536 Abrupt Lesions Pitt Stuff
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
False (opposite)
True or False? total TBIs have decreases in recent years while the number of TBI related deaths has increased.
elderly
what age group has the highest incidence of hospitalization for
TBIs
child abuse
common cause of TBI-related deaths among those ages 0-4
MVAs
common cause of TBI-related deaths among young children and young adults
self-inflicted TBIs
common cause of TBI-related deaths among middle and late adulthood
falls
common cause of TBI-related deaths among the elderly
falls
account for the majority of TBI-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths
reduced mobility, impaired senses
why are the elderly particularly vulnerable to TBIs
elderly 65+
have the highest rate and greatest number of TBI-related deaths
age 15-24
account for the majority of TBI-related emergency department visits
5.4 per 100,000
incidence of SCIs
43 (used to be 29)
avg age of SCIs
incomplete quadriplegia
most common neurological level of SCIs

20
% of incomplete paraplegia cases
20
% of complete paraplegia

10
% of complete quadriplegia

1. MVAs
2. falls
3. violence
4. sports injuries
5. medical/surgical
most common causes of SCIs from greatest to least
males (80%), black americans
Risk factors or vulnerable groups for SCIs
ischemic stroke
stroke occurring from disruption of blood flow and leading to infarction
penumbra
area of damaged tissue around an infarct
hemorrhagic stroke
stroke caused by a rupturing of blood vessels within the cerebrum, subarachnoid space, subdural space, or epidural space that leads to infarction downstream from the rupture
240/100,000
incidence of strokes
first strokes (75%)
are first strokes or recurrent strokes more common?
ischemic (85%)
are ischemic strokes or hemorrhagic strokes more common?
65+ (risk doubles after age 55 every 10 years)
age that most commonly has strokes
- gene mutations causing malformation of vascular smooth muscle
- sickle cell disease
genetic risk factors for stroke
hypertension, cardiac disease (forming emboli), athersclerosis
cardiovascular risk factors for stroke
high LDL, low HDL, obesity
dietary risk factors for stroke
statins, dietary fiber & phytosterol consumption
ways to reduce LDLs
smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, cocaine and amphetamine usage
drug risk factors for stroke
increasing HDL levels, thinning blood
why would lower levels of alcohol consumption result in a 20% lower stroke risk?
leukemia, diabetes mellitus
systematic risk factors for stroke
open injury
primary injury in which the skull in penetrated
closed injury
primary injury in which the skull remained in tact
diffuse axonal injury
brain injuries that occur in the absence of physical contact with the skull, caused by rotational forces
Wallerian degeneration
in diffuse axonal injury, axons are rip apart by shearing forces,, resulting in what type of degeneration?
wallerian degeneration
degeneration of the distal portion of the axon and myelin sheath
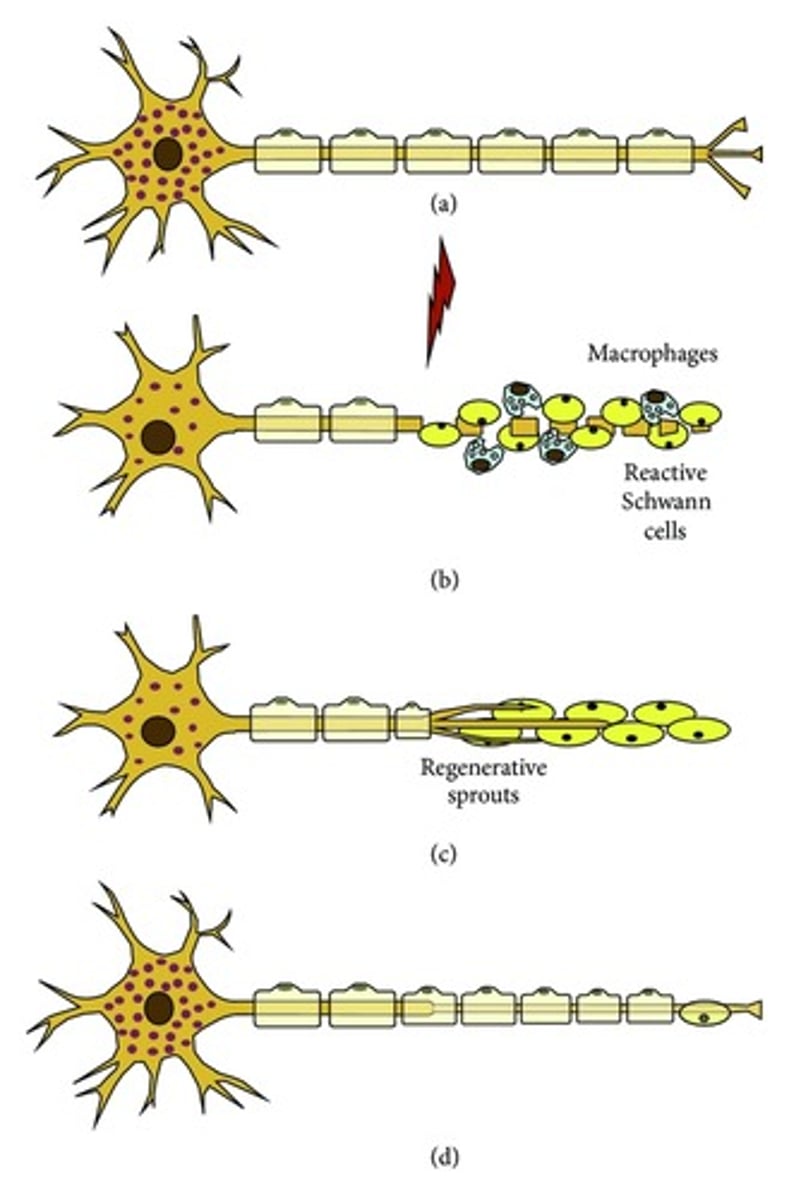
PNS; allows axon regrowth
CNS; does not allow axon regrowth
What part of the NS are axons able to regrow?
oligodendrocytes, astrocytes
what specific aspects of the CNS inhibit axon regrowth
Schwann cells
what specific aspects of the PNS facilitate axon regrowth
secondary inflammation
injuries that occur over the course of days to months as a result of swelling and
inflammation
MAP-ICP
Equation for CPP
reduces CPP
how can hypotension, or increased ICP affect CPP
increased ICP
how do swelling/inflammation from a primary injury affect ICP?
neurovascular coupling
Changes in neural activity produce changes in blood flow and brain metabolism
dilate
Following TBI, neurovascular coupling is disrupted and cerebral blood vessels vaso________.
nitric oxide
a gas released by the endothelial cells to promote blood flow via vasodilation, which is not release following TBI
vasoconstriction
If NO is not released following TBIs, what happens to peripheral blood vessels?
BBB
this structure becomes more permeable following a TBI, due to vascular damage or inflammation
1. mechanical stimulation via TBI or swelling
2. reactive gliosis (↓ glutamate and K⁺ uptake)
3. ATP depletion due to hypoxia/ischemia
How can a TBI induce excitotoxicity?
1. oxidative damage
2. osmotic necrosis
3. glutamate/calcium toxicity
specific mechanisms of neurodegeneration as a result of elevated neuronal activity after a TBI
anticonvulsants
how can we control excessive neuronal activity
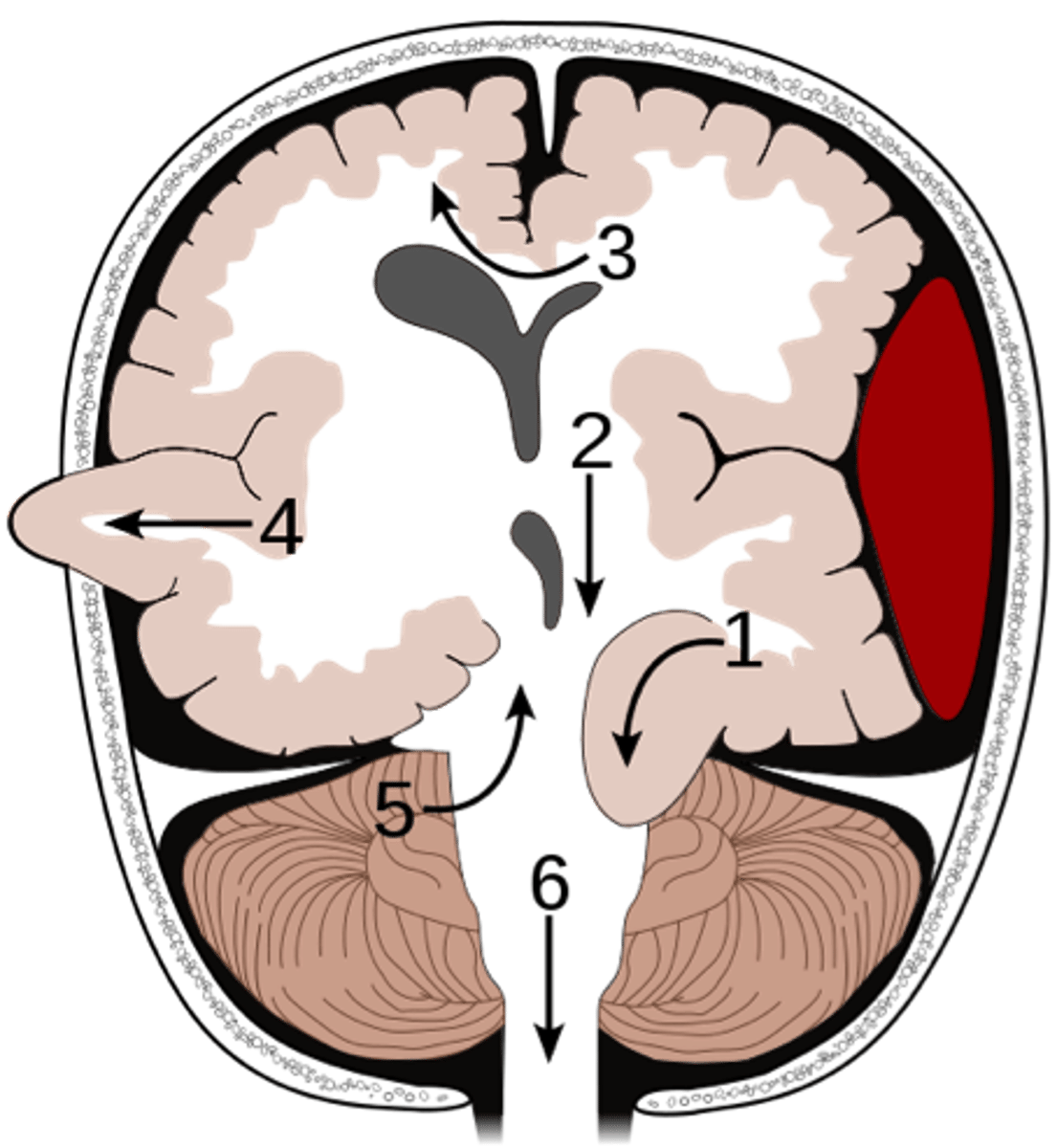
subfalcine herniation
herniation in which the cingulate gyrus crosses the midline, passing under the falx cerebri to compress the contralateral cerebral hemisphere
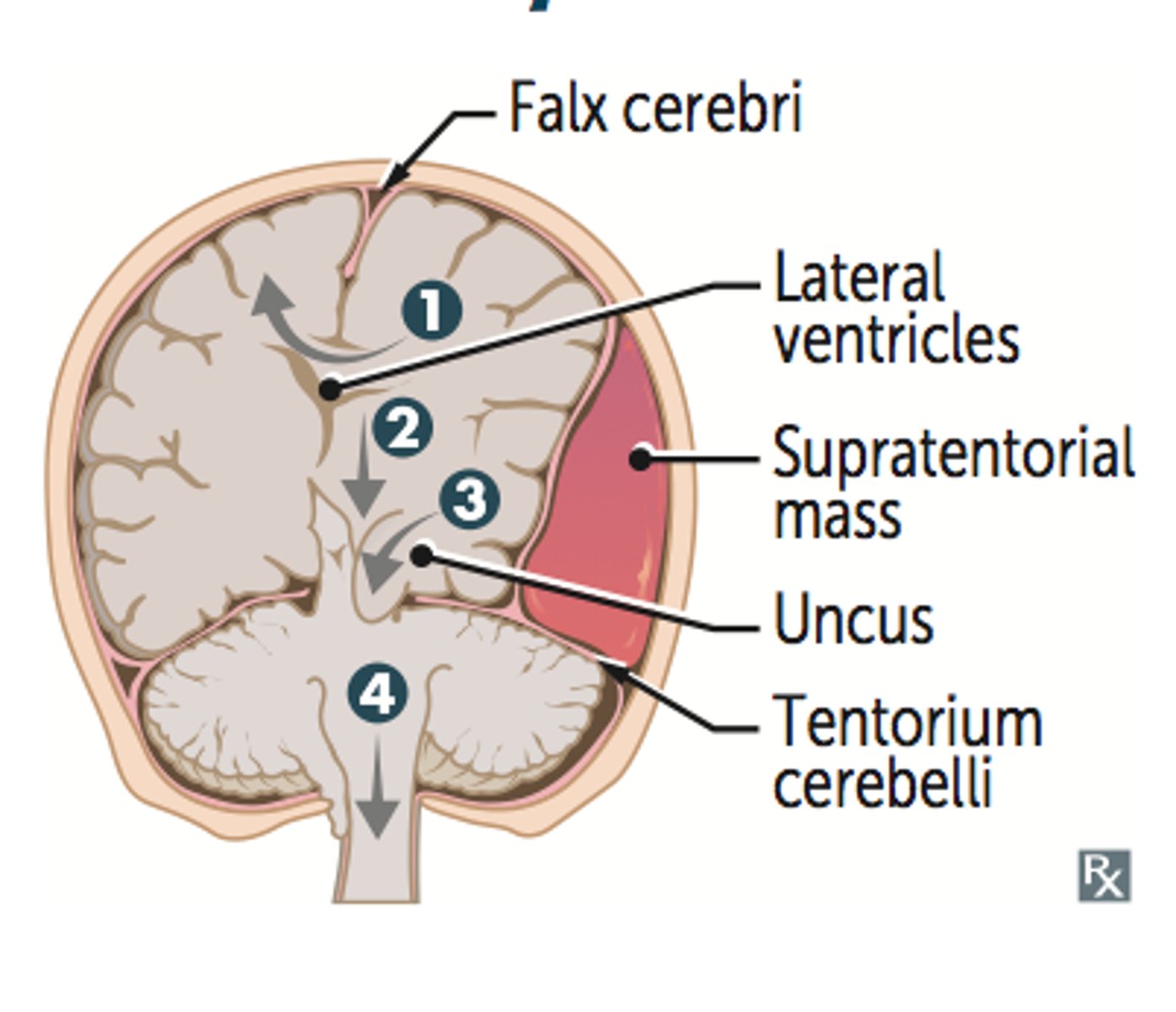
transtentorial herniation
herniation in which brain matter is pushed past the tentorial membrane, which separates the cerebrum from the brainstem (1)
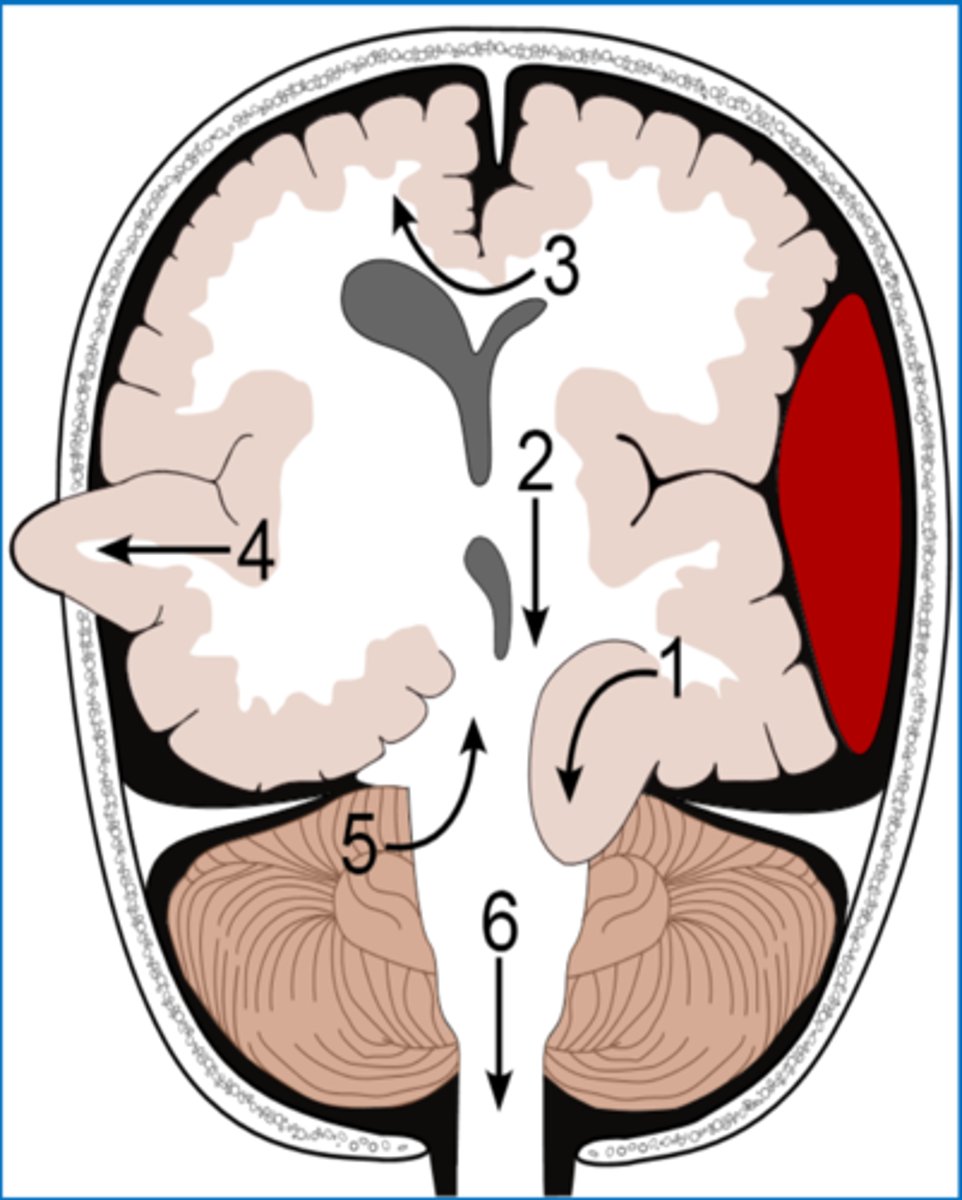
central herniation
transtentorial herniation where the diencephalon and midbrain are pushed downward onto the brainstem
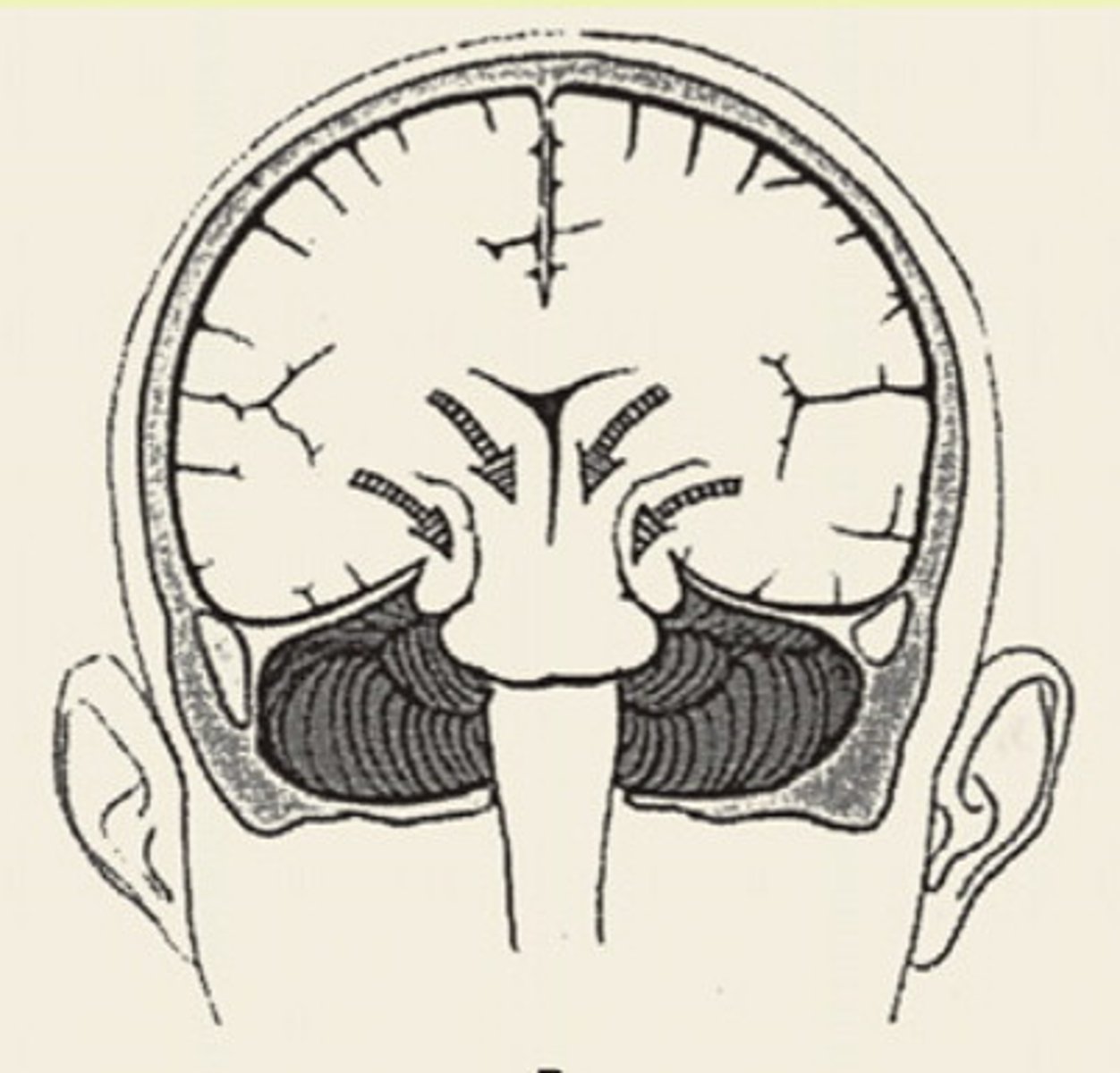
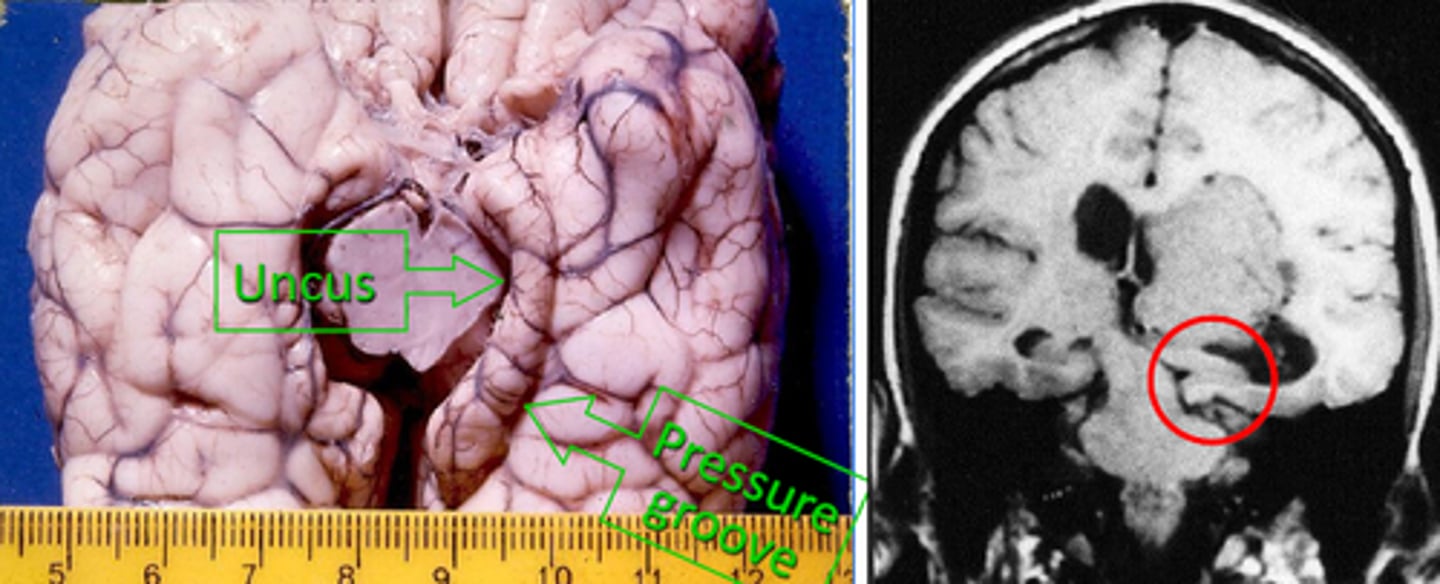
uncal herniation
transtentorial herniation where the uncus of the temporal lobes is pushed downward onto the brainstem
upward herniation
transtentorial herniation where the midbrain is push upward into the cerebrum (5)
tonsillar herniation
the cerebellum herniates downward, pushing caudal portions of the brainstem through the foramen magnum. This has a high chance of compressing the medulla. (4)
transcalvarial herniation
brain matter squeezes through a fracture or opening in the skull. This only occurs in the case of open injuries or craniotomy (4)
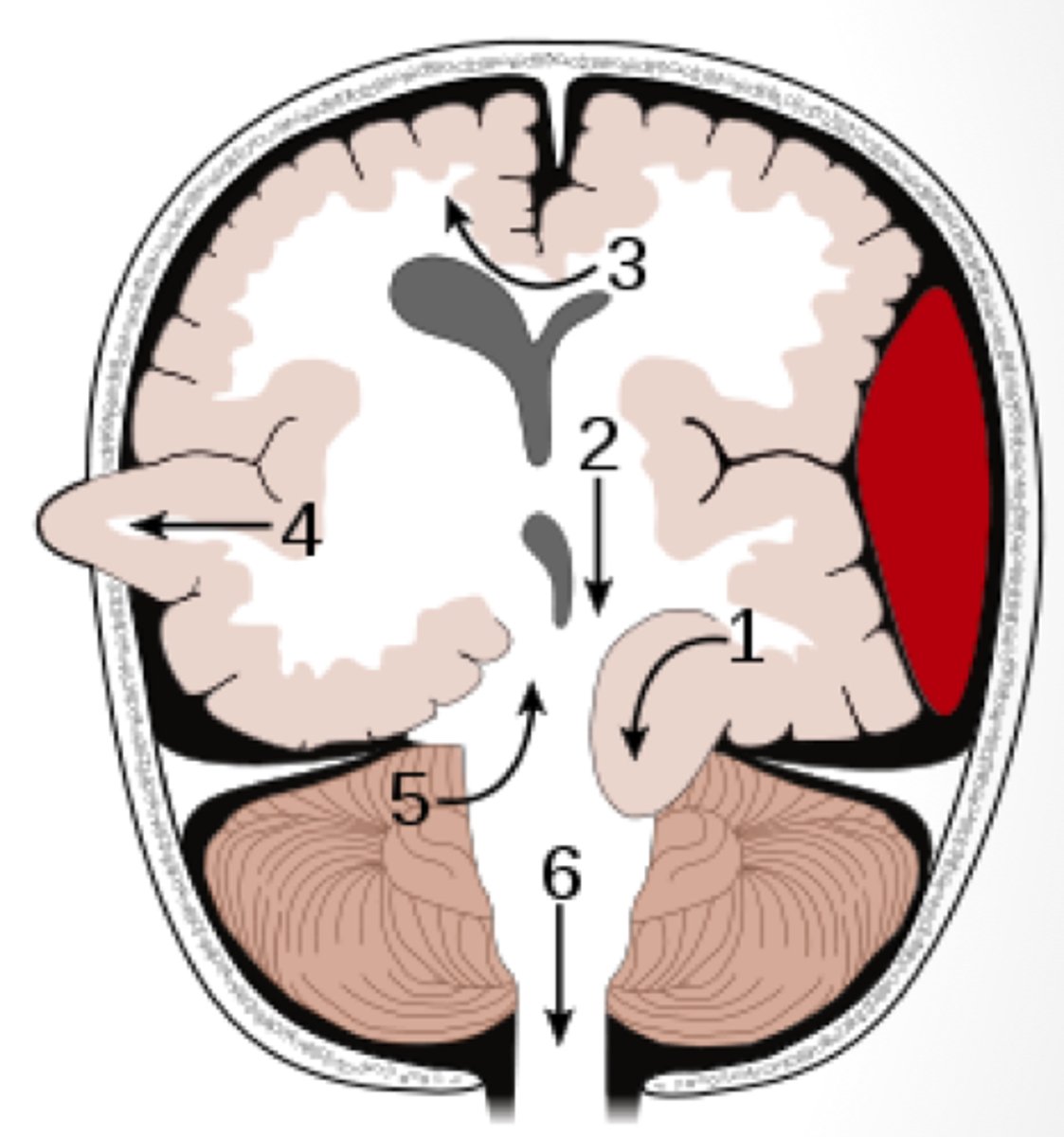
medulla
Herniation that compresses the brainstem, particularly the ______________, can cause paralysis or death due to respiratory failure
respiratory function controlled in the medulla
why would herniation onto medulla increase risk of respiratory failure?
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
progressive neurodegenerative disorder marked by cortical degeneration and the accumulation of tau neurofibrillary tangles (often from repeated injuries)
cognitive impairments, behavioral changes, dementia
cortical degeneration from CTEs can lead to:
axonal transport
neurofibrillary tangles impair what function of a neuron?
Aβ
plaques often found in those with TBI
ApoE
gene product that is used to clear Aβ
ApoE4
gene product that is associated with poor outcomes following TBI dues to decreased ability to clear Aβ
alzheimer's disease
what condition associated with Abeta and tau tangles is also commonly associated with TBIs
hyperextension/flexion
accounts for 50% of SCIs
hangman's fracture
Unstable, serious fracture of posterior elements of C2 usually with C2 anterolisthesis on C3. Caused by hyperextension and distraction (head against dashboard). Possibly compresses the spinal cord
1. compress SC and kill nervous tissue
2. compress vertebral arteries and disrupt blood flow, killing nervous tissue
how can any type of enlargement or shifting of the vertebra affect the nervous system?
neurapraxia
a temporary loss of motor and sensory function caused by narrowing of the vertebral canal and aggravated by any bending
False (both deal with primary and secondary)
TBIs can involve primary and secondary injuries, but SCIs only deal with primary injuries. True or False
structural damage
common causes primary injury
1. impaired synaptic communication (neutroptrophic support)
2. altered blood flow
3. inflammation (reactive gliosis, toxicity from macrophages)
common causes of secondary injury
syringomyelia
a tube-shaped cystic lesion (called a syrinx) forms over multiple spinal levels, often in the cervical and thoracic regions; typically develop from SCIs
CSF
what are syrinx's filled with in a syringomyelia
sharp neck pain, decreased pain and temp sense in cape-like distribution, muscle atrophy and weakness, autonomic dysfunction
common signals of a syringomyelia
posterior column/dorsal columns
tract of the spinal cord which contains ipsilateral somatosensory fibers that convey fine touch
anterolateral tract / spinothalamic tract
tract of the spinal cord which contains contralateral nonconscious tactile sensation as well as conscious nociceptive and temperature information
lateral corticospinal tract
tract of the spinal cord which runs on the lateral portion of the spinal cord and controls ipsilateral limbs
anterior corticospinal tract
tract of the spinal cord which runs on the anterior portion of the spinal cord and controls the trunk and contains a mix of crossed and uncrossed fibers
hypothalamospinal tract, reticulospinal tracts
tracts of the spinal cord which innervate the preganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system. Damage to these tracts
affects autonomic function
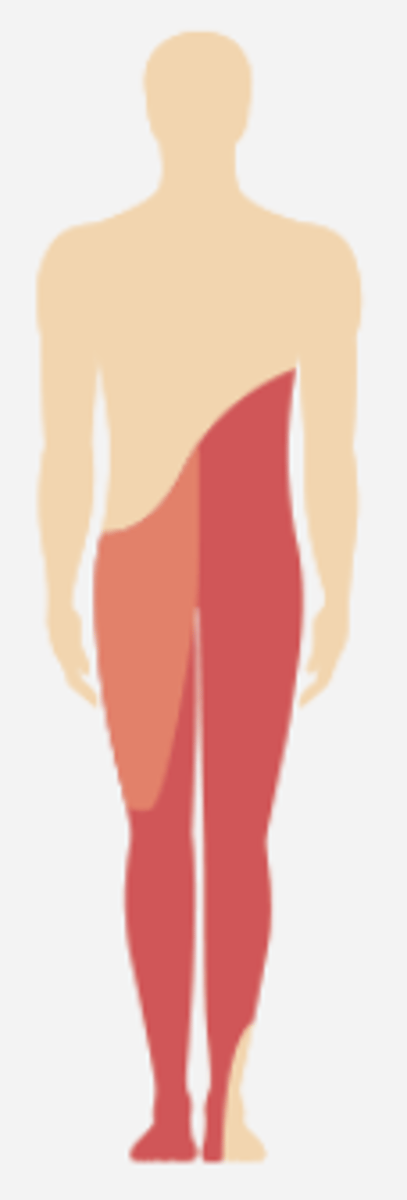
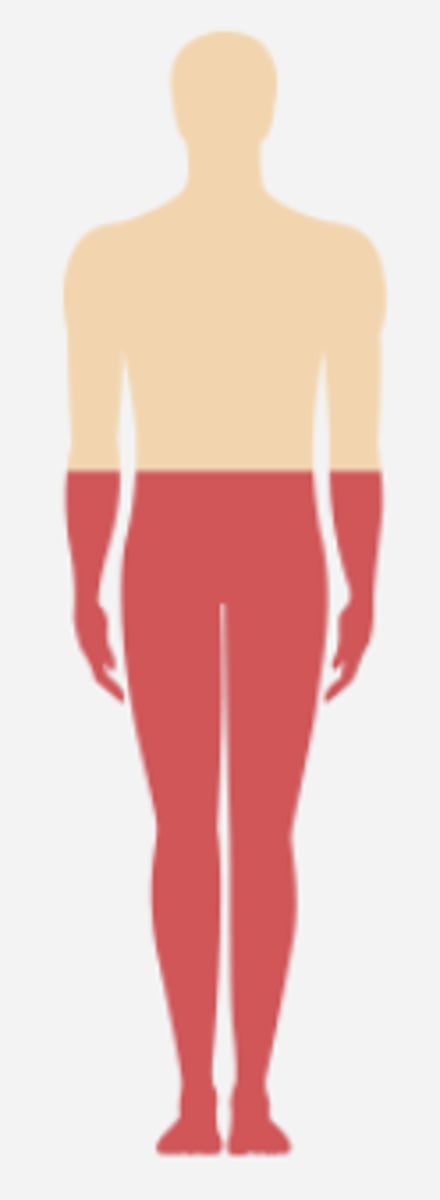
Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS)
caused by damage to one side of the spinal cord; typically the result of gunshot or stab wounds.
ipsilateral sensory loss
in Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS), damage to the posterior columns creates:
contralateral temperature and pain loss
in Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) damage to the anterolateral tract creates
ipsilateral motor weakness/paralysis
in Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) damage to the CST creates:
LMN weakness
in Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) damage to the anterior horn at the level injury creates:
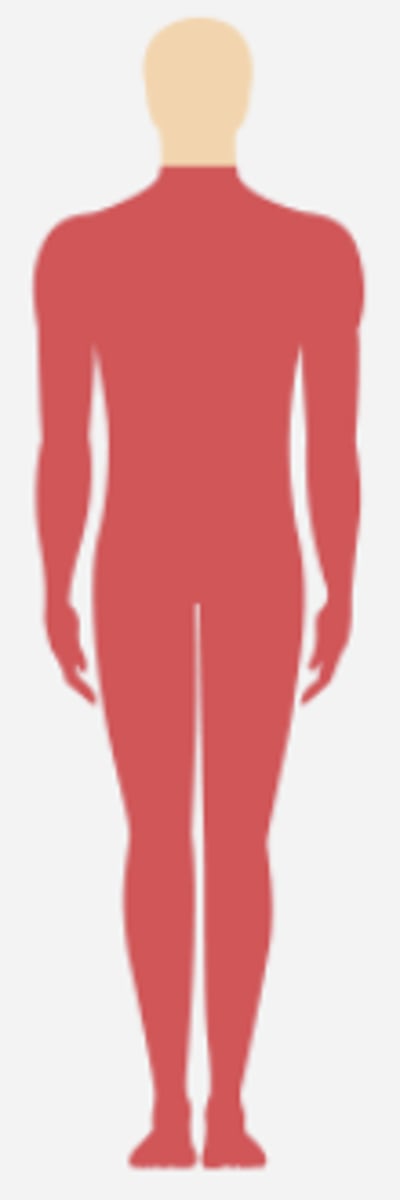
anterior cord syndrome
caused by bilateral damage to the anterolateral
tract and CST
loss of blood supply by anterior spinal artery
typical cause of anterior cord syndrome, orbilateral damage to the anterolateral
tract and CST
posterior cord syndrome
SCI caused by damage to the posterior columns
- preserved motor function, pain, and temperature sensation
- sensory ataxia/uncoordinated walking
symptoms of posterior cord syndrome
central cord syndrome
caused by damage to the central aspect of the spinal cord, usually by syringomyelia or intramedullary tumors
sacral
what part of the spine is commonly spared from central cord syndrome?
Conus medullaris syndrome, cauda equina syndrome
caused by damage at the base of the spinal cord. These cause flaccid paralysis of the lower limbs and pelvic floor
first 6 months, in muscles with some level of strength after injury
when does most motor recovery occur after a SCI?
limited axonal regrowth in CNS
What contributes to the inability to restore function after an SCI?
true
True or false? Neurons in the spinal cord adapt over time following SCI
spinal shock leading to flaccid paralysis below levl eof lesion
immediately following a SCI, what symptoms occur
sensory feedback
over time, neurons in the spinal cord can adapt to loss of descending input and become more excitable via what input?