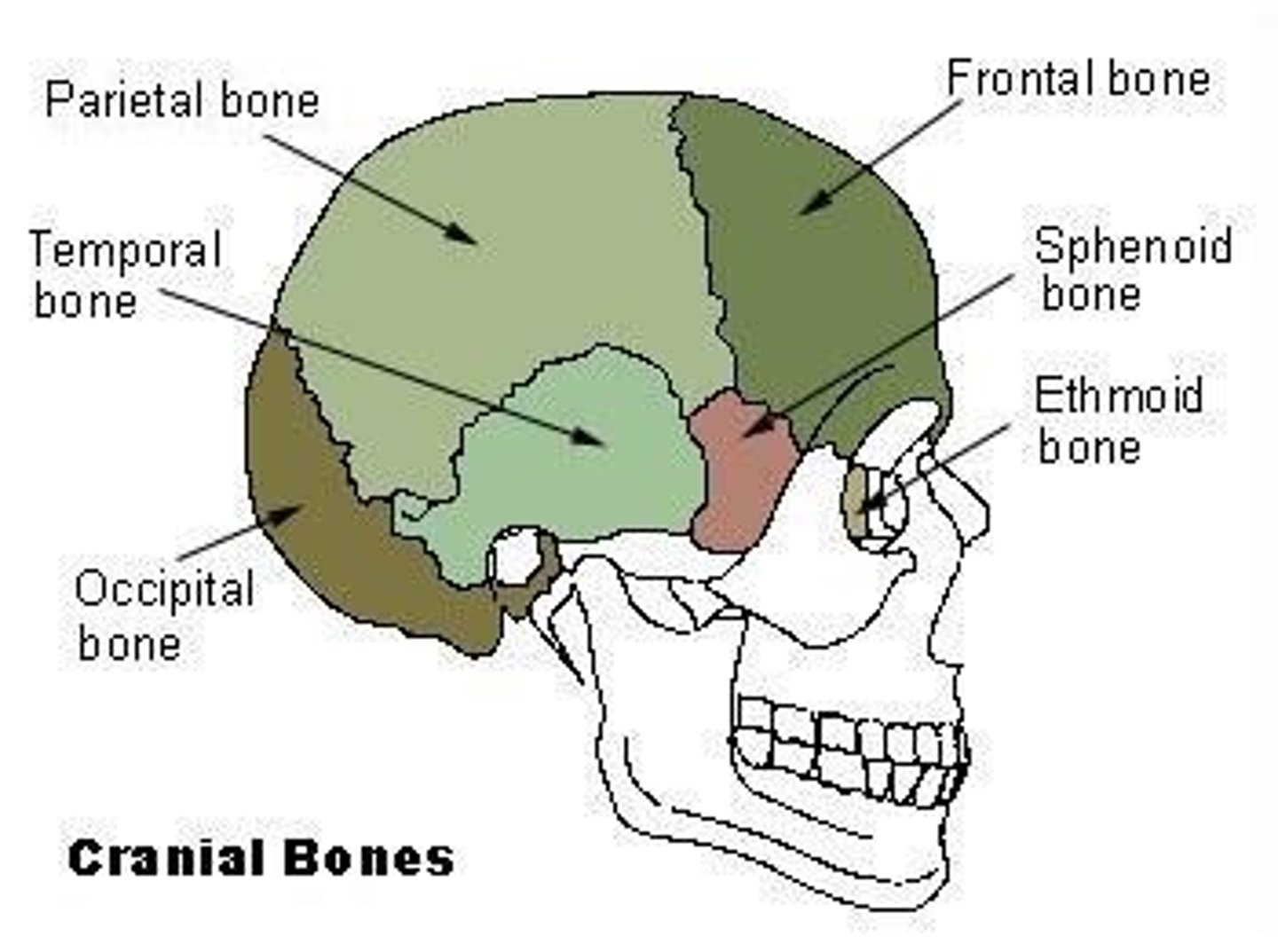
How many bones make up the cranium?
8 bones.
What are the names of the bones that comprise the cranium?
Occipital (1), Temporal (2), Sphenoid (1), Ethmoid (1), Parietal (2), Frontal (1).
What is the function of the frontal bone?
It forms the forehead, the anterior part of the skull, and the roof of the orbital cavities.
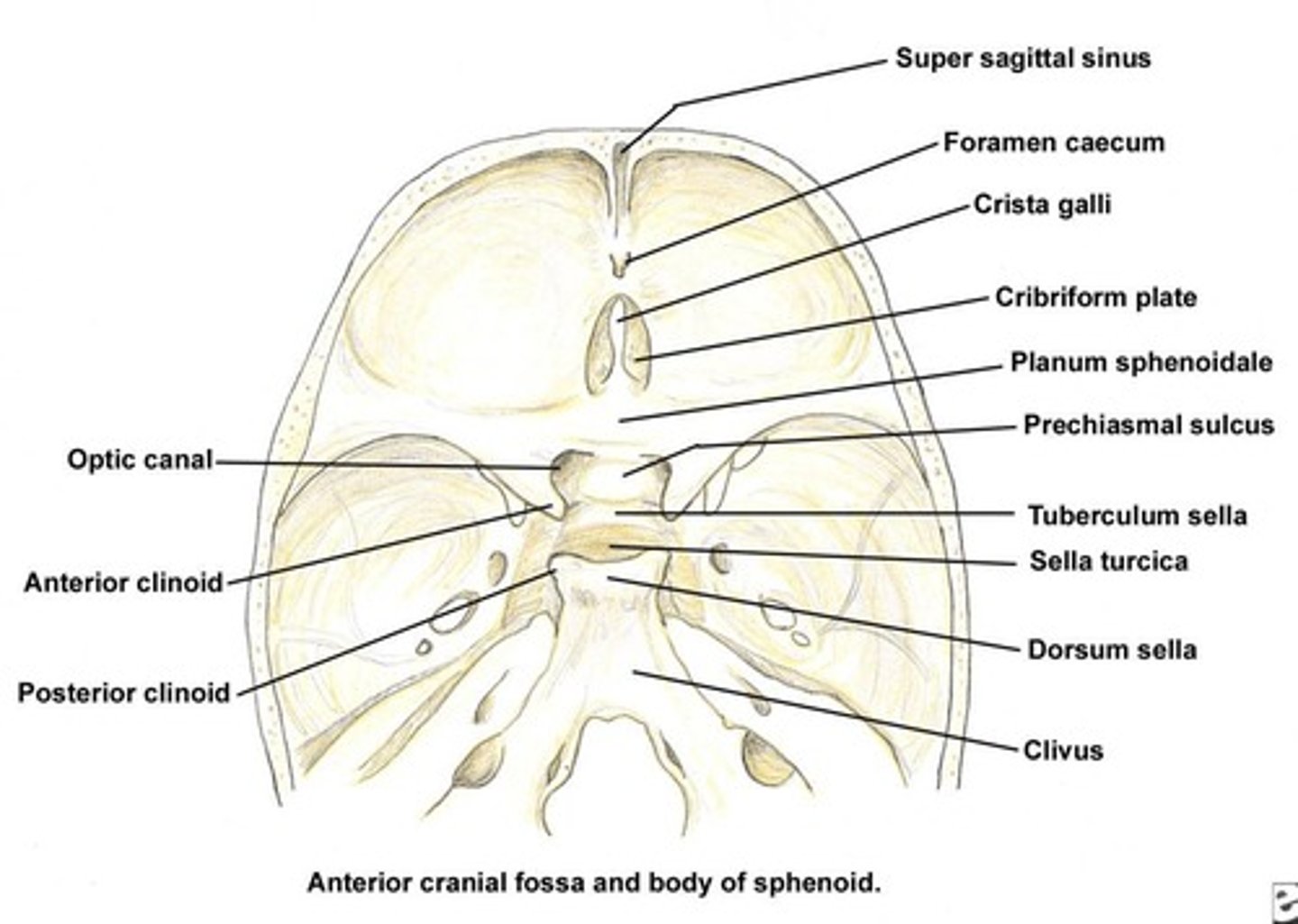
What is the significance of the sphenoid bone in the cranium?
It is called the 'keystone' of the cranium and articulates with all other cranial bones.
Where does the pituitary gland sit?
In the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
What is the optic nerve responsible for?
It is the nerve of sight.
What is the optic chiasm?
The point where the optic nerves from both eyes cross.
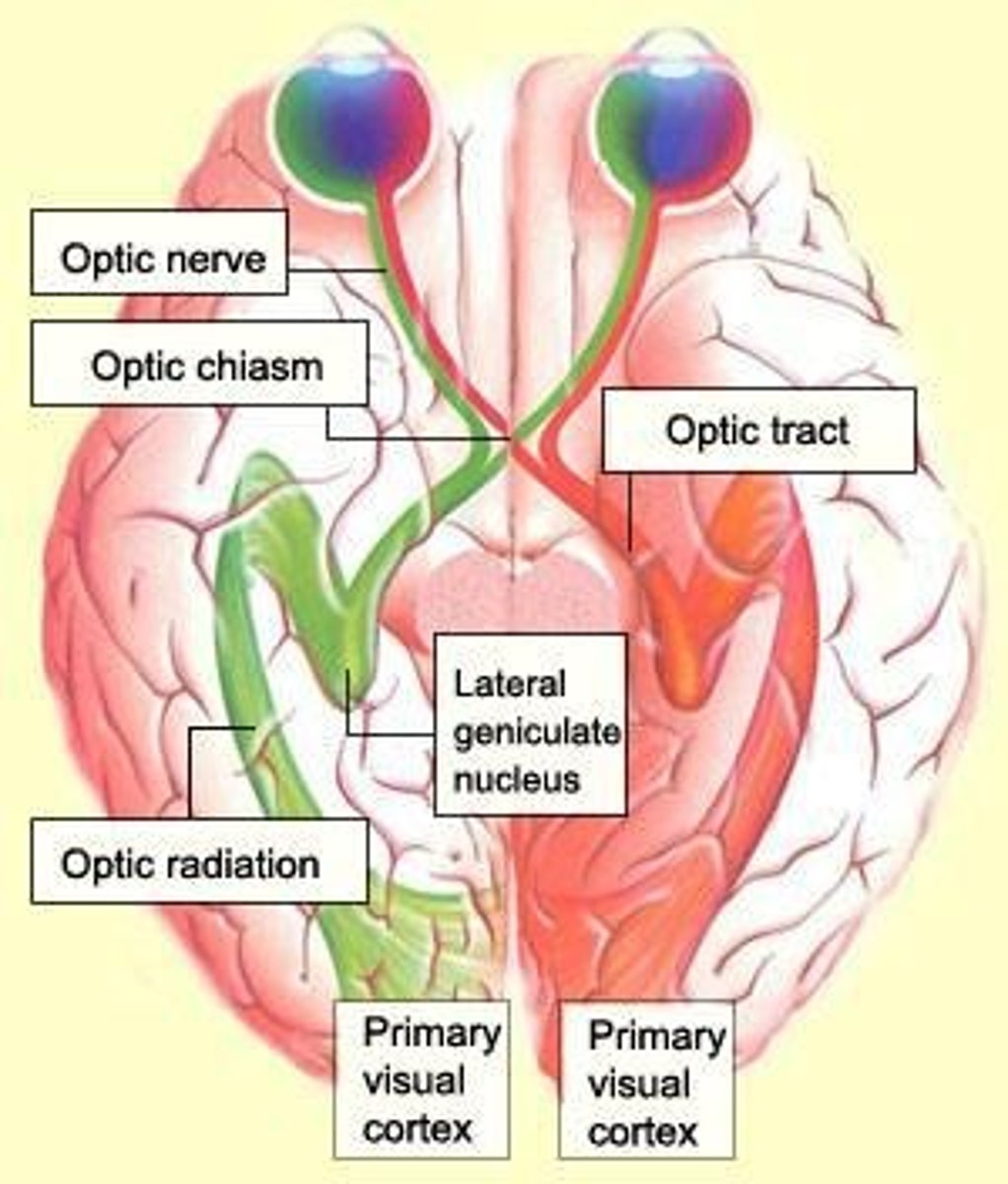
What is the consequence of exposure to 5000 cGy to the optic nerve?
Blindness.
What does the occipital bone form?
The posterior cranial fossa and the inferoposterior portion of the cranium.
What is the foramen magnum?
The passage for the brain stem into the spinal canal.
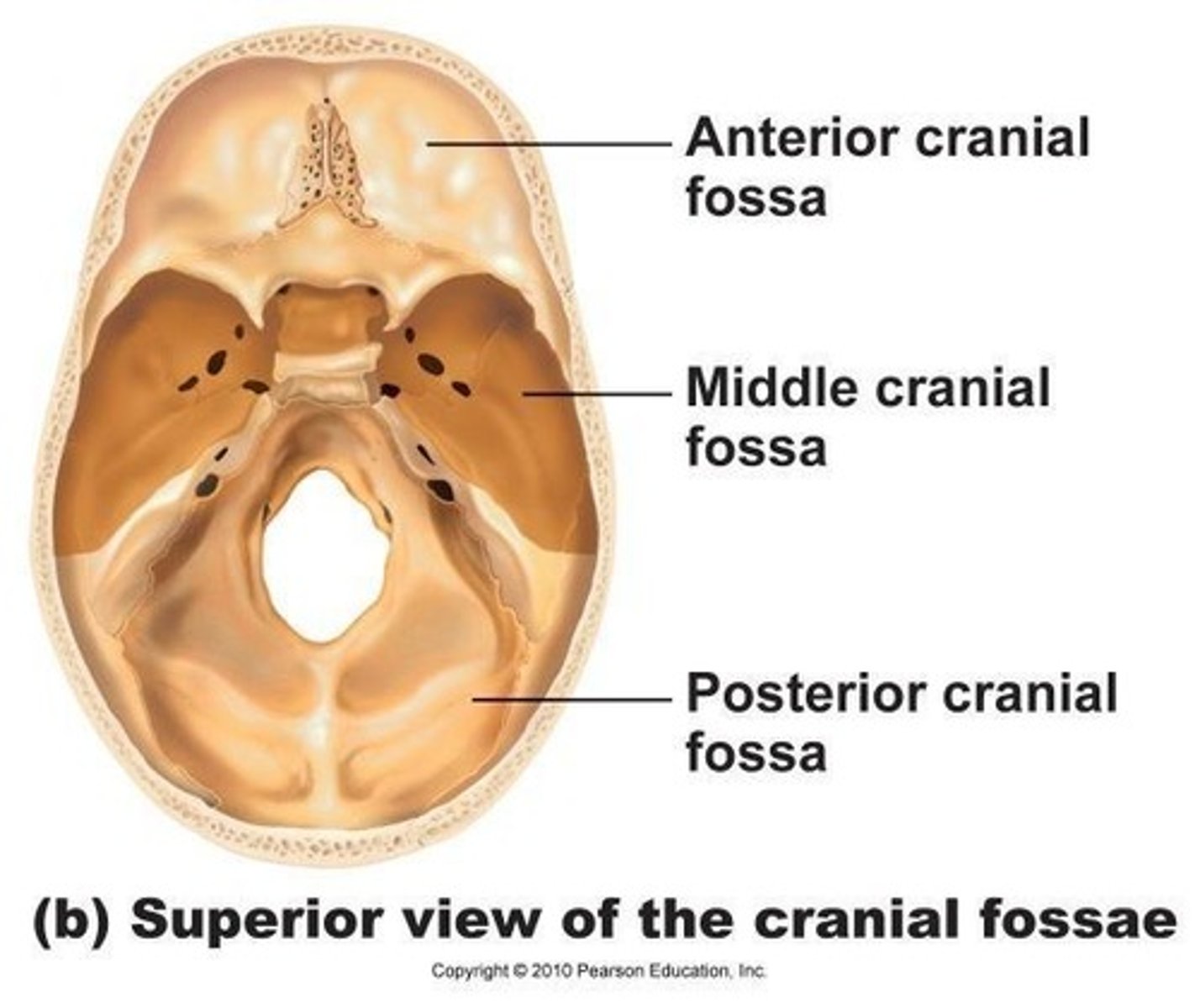
What bones form part of the sides and base of the cranium?
The temporal bone and sphenoid bone.
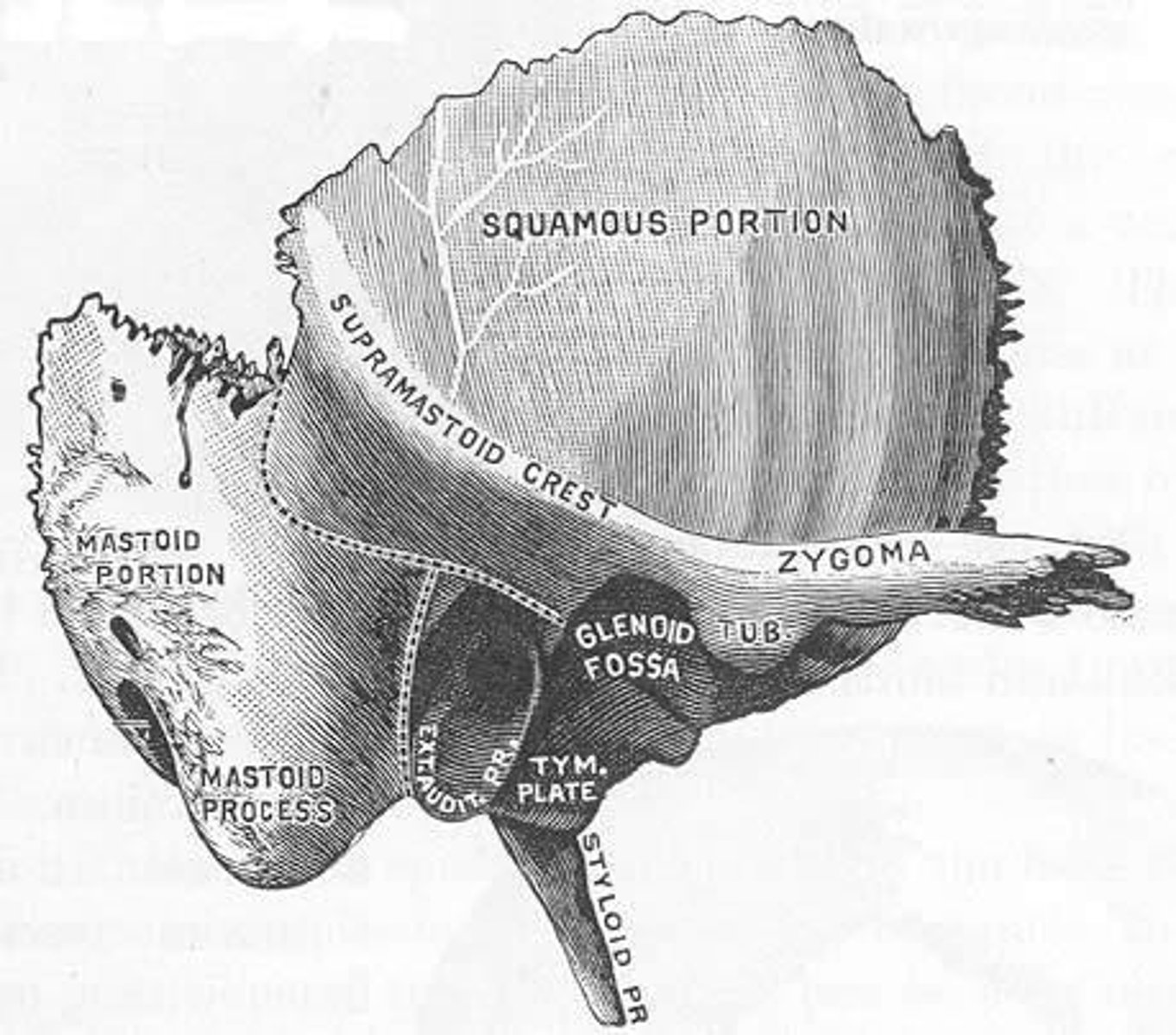
How many facial bones are there?
14 facial bones.
Which facial bone articulates with every bone in the face except the mandible?
The maxilla.
What is the largest and strongest facial bone?
The mandible.
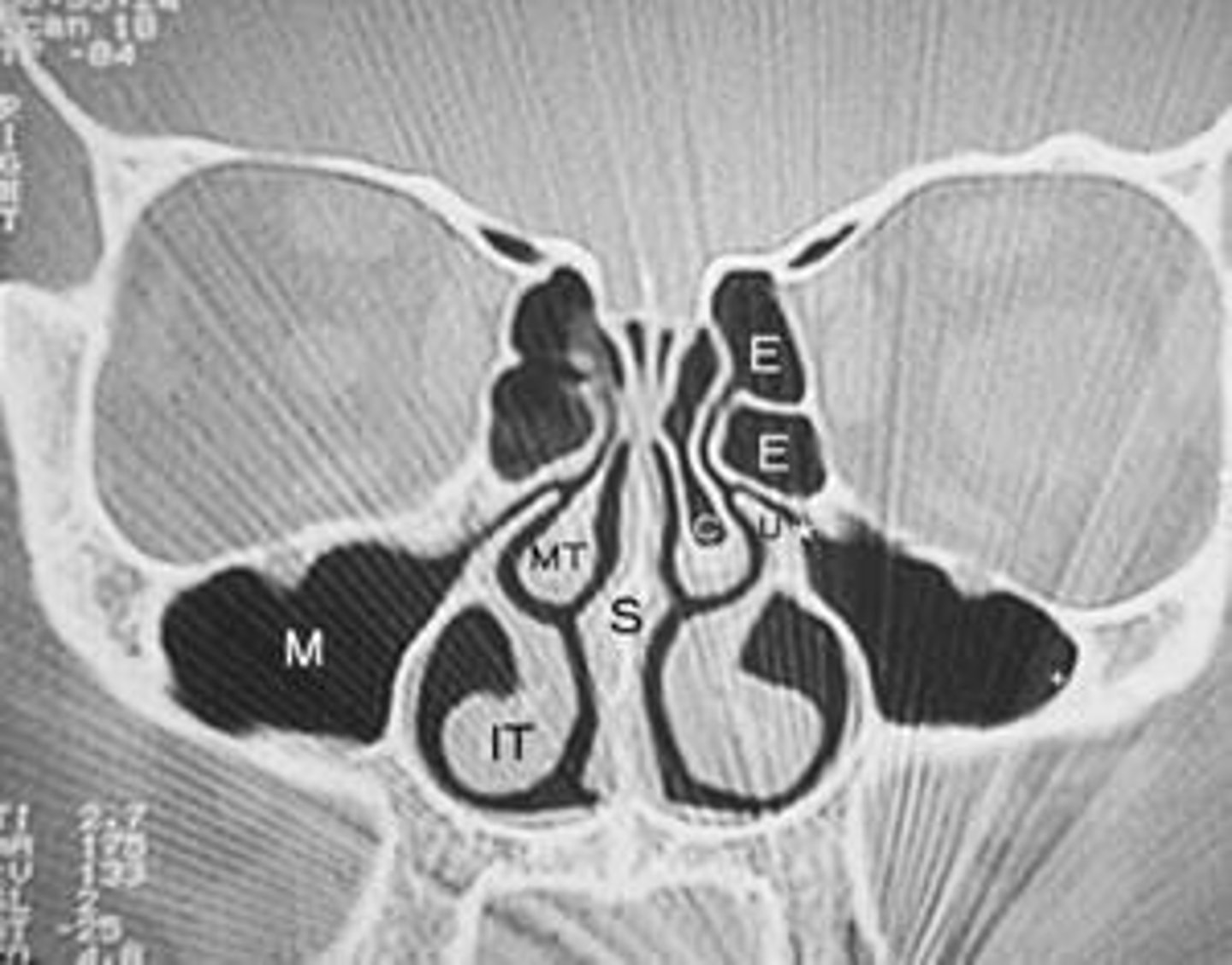
What are the paranasal sinuses?
Ethmoid, Maxillary, Sphenoid, and Frontal sinuses.
What structures make up the globe of the eye?
Lens, Cornea, Iris, Retina, and Lacrimal gland.
What is the role of the superior orbital margin (SOM)?
It forms the roof of the orbit and delineates the inferior border of whole brain fields.
What is the mastoid process?
An extension of the temporal bone at the level of the ear lobe.
What landmark corresponds to the posterior wall of the nasopharynx?
The tragus.
What is the significance of the tragus in treatment positioning?
Lasers can be focused on the tragus to ensure the head is not tilted.
What are the four major lobes of the cerebrum?
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital.
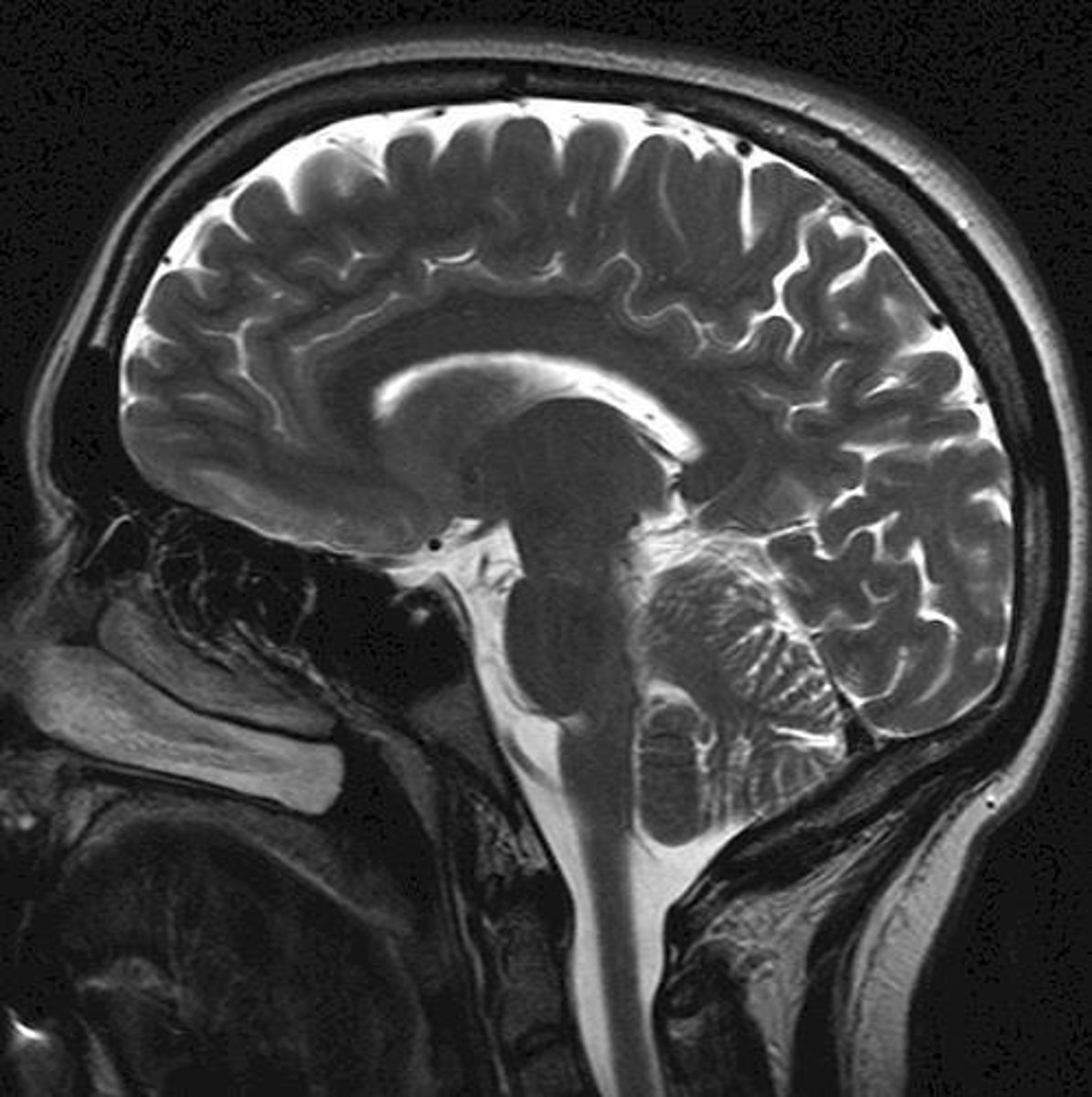
What functions does the frontal lobe primarily control?
Behavior, emotions, and higher intellectual thoughts.
What is the primary function of the parietal lobe?
Sensory functions.
What is the role of the occipital lobe?
It is the seat of the visual center.
What functions are associated with the temporal lobe?
Hearing and smelling.
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
Coordination of the limbs and eye movements.
What organs are primarily located in the anterior and middle portions of the neck?
Pharynx, larynx, esophagus, trachea, salivary glands, thyroid gland, cervical lymph nodes.
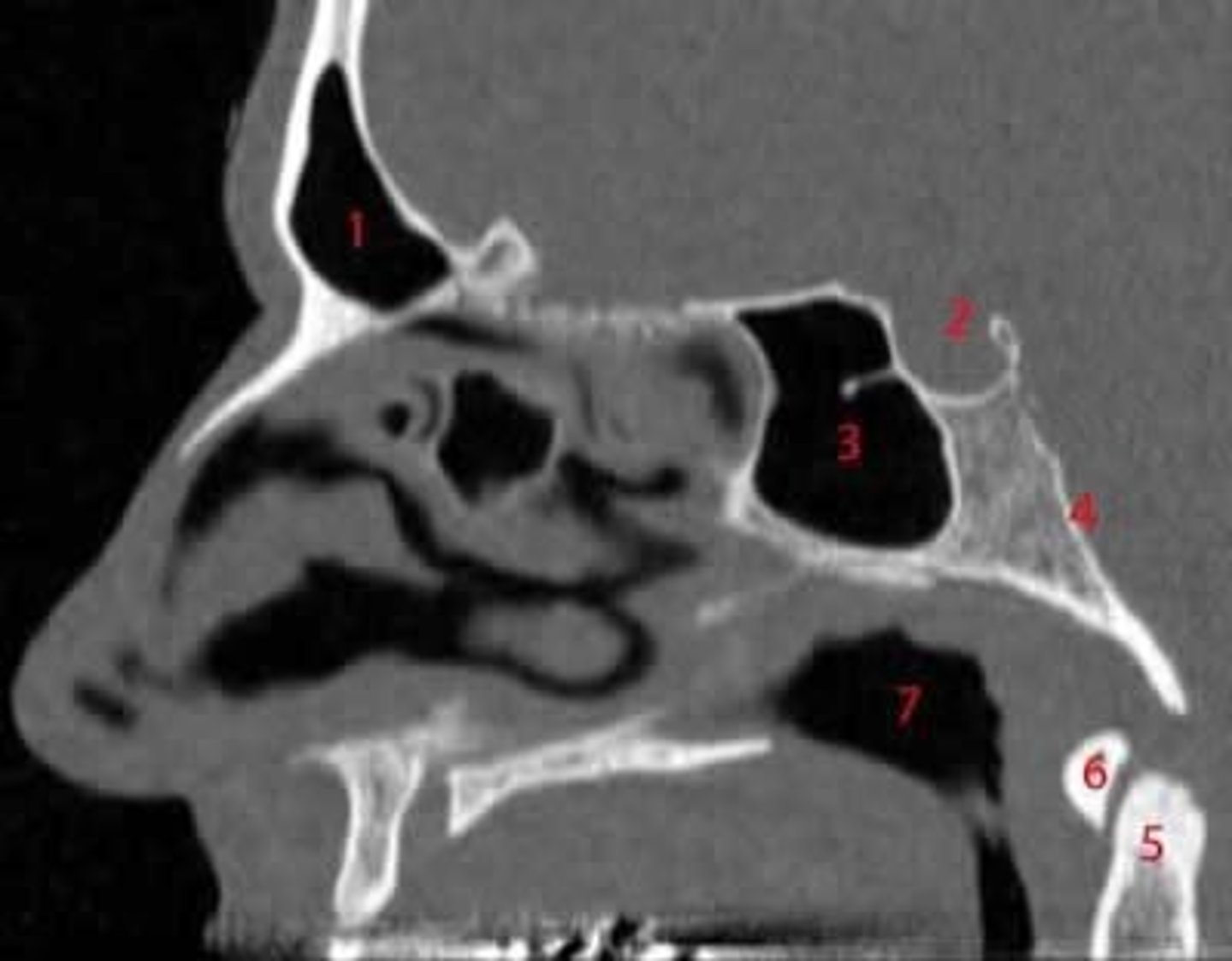
What are the three divisions of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx (Hypopharynx).
What is the length of the pharynx?
About 12 cm long.
Where does the pharynx extend from and to?
From the base of the skull to the continuation of the esophagus at C6.
What is the location of the nasopharynx?
Posterior to the nasal cavity, extending from the base of the skull (clivus) to the soft palate (C-2).
What structures are found in the lateral walls of the nasopharynx?
Eustachian tubes (auditory tubes) that connect the nasopharynx to the middle ear.
What is the oropharynx and where is it located?
The second division of the pharynx, located posterior to the oral cavity, extending from the soft palate to the tip of the epiglottis.
What is the function of the valleculae during swallowing?
The tongue moves the valleculae, bending the epiglottis to close the opening of the larynx.
What is the laryngopharynx and its location?
The third division of the pharynx, located posterior to the larynx, extending from C3 to C6.
What are pyriform sinuses?
Found on either side of the larynx, they divert food from the larynx and are the most common site for hypopharynx cancers.
What is the hyoid bone and where is it located?
A U-shaped bone located just below the mandible at the level of C3-C4.
What is the function of the larynx?
Connects the pharynx to the trachea and is involved in voice production.
What is the significance of the epiglottis?
It closes the opening of the larynx when food or drink is moved down the pharynx.
What is the glottis?
The middle part of the larynx where the vocal cords are located.
What does the subglottis refer to?
The lower part of the larynx just below the vocal cords, extending to the top of the trachea.
Where does the trachea extend from and to?
From the larynx to the main bronchi, between C6 and T4.
What is the thyroid gland's location and function?
Located just inferior to the larynx, it surrounds the upper region of the trachea.
What are the parathyroid glands?
Four glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid.
What is the cricoid cartilage?
A complete ring that forms the base of the larynx, marking the junction between the larynx and trachea.
What distinguishes cervical vertebrae from other vertebrae?
Their small size and the presence of foramina in the transverse processes.
What is the atlas (C-1) known for?
It supports the head and lacks a body and true spinous process.
What is the axis (C-2) and its function?
It forms the pivot for rotation of the atlas and head, distinguished by the dens (odontoid process).
What is the vertebral prominens?
C7, the most distinctive cervical vertebra, used as a landmark for separation between cervical and thoracic vertebrae.
What are the common sites for lymph node enlargement in the head and neck?
Cervical lymph nodes, often associated with upper respiratory infections or metastatic disease.
What are the occipital lymph nodes?
1 to 3 nodes located at the back of the head, providing efferent flow to the deep cervical nodes.
What is the role of the submandibular lymph nodes?
They drain the scalp, nose, cheek, floor of the mouth, and provide efferent drainage to the superior deep cervical nodes.
What are the two main types of contrast media mentioned?
Heavy Metal Salt and Organic Iodides.
How is Barium Sulfate administered for imaging?
Rectally and/or orally.
What is the method of administering Iodine Contrast?
Injected into the vein or retrograde into the bladder.
What type of contrast is characterized as low osmolality and viscous?
Non-ionic contrast.
What must be done before administering Iodine Contrast to patients?
Patients must be carefully screened for reactions.
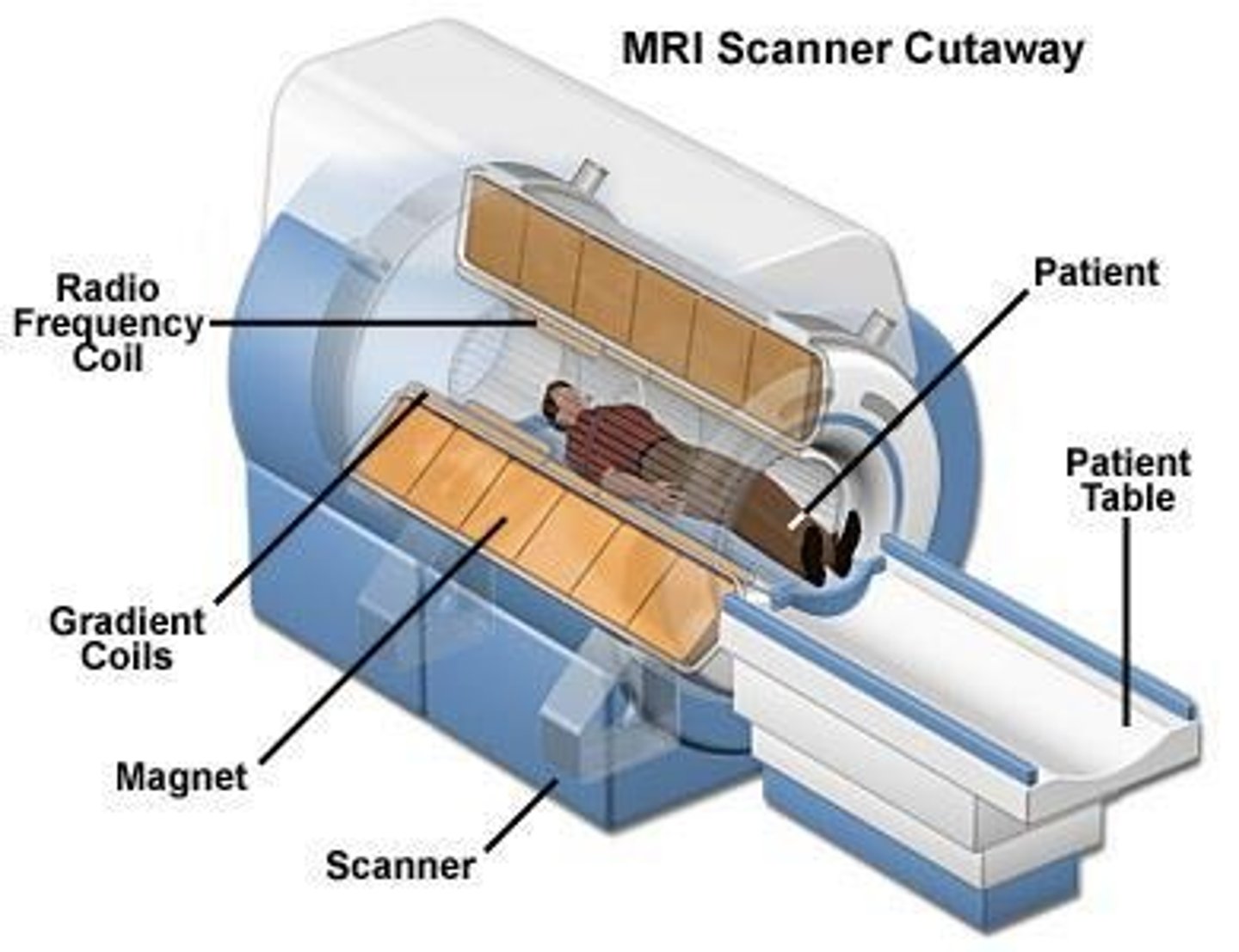
What imaging modality uses magnets for imaging?
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging).
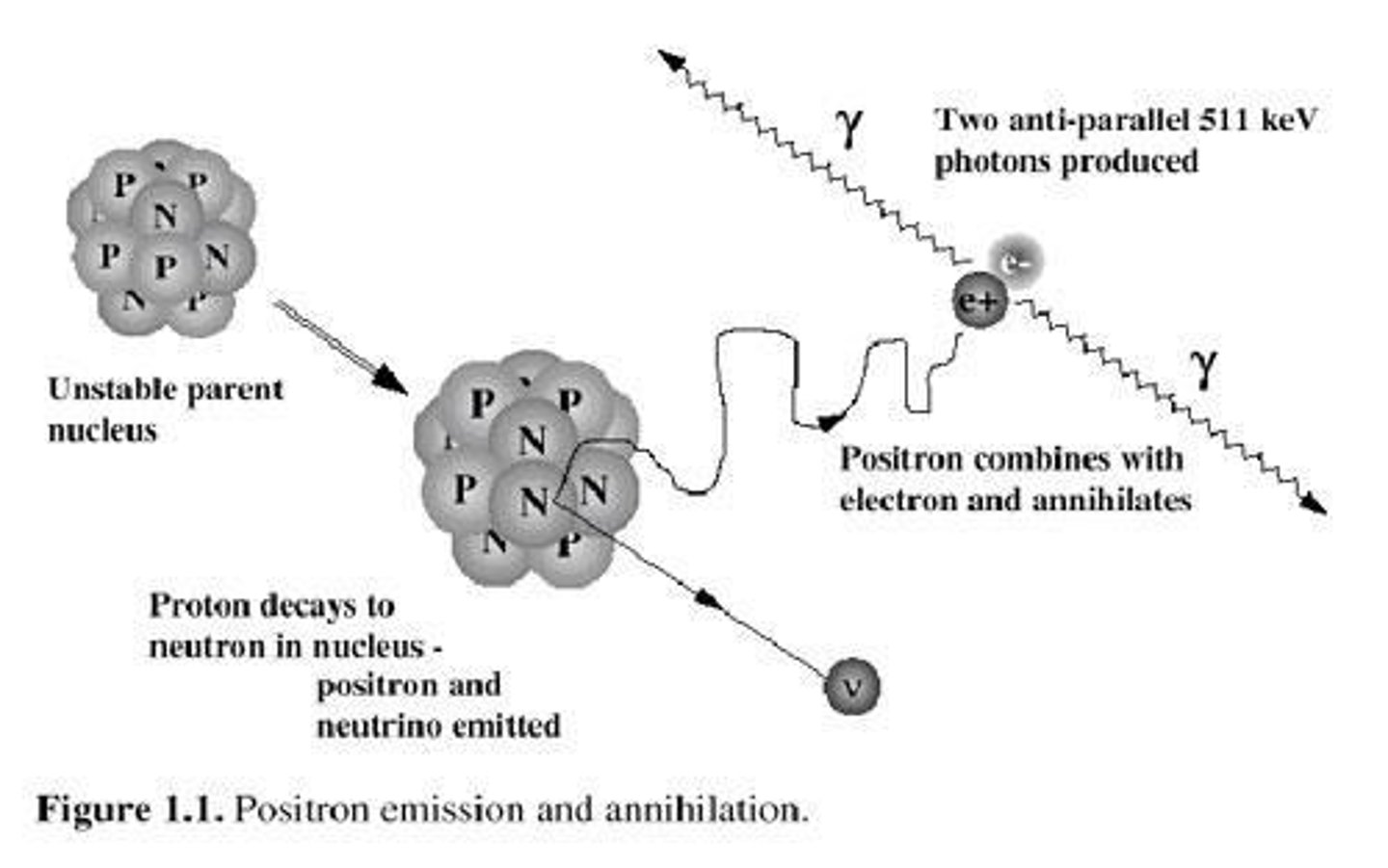
What is the primary use of PET (Positron Emitting Tomography)?
To visualize metabolic processes in the body after injecting a radioactive sugar (FDG 18).
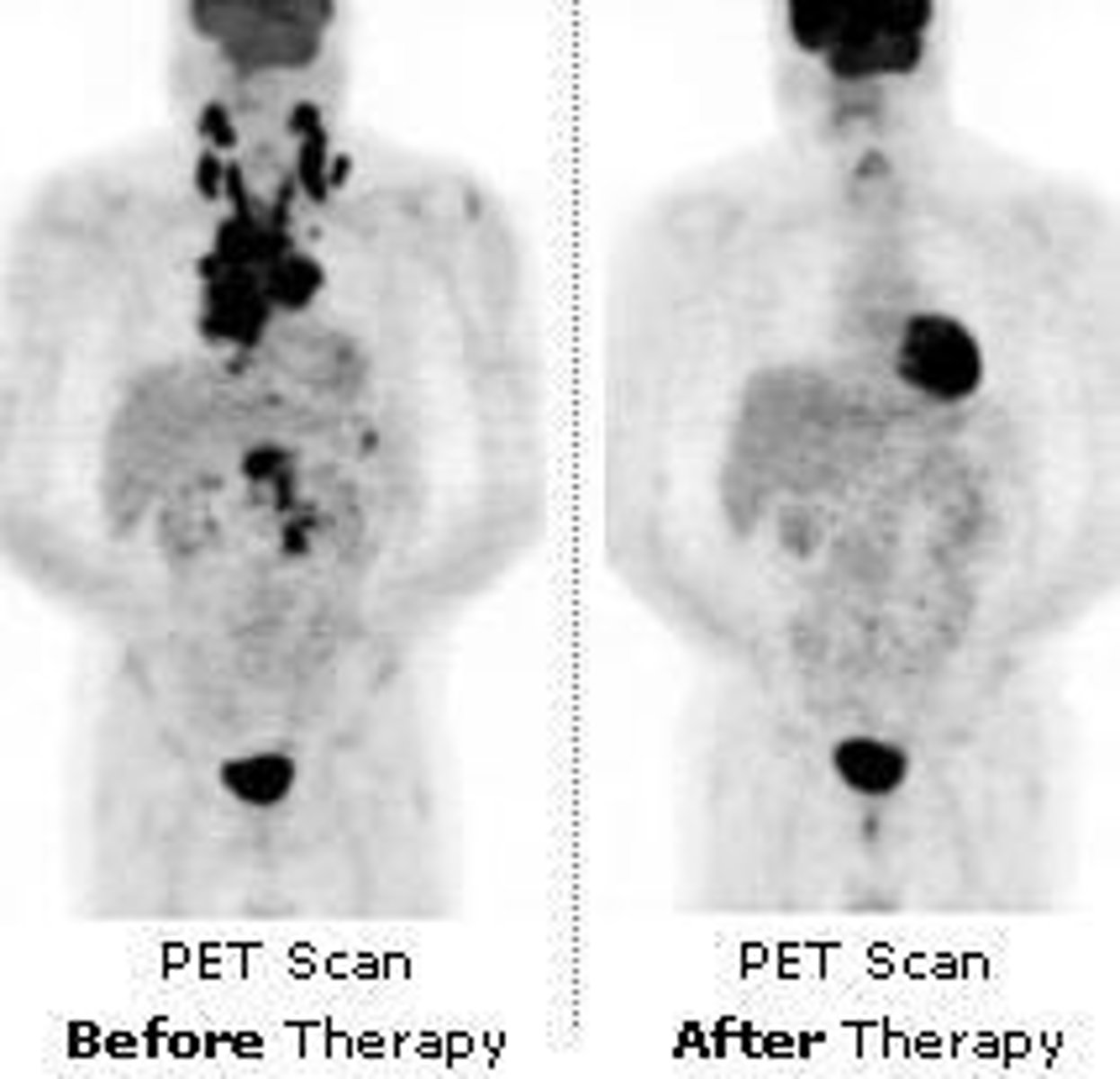
What is the significance of FDG 18 in PET scans?
It is a radioactive sugar that emits gamma radiation, which is detected to form images.
What is a common application of Nuclear Medicine in cancer diagnosis?
Staging lymphomas and lung cancers.
What is the purpose of a Bone Scan in Nuclear Medicine?
To detect bone metastases in patients with known cancer.
What technology does Ultrasound utilize to create images?
High frequency sound waves and the piezoelectric effect.
What is IGRT (Image Guided Radiotherapy)?
A technique that uses on-board imaging systems for precise treatment delivery.
What is the difference between SRS and SRT in Stereotactic Radiation Therapy?
SRS (Stereotactic Radiosurgery) is a single fraction treatment, while SRT (Stereotactic Radiation Therapy) involves fractionation.
What is the goal of Stereotactic Radiation Therapy?
To deliver treatment with great accuracy while sparing surrounding tissue.
Name one type of Linear Accelerator mentioned in the notes.
Varian 2100 EX.
What is HDR in the context of radiation therapy?
High Dose Radiation.
What is the role of a therapist in patient education?
To communicate what patients will experience during radiation treatment.
What should a therapist do to advocate for their patient?
Uphold the patient's rights and create a comfortable environment.
What is a key component of effective communication with patients?
Solid and honest communication to build trust.
What should therapists avoid when addressing patients?
Calling a patient by their first name unless permitted.
What is one way to ensure good communication as a therapy student?
Ask appropriate questions at the right time.
What should a therapist do if they cannot answer a patient's question?
Offer to find the answer or direct them to the right source of information.
What is the importance of maintaining professionalism in patient interactions?
To gain the patient's respect and cooperation.
What is the piezoelectric effect used for in Ultrasound technology?
To convert sound waves into electrical signals.
What is the purpose of Cone Beam CT (CBCT)?
To provide 3D reconstruction data for imaging.
What is the significance of the AAPM Task Group 76?
It addresses the management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology.
What should a therapist do after each treatment session?
Thank the patient.
Is there a separate prescription for contrast media?
NO
Can vagina or rectal markers be considered contrast media?
Yes
Do you have to do kidney function test for retrograde cyistoogram contrast?
No, since it's not going into the bloodstream, it's considered non-invasive
Do most men have an allergic reaction with retrograde contrast
No reactions are rare since it's considered non-invasive
Gastrografin is ___ based
Water Based
What is the paramagnetic contrast media for MRIs?
Gadolinium
How does injecting contrast help you visualize cancer?
Helps you visualize the tumor, but more importantly helps you visualize the angiogenesis or the blood flow of the tumor
Do contrast injections have their own consent form or is it the same consent form for radiation therapy?
No, it has its own consent form only for IV contrast though
For example, you need a consent form for IV iodinated contrast or gadolinium
What type of contrast would you need with an esophagram?
Barium or Gastrografin
Do you need a bun creatine GFR before administering gadolinium for MRI
Yes, it is required
What is the most common side effect from contrast injection?
urticaria aka hives
People that are allergic to shellfish why can't they have a Iodinated contrast?
Shellfish have lots of iodine, most likely they are allergic to the iodine in the shellfish and a contrast media. They'll be allergic to it too.
Why is type two diabetes contraindicated for iodinated contrast?
People with type two are on metformin and metformin needs to be discontinued before administering Iordinates contrast
Is sickle cell contraindicated for iodinated contrast
Yes
What is another name for multiple myeloma?
B cell plasmacytoma
What is multiple myeloma or B cell plasmacytoma?
A type of primary bone cancer that causes lytic lesions
What is the definition of lyric lesion?
Holes in the bone look like the bone has been hole punched all over
Why is multiple myeloma or B cell Cytoma contraindicated for iodinated contrast?
Can cause the kidneys to fail
Pheochromacytoma Or an adrenal tumor is it contraindicated for iodinated contrast?
It is contraindicated
Can a person eat before IV contrast
Npo Four hours before contrast because iodine can make you nauseous