PSYO 343 - Ch. 6 Depressive & Bipolar Disorders (Unipolar Depression)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
People are ________ likely to disclose ___________ ____________ _________________ than physical health.
less; mental health disorders
____________ is a major barrier people face when disclosing mental health problems.
Stigma
What is depression?
Low, sad state marked by significant levels of sadness, lack of energy, low self-worth, guilt, or related symptoms
What is mania?
State or episode of euphoria or frenzied activity in which people may have an exaggerated believe that the world is theirs for the taking
What are depressive disorders?
The group of disorders marked by unipolar depression
What is unipolar depression?
Depression without a history of mania
What is bipolar disorder?
A disorder marked by alternating or intermixed periods of mania and depression
Major depression affects approximately _____% of the Canadian population.
5.4
By age 40, _____% of the population will have or have had a ___________ _____________.
50; mental illness
The average age of onset for unipolar depression is _____.
19
There is a higher rate of unipolar depression among which group?
Chronically ill elderly people
In which SES group is depression more common?
Low SES
Women are ________ as likely as men to have episodes of severe unipolar depression.
twice
Prevalence of unipolar depression among children is (similar/different) for girls and boys.
similar
At any given time, the rate of severe depression is twice as high among adults _________ _____ than those above.
under 65
_________ people with unipolar depression recover within _____ __________, even without ________________.
Most; 6 months; treatment
Unipolar depressive symptoms span 5 areas of functioning:
1. Emotional
2. Motivational
3. Behavioural
4. Cognitive
5. Physical
What is anhedonia?
Inability to experience pleasure
What are the DSM-5 depressive disorders?
- Major depressive disorder
- Persistent depressive disorder
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
What is major depressive disorder (MDD)?
A severe pattern of depression that is disabling and not caused by drugs or a medical condition
With MDD, for a ____ _________ period, a person displays an ______________ in depressed mood for the majority of each day, or a ______________ in enjoyment of interest across most activities.
2 week; increase; decrease
With MDD, for that same period, a person must experience at least ____ or ____ symptoms.
3; 4
What are the symptoms of MDD?
- Considerable weight change or appetite change
- Daily insomnia or hypersomnia
- Daily agitation or decrease in motor activity
- Daily fatigue or lethargy
- Daily feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Daily reduction in concentration or decisiveness
If someone has a history of _________, they will not meet the requirements for a depressive disorder.
mania
What is seasonal MDD?
MDD that changes with the seasons
What is catatonic MDD?
MDD marked by either immobility or excessive activity
What is peripartum MDD?
MDD that occurs during pregnancy or within 4 weeks of giving birth
What is melancholic MDD?
MDD where the person is almost totally unaffected by pleasurable events
What is persistent depressive disorder (PDD)?
A chronic form of unipolar depression marked by ongoing and repeated symptoms of either major or mild depression
With PDD, the person experiences symptoms of mild or major depression for at least ____ _________ where symptoms are not absent for more than ____ _________ at a time.
2 years; 2 months
What is premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)?
A disorder marked by repeated episodes of significant depression and related symptoms during the week before menstruation
What is controversial about DSM-5's inclusion of PMDD?
It can pathologize severe cases of PMS that are normal among women
What is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder?
Characterized by a combination of persistent depressive symptoms and recurrent outbursts of severe temper
__________ can trigger a depressive episode.
Stress
_____% of severe depressive episodes occur within a month or 2 of a significant ____________ ________.
80; negative event
What is reactive (exogenous) depression?
Depression that follows clear-cut stressful events
What is endogenous depression?
Depression in response to internal factors
What is post-partum depression (PPD)?
Depression experienced following giving birth to a child
What are the causes of PPD?
- Hormonal changes of childbirth
- Genetic predisposition
- Psychological and social change
What is the biological model of unipolar depression?
It studies genetic factors, biochemical factors, brain circuits, and the immune system to suggest unipolar depression has biological causes
Genetic factors of unipolar depression
- Family pedigrees and twin studies suggest moderate genetic contribution
- Gene studies
Biochemical factors of unipolar depression
- Low activity of serotonin and norepinephrine
- Overactivity of the HPA pathway causing excessive releases of hormones during stress
Brain circuits of unipolar depression
- Brain circuit dysfunction
- Abnormal activity and flow rate in brain locations
- Structure problems leading to issues in interconnectivity
What brain region is heavily involved in the depression-related circuit?
Subgenual cingulate
The immune system and unipolar depression
- Under stress, dysregulation of the immune system contributes to depression
- Slower functioning of lymphocytes
- Increased CRP production
- Greater inflammation
What types of biological treatments are there for unipolar depression?
- Antidepressant drugs
- Brain stimulation
What are the classes of antidepressant drugs?
- MAO inhibitors
- Tricyclics
- Second-generation
- Ketamine-based
MAO inhibitors (MAOIs)
Work biochemically by slowing the body's production of MAO that typically breaks down serotonin and norepinephrine
People who take MAOIs and eat foods with _____________ risk high ___________ _______________.
tyramine; blood pressure
Approximately ________ of patients who take MAOIs are helped by them.
half
Tricyclics
Act on NT reuptake mechanisms by blocking reuptake process and allowing serotonin and norepinephrine to remain in synapses longer
For patients taking tricyclics, ____________ may occur if therapy is ended too quickly.
relapse
Second-generation antidepressants
Classified into SSRIs that increase serotonin activity, sNRIs that increase norepinephrine activity, and SNRIs that increase both serotonin and norepinephrine
Second-generation antidepressants have fewer:
Undesired side effects
Second-generation antidepressants are __________________ different from MAOIs and tricyclics.
structurally
_____________ rate is higher for second-generation antidepressants, sitting at _____%.
Failure; 40
Ketamine-based antidepressants
Increases activity of glutamate in the brain and aids a new neural pathway development
Ketamine-based antidepressants are mainly used for who?
People who are unresponsive to other drugs or are suicidal, therefore a short-term solution
What is brain stimulation?
Biological treatments that directly or indirectly stimulate certain areas of the brain
What are the types of brain stimulation?
- ECT
- VNS
- TMS
- DBS
ECT
Procedure consists of targeted electrical stimulation to cause a brain seizure
VNS
Implanted pulse generator sends regular electrical signals to the vagus nerve which stimulates the brain and provides significant relief for severely depressed people
TMS
Use of an electromagnetic coil placed above a patient's head and sends a current into the brain that increases neuron activity and function throughout the depression-related circuit
DBS
Implanting electrodes into the brain, typically for Parkinson's treatment
What is the psychodynamic model of unipolar depression?
Depression occurs when people experience real or imagined losses (symbolic loss)
What is symbolic loss?
The loss of a valued object that is unconsciously interpreted as the loss of a loved one
What are the stages that lead to depression according to Freud?
- Regression to an earlier stage of development
- Introjection of feelings for the lost object
- Eventually becoming depressed
According to Freud, those with ________ fixation are at highest risk of depression.
oral
How do object-relations theorists explain depression?
It results when people's relationships leave them feeling unsafe and insecure
Psychodynamic therapists aim to do what in treatment for unipolar depression?
Bring issues into consciousness and work through them using free association, therapist interpretation, and a review of past events and feelings
Psychodynamic therapy is likely best for people with _________-______________ ___________ associated with their depression.
deep-seated trauma
What is the cognitive-behavioural model of unipolar depression?
Depression results from problematic behaviours and dysfunctional thinking
The behavioural dimension perspective and unipolar depression
The number of life rewards is related to the presence or absence of depression, where a large reduction in positive life rewards may cause increasingly fewer positive behaviours and eventual depression
The behavioural dimension highlights __________ ___________ as an important factor in downward depression spiral.
social rewards
The negative thinking perspective and unipolar depression
Unipolar depression is produced by a combination of maladaptive attitudes, cognitive triad, errors in thinking, and automatic thoughts
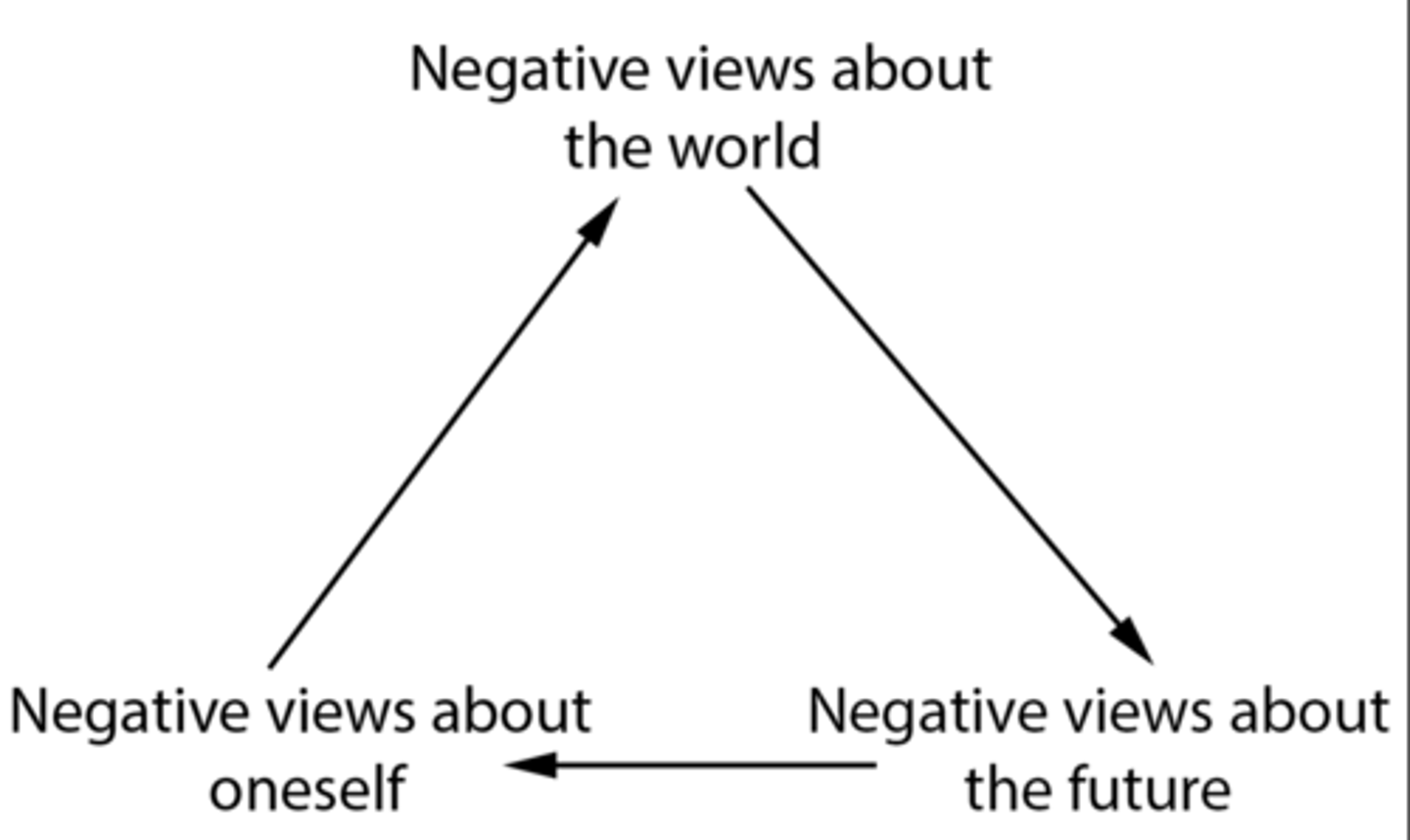
What is the cognitive triad?
Negative views of experiences, oneself, and the future that make someone more likely to be depressed
What is learned helplessness?
Depression occurs when people believe they have no control over life's reinforcements and assume responsibility for this helpless state
What is attribution-helplessness theory? (Rubenstein)
People question self when events are beyond their control, where attribution to some internal, global, and stable cause results in depression
What is attribution-helplessness theory? (Liu)
Attributions that produce hopelessness result in depression
How does texting negatively affect relationships?
- Avoidance of direct communication or possible confrontations
- Reduction of emotional connections
- Misunderstandings and relationship damage
- Broader feelings of stress and unhappiness
___________________ _______________ is when the therapist works systematically to increase the number of constructive and pleasurable activities and events in a client's life.
Behavioural activation
Behavioural activation is most effective when combined with ________________ ___________________.
cognitive techniques
Beck's cognitive therapy uses 4 phases. What are they?
1. Increasing activities and elevating mood
2. Challenging automatic thoughts
3. Identifying negative thinking and biases
4. Changing primary attitudes
What is the family-social perspective on depression?
A decline in social rewards impacts depression, where depressed people often demonstrate social deficits that may cause avoidance by others and decrease social contacts and rewards
What are some causes of depression according to family-social theory?
- Weak or unavailable social support, isolation, and lack of intimacy
- Social isolation and imposed social distancing
What is a family-social treatment type for depression?
Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT)
Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT)
- Interpersonal problems may lead to depression
- Useful for depression related to social conflicts or social role changes
Traditional studies suggest that _______ is as effective as ______________ therapy for treating depression.
IPT; cognitive
What is the multicultural perspective of unipolar depression?
There is a strong link that exists between gender and depression
Women with depression appear to be ______________, have more ________________ and longer-lasting bouts, and respond ________ successfully to treatment.
younger; frequent; less
Artifact theory
Women and men are equally prone to depression but clinicians often fail to detect depression in men
Hormone explanation
Hormone changes trigger depression in many women
Life stress theory
Women in our society experience more stress than men
Body dissatisfaction explanation
Explains that depression may stem from the fact that females in Western society are taught, almost from birth, to seek a low body weight and slender body shape (goals that are unreasonable, unhealthy and often unattainable)
Lack-of-control theory
Draws on the learned helplessness research and proposes that women may be more prone to depression because they feel less control than men over their lives
Rumination theory
Women are more likely than men to ruminate when their moods darken, perhaps making them more vulnerable to the onset of clinical depression
Depression is found ________________.
worldwide
Depressed people in non-Western countries are more likely to be troubled by what kind of symptoms?
Physical
As countries becomes more Westernized, depression seems to take on the more ______________ character it has in the West.
cognitive
What is the developmental psychopathology model on unipolar depression?
It is caused by a combination of the factors cited by various models, including a genetic predisposition influenced by significant early life trauma, magnitude and timing of negative factors, and resiliency