AP Bio- Micro/Molecular Biology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
F+/F-
Having or lacking the F factor plasmid in prokaryotes. F+ means having the f factor/male and F- means not having the f factor/female.
Hfr cells
stands for ‘high frequency recombination’. This means the f factor is integrated into the prok’s chromosome instead of existing as an autonomous plasmid. This is one of the best tools for evolution and diversity.
Recombinant
DNA forged by combining genetic material from two different sources
Conjugation
A type of horizontal gene transfer that occurs between two cells of the same species by forming a pili ‘mating bridge’ to transfer DNA.
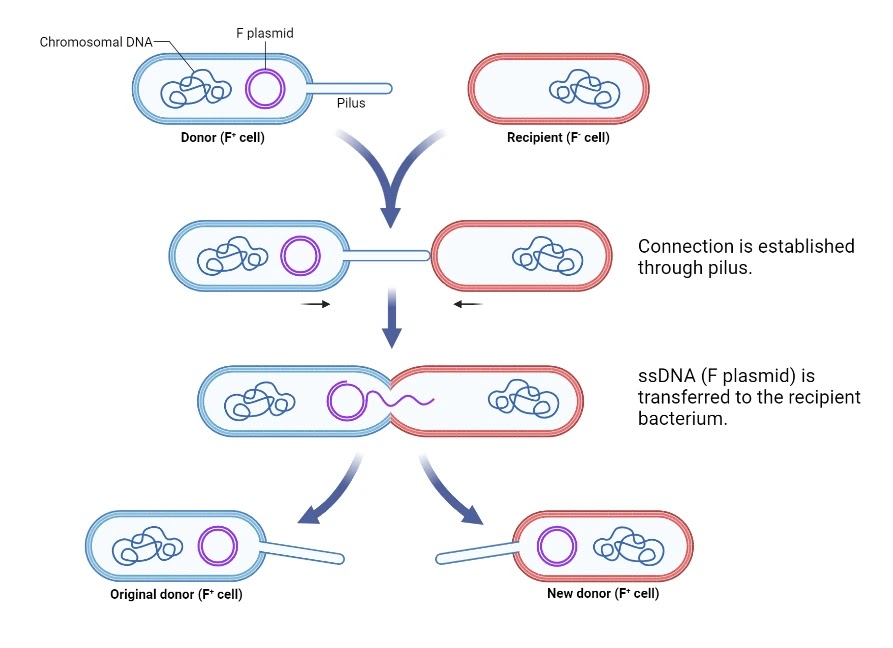
Conjugation (F plasmid)
A single strand of DNA coming from the double stranded plasmid breaks off and enters the recipient (F-) cell through the pili bridge.
A new strand is synthesized to make up for the lost strand in the donor cell. The DNA is then replicated to make the double stranded plasmid in the recipient cell .
The DNA becomes circular and the recipient cell becomes a donor cell.
Conjugation (Hfr)
F Plasmid is integrated into the donor cell’s chromosome
single strand of DNA coming from the double stranded F factor breaks off and enters the recipient (F-) cell through the pili bridge.
A new strand is synthesized to make up for the lost strand in the donor cell. The DNA is then replicated to make the double stranded segment (F factor included) in the recipient cell .
Homologous genes/regions of the donor cell’s DNA fragment and the recipient cell’s chromosome are exchanged.
Enzymes then break down irrelevant linear DNA. Recipient now becomes a recombinant F- cell.
Photoautotroph
Organisms that utilize light energy, carbon compounds (most commonly CO2) and water to produce organic compounds.
I.e Cyanobacteria
Chemoautotrophs
Organisms that use inorganic compounds such as co2 and HCO3 to make energy and organic compounds by oxidation (commonly H2o or Hydrogen Sulfide) They can live in regions that have little to no sunlight.
I.e Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and methanogens
Photoheteroptrophs
Organisms that use light source for energy but also have to utilize organic compounds to make food
Chemoheterotroph
Organisms that get their energy and carbon source from organic compounds
I.e Plants and animals
Obligate aerobes
Need oxygen to grow and perform metabolic processes.
Obligate anaerobes
Cannot use oxygen to grow and perform metabolic processes and have to use fermentation or anaerobic respiration instead.
Facultative anaerobes
Can use both oxygen and anaerobic respiration/fermentation to grow and thrive.
Heterocytes
Specialized cells that perform Nitrogen Fixation in a filament-based prokaryotic colony
Nitrogen Fixation
Turning atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen usable for the body (Nitriates i.e ammonia: NH3 )
Capsomeres/capsid
Protein subunits that make up the capsided: a protein coat that helps protect DNA/RNA and attach to other cells
Glycoproteins
Sugar chain proteins dotted on the surface of a virus that act as signal receptors and attach to other cells
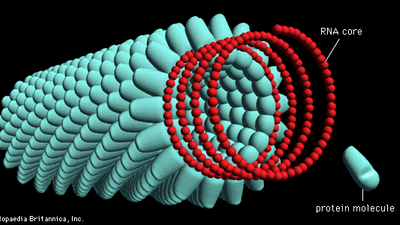
Helical Viruses
A virus with a spiral, rod-like structure made up of protein subunits that stack around a central axis, forming a hollow tube
Bacteriophages/phages
Viruses that attack bacteria
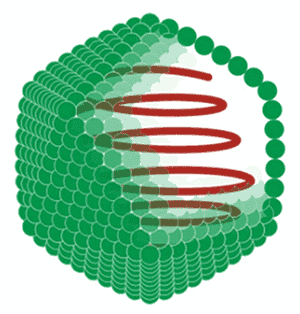
icosahedral viruses
20 sided capsid made up of triangular subunits
Endocytosis
a process where a host cell engulfs a virus particle by wrapping its plasma membrane around it
Host Range
Limited # of host species a virus targets
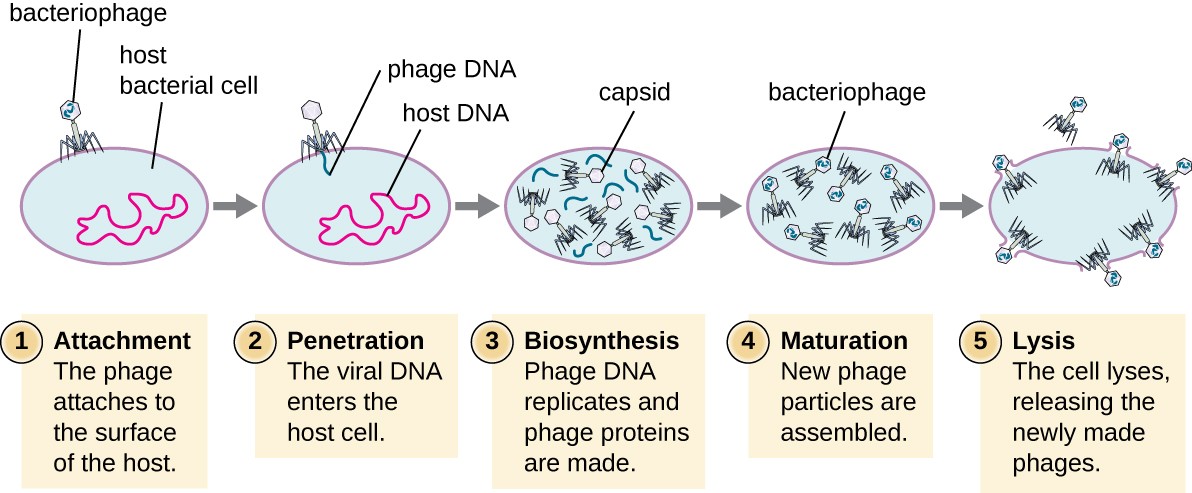
Lytic Cycle
The destruction replicative process where a phage attaches to a cell, injects its DNA, which causes the rapid replication of viruses, eventually causing the cell to burst and die.
Lysogenic Cycle
A covert viral replication process where the virus attached to the cell, injects DNA but instead integrates the viral DNA into the host’s genome allowing its DNA to be replicated in the host’s daughter cells while it hides. Can turn lytic from factors such as temperature and stress
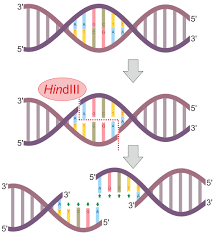
Restriction enzymes
A form of self defense from the bacterial cell:
Special digestive enzymes that cut viral foreign DNA into fragments, ultimately destroying it
Viral envelopes