Neuroanatomy Exam 2 Ch 7 + 8
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 7 + 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
The learner will list four structures/systems that nourish and protect the brain.
The learner will identify important features of the cerebral hemispheres, including the lobes of the brain.
The learner will describe the phenomenon of hemispheric specialization, especially how it relates to language.
The learner will list and briefly describe causes of damage to the cerebral hemispheres.
The learner will describe the phenomenon of brain plasticity and its principles.
The meninges
the protection, surrounds the delicate brain
what are the parts of the meninges
Dura mater: most outer layer
Arachnoid mater: middle layer
Pia mater: inner layer
Where there are layers, spaces result
Potential spaces, and actual space
What is potential spaces and what is actual space
POTENTIAL SPACES - Epidural space: between skull and dura mater
subdural space: between dura mater and arachnoid mater
ACTUAL SPACE: Subarachnoid space: between arachnoid mater and pia mater
What is another way the brain is protected other than the meninges
the blood -brain barrier
what is the function of the blood-brain barrier
protects the brain
-Protects against foreign invaders
-Protects against hormones/neuro-transmitters in rest of body
-Maintains constant environment for brain
what are some (BBB) blood brain barrier problems
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Developmental problems with BBB
Hyperosmolality (increased movement of particles)
Microwaves
Radiation
Infection
Trauma, ischemia, inflammation, pressure
Nourishment: The Cerebral Arteries
Brain consumes ___ of body’s oxygen
Blood enters brain through:
_______
_______
These feed the _______
Brain consumes 20% of body’s oxygen
Blood enters brain through:
Carotid arteries
Vertebral arteries
These feed the circle of Willis
Arteries are ____ from the heart
away
arteries pump _____ blood away and veins bring ______- blood back
oxygenated, deoxygenated
The circle of Willis feeds the brain oxygenated blood through
_______
_______
_______
_______
Anterior cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior cerebral artery
What does the venous system do
moves deoxygenated blood away from the brain , removed through 4 sinuses in meninges
How does the Venous system move deoxygenated blood through 4 sinuses in the meninges
Superior sagittal
Transverse
Occipital
Sigmoid
-Superficial and deep cerebral veins then remove
Cerebrum - two cerebral hemispheres (left and right)
Major layers from superficial to deep
Surface gray matter (cerebral cortex; neuron somas)
White matter (axons)
Deep gray matter (e.g., thalamus, basal ganglia)
Ventricles (4 ventricles)
CEREBRAL CORTEX FEATURES
Cortex means “___”
Features include: ____. ______, ____
Cortex means “bark”
Gyri
Sulci
Fissures (deep sulci):
Longitudinal
Central
Lateral
Lobes of the brain
Frontal lobe: reasoning, planning, motor movement
Parietal lobe: sensory perception and interpretation
Occipital lobe: vision
Temporal lobe: memory, receptive language
Interhemispheric connections
corpus callosum is a band of fibers that connects the right and left hemispheres together.
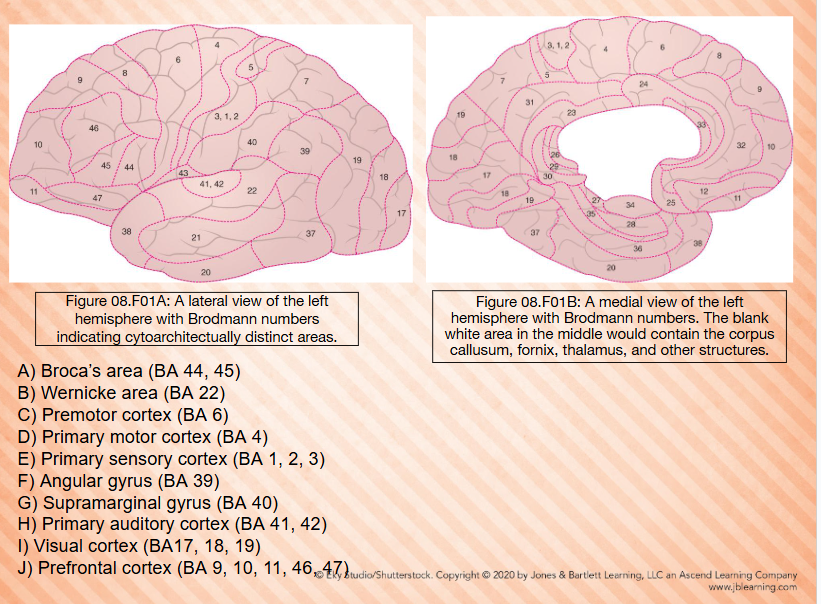
Brodmann Map - Developed by Korbinian Brodmann
Divides brain into 52 area based on - Brain’s gross anatomy and cellular structure of brain —— Brodmann area
Frontal Lobe: prefrontal cortex
occuies BA 9, 10, 11, 12, 45, 46, 47 - Functionally involves with cognition (executive control) personality, decision, making, and social behavior
Frontal Lobe: Frontal Eye Fields
-Occupies BA 8
-Controls eye movements ( up, down, left, and right)
-Damage results in eyes deviating towards the side of injury
Involved in uncertainty and hope
-Sometimes included as part of prefrontal cortex
Frontal Lobe: Broca’s Area
-Occupies BA 44 and 45
-Found on third frontal convolution (inferior frontal gyrus)
-Area 45 is known as pars triangularis, involved in interpretation of language (syntax) and planning/programming of verbal responses
Frontal Lobe: Broca’s area
-Area 44 is known as pars opercularis, involved in coordination of speech organs for language production
-Paul Broca, through observations of Tan, one of first to associate BA 44 45 with speech production
-Impairments to this area my lead to Broca’s aphasia
Frontal Lobe: Premotor
-Occupies BA 6
-Close relationship to BA 44
Involved in selecting and planning of motor movements
-Supplementary motor area (SMA) located at top of BA 6 and s involved in sequencing and “turning on” motor plans
Frontal Lobe: Primary Motor Cortex
-Occupies BA 4
Sends motor plans developed in Ba 6 to the muscles for them to act (e.g., speech muscles)
BA 4 has been mapped to form a homunculus or “little man”
Parietal Lobe: Primary Sensory Cortex
-Occupies BA 1, 2, and 3
-processes somatosensory information such as
vibration
proprioception
Touch
Stereognosis
-Homunculus present
Parietal Lobe: Somatosensory Association Cortex
-Occupies BA 5 and 7
-Interprets sensory experience during motor movements
-This sensory experience is used to refine motor action
Involved in the fine movements associated with speech
Plays role in writing sensory and motor experience
Parietal Lobe: Angular Gyrus
Occupies BA 39
-Involved in reading and math abilities
-Damage can lead to alexia and acalculia
-May also be involved in understanding metaphors and our sense of embodiment
Damage can lead to outer body experiences
-Damage can also lead to Gerstmann syndrome
Parietal Lobe: Supramarginal Gyrus
-Occupies BA 40
-Closely rated to the angular gyrus (BA 39)
-Involved in phonological system; stores auditory representations of phonemes (auditory images)
-This helps us sound out words
-Damage can result in phonological dyslexia, difficulty reading new and nonwords
Occipital Lobe: Visual Cortex 1/2
-Occupies BA 17, 18, and 19
-Where information from eyes is received and processed
Occipital Lobe: Visual Cortex 2/2
Two streams of vision
-Dorsal Stream (18, 19, 7 and 39) the where of vision, analyzes motion and spatial relationships
Ventral stream (18, 19, and 37) the what of vision, analyzes forms, colors, and faces
Temporal Lobe: Inferior Temporal Area
-Occupies BA 20 and 21
-Involves in processing of auditory and language information as well as reading facial emotions
May play a role in hallucinations
Temporal Lobe: Parahippocampal Gyrus
-Occupies BA 27, 28, 34, 35, and 36
-Located on medial surface of temporal lobe
Two structures of note:
-Hippocampus: associated with declarative memory
Entorhinal cortex (BA 28 and 34): major input/output relax between the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus
Temporal Lobe: Fusiform Gyrus
-Occupies BA 37
-Also known as occipitemporal gyrus
Important in remembering and naming seen objects
-Functions as a visual lexicon
-Lesions can cause anomia and lexical agraphia
Temporal Lobe: Temporal Pole
-Occupies BA 38
-Involves in language
Left: Semantic processing
Left: speech comprehension
Left: narrative comprehension
Right: integration of emotion into narratives
Right: identifying familiar voices
Both: theory of mind
Both: empathy
Temporal Lobe: primary Auditory Cortex
-Occupies BA 41 and 42 (42 is the secondary cortex, but 41/42 usually discussed as a unit called primary auditor cortex
-Also known as Heschl’s gyrus
Initial cortical region that receives auditory information from the ears via CN VIII and the auditory pathways
-Processes sound intensity and frequency
Organized by tones (tonotopically))
Cingulate Cortex
-Name means ‘band that encircles
-Occupies BA 23- 26, 30, 33
-Sandwiched between corpus callosum and frontal and parietal lobes
Is part of the limbic system and has connections to the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus
Cingulate Cortex
Functionally involved in the following
-Anterior parts: cognitive control, detecting errors, detecting conflicts, and problem solving
-Posterior parts: autobiographical memory, managing risk behavior, and emotional processing
Overall, there appears to be a filter and focus process
-ACC filters out irrelevant information
-PCC detects important information
Insular Cortex
-Located deep in the lateral sulcus
-Also known as insula or island
Two main parts-
-Posterior-dorsal area: orofacial programs and emotions (eg. disgust over drinking spoiled milk)
-Dorsal-caudal area: connections to BA 5 and 7, so involved in integrating sensory feedback into motor behavior (refinement)
Insular Cortex
Clinical date suggests role in language
Perhaps plays role in lexical decision making
May be involved in some cases of global aphasia