TOPIC 1- 10. Macroscopy of the brainstem and the cerebellum
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
The most inferior portion of the brain, that connects the spinal cord to the diencephalon
What is the brainstem?
- Information transfer between the hemispheres, spinal cord and cerebellum
- Origin of most of the cranial nerves
What is the function of the brainstem?
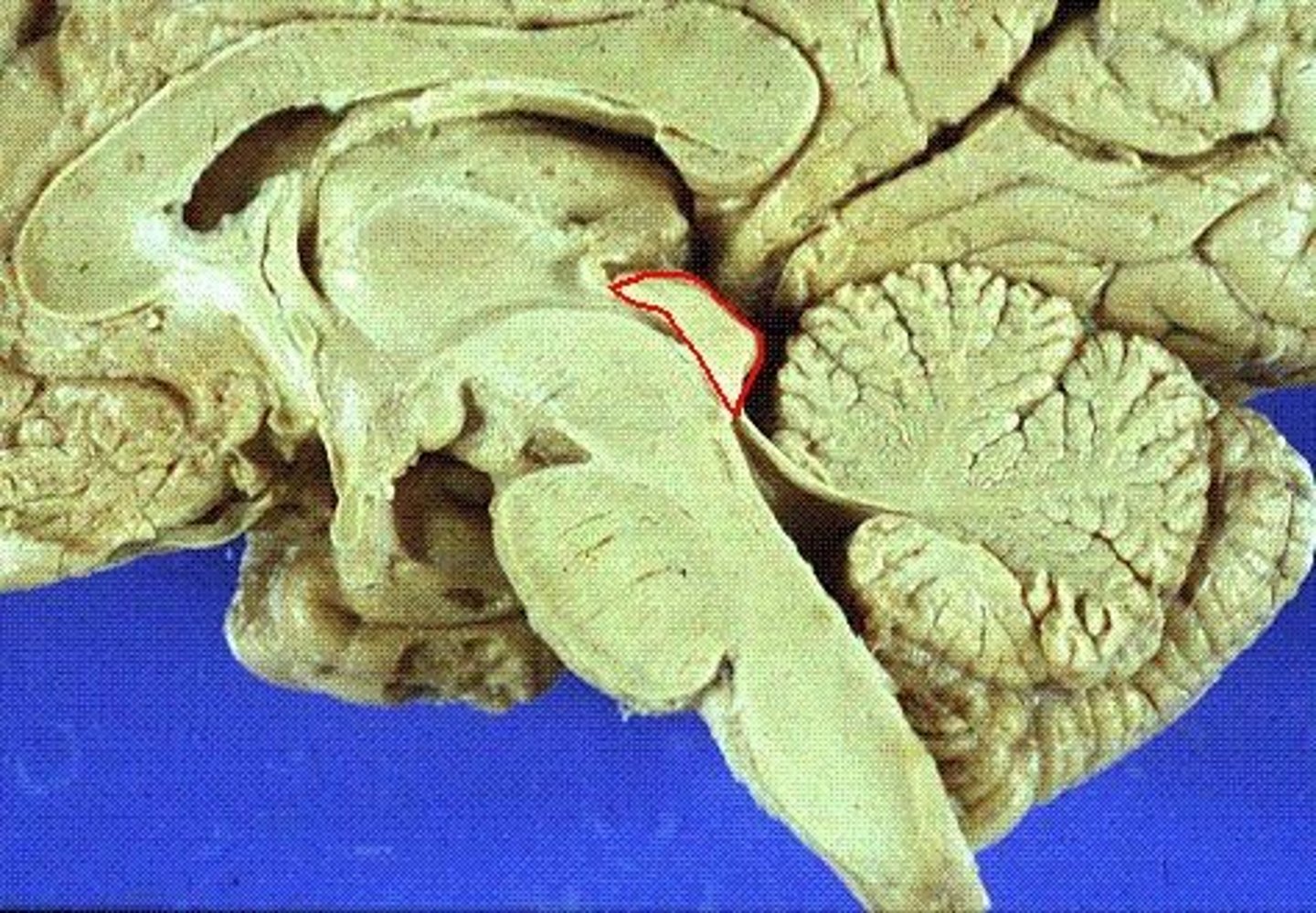
- Mesencephalon
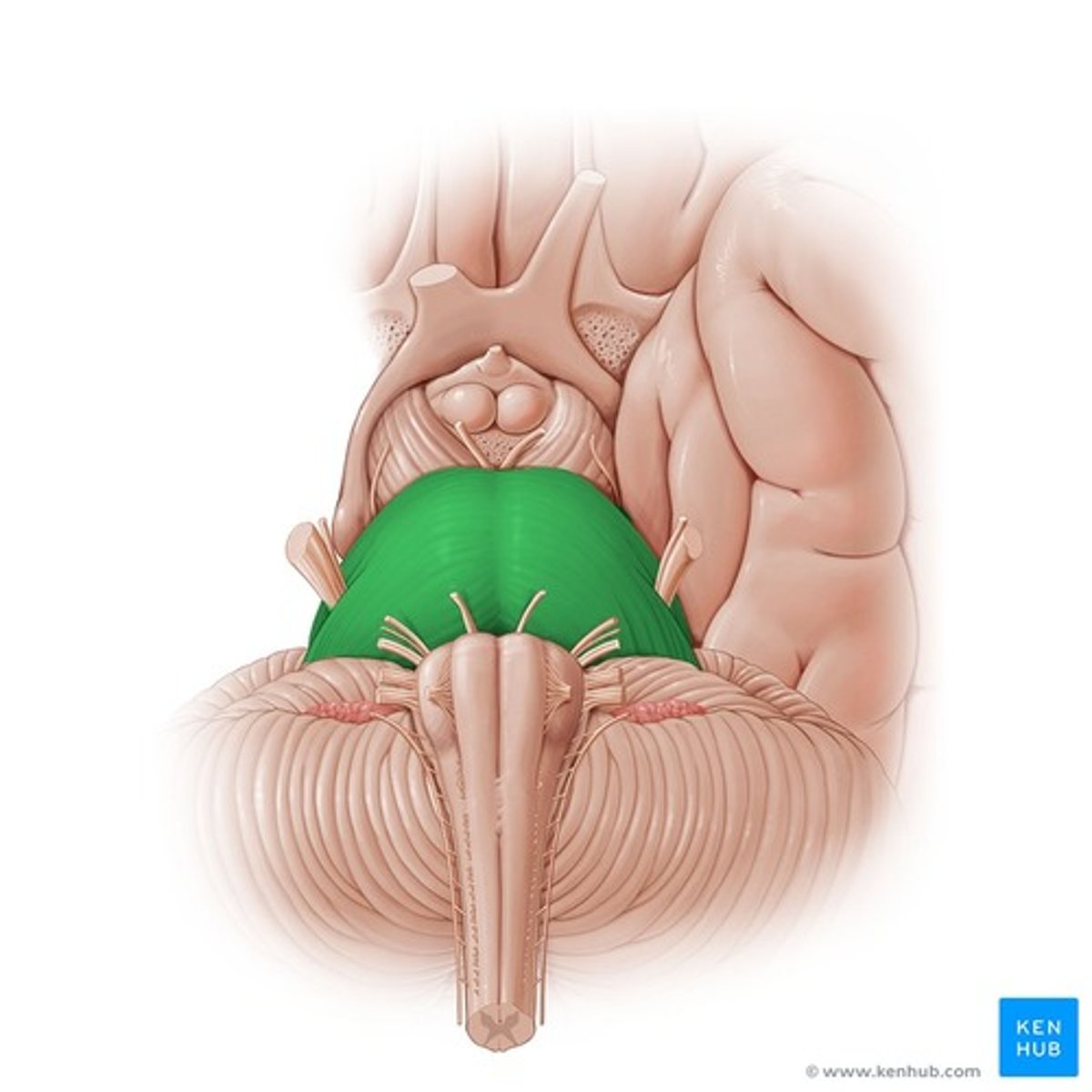
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
How can you macroscopically divide the brainstem?
- Control movements of the eye
- Process auditory and sensory information
Main functions of the mesencephalon?
- Tectum
- Cerebral peduncle
What are the main parts of the mesencephalon?
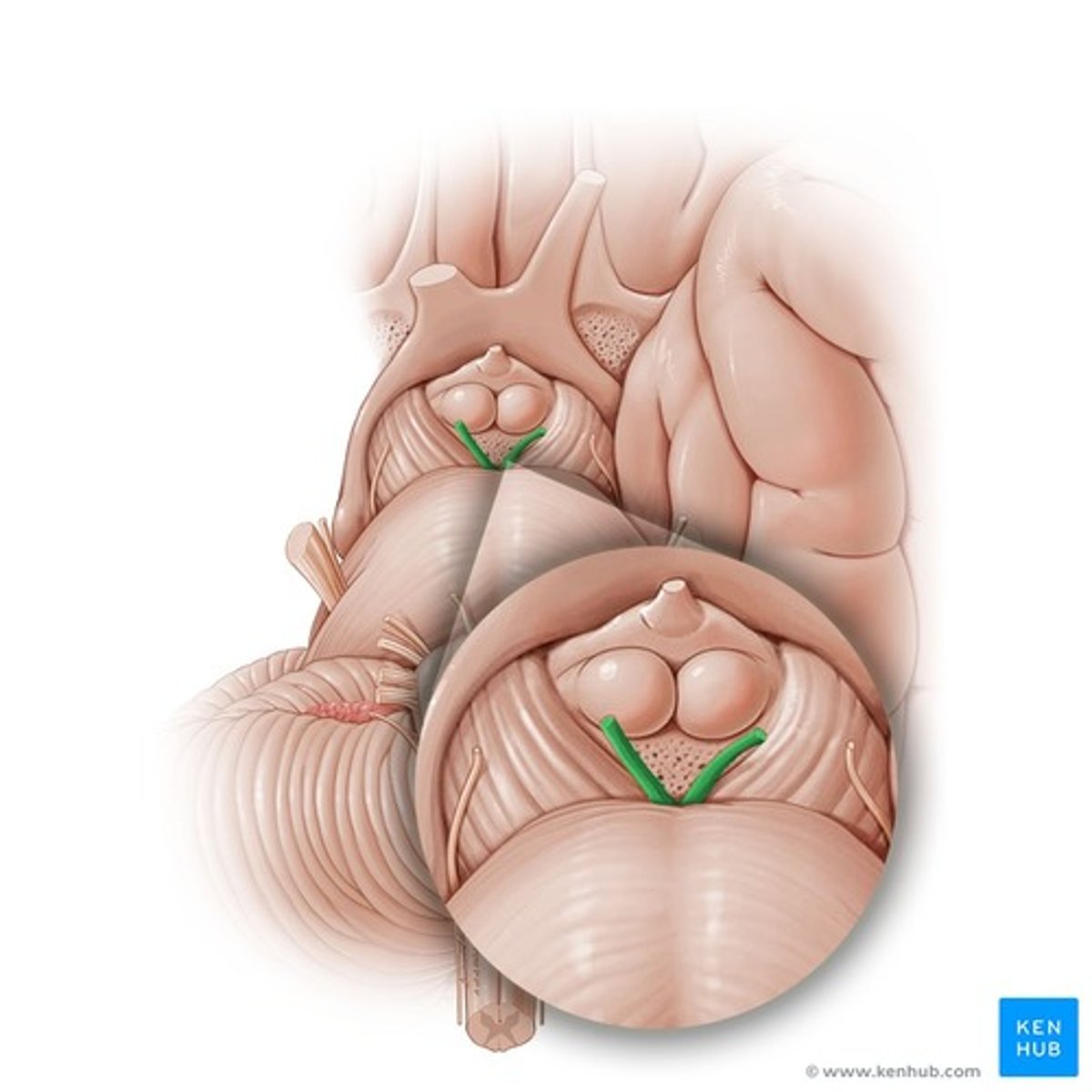
Tectum
Superior colliculus
Relay station for visual reflexes
Function of superior colliculus
Inferior colliculus
Relay station for audio pathway
Function of the inferior colliculus
Cerebral peduncles
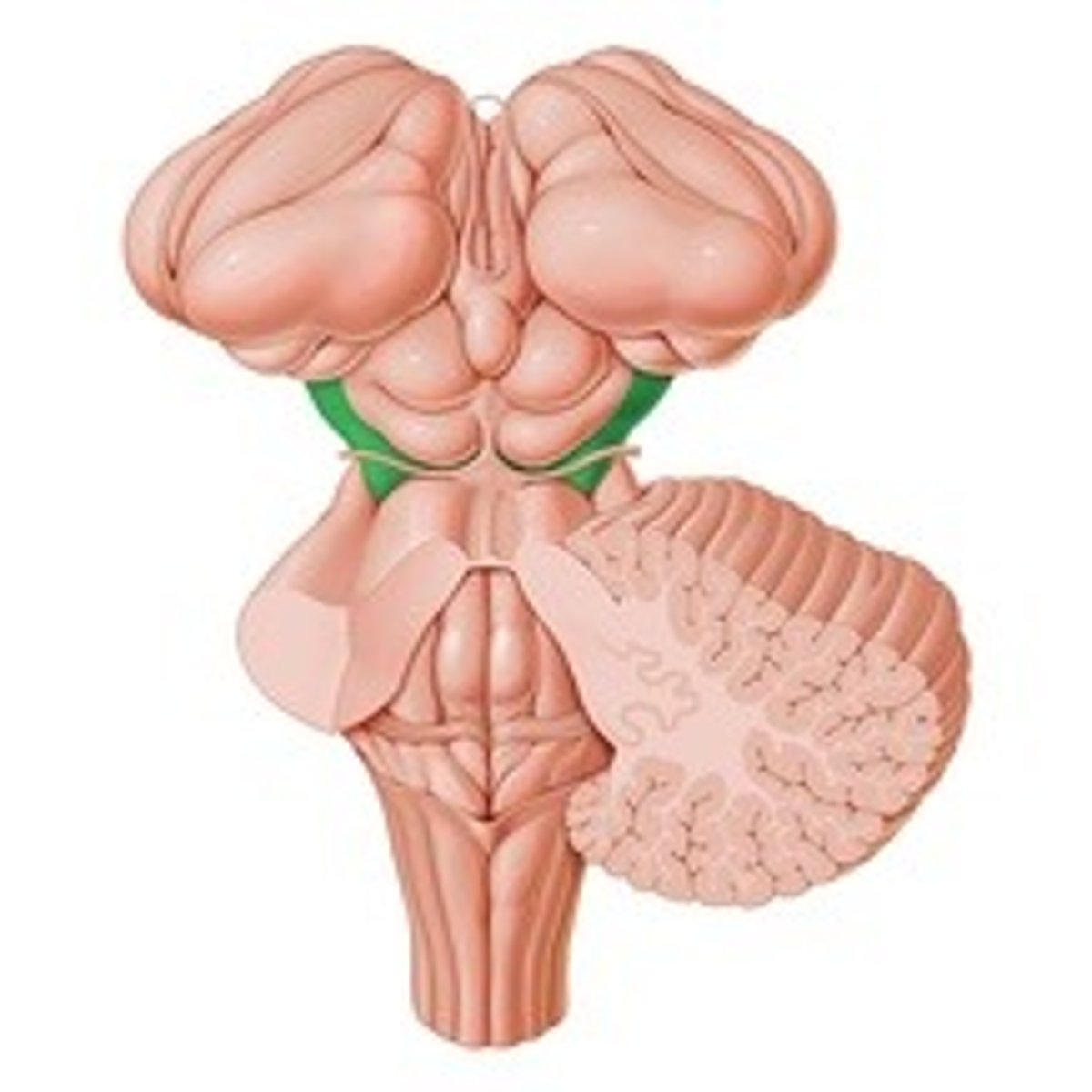
Cerebral peduncles
- Tegmentum
- Cerebral crus
What does cerebral peduncles consist of?
Cerebral crus
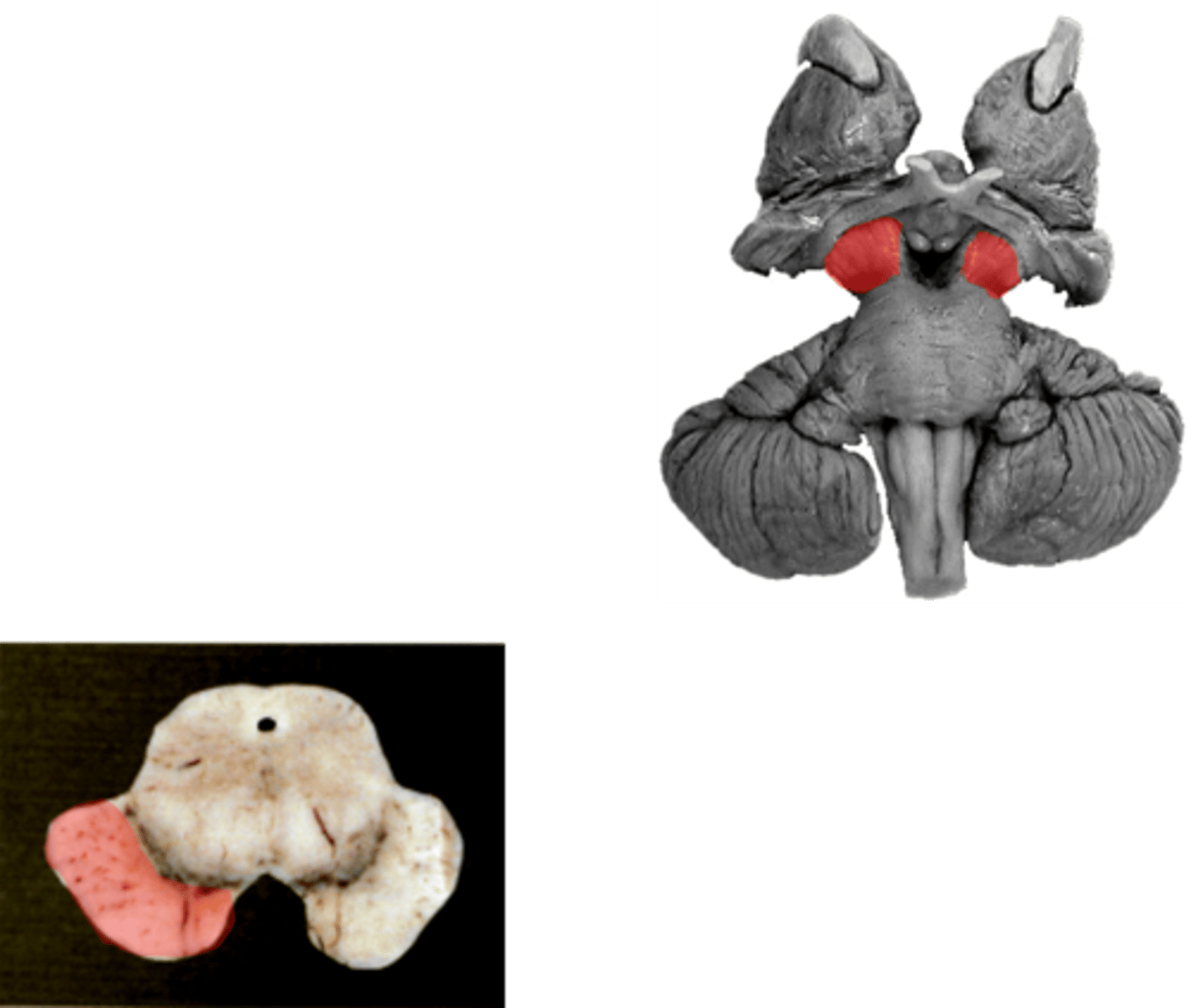
Contain fibers that transfer information between the brainstem and the thalami
What is the function of the cerebral peduncles?
- Arnold´s pathway
- Türk pathway
- Pyramidal pathway
Which pathways go through the cerebral peduncles?
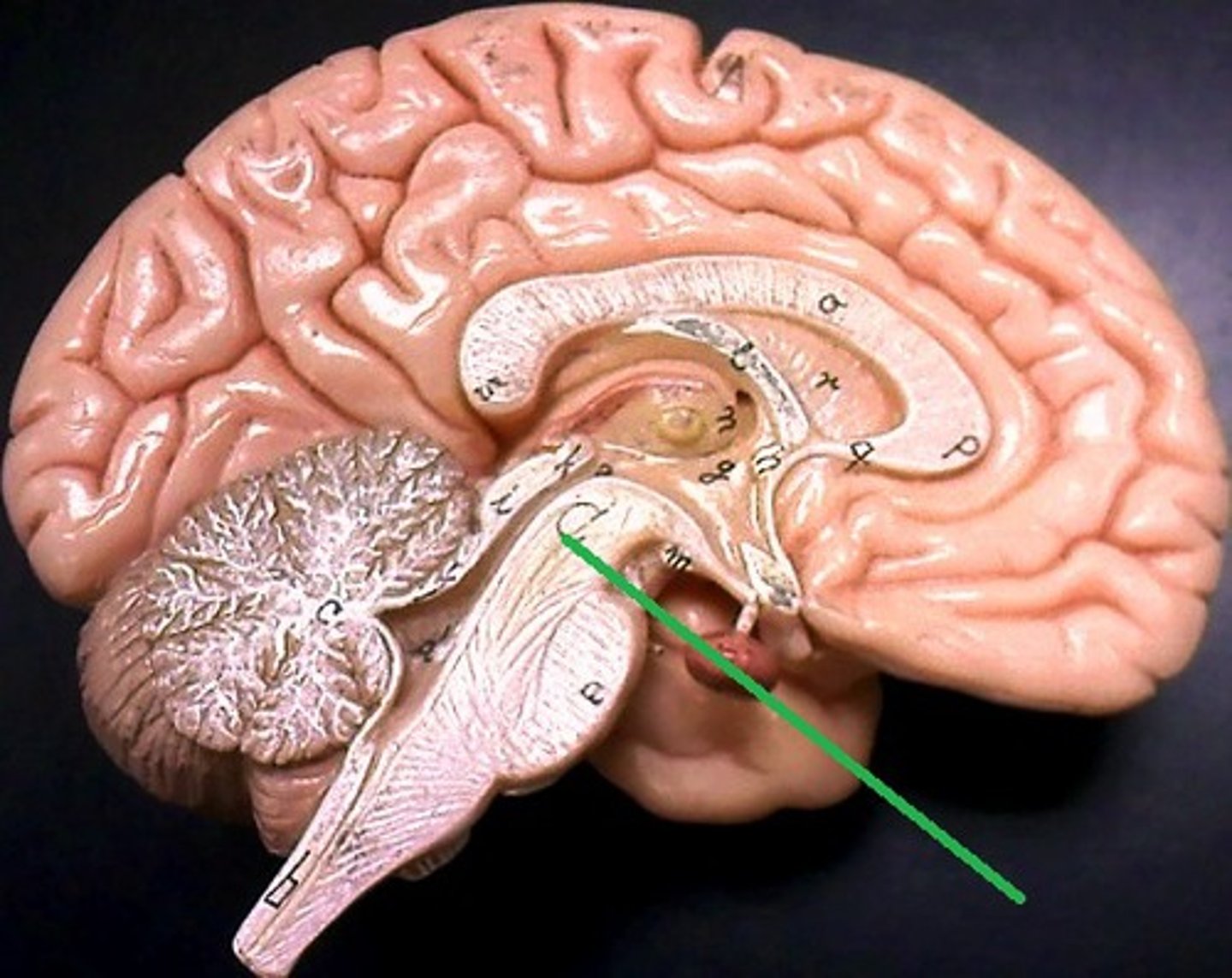
Superior medullary velum
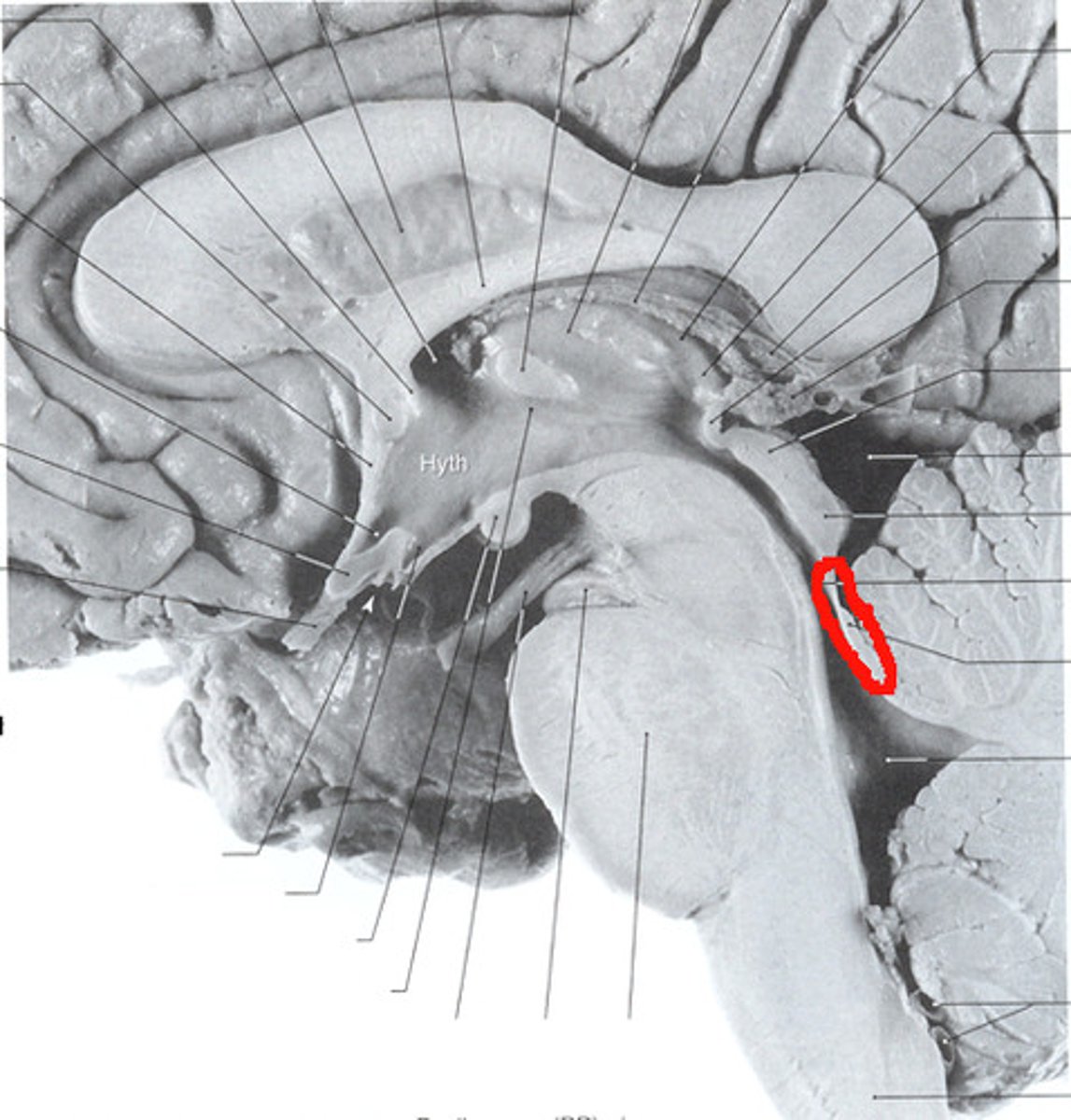
Superior medullary velum
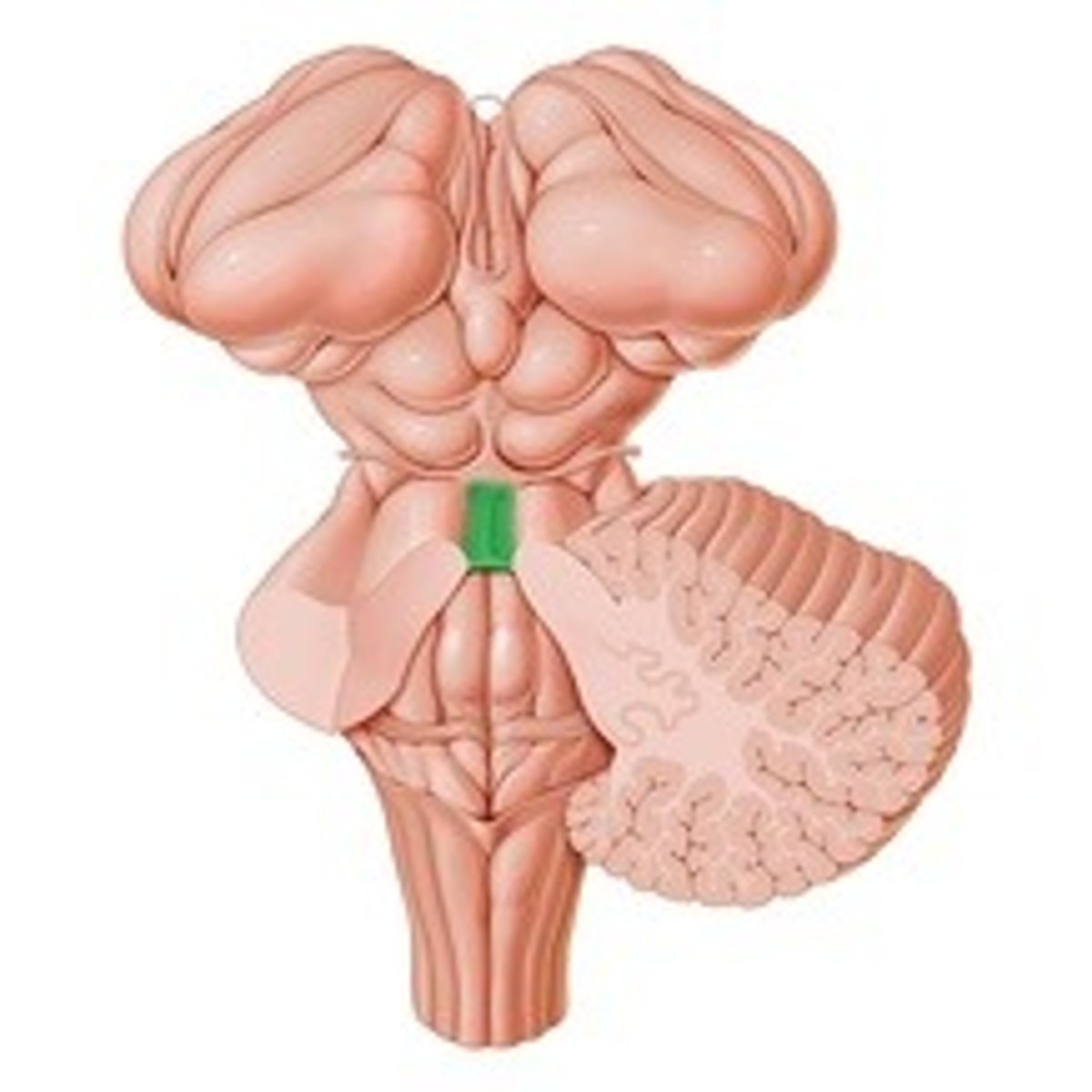
Superior medullary velum
Structure of white matter between the superior cerebellar peduncles?
The 4th ventricle
What is between the brainstem and the cerebellum?
Frenulum of the superior medullary velum
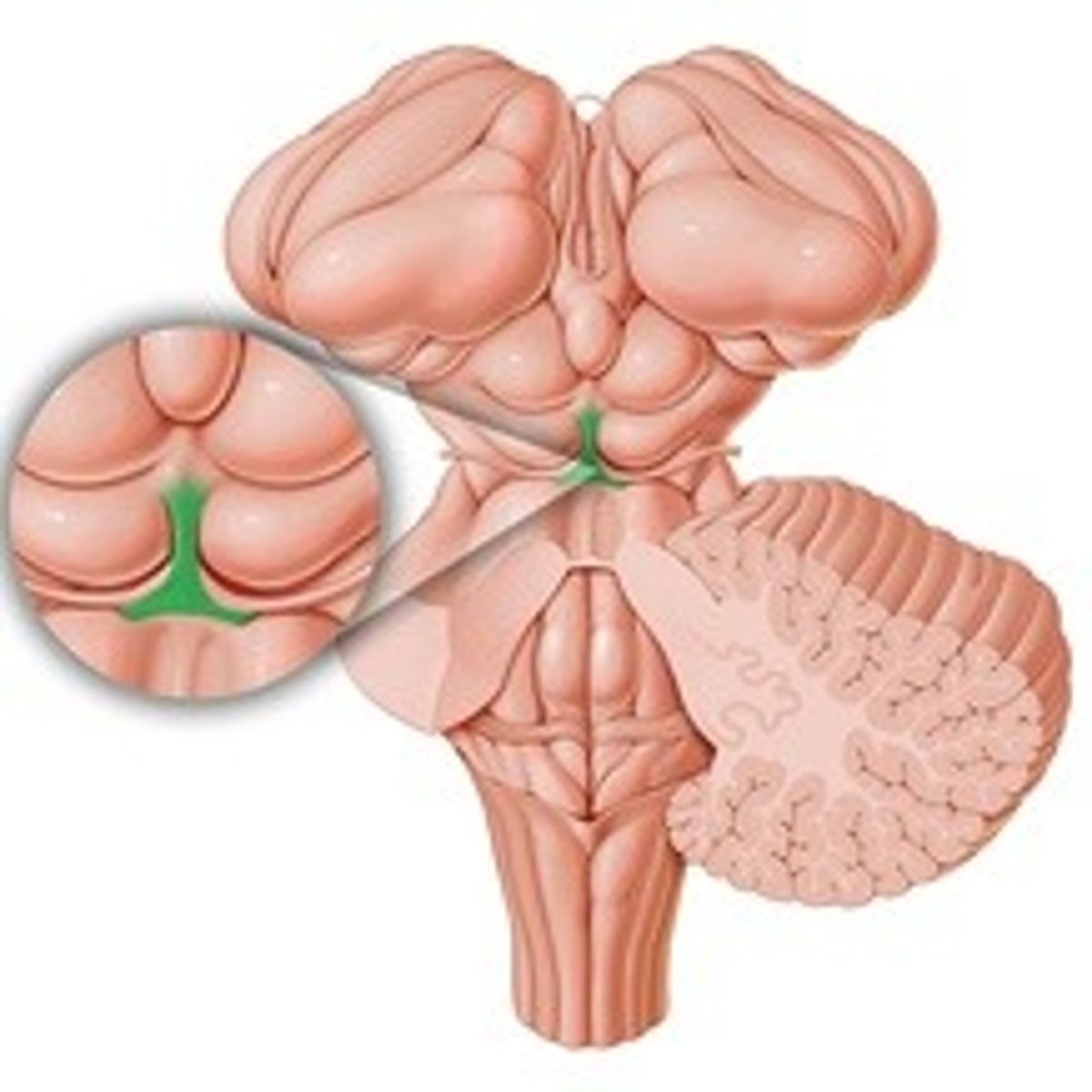
- Oculomotor nerve
- Trochlear nerve
Which cranial nerves exit in the mesencephalon?
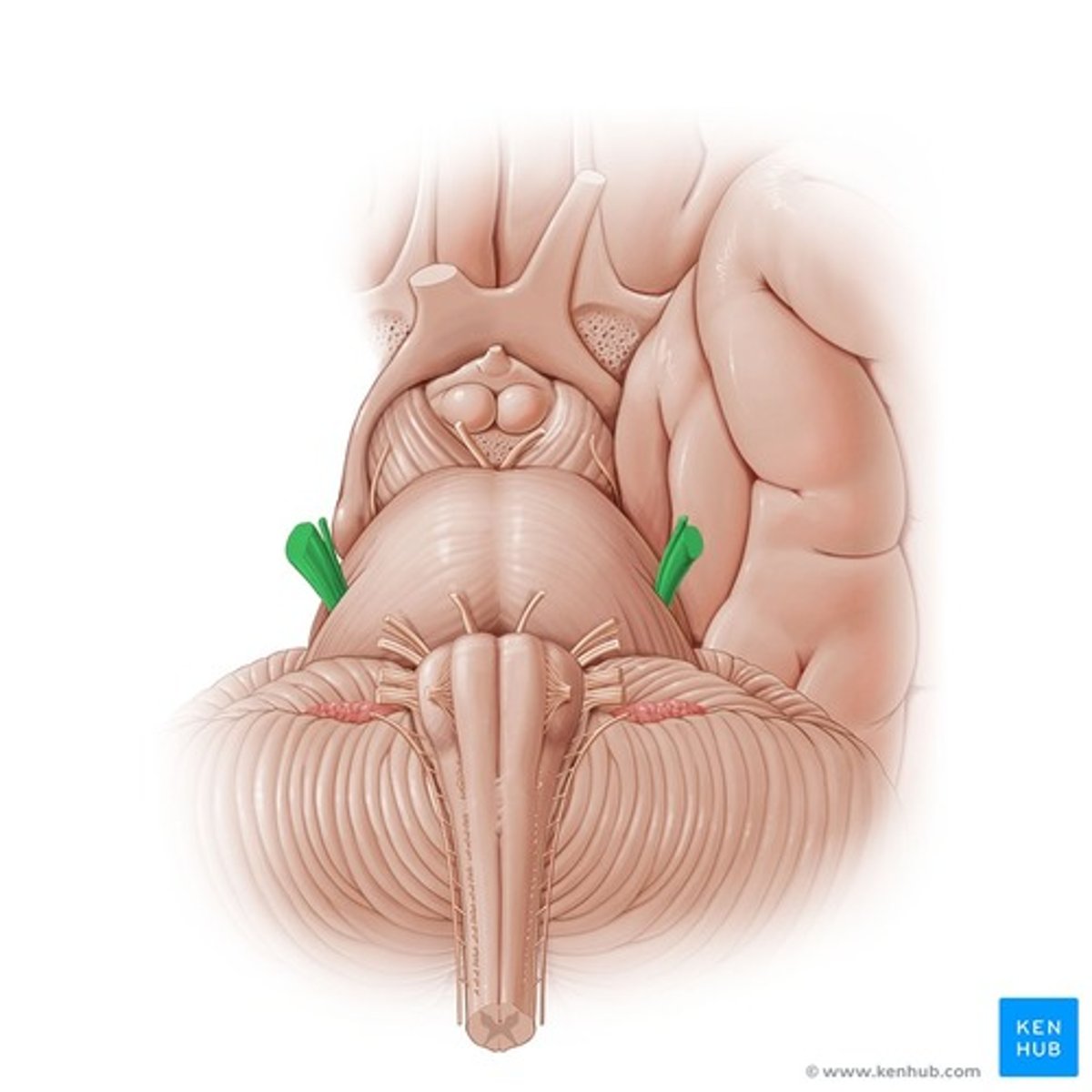
Trochlear nerve
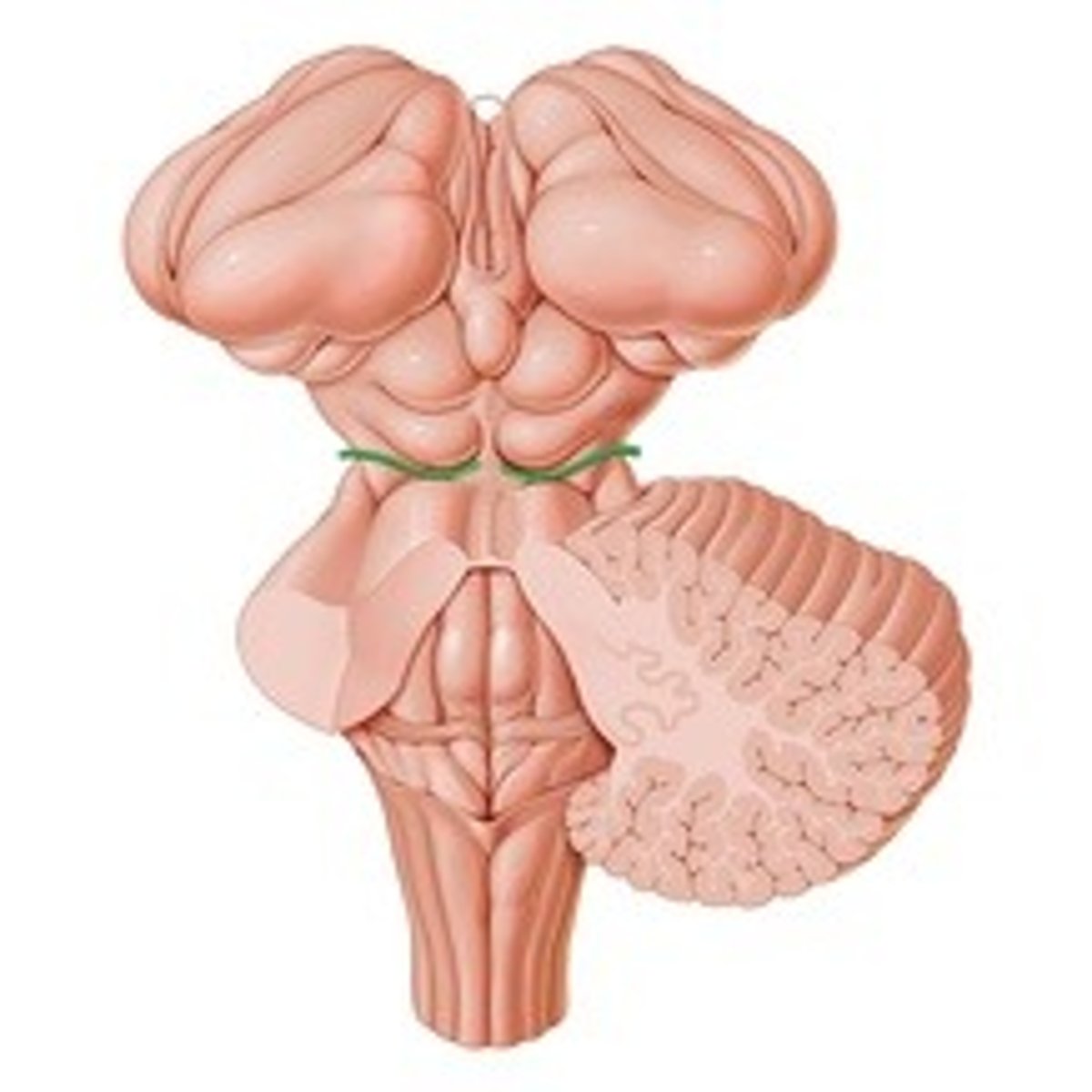
Below inferior colliculus, above superior medullary velum
Where does the trochlear nerve originate?
Rhomboid fossa
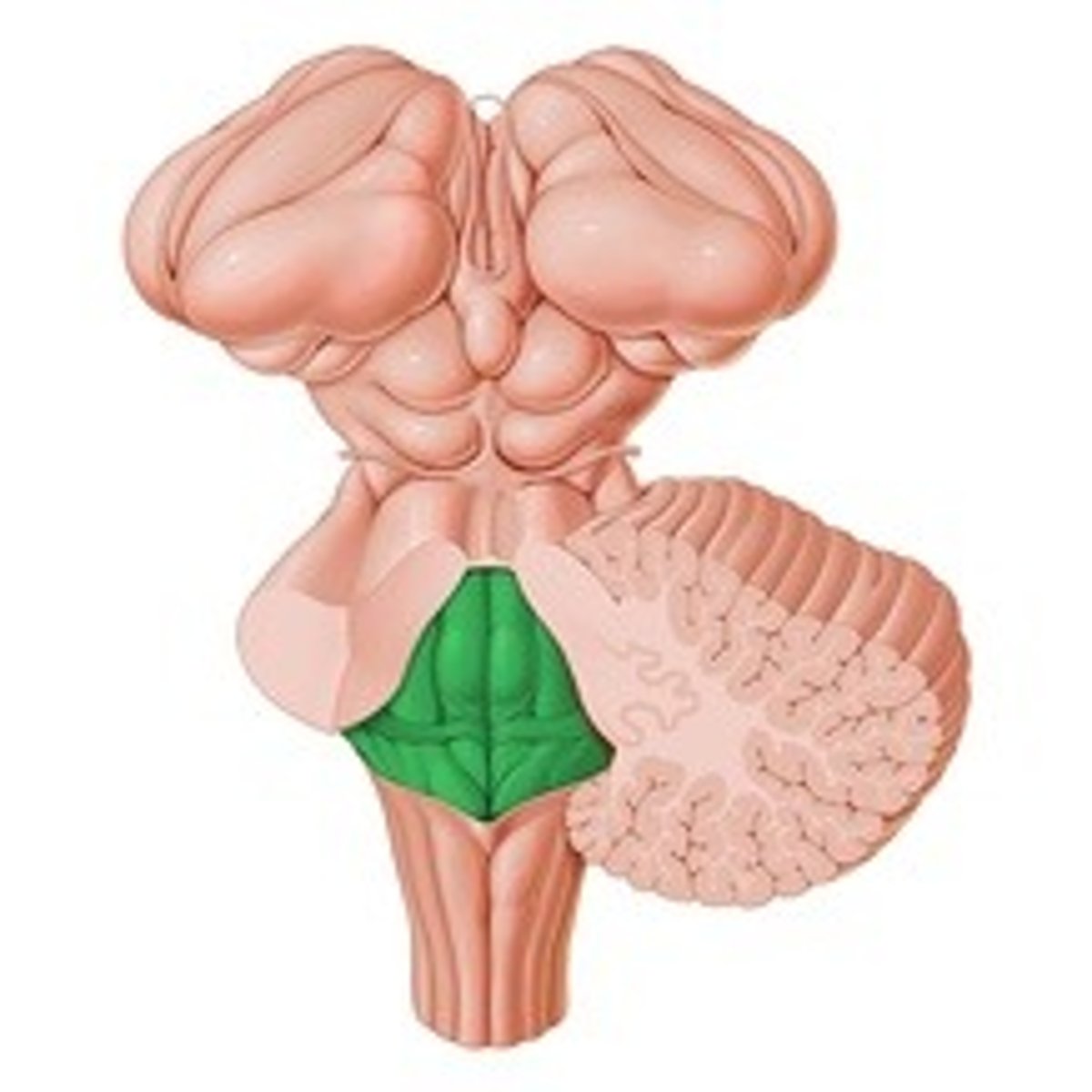
- Upper triangular part
- Intermediate part
- Lower triangular part
Which are the three parts of the rhomboid fossa?
- Medial eminences (facial colliculus)
- Locus coeruleus
- Upper part of the vestibular area
Which are the different parts of the upper triangular part?
Medial eminence
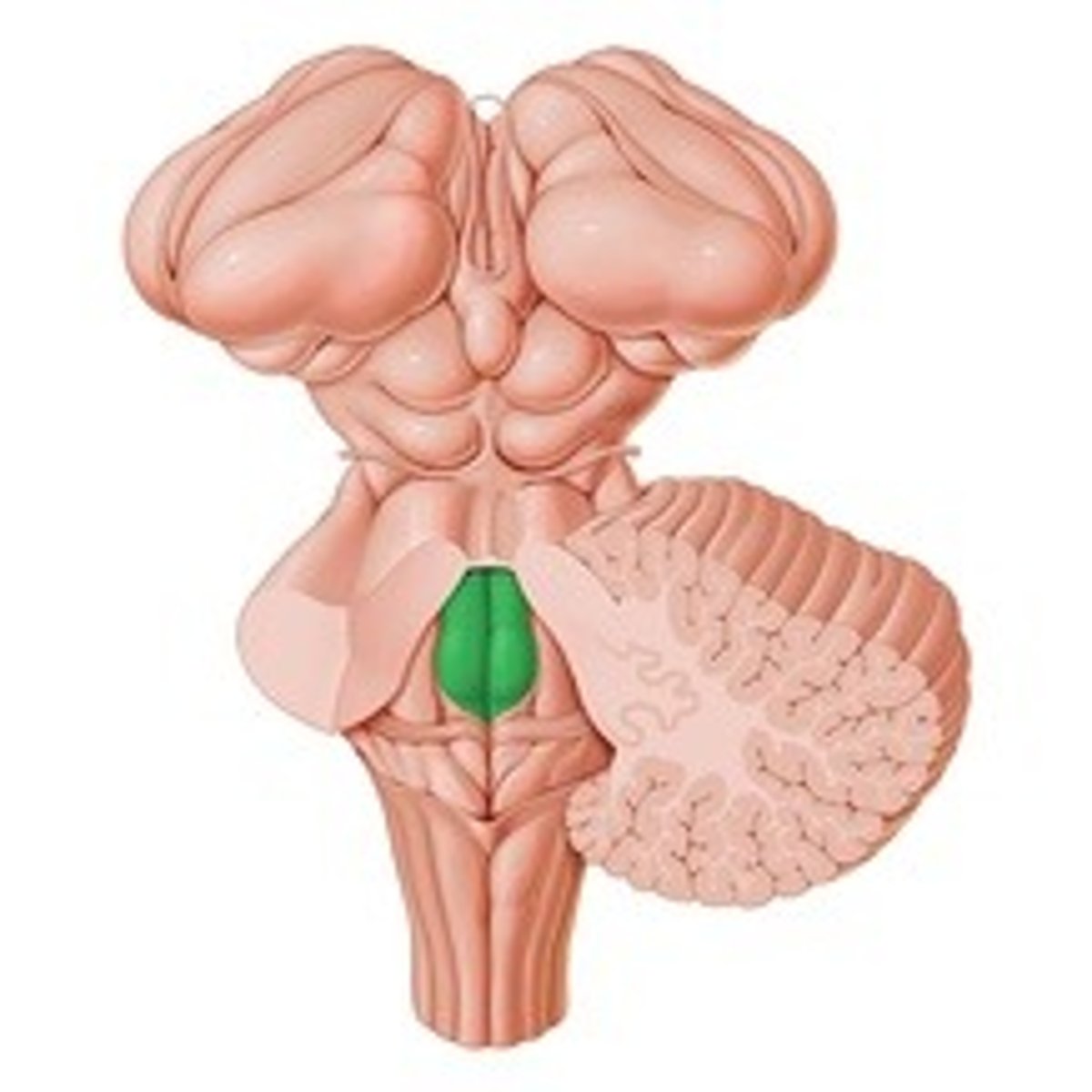
Facial colliculus
What does the medial eminence overlie?
- Motor nucleus of abducent nerve
- Axons of facial nucleus
Which structures does the facial colliculus overlie?
- Lower portion of the vestibular area
- Hypoglossal trigone
- Vagal trigone
- Obex
Which are the different parts of the lower triangular part?
Posterior median sulcus
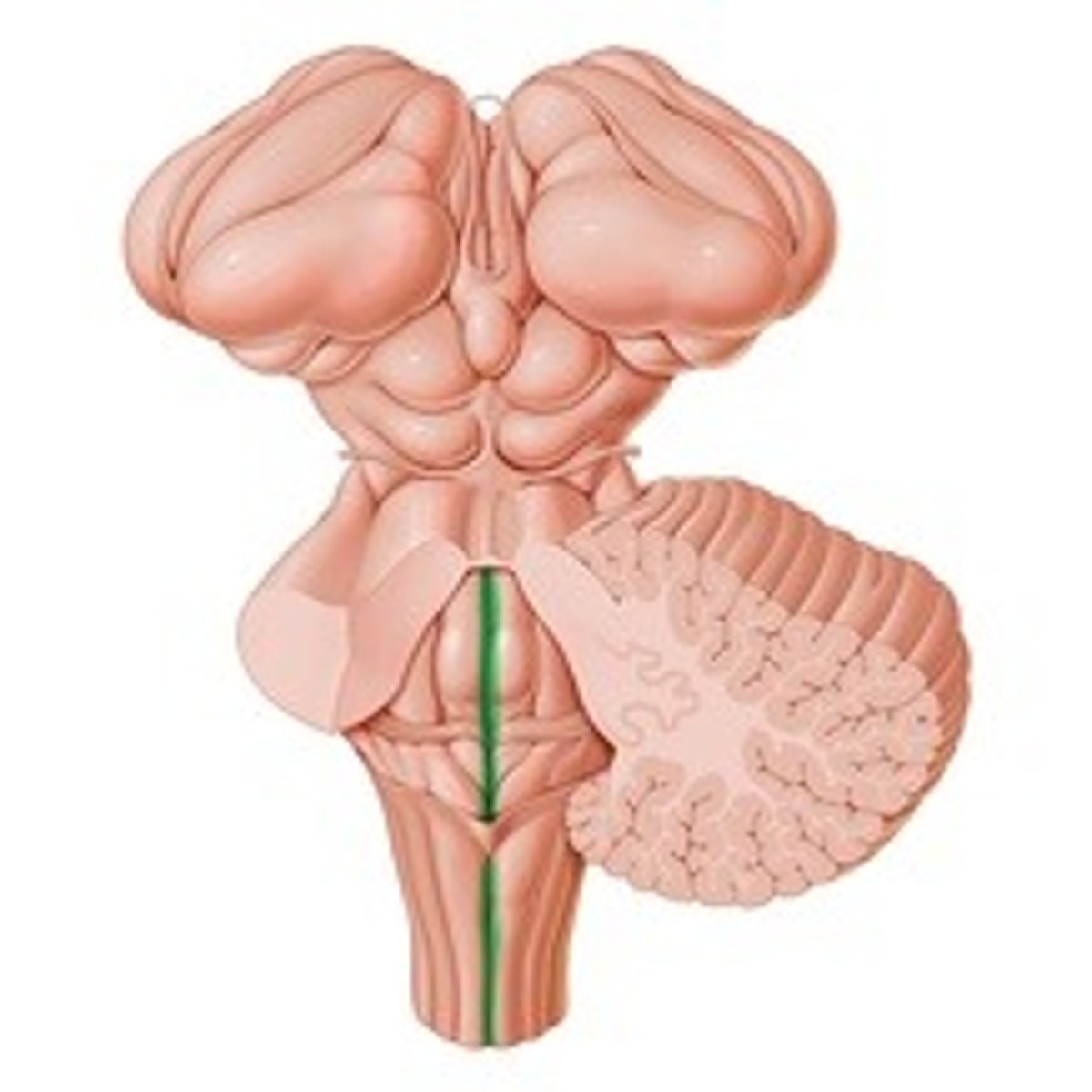
Sulcus limitans
- Posterior median sulcus
- Sulcus limitans
Which sulcuses are the borders of the medial eminence?
Contains melanin cells
Why is the locus coeruleus gey-bluish in color?
Locus coeruleus
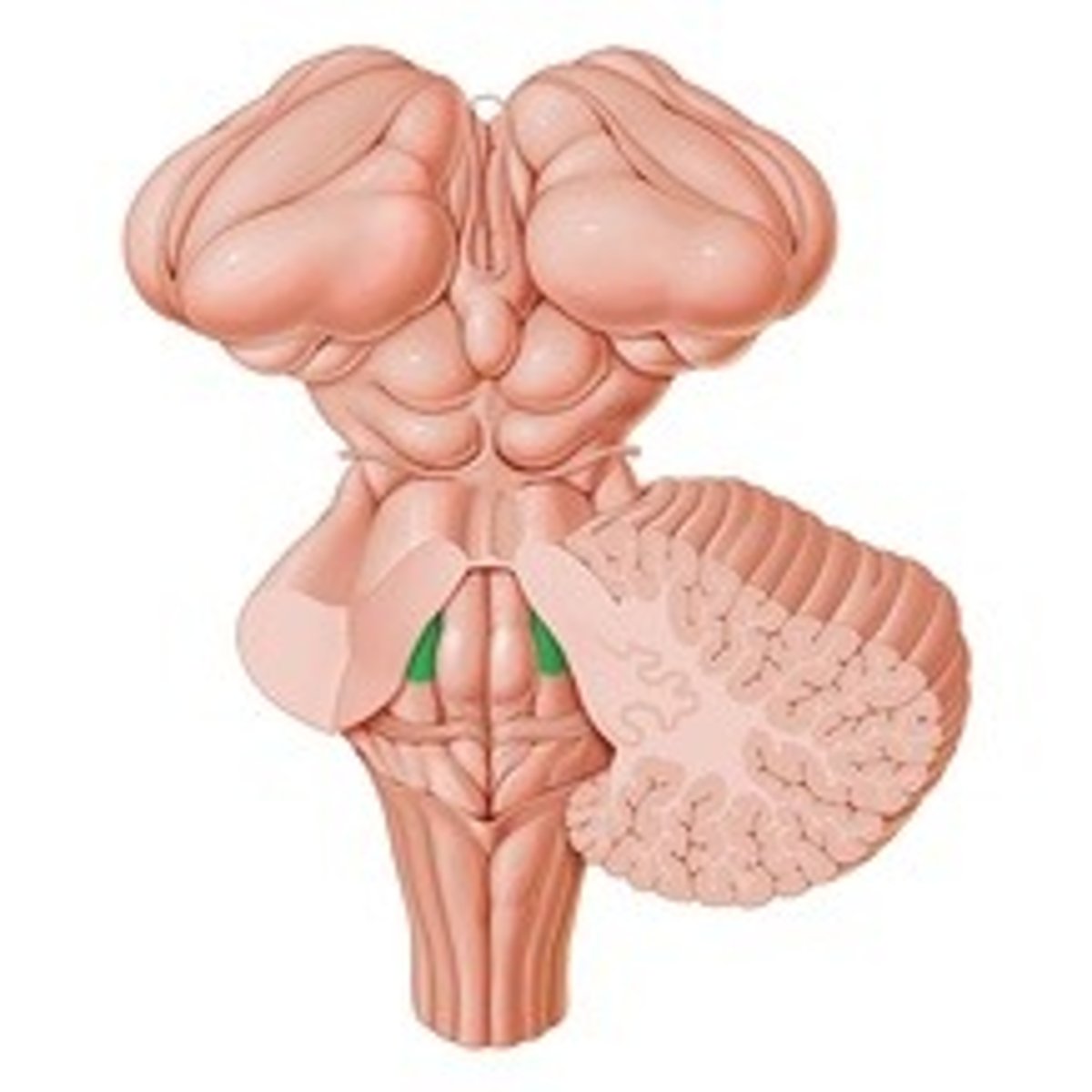
Chemo-receptor zone
- blood control analysis
What is the function of locus coeruleus?
Vestibular area
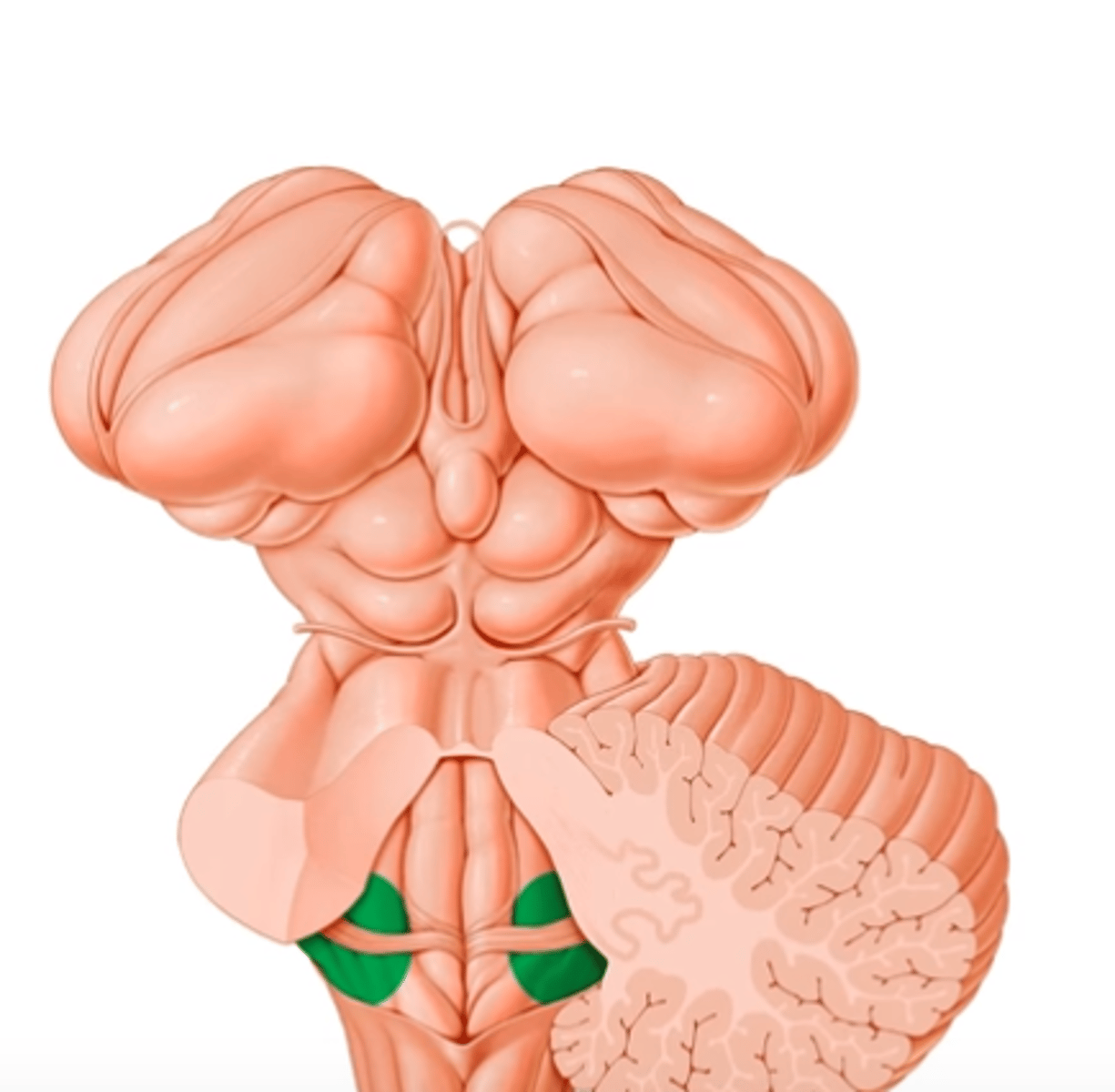
Vestibular nuclei
Which structure does the vestibular area overlie?
Medullary striae of the fourth ventricle
Leading auditory fibers
Function of the medullary stria?
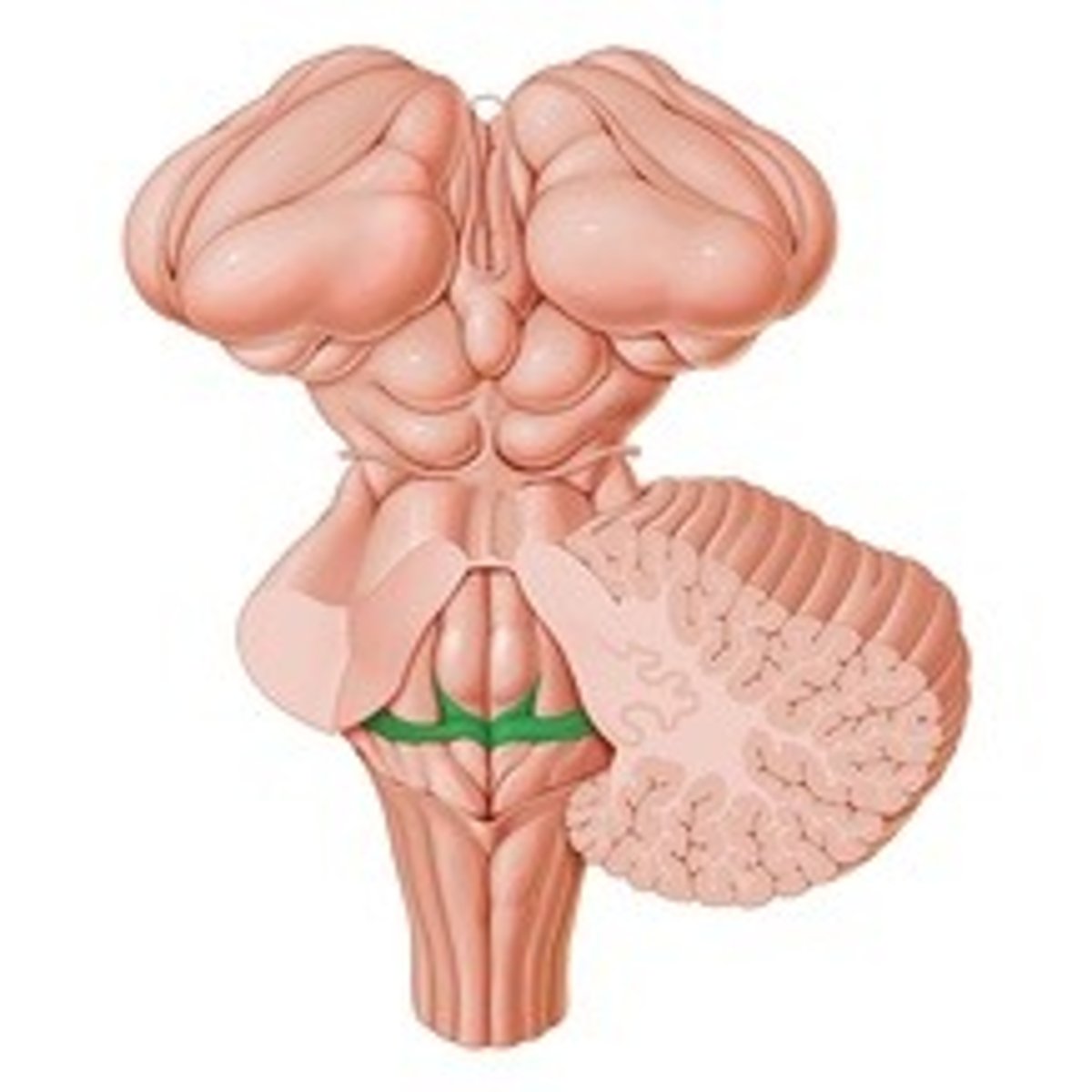
Lower triangular part
Which part of the rhomboid fossa is located in the medulla oblongata?
Hypoglossal trigone
Dorsal nuclei of the hypoglossal nerve
What is the hypoglossal trigone formed by?
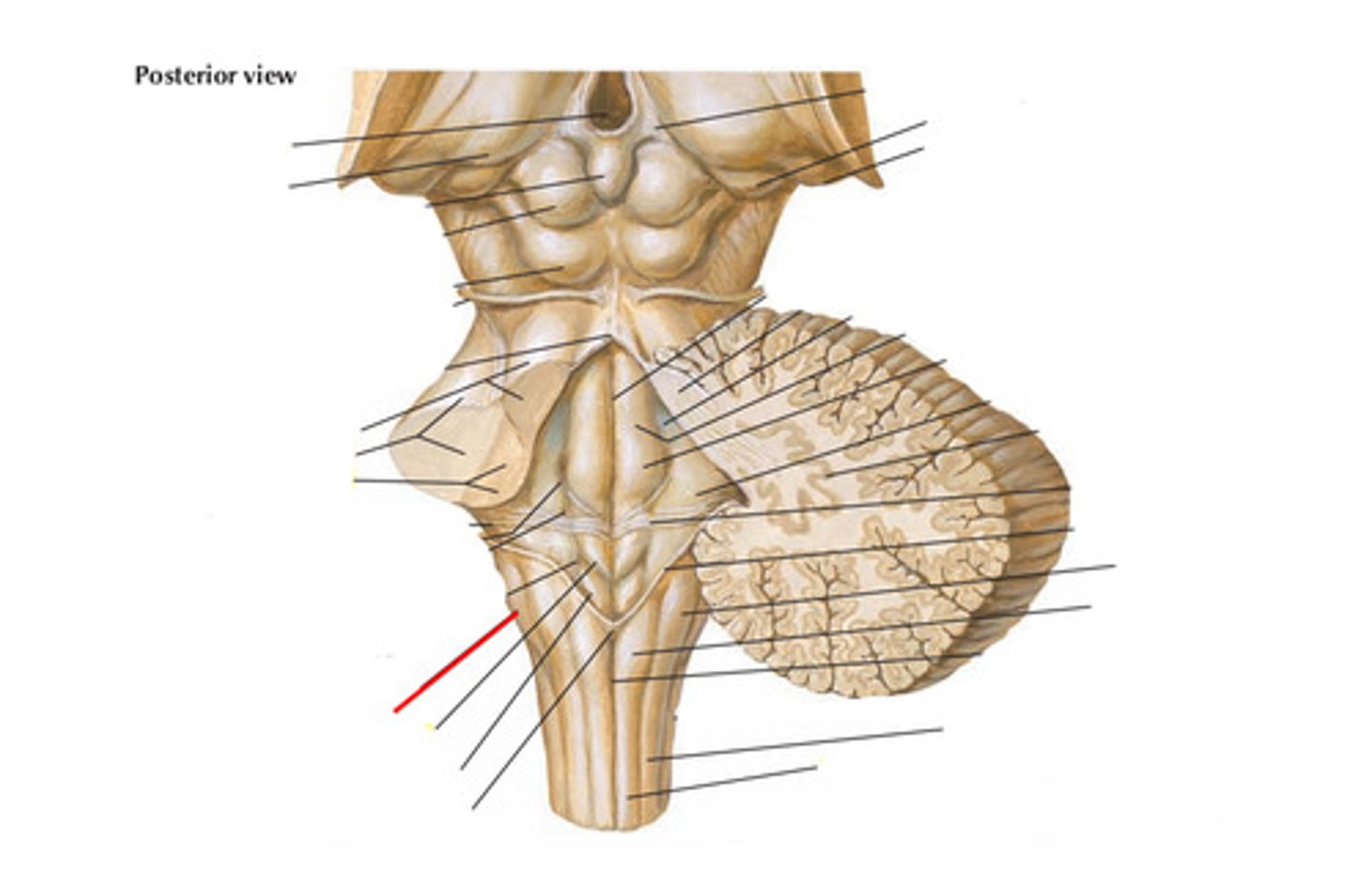
Vagal trigone
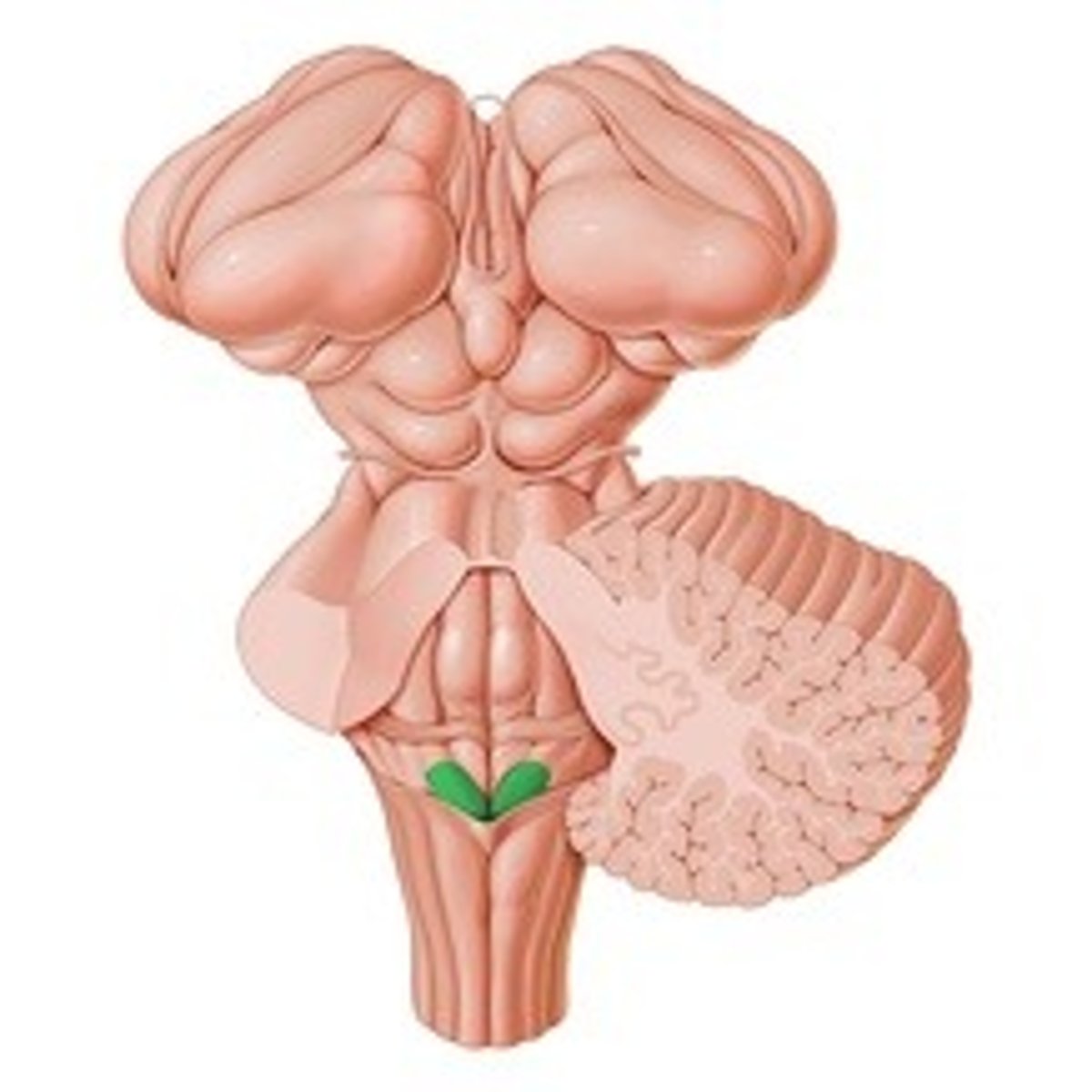
Dorsal nuclei of the 9th, 10th and 11th cranial nerve/nucleus ambiguus
What is the vagal trigone formed by?
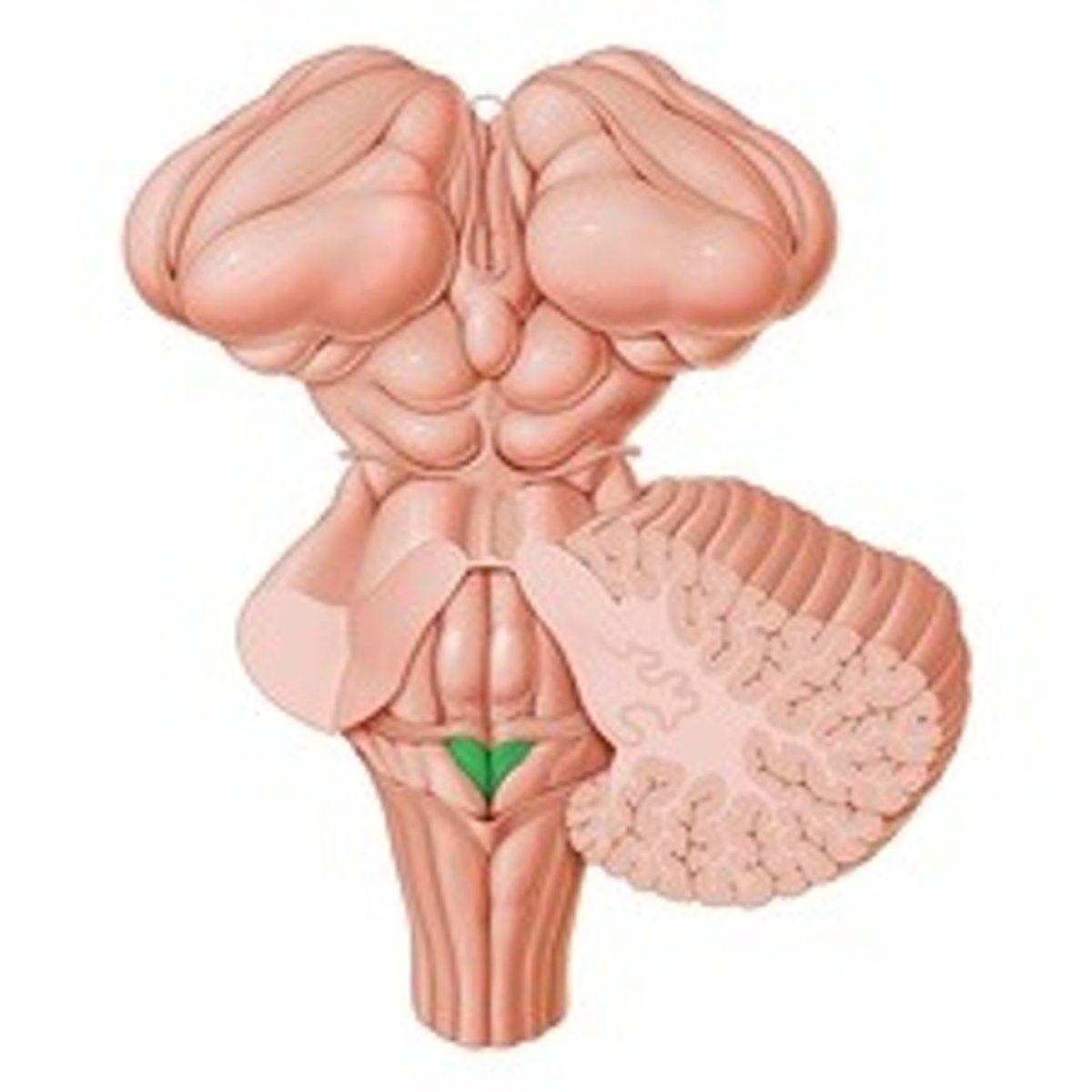
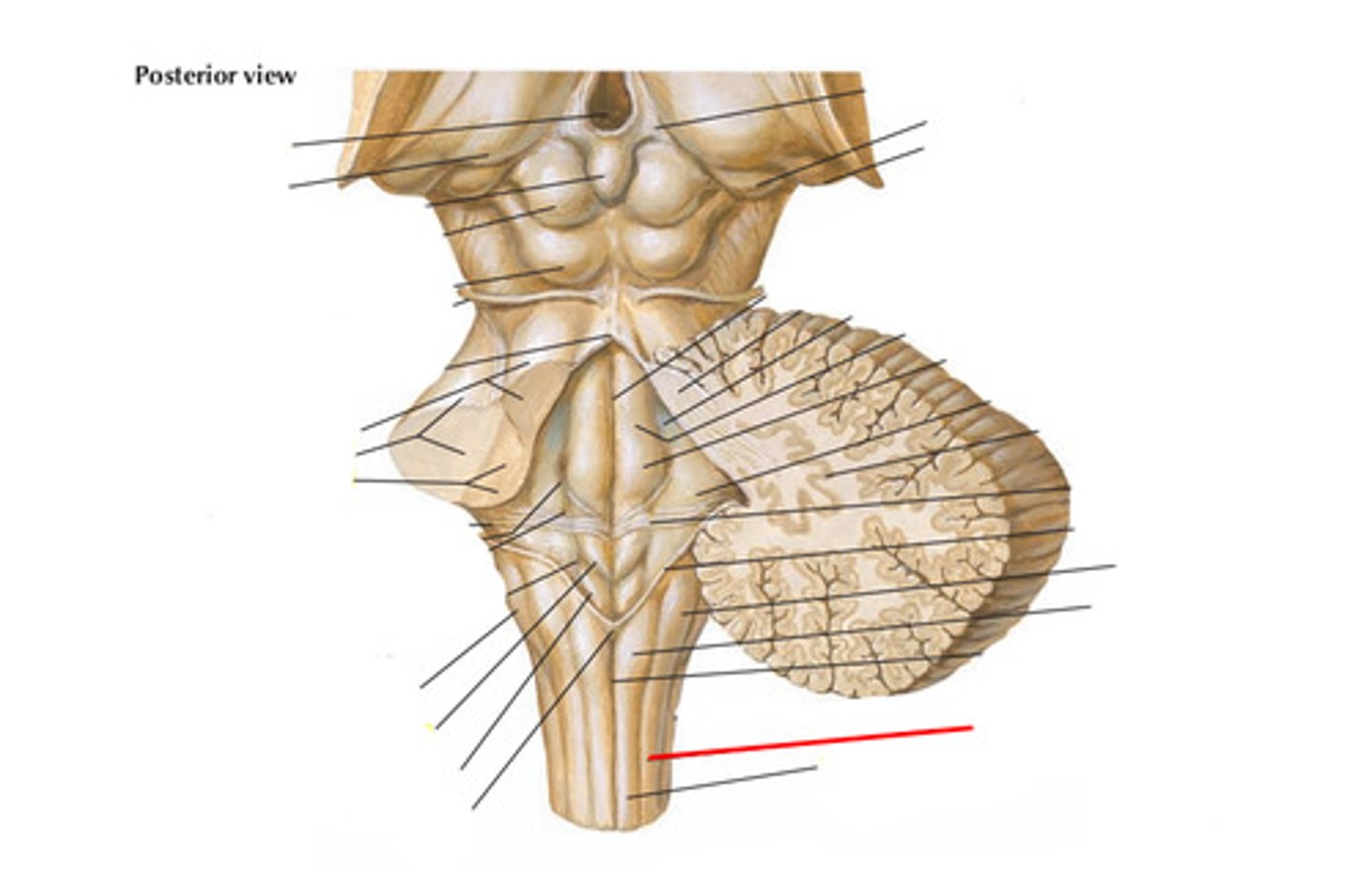
Obex
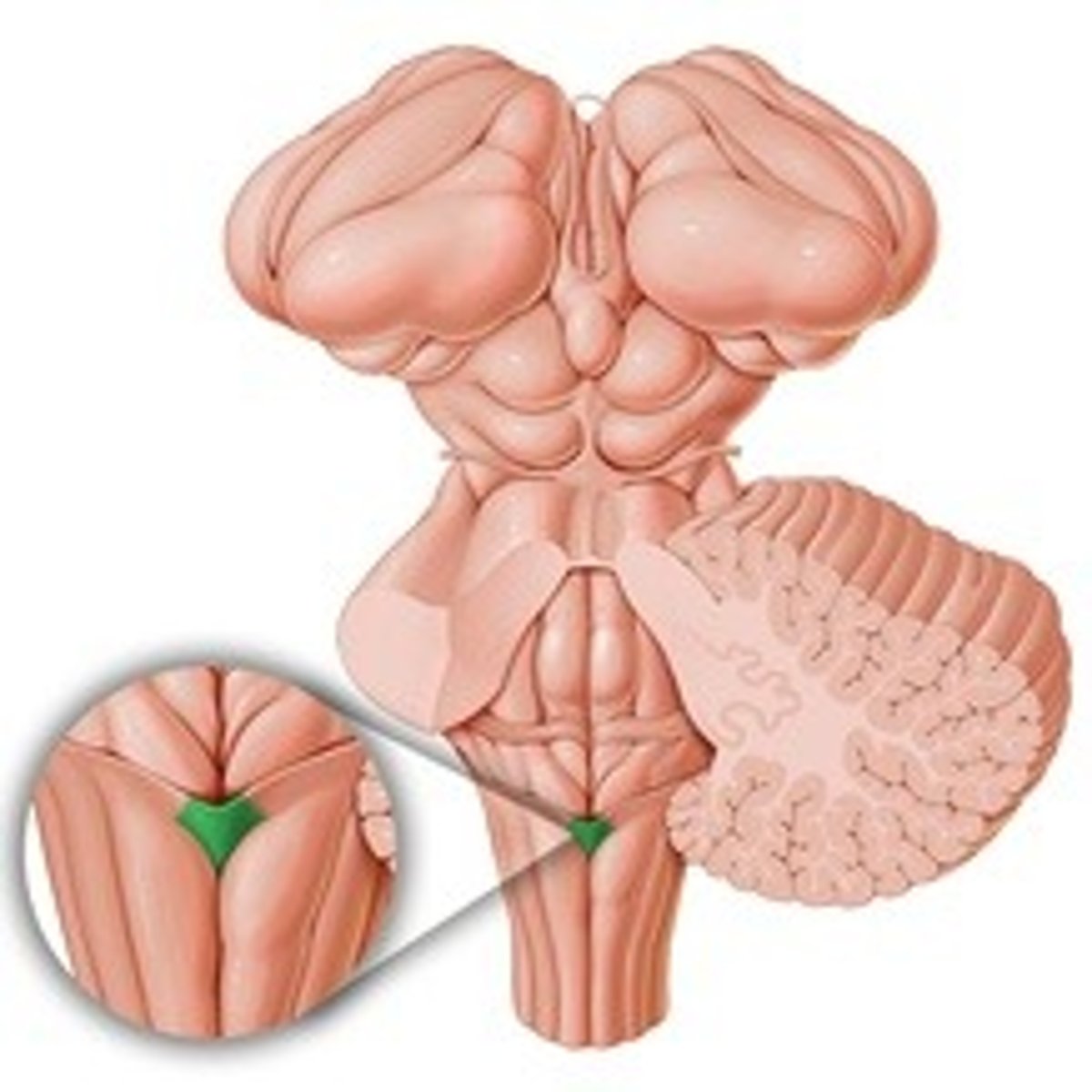
The opening of the central canal
What is the obex?
Area postrema
Center of vomiting
Function of area postrema
Gracile tubercle
Gracile fasciculus
Cuneate tubercle
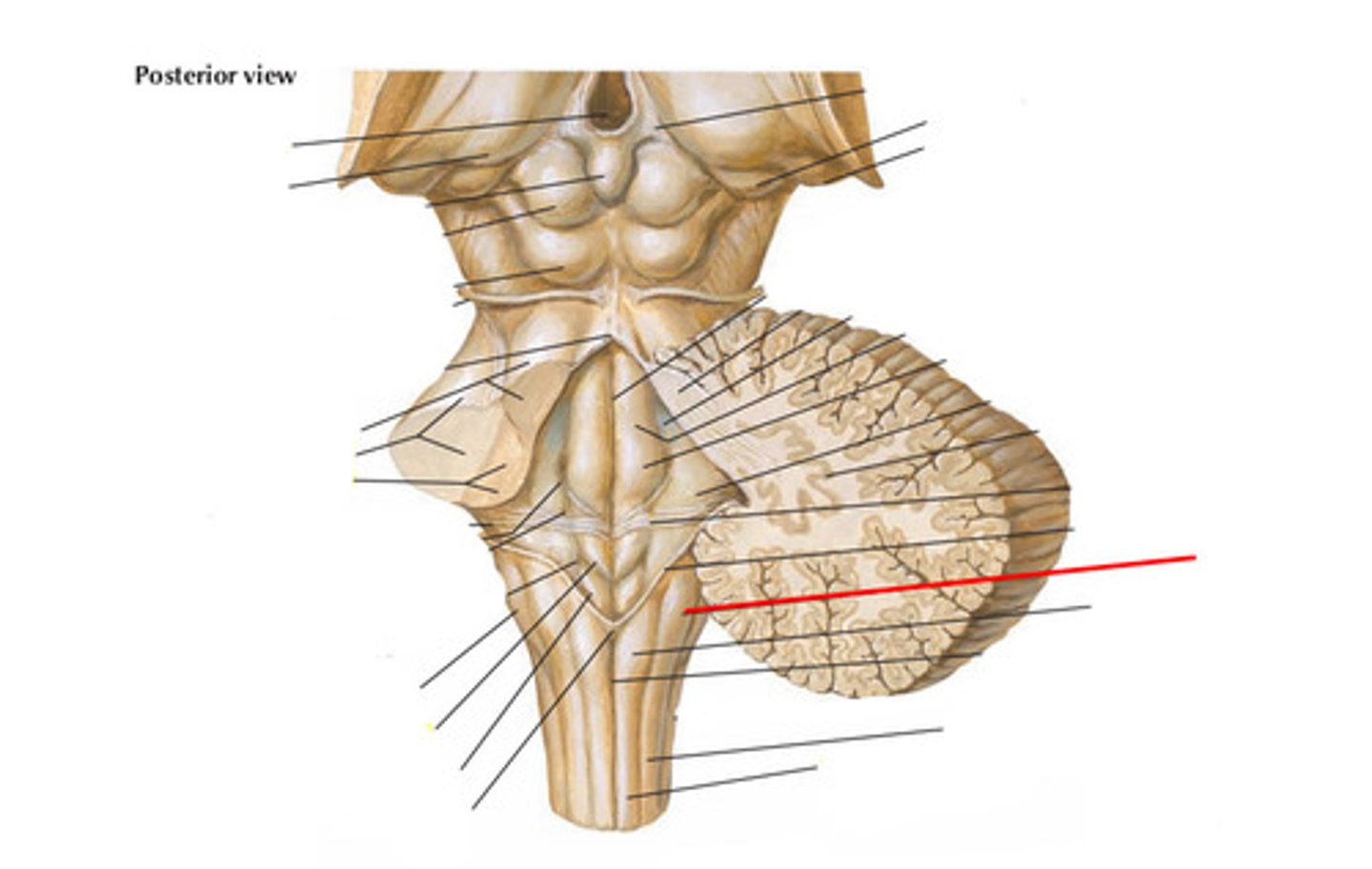
Cuneate fasciculus
Trigeminal tubercle
Lateral funiculus
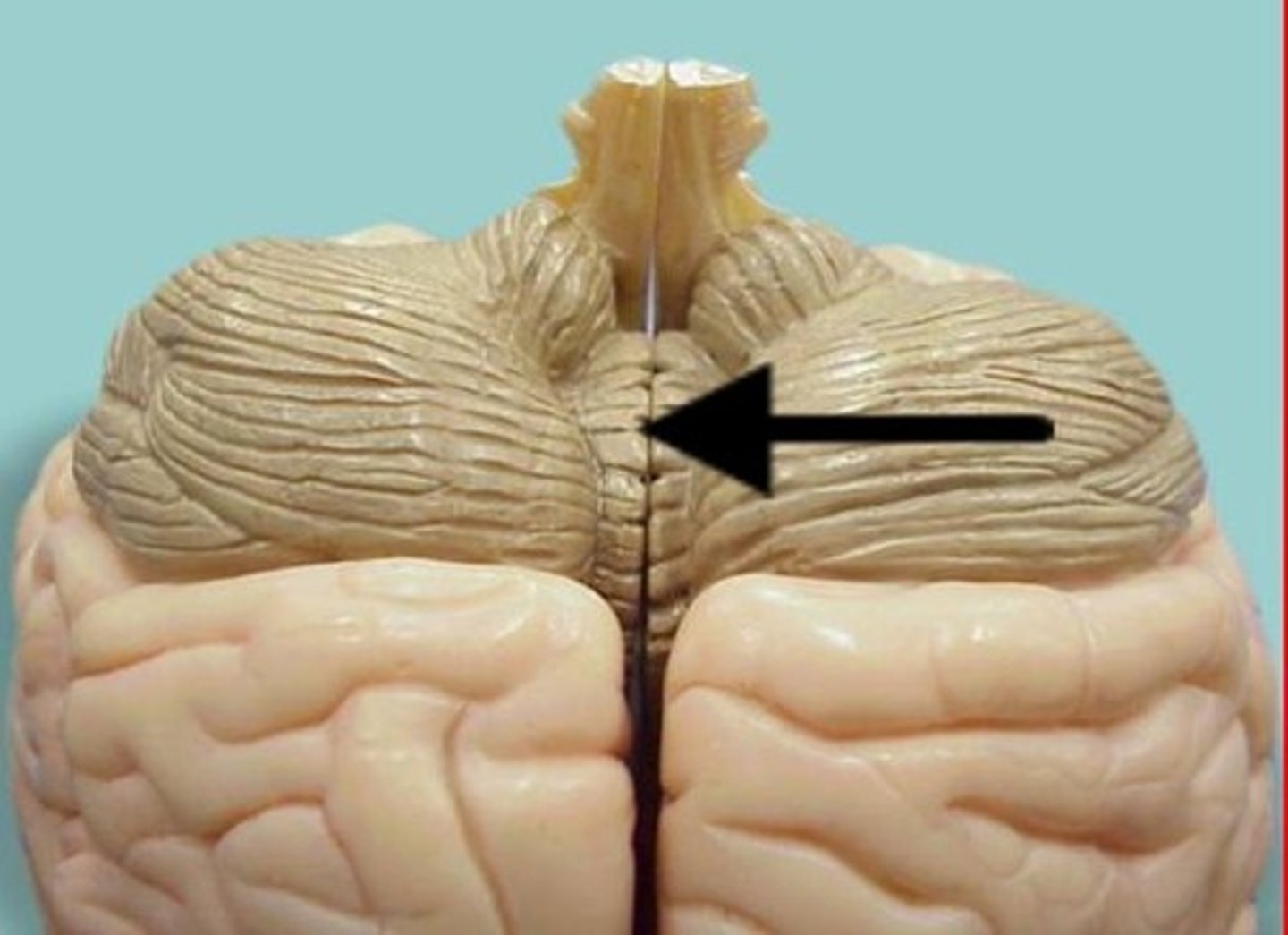
Habenular trigone
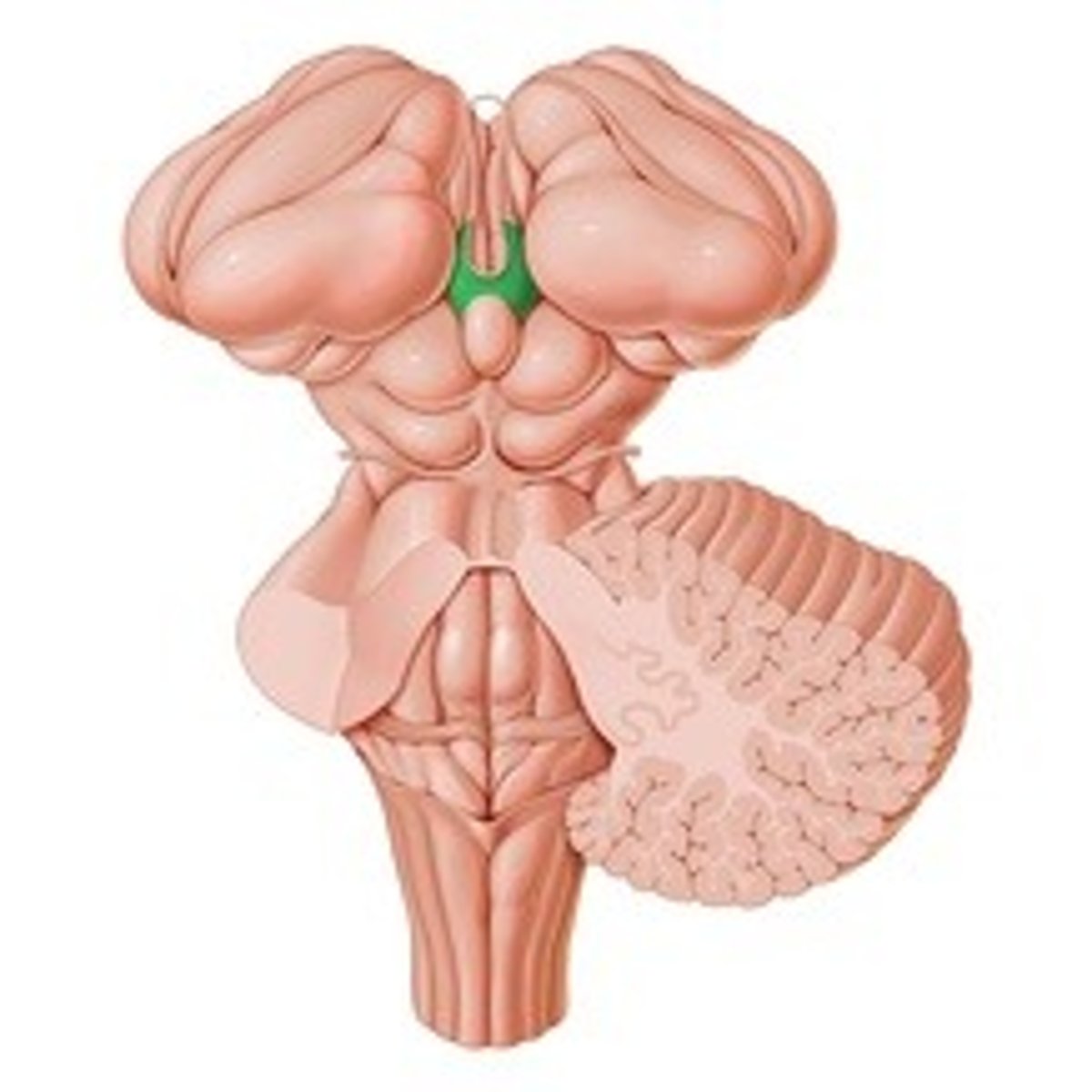
Pineal gland
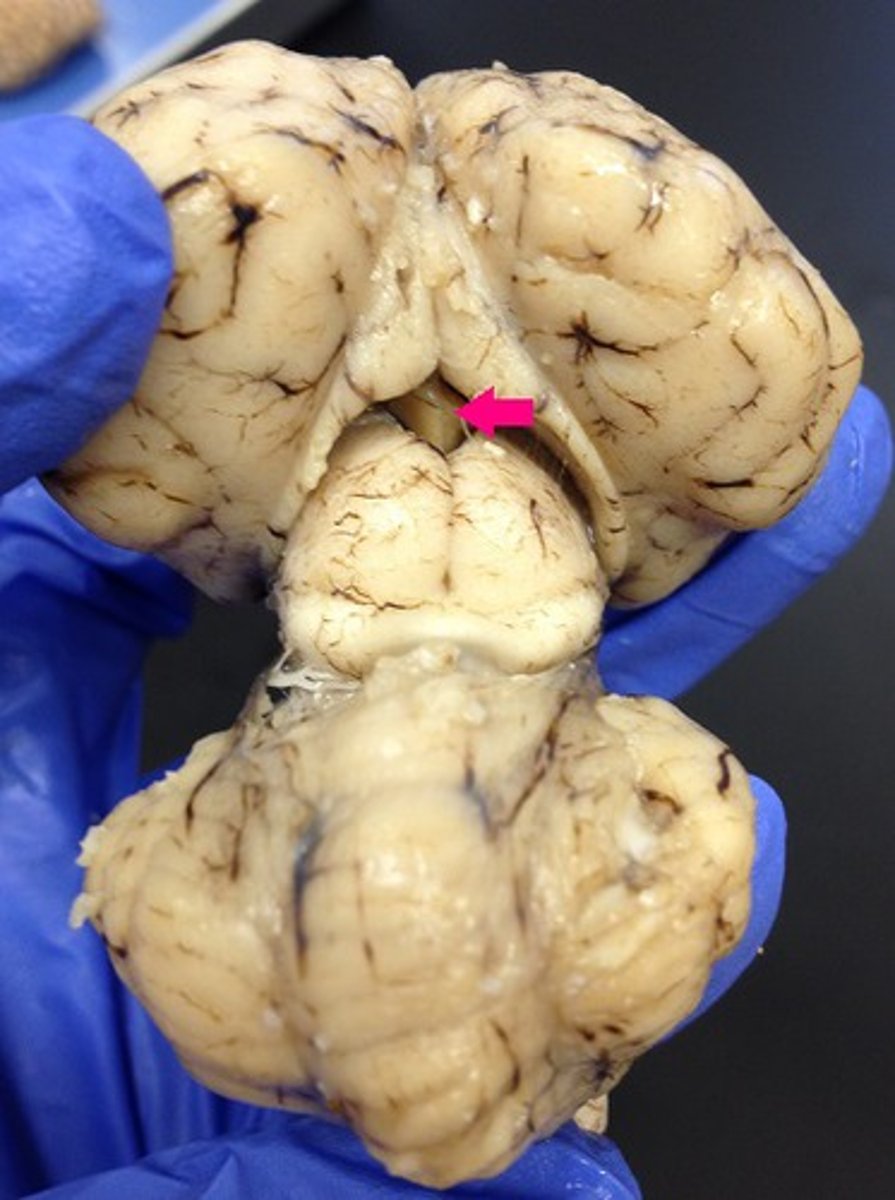
Release melatonin
Function of the pineal gland
The cerebellum is a part of the motor system
- cannot initiate conscious movements by itself, but is responsible for unconscious coordination and fine control of the muscle actions
Functions of the cerebellum?
- Cerebellar hemispheres
- Vermis
What does the cerebellum consist of?
Each hemisphere consist of three lobes:
- Anterior lobe
- Posterior lobe
- Flocculonodular lobe
What does each hemisphere consist of?
Vermis
Through the superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles
Through what is the cerebellum in contact with the brainstem?
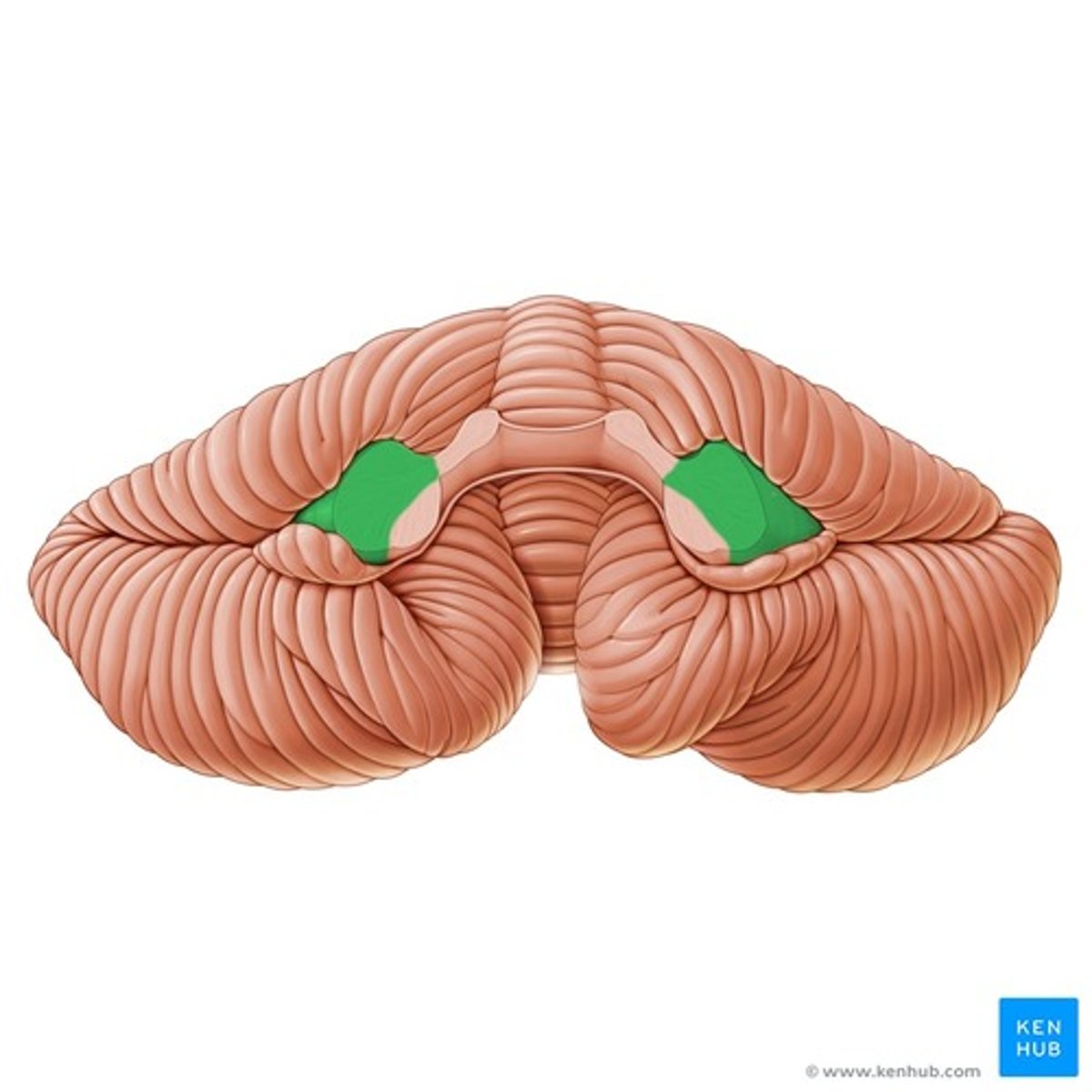
Superior cerebellar peduncle
A
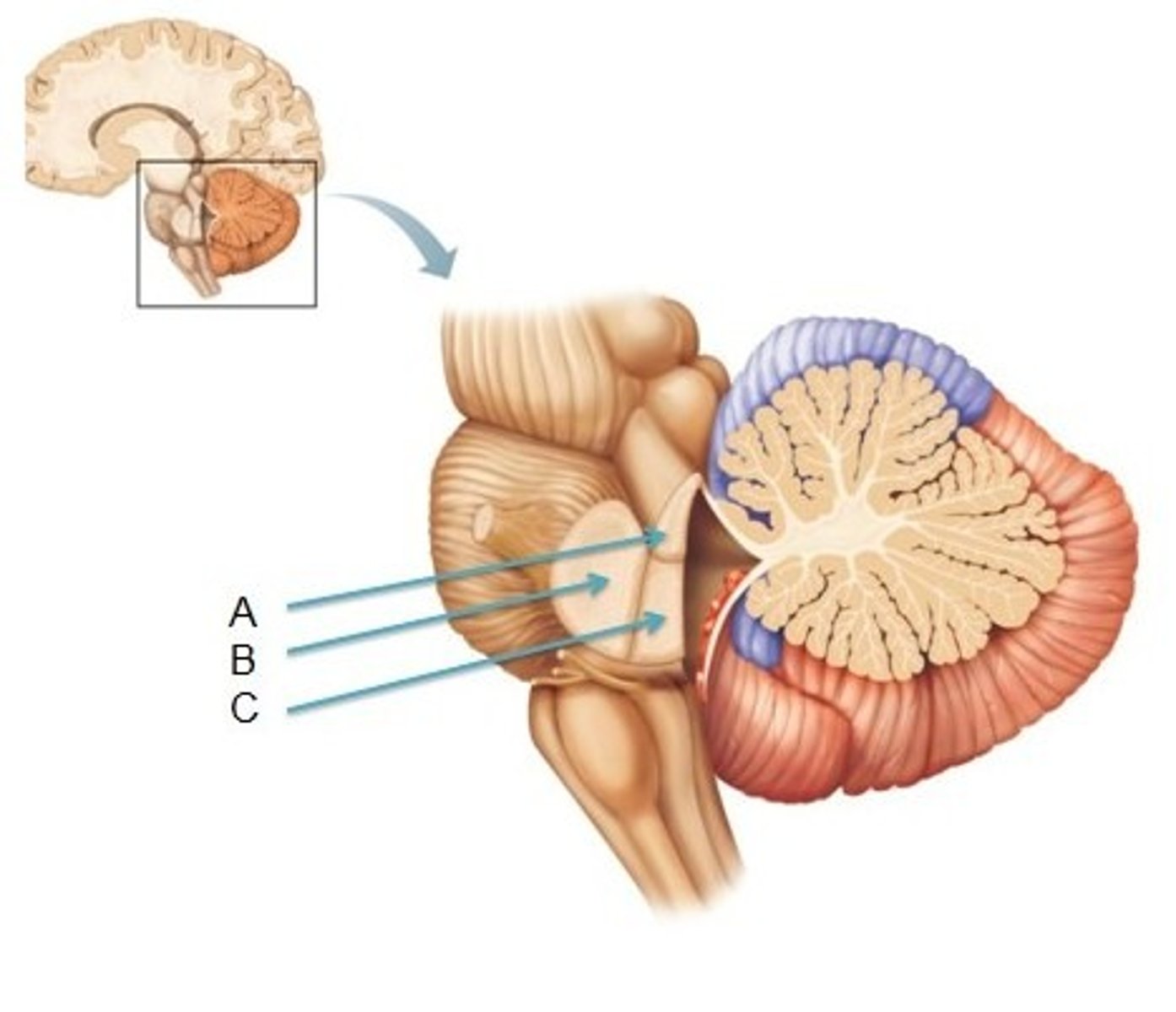
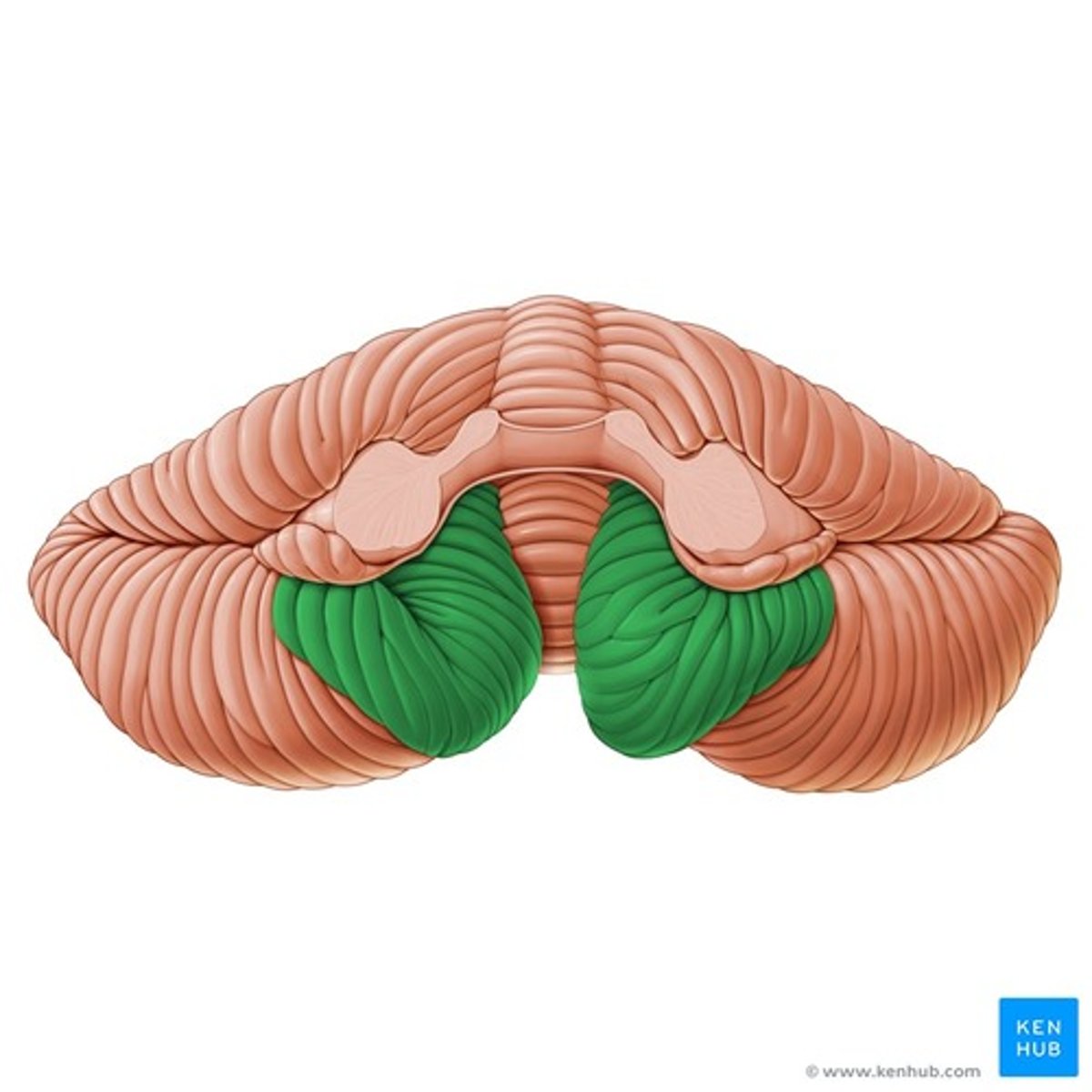
Middle cerebellar peduncle
B
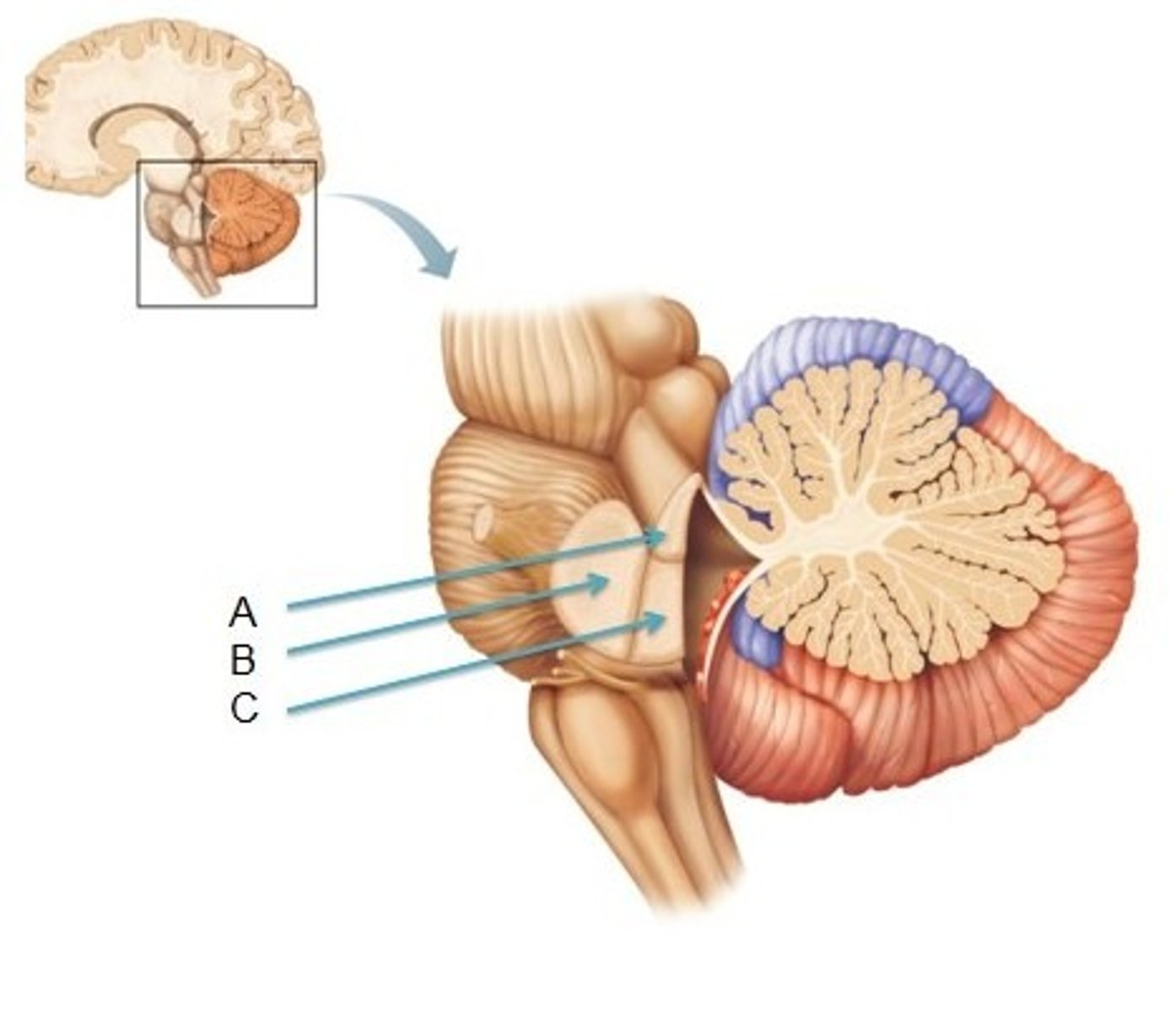
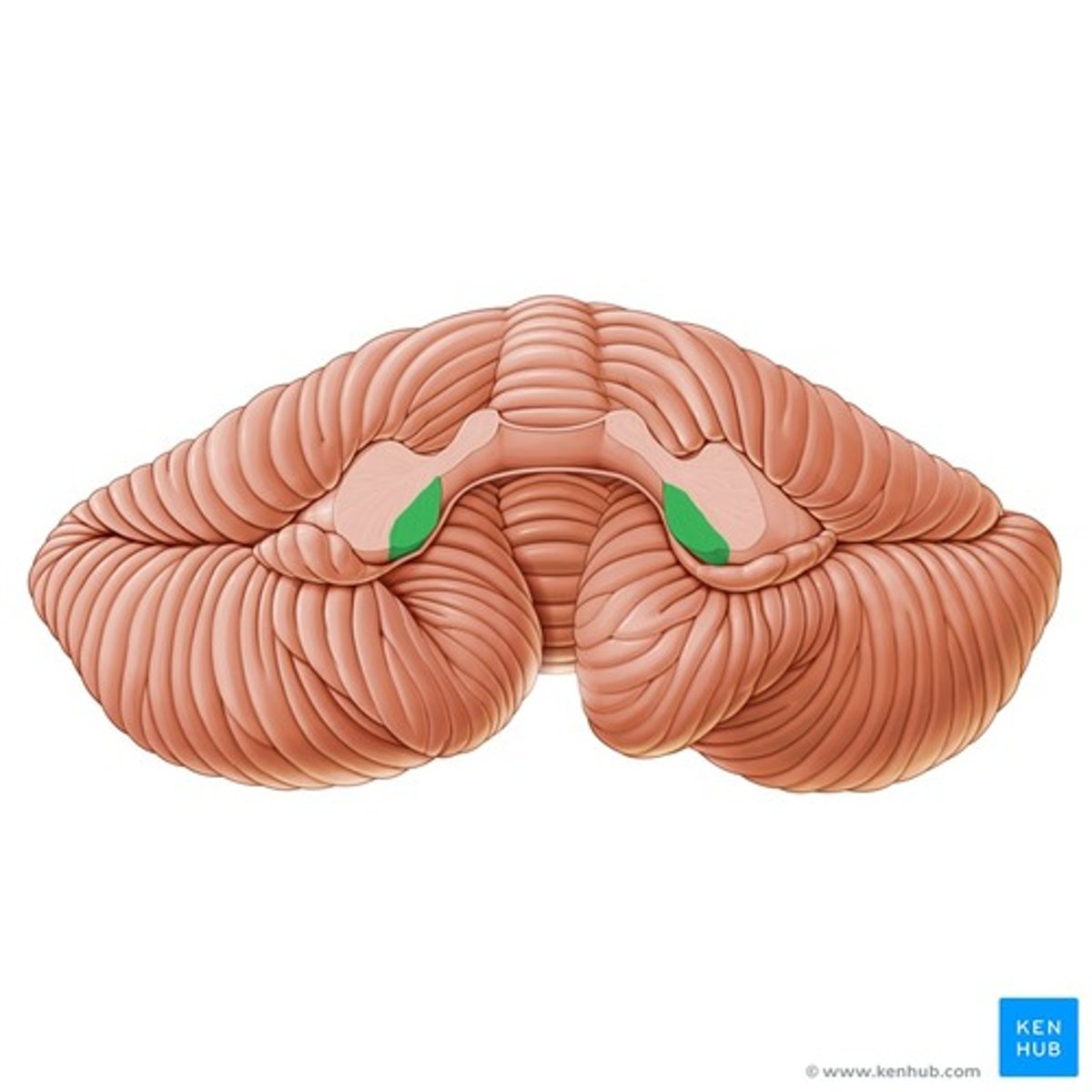
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
C
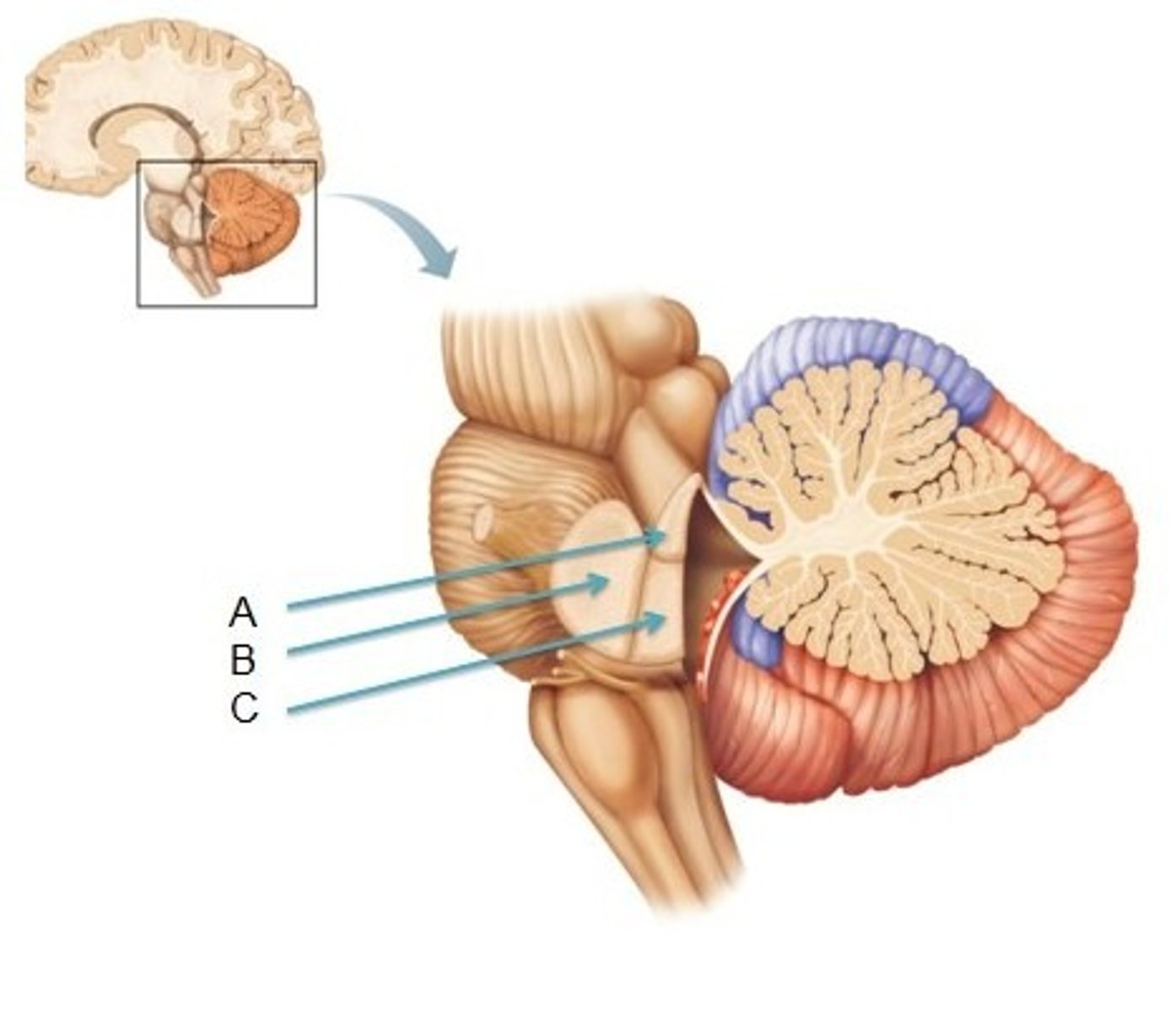
Connecting cerebellum and the brainstem and convey information
Function of the cerebellar peduncles?
Primarily efferent
Which way does the superior cerebellar peduncle convey information?
Primarily afferent
Which way does the inferior cerebellar peduncle convey information
Anterior lobe of the cerebellum
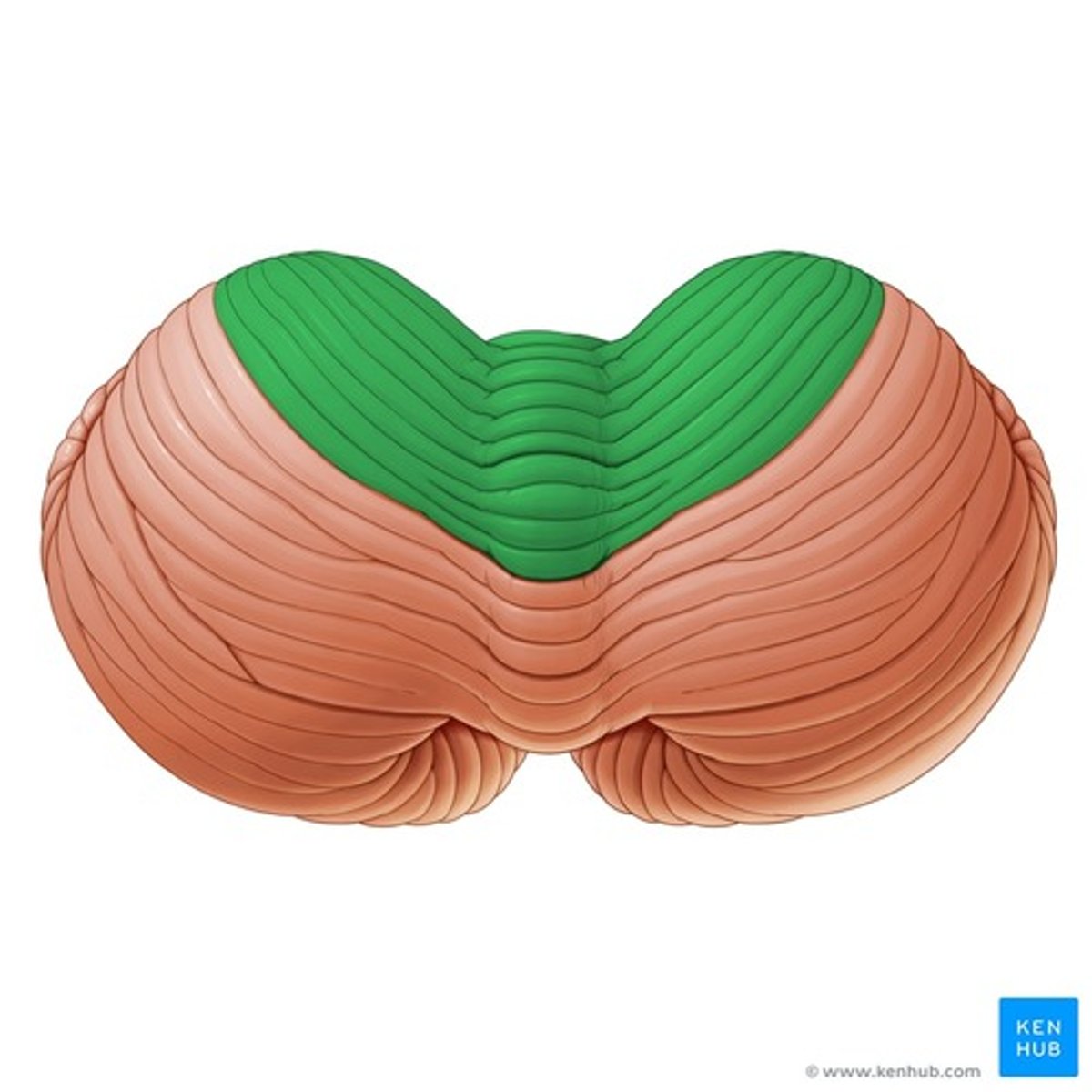
Flocconodular lobe
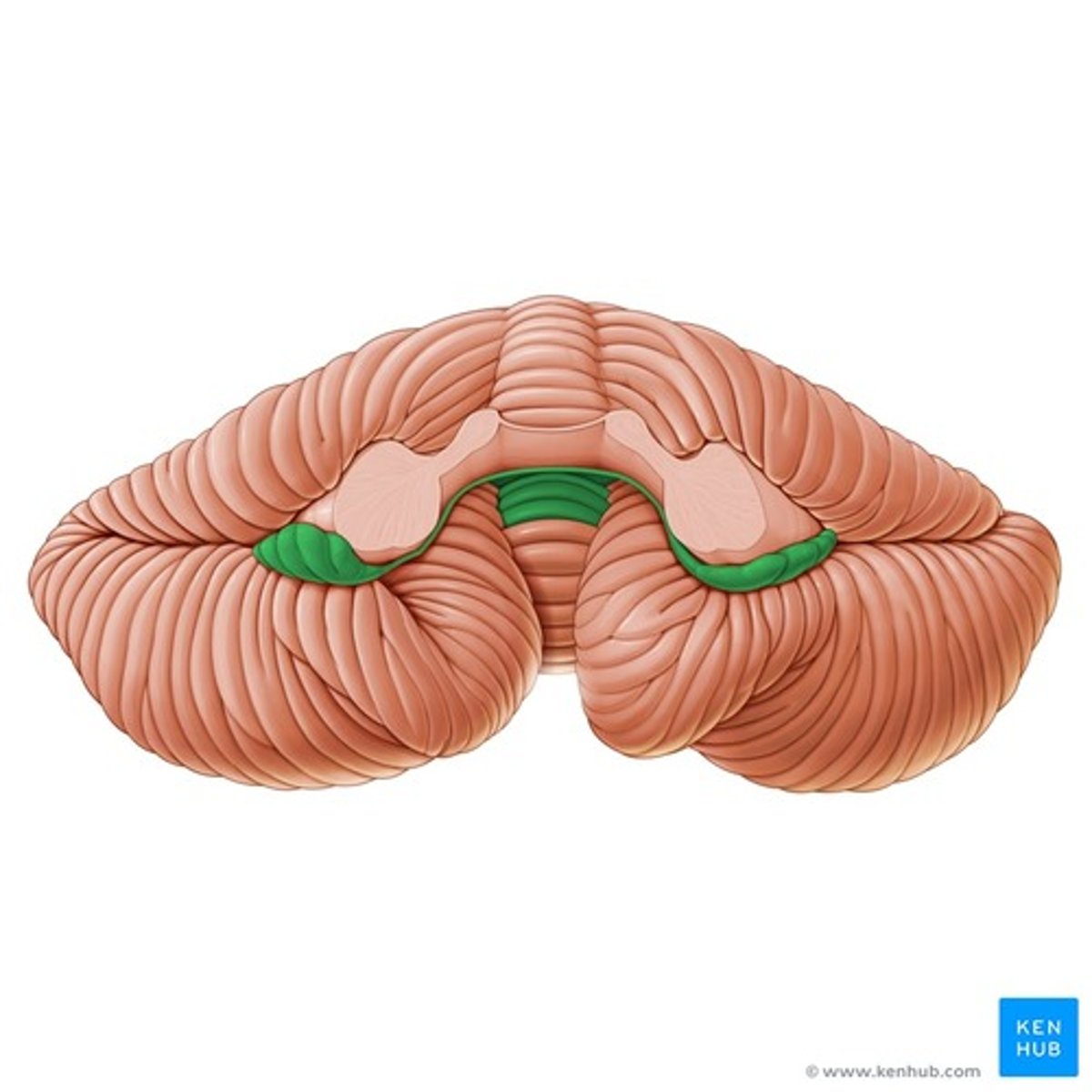

Superior cerebellar peduncle
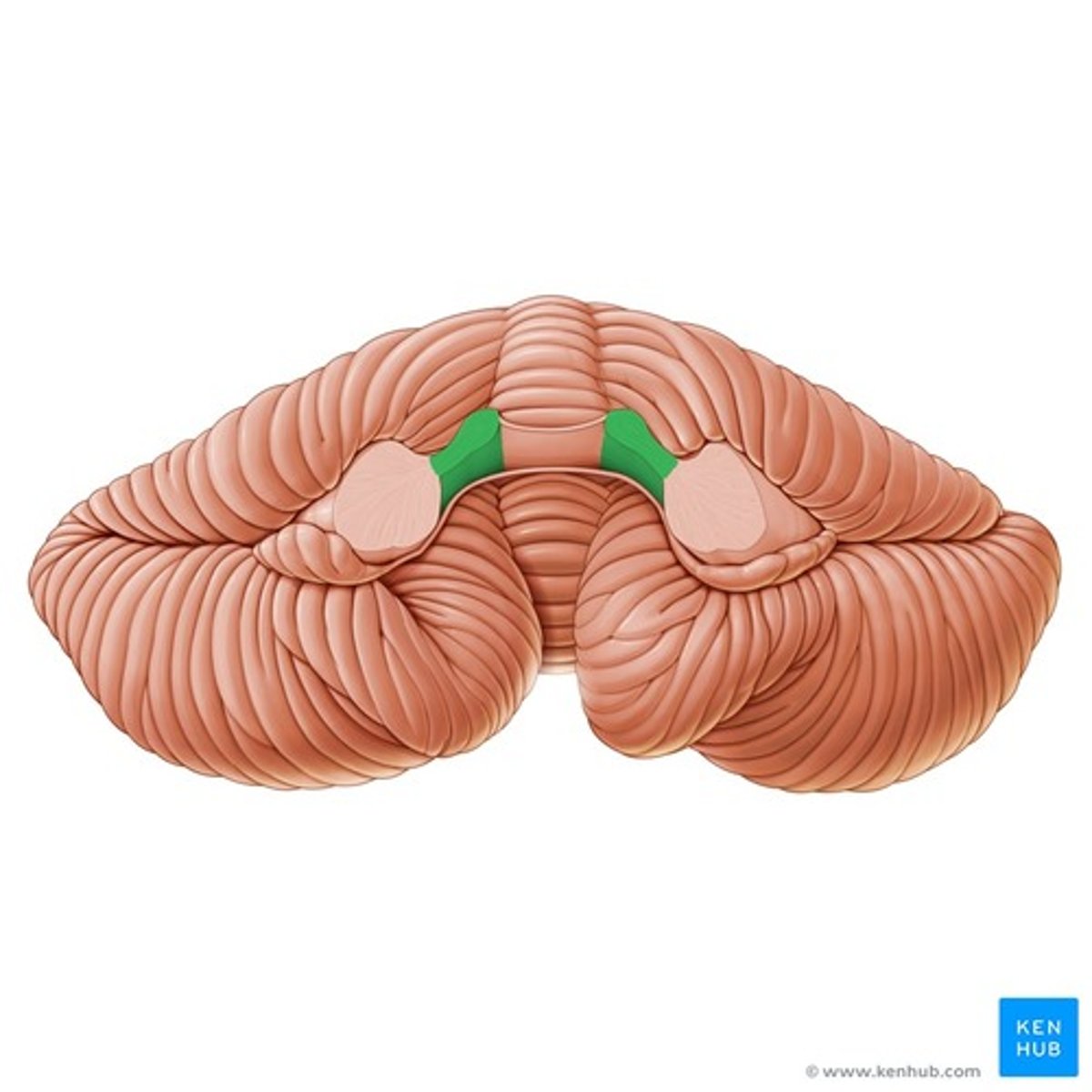

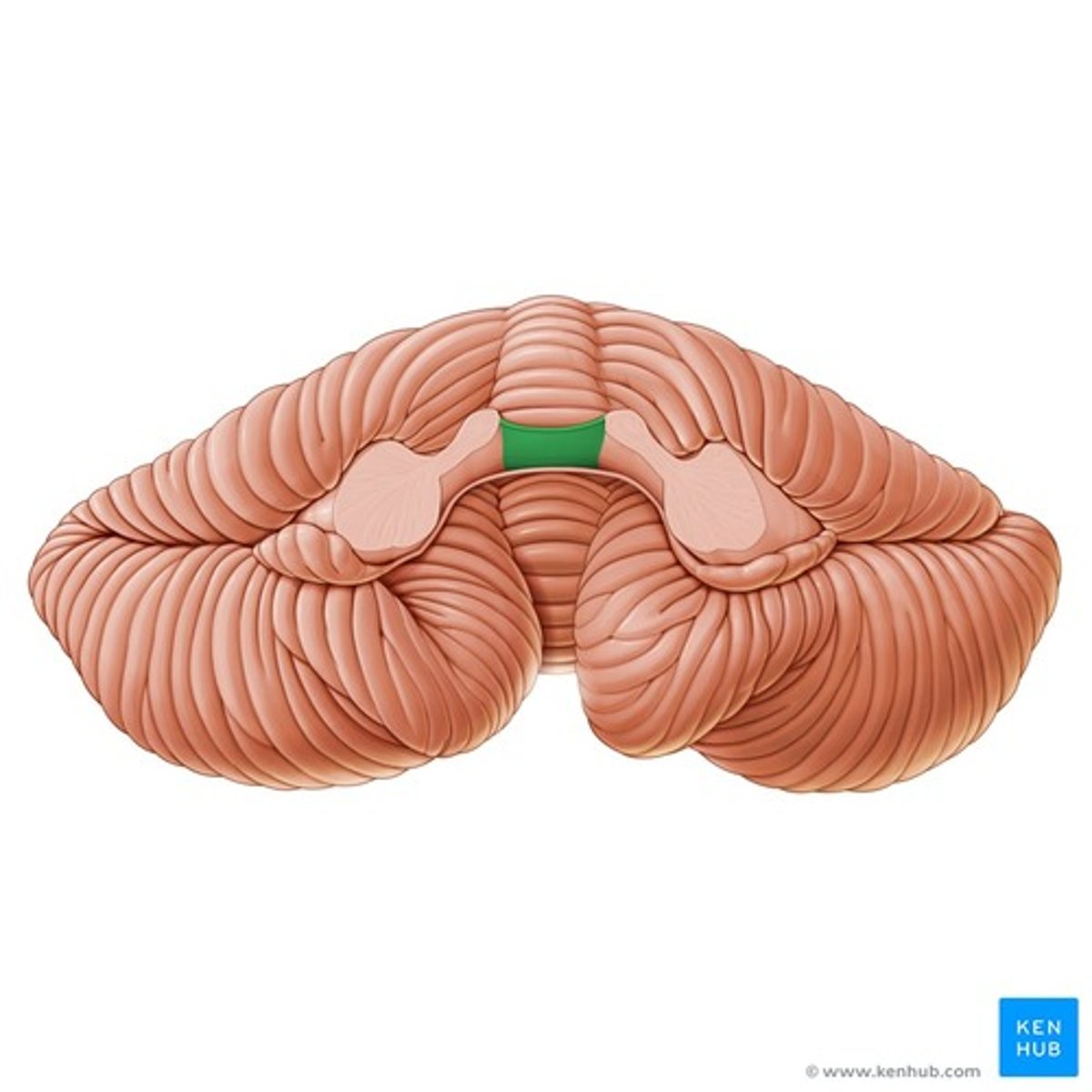
Superior medullary velum

Middle cerebellar peduncle

Cerebellar tonsil

Inferior cerebellar peduncles

Posterior lobe of the cerebellum
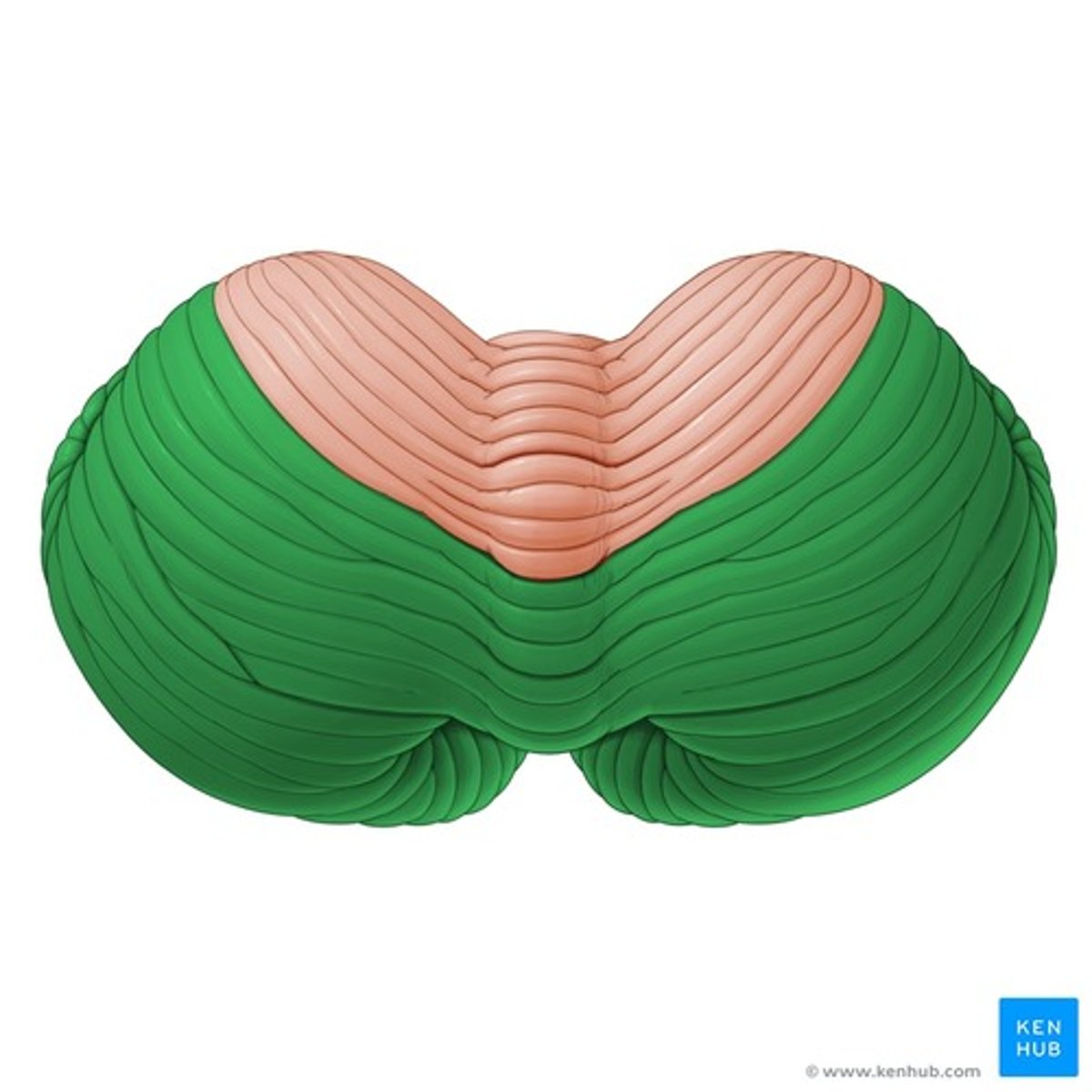
Inferior medullary velum
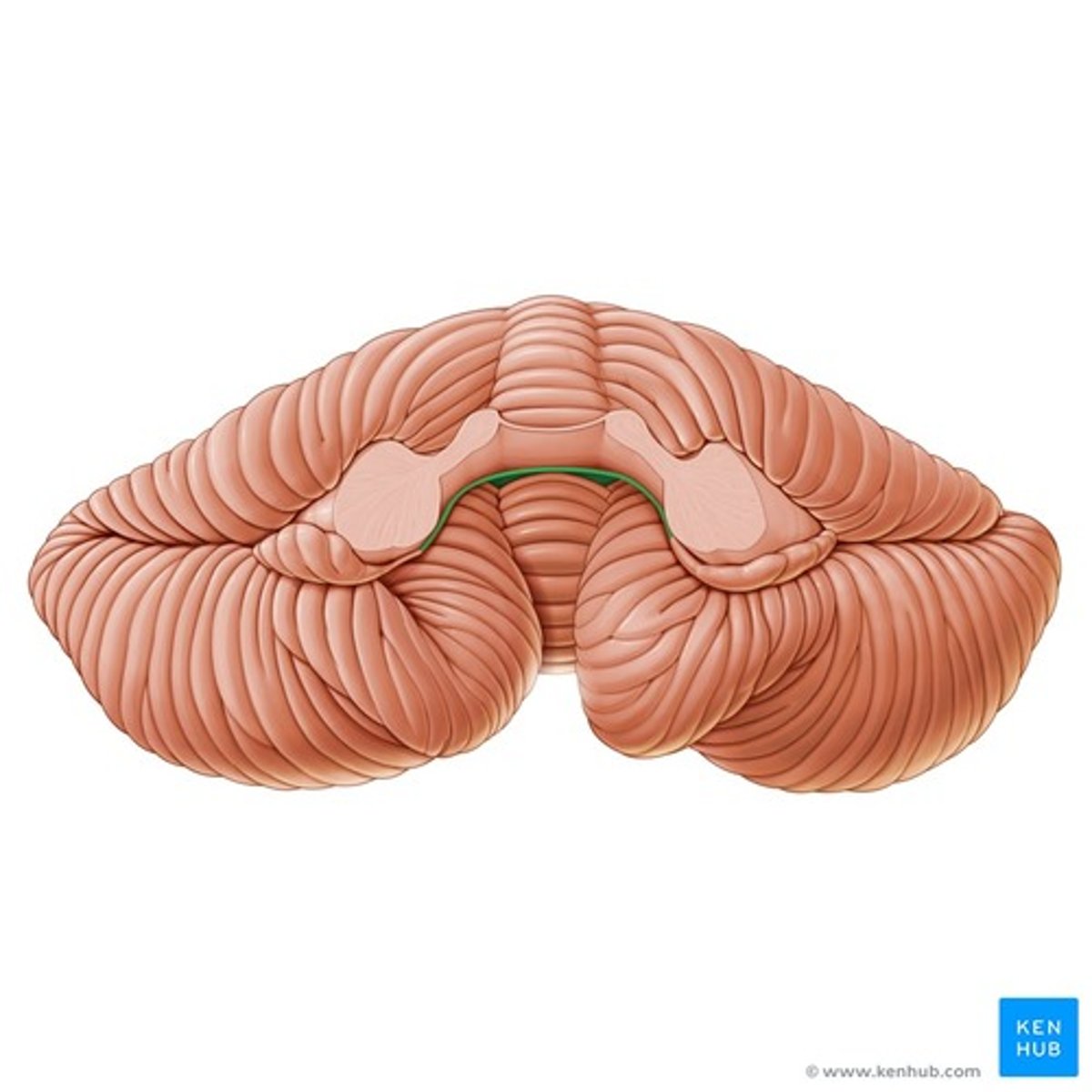

Fourth ventricle
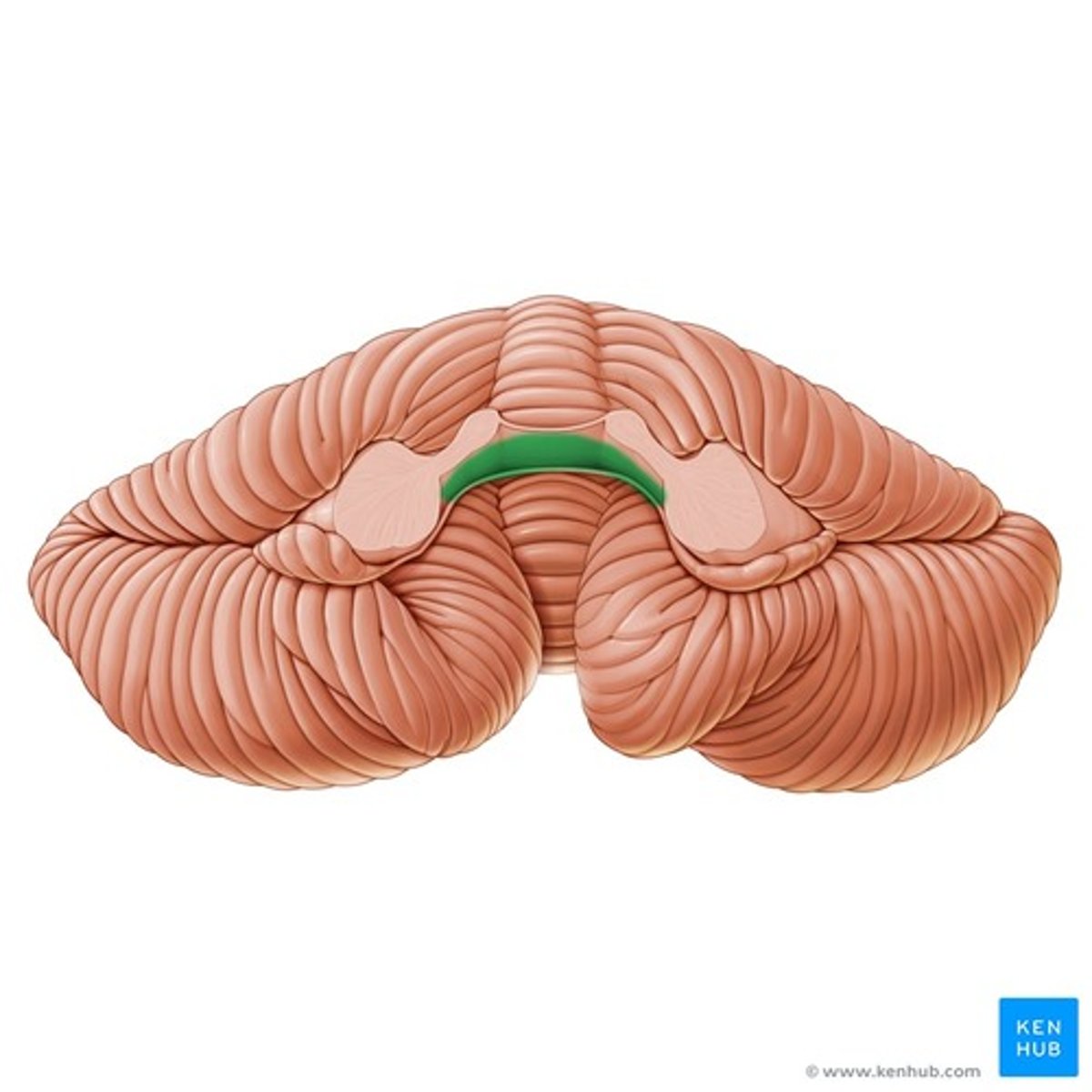

Floccular lobe
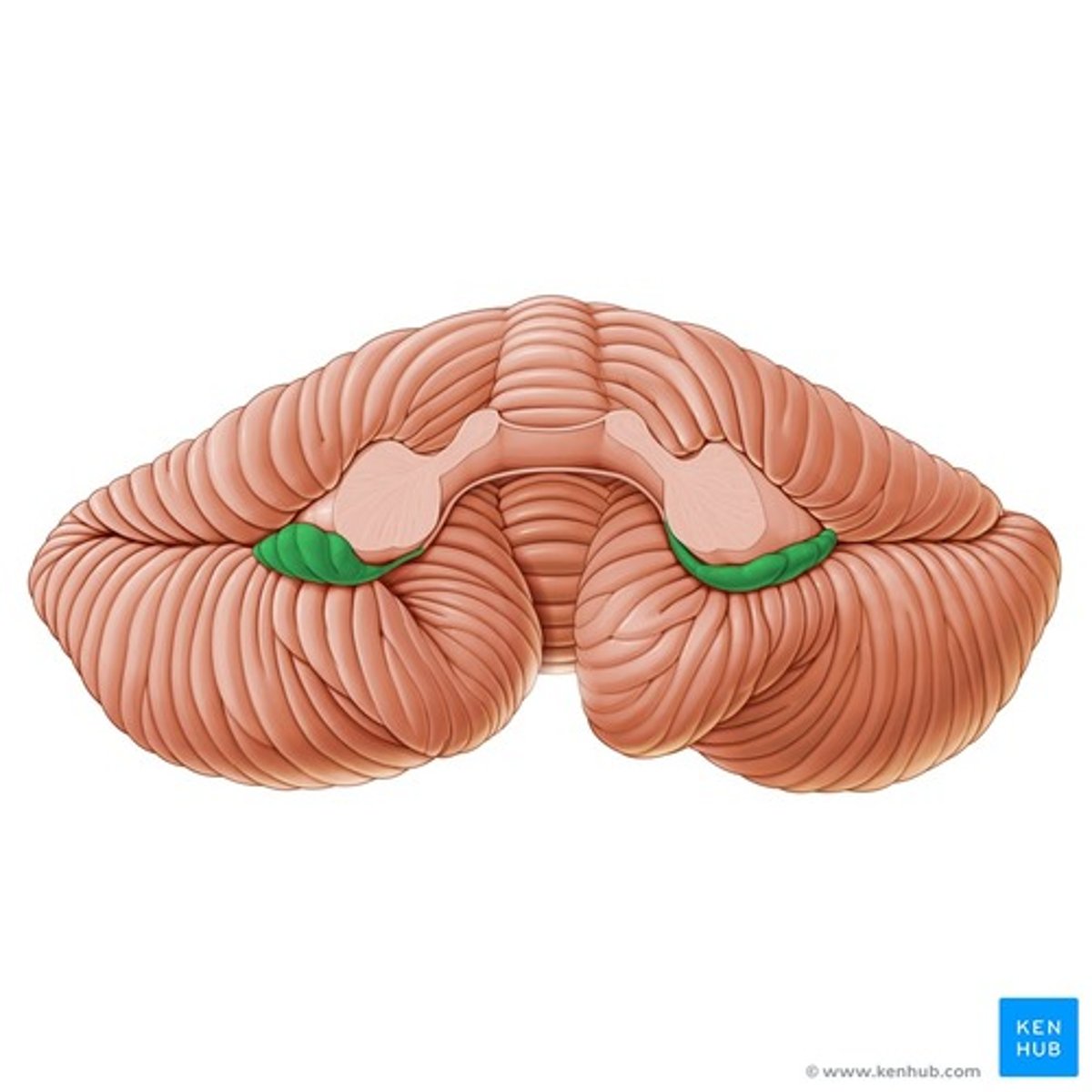

Vermis
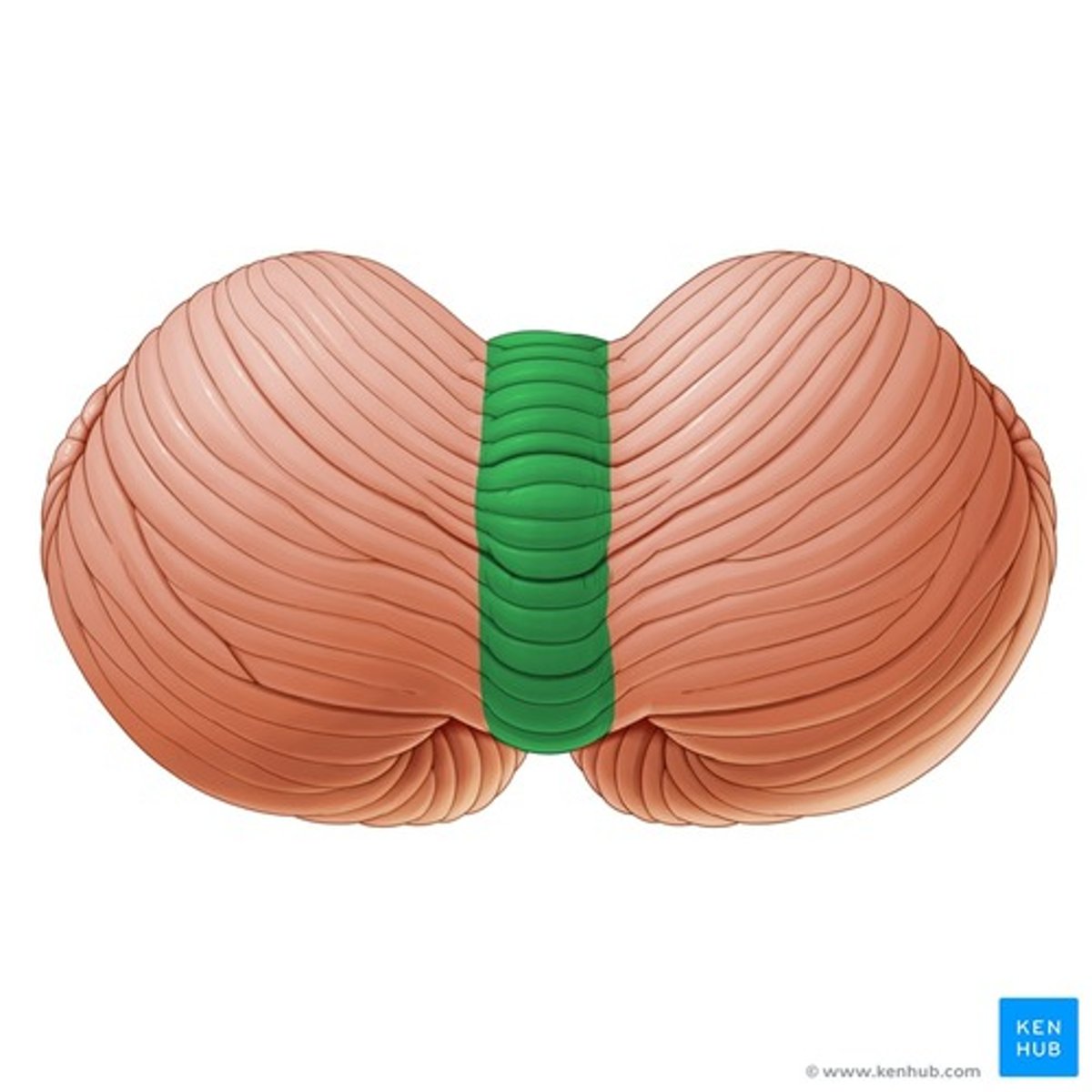
Nodule of vermis
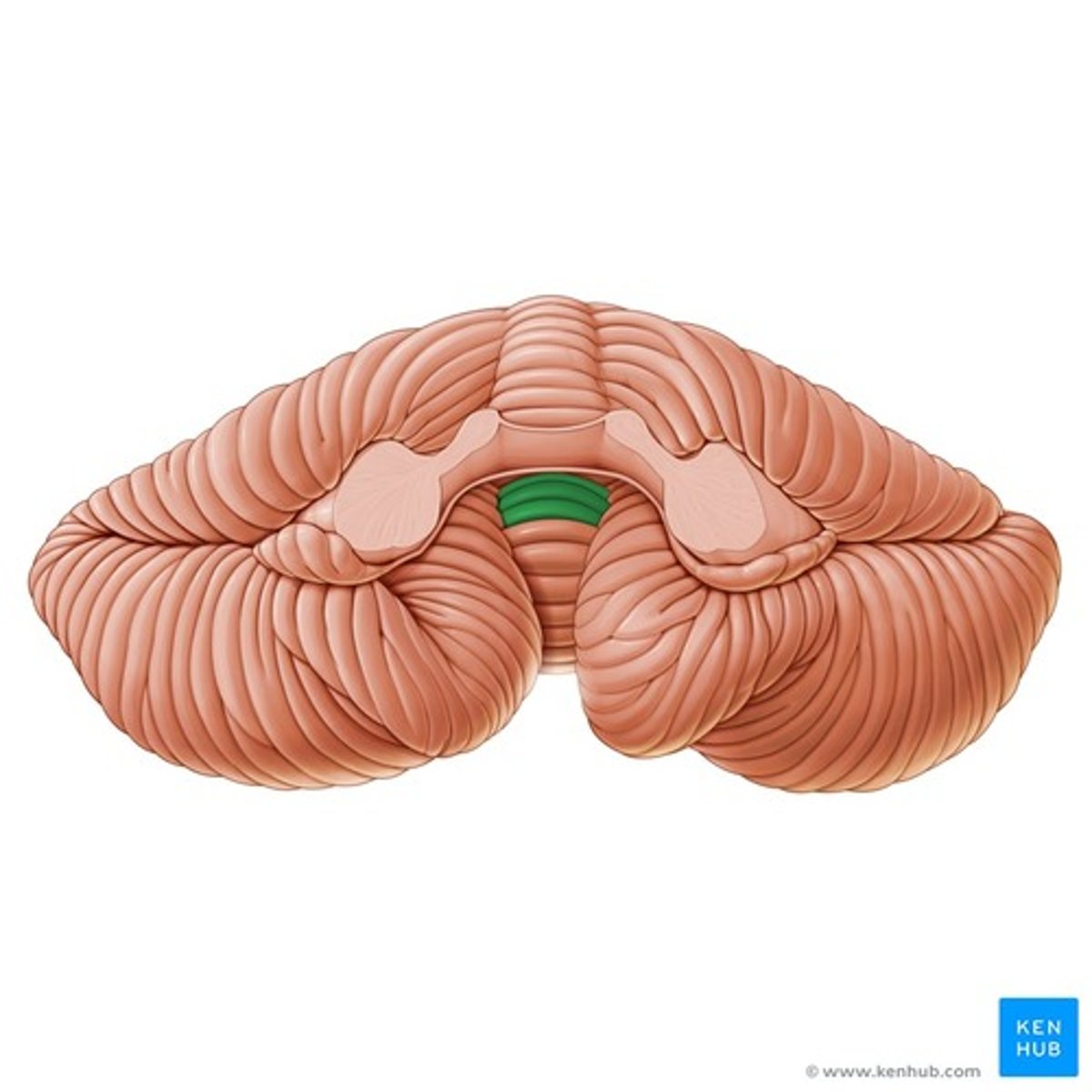

Pyramidal decussation
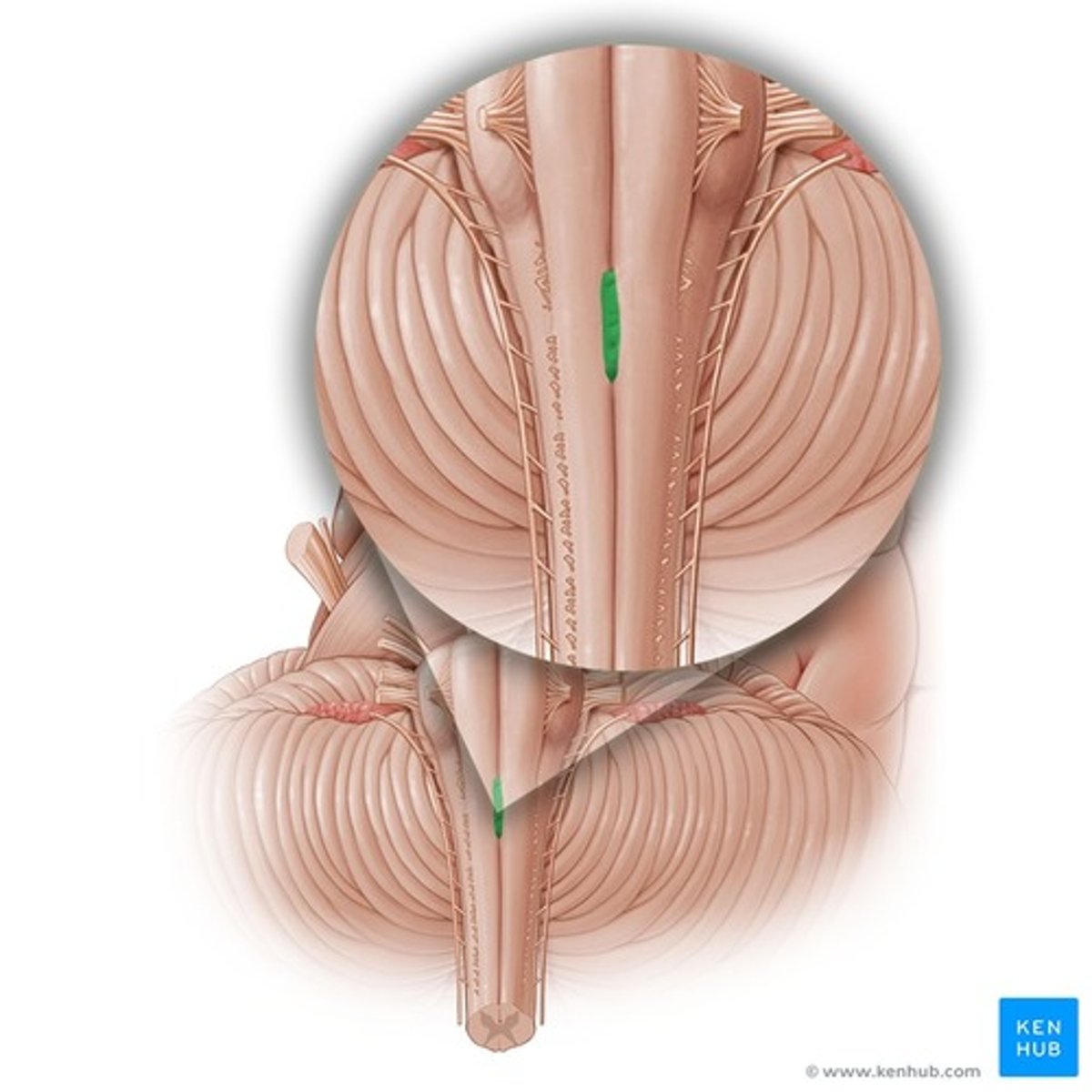
Accessory nerve
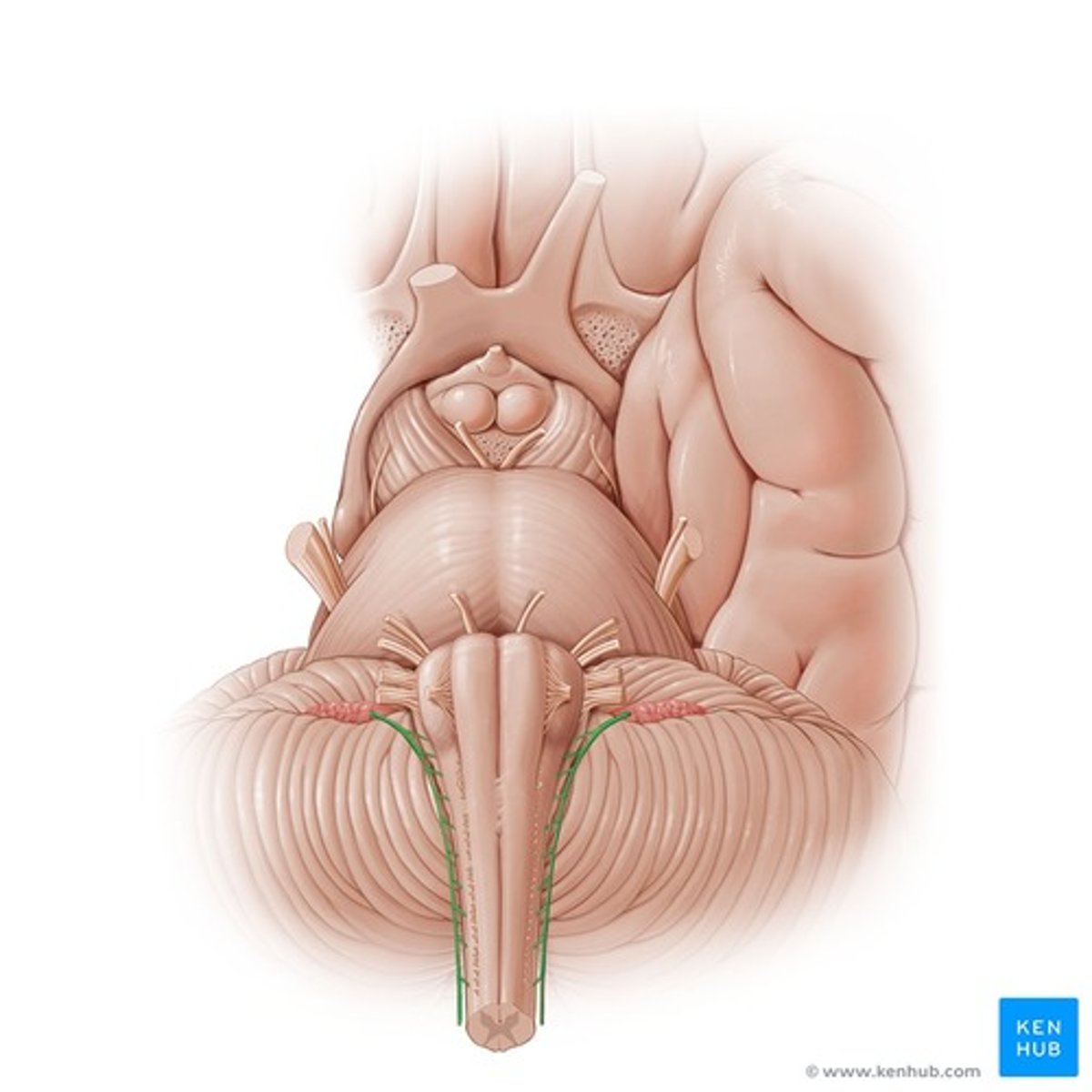
Choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle
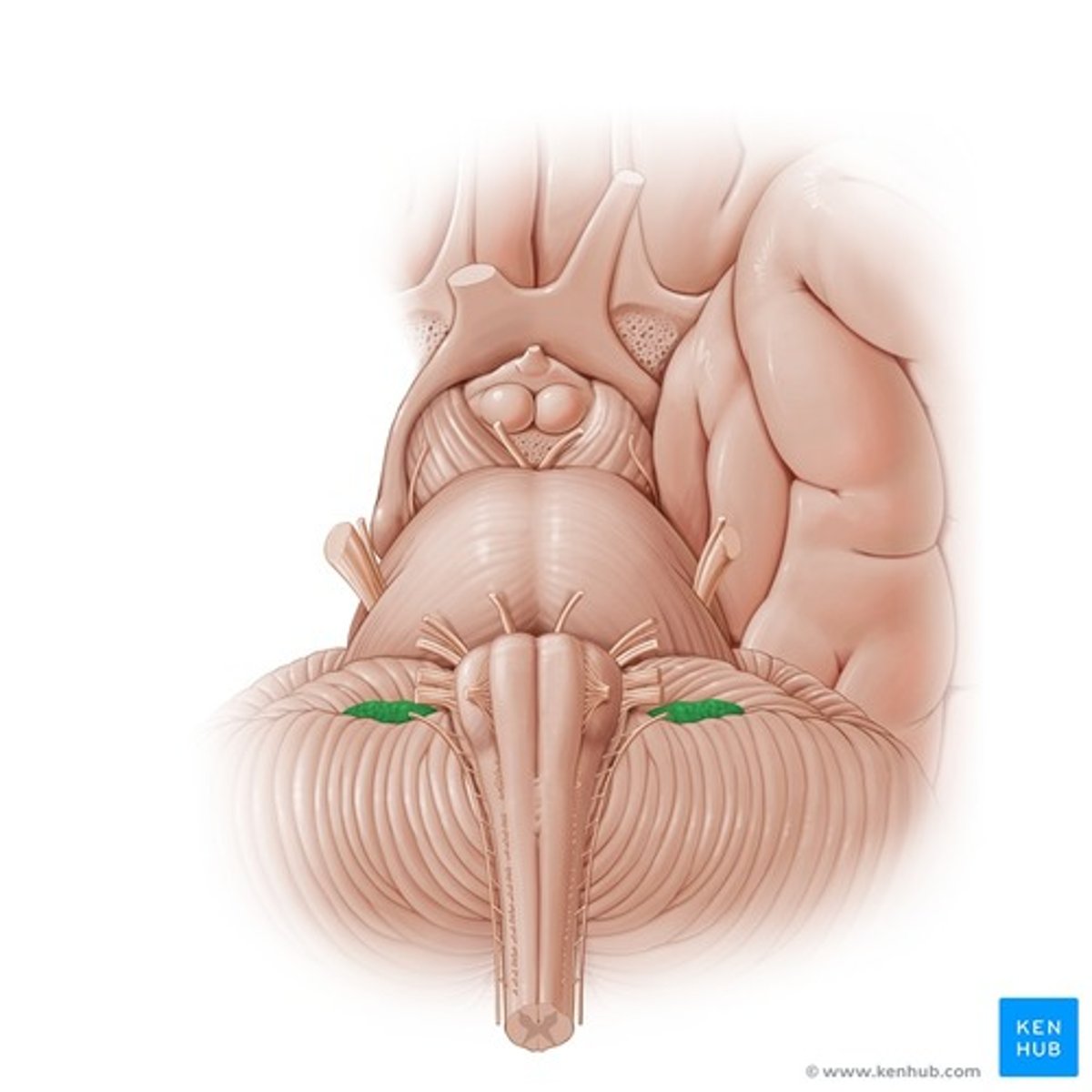
Flocculus
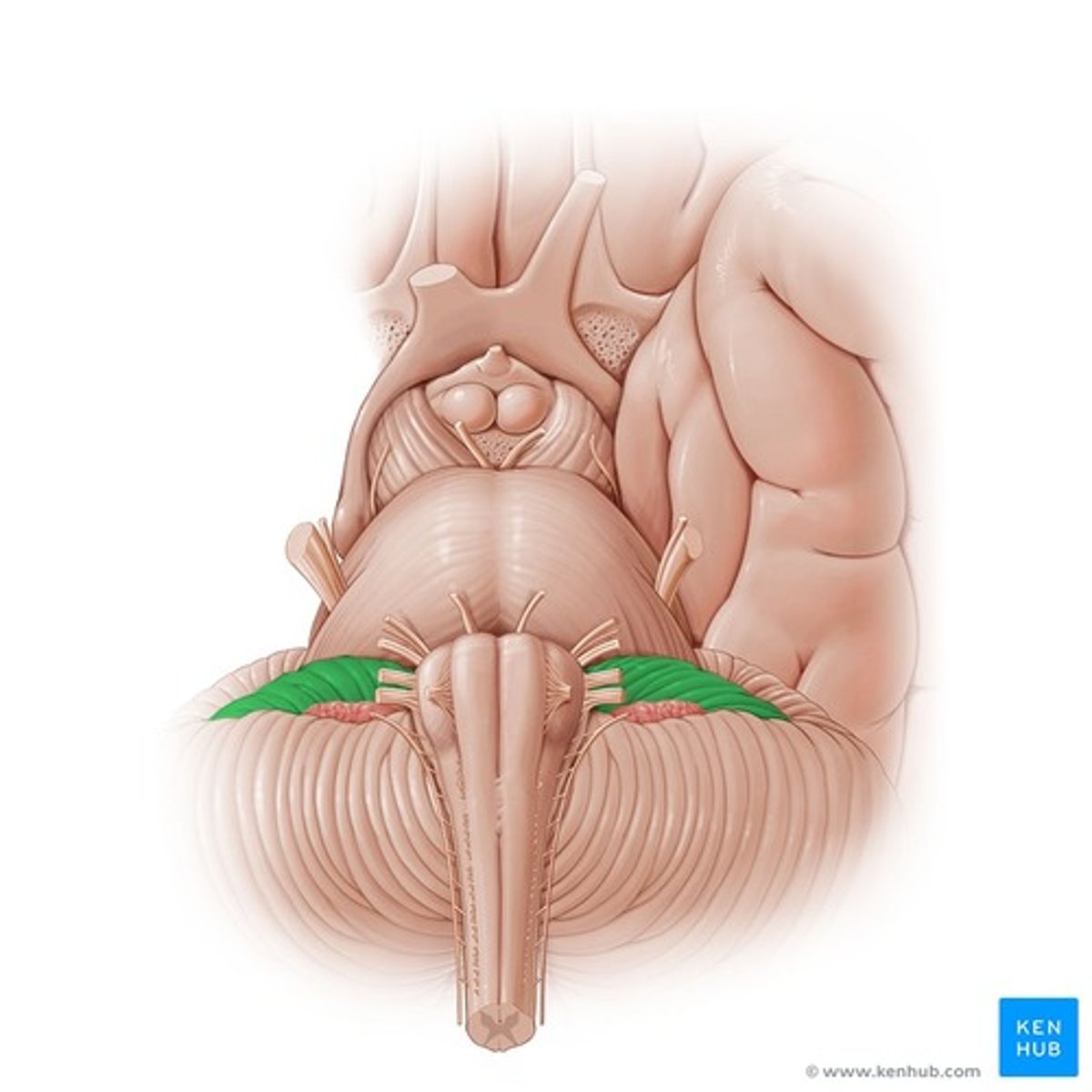
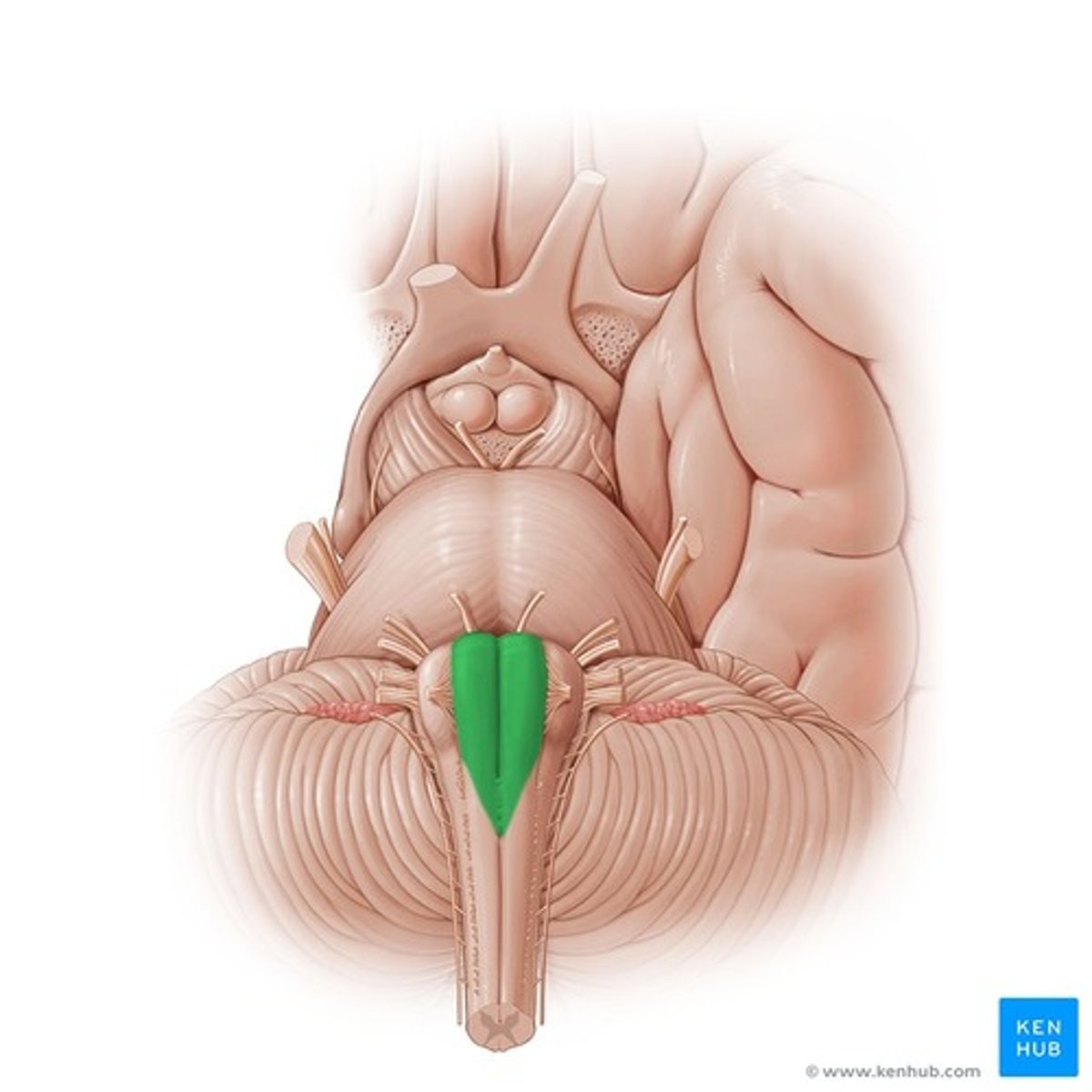
Medullary pyramids
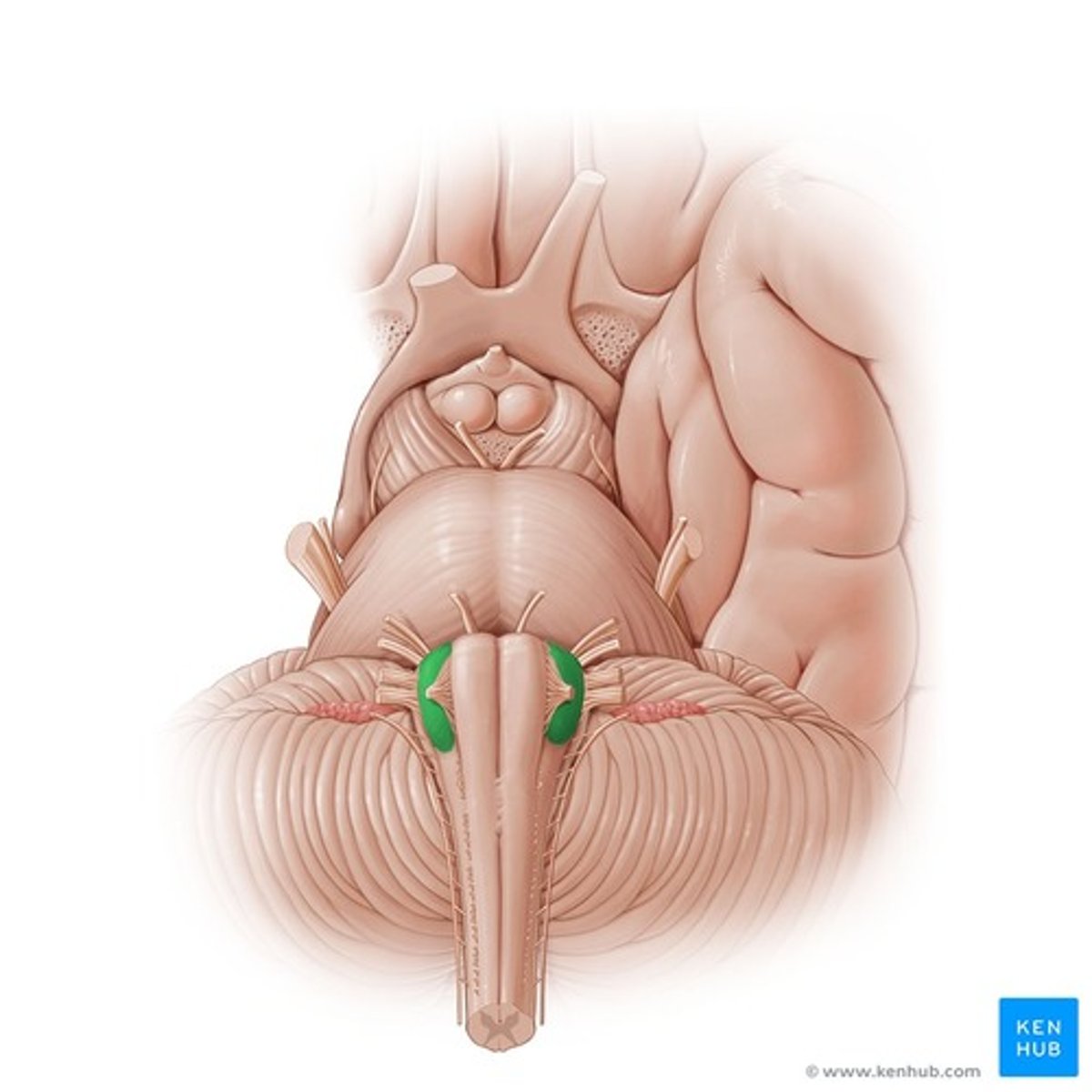
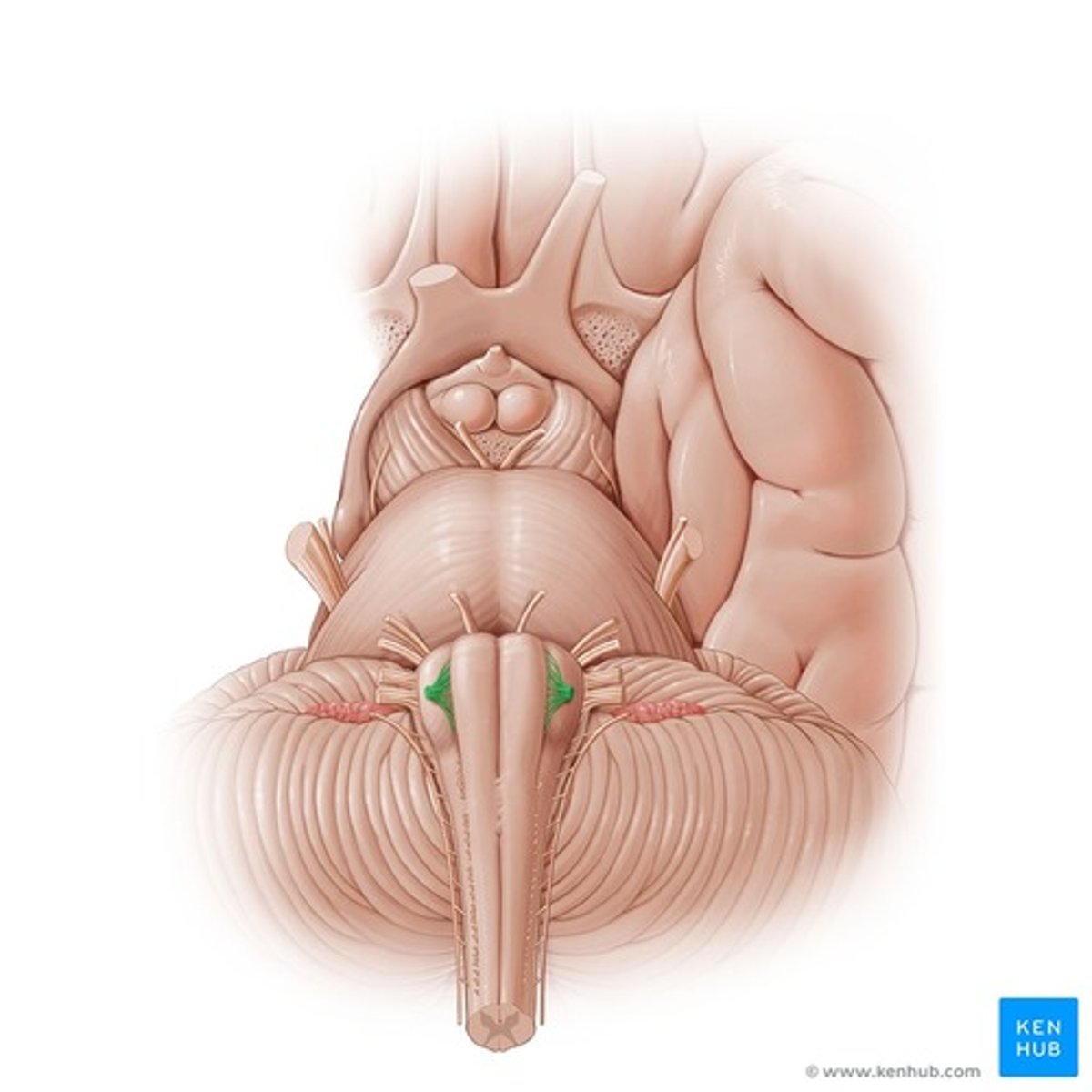
Olivary nuclei
Hypoglossal nerve
Vagus nerve
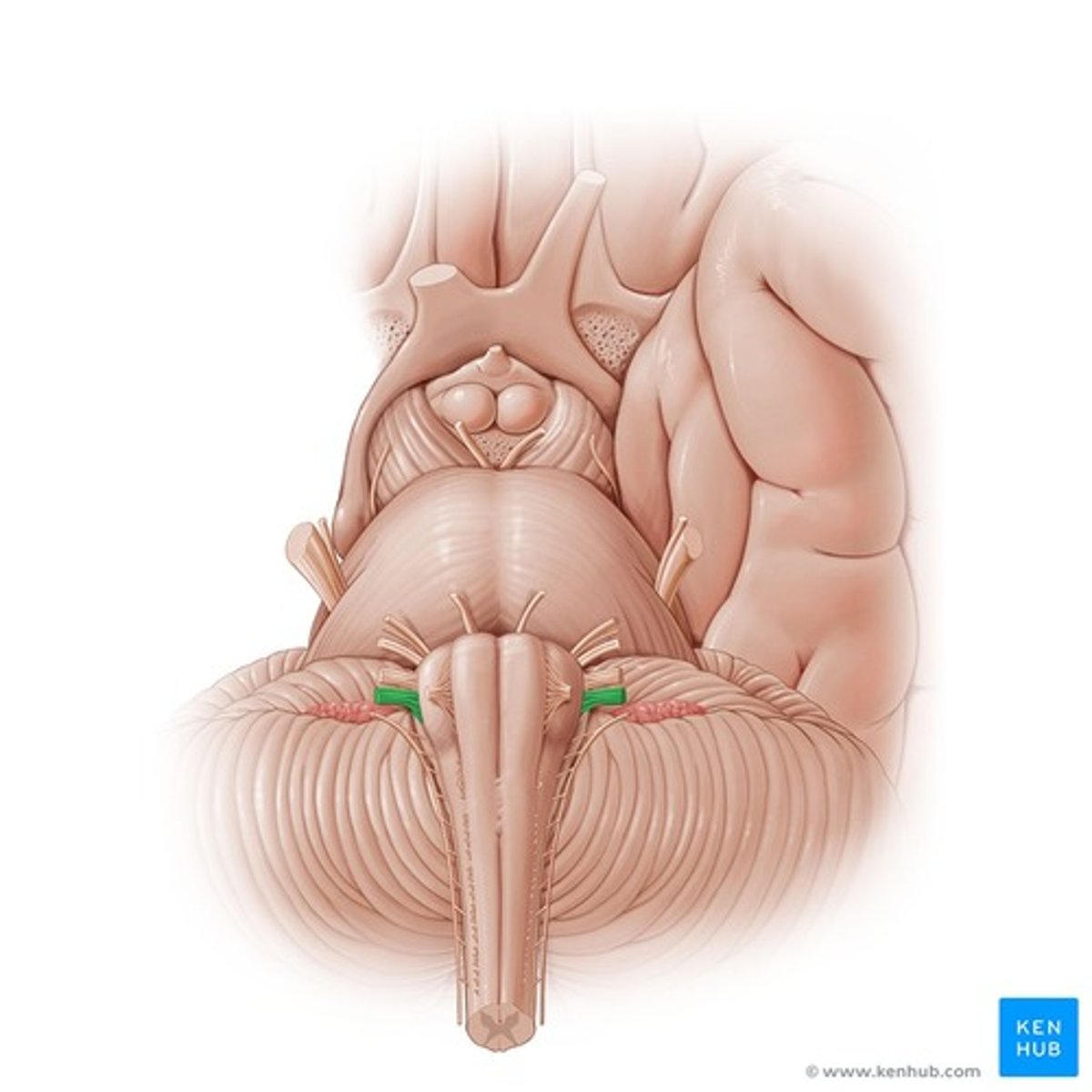
Glossopharyngeal nerve
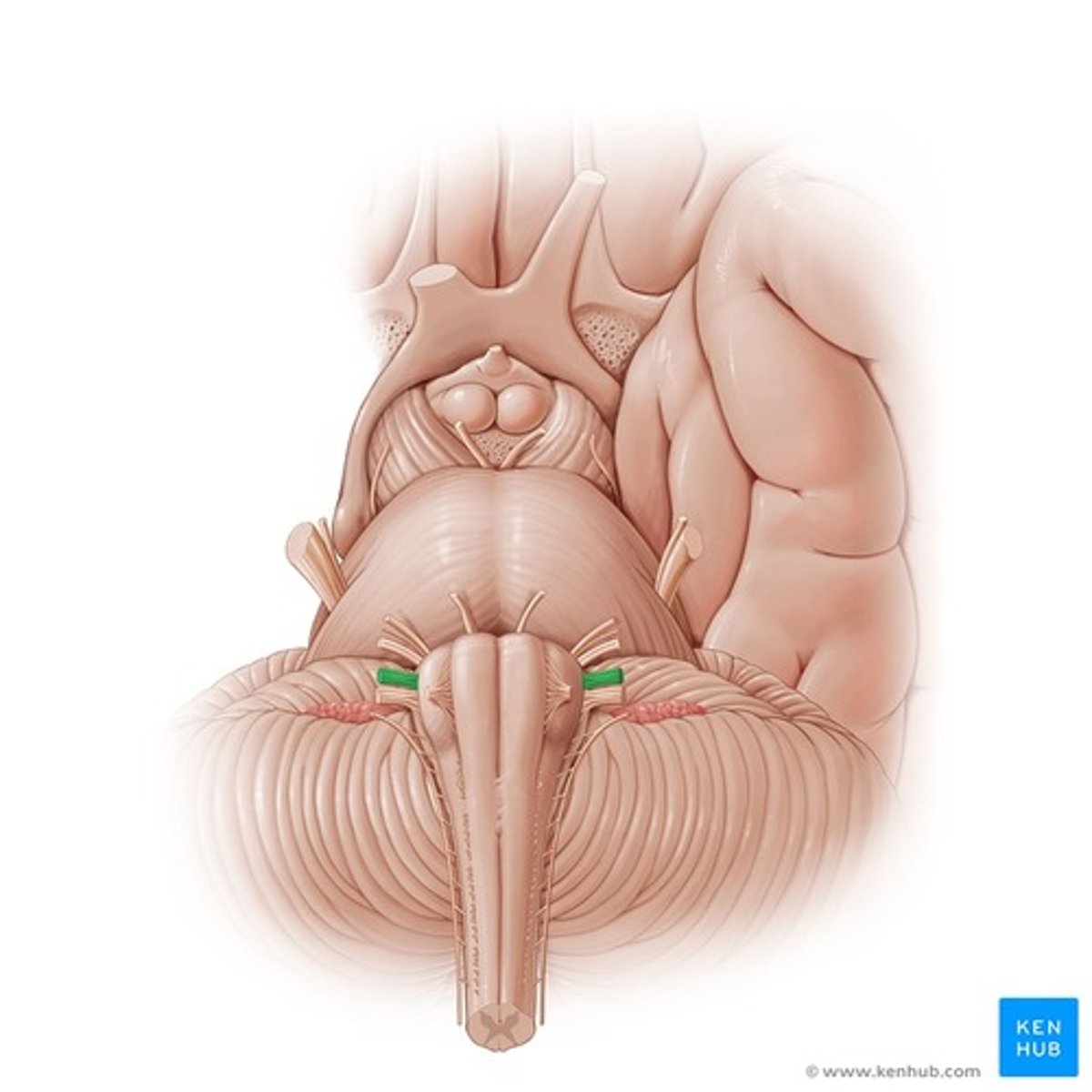
Vestibulocochlear nerve
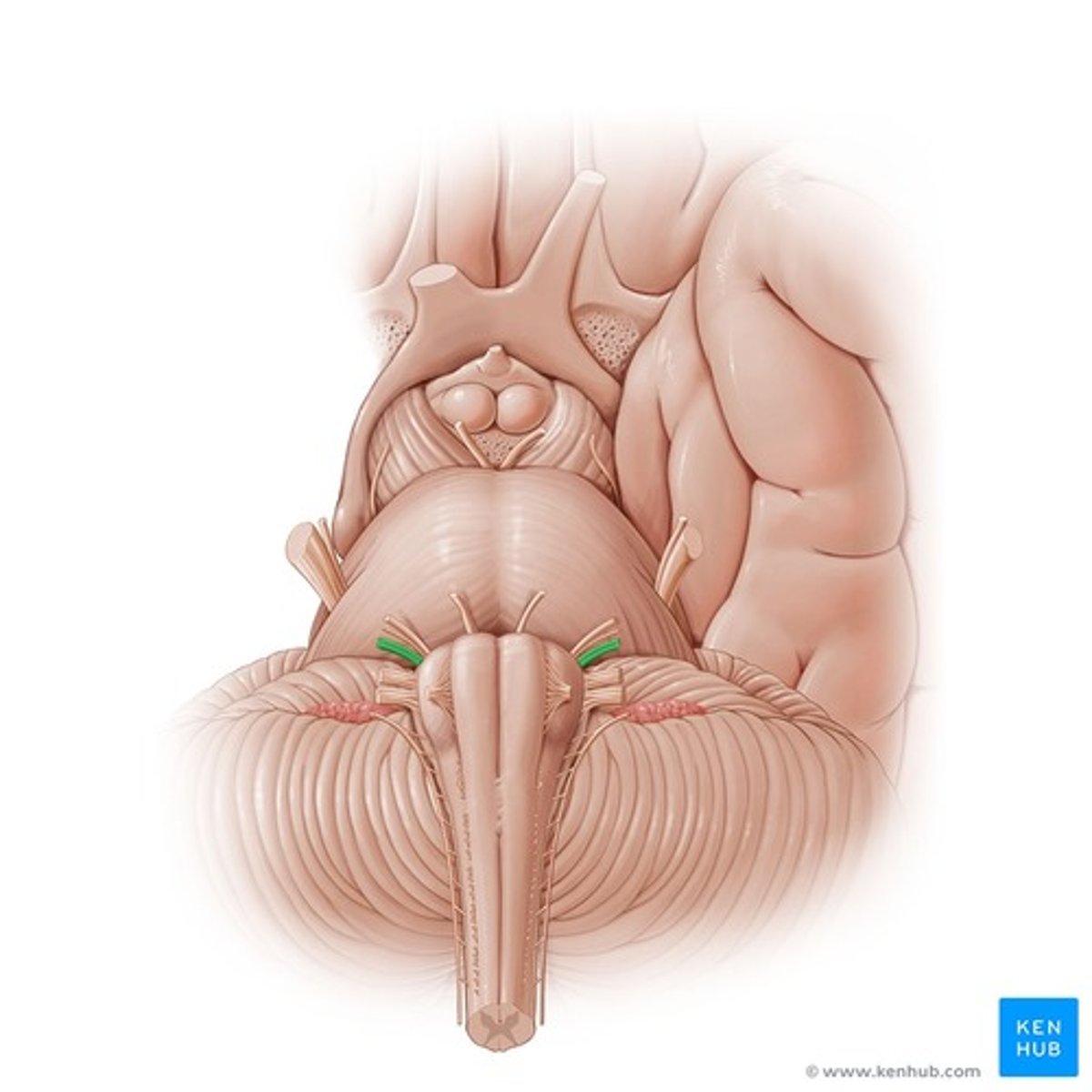
Facial nerve
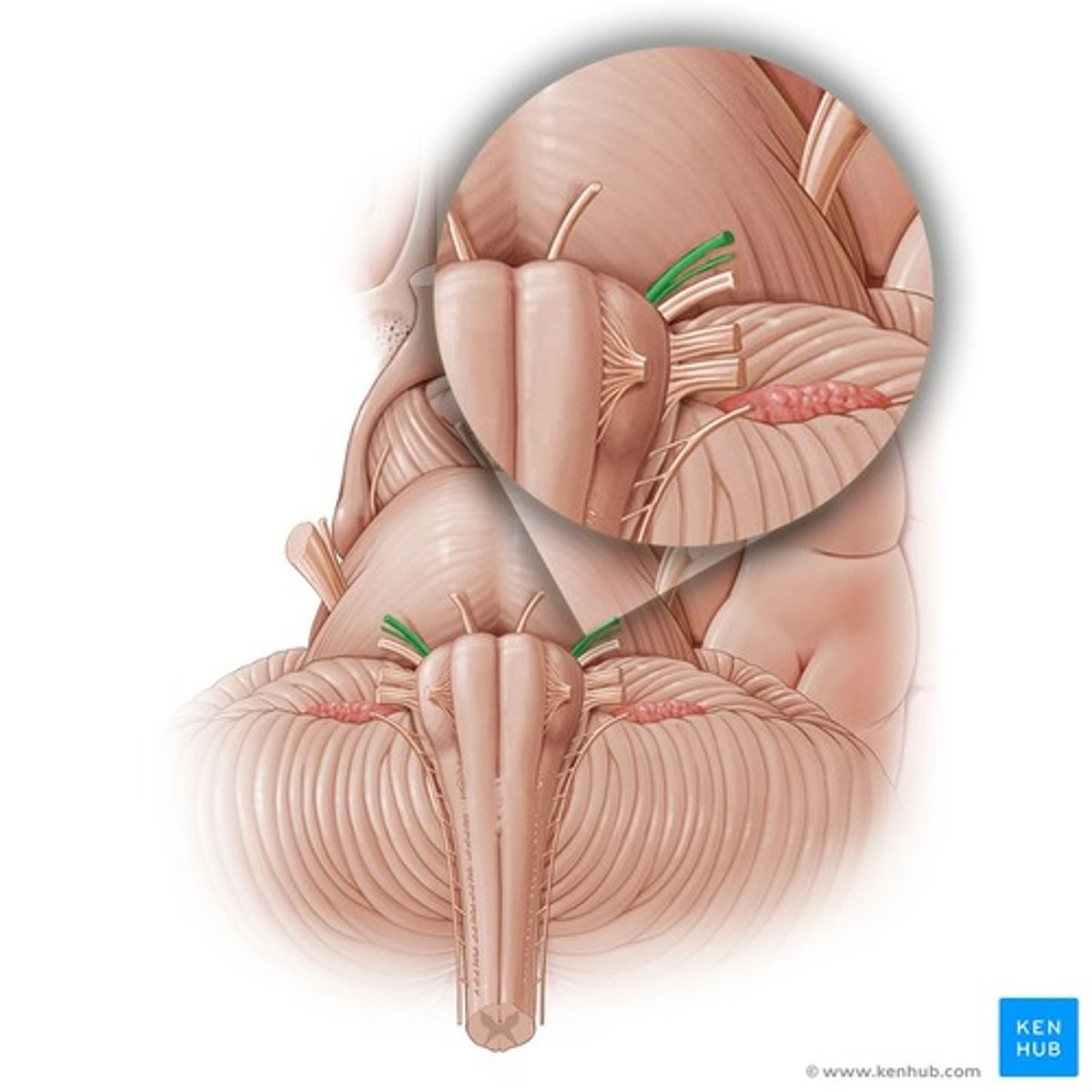
Abducens nerve
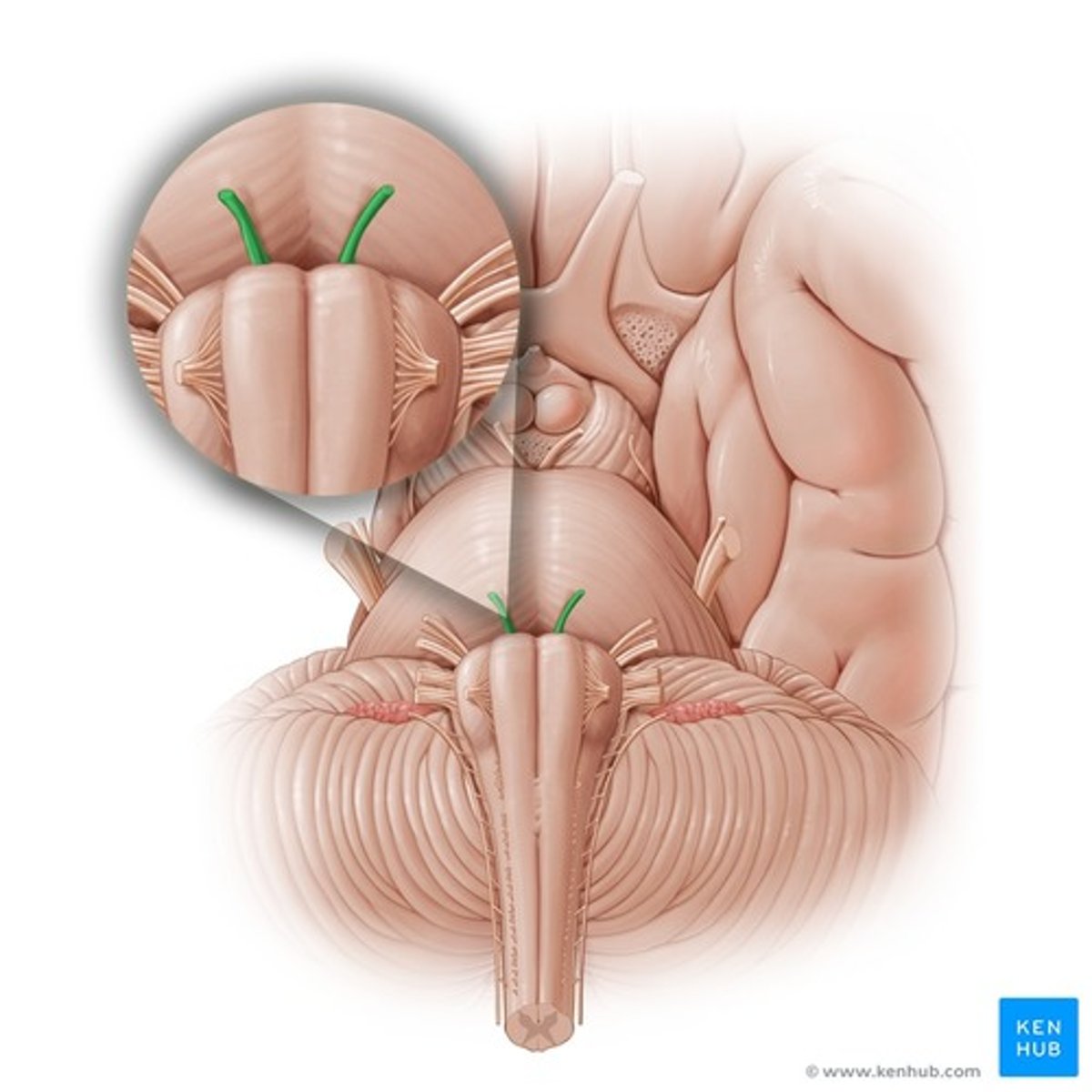
Trigeminal nerve
Pons
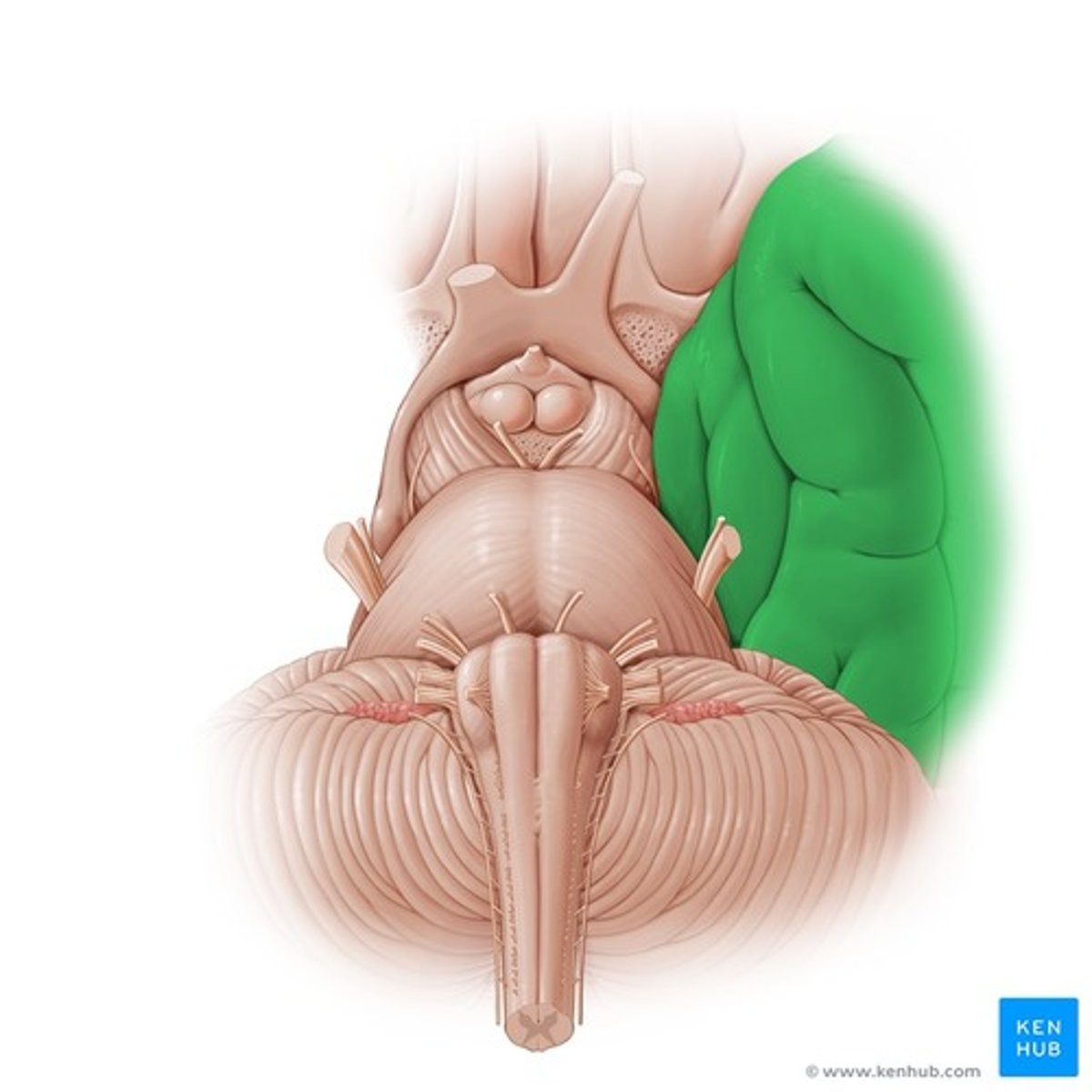
Temporal lobe
Trochlear nerve
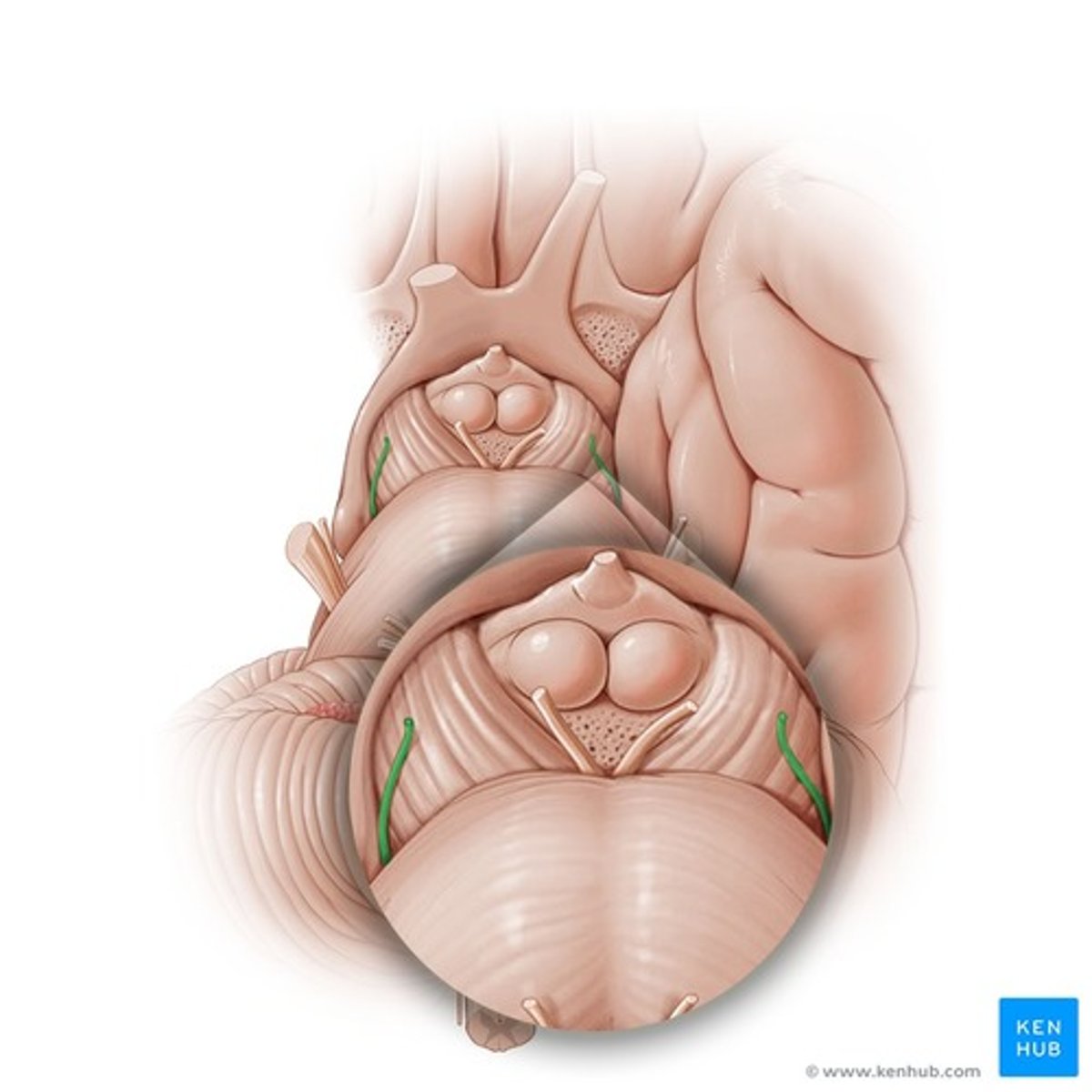
Oculomotor nerve