Organization of the Body and Cell Components, Division, and Genetics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
cell
basic structural unit of the body
tissue
combination of similar cells
organ
collection of tissues working together to perform a specific function
body system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.
organism
life form made up of interdependent parts (cells, tissues, organs, and body systems), all of which work together to maintain life.
Cytology
is the study of the formation, structure, and function of cells.
organelles
specialized structures that enable specific functions. Most cells have certain organelles in common.
cell/plasma membrane
surrounds every cell. The cell membrane separates the cell from its external environment. Because the membrane is responsible for what enters and leaves the cell, it is also known as a selective semipermeable membrane.
nucleus
controlling structure of the cell. It is responsible for the main function and reproduction of the cell. The nucleus of every human cell (except for the sex cells, the egg and sperm) contains 46 chromosomes arranged into 23 pairs, 22 of which are identical.
chromosomes
contain genes
genes
composed of a chemical called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is responsible for each person’s unique genetic makeup.
cytoplasm
a sticky, semifluid material between the nucleus and the cell membrane. The cytoplasm contains organ-elles that the cell needs to function properly. It is the area of the cell in which all chemical reactions occur.
electrolytes
compounds made up of charged particles called ions
Ions
can conduct electrical currents in water or in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cation
positive-charge ion that creates an acid
Acid
chemical sub-stances that taste sour and neutralize bases. (You are familiar with the weak acids that are present in many different kinds of foods, from citrus fruits to fermented dairy products such as yogurt and sour cream.)
Bases
substances that react with acids to form salts.
Anion
negative-charged ion that creates bases
pH (Potential of Hydrogen)
a measurement of how much acid or base is present.
Muscle cells
long, slender cells within muscle tissue. Muscle cells contain fibers that allow muscular tissue to con-tract and relax.
Epithelial cells
typically flat, square cells that cover the skin and line the digestive tract and other hollow organs.
Fat cells
contain large, empty spaces for fat storage in the body.
Nerve cells
tend to be long, have several fibrous extensions that carry nerve impulses.
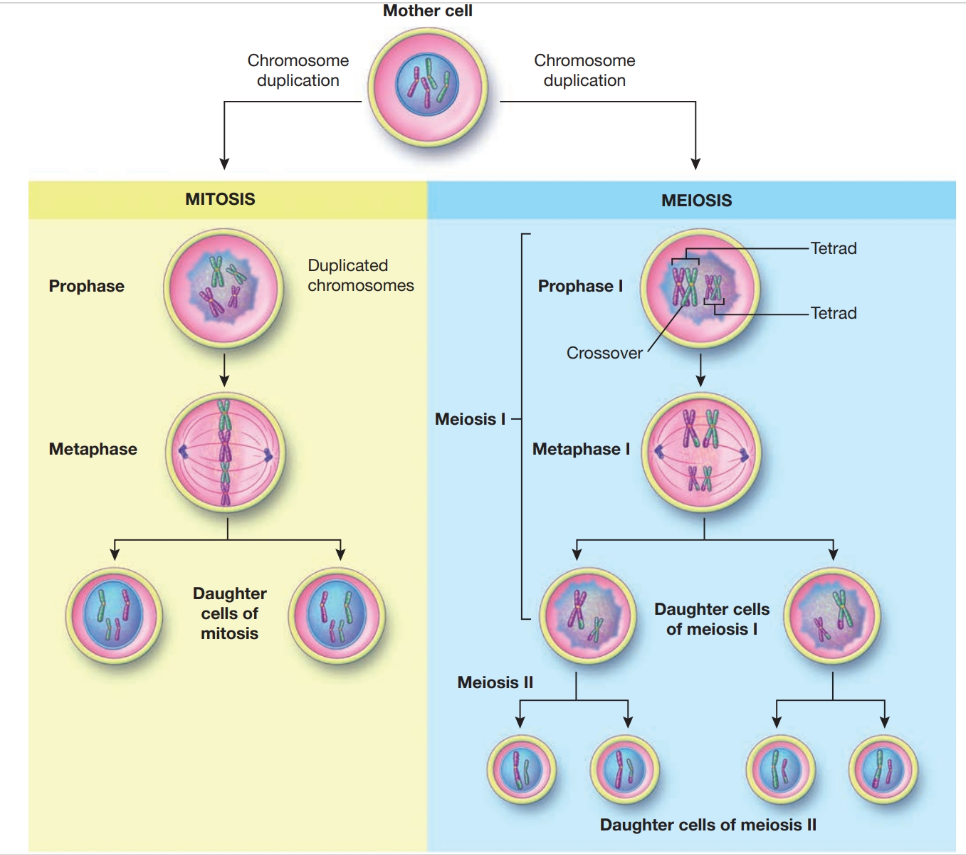
cell division
growth and development of cells and replacement of old, dead, or damaged cells.
Meiosis
Sex cells, which are involved in the reproduction of an organism, require a different process called meiosis
Genetics
the study of the ways in which genes are transferred from individuals to their offspring and of the role that genes play in the health of off-spring.
genetic disorder
a disease or condition caused by a defective gene. Genetic disorders, while present at birth, may not manifest until later in life.