The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 312
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
hypothalamus
region of the brain that links the nervous and endocrine system by sensing internal and external conditions of the body and releasing regulatory hormones that control pituitary function and maintain homeostasis
infundibulum
a stalk of nervous tissue (primarily axons) attaching the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus; pituitary stalk
pituitary gland
glandular structure associated with the hypothalamus which releases hormones; also called hypophysis
adenohypophysis
the glandular portion of the pituitary gland; aka Anterior Pituitary or Pars Distalis
neurohypophysis
the neural portion of the pituitary gland; aka Posterior Pituitary or Pars Nervosa
tropic hormones
hormones from the anterior pituitary that stimulate the secretion of other hormones in the body; also called trophic hormones
hypothalamohypophysial portal system
a unique vascular connection joining the capillary network of the hypothalamus to the glandular portion of the pituitary gland
hypothalamus
a glandular structure below the thalamus of the brain
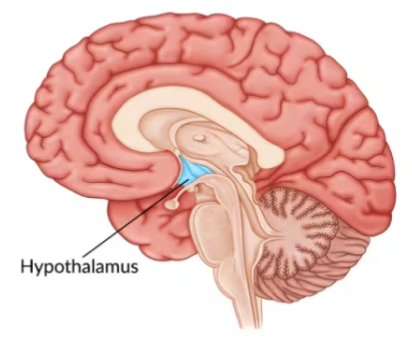
almost all hormonal secretions from the pituitary gland are controlled by the ____________
hypothalamus
the hypothalamus senses external and internal stimuli and then communicates with the rest of the body via the ___________ _________
pituitary gland
what stimuli does the hypothalamus sense?
pain
fear
excitement
odors
circulating hormones
the hypothalamus consists of neurosecretory neurons with axons extending distally towards the pituitary gland. Give the detailed description of the way these axons extend into it.
to the proximal infundibulum associated with the anterior pituitary
to the distal infundibulum associated with the posterior pituitary
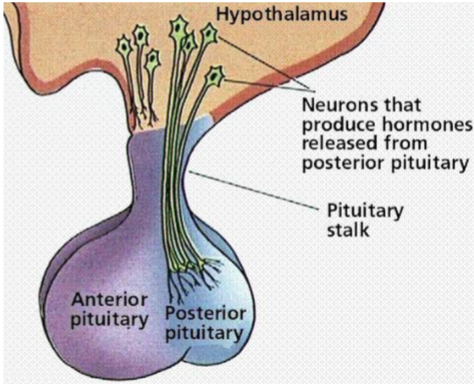
what does the hypothalamus produce?
neurohormones
what are the two classifications of neurohormones?
protein/peptide hormones
amine hormones
inhibiting hormones
releasing hormones
list the peptide/protein neurohormones produced by the hypothalamus
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (somatostatin, GHIH)
growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
prolactin-releasing factor (PRF)
list the amine neurohormone produced by the hypothalamus
prolactin-inhibiting hormone (dopamine, PIH)
list the hypothalamic inhibiting neurohormones
growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (Somatostatin, GHIH)
Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (Dopamine, PIH)
list the hypothalamic releasing neurohormones
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
prolactin-releasing factor (PRF)
hypothalamic neurohormones can cause the anterior pituitary to release _________ __________ , which stimulate distant endocrine glands to increase production of their own hormones which act of distant target cells
tropic hormones
hypothalamic neurohormones can cause the _________ __________ to release non-tropic hormones directly on target cells in the body
posterior pituitary
the hypothalamus communicates with the pituitary gland in 2 different ways. explain them.
direct neural connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary
vascular portal system connecting the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
what is the vascular portal system connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary?
Hypothalamohypophysial Portal System
another name for the pituitary gland…
Hypophysis
function of the hypophysis
an organ within the head below the brain and controls chemical messaging that affects many crucial organs and body functions
morphology of the hypophysis
anterior pituitary more externally located
posterior pituitary more internally located
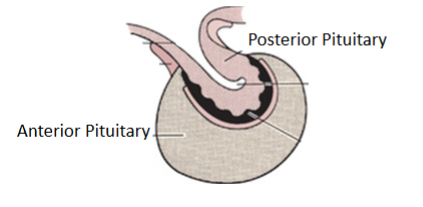
list all terminology regarding the pituitary gland
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)
list the sections of the hypophysis
strictly endocrine
pars distalis
pars intermedia
a tissue section that separates the posterior pituitary from the anterior lobe. it marks the boundary between the two pituitary lobes.
pars tuberalis
wraps around the pituitary stalk
strictly neuroendocrine (neurohormones)
pars nervosa (associated with posterior pituitary)
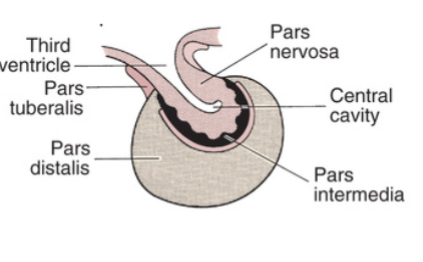
hormones secreted by posterior pituitary:
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH, Vasopressin)
oxytocin
how are the hormones made and secreted by the posterior pituitary?
synthesized in the neuron cell bodies within the hypothalamus and carried by the neuron axons to the posterior lobe where they are released
what is the most important hormone for the control of water balance in the body?
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH, Vasopressin)
the anti-diuretic hormone is produced in response to…
increased blood osmolality (too concentrated; not enough water)
ex: dehydration
hypotension (severe decreased BP)
what are the effects that the anti-diuretic hormone has on the body?
water retention by kidneys
vascular constriction to increase BP
function of oxytocin
induces smooth muscle contractions in the mammary glands and uterus
effects of oxytocin on the body:
milk let-down reflex
contraction of alveoli in the mammary gland
uterine contractions
contractions of the myometrium of the uterus
list the hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary (Adenohypophysis, Pars Distalis)
corticotropin (Adrenocorticotropic hormone, ACTH)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
growth hormone (GH, somatotropin)
prolactin (PRL)
what hormones are considered tropic hormones?
ACTH
TSH
GH
FSH
LH
they stimulate other endocrine glands to produce their hormones
why is Prolactin not a tropic hormone?
it acts directly on the mammary tissue to produce milk