Ch 3: Biodiversity and Conservation
Ch 3 - Biodiversity and Conservation
3.1 - An Introduction to Biodiversity
Biodiversity: broad concept encompassing total diversity which includes diversity of species, genetic diversity, habitat diversity
- Species diversity: usually in communities, product of number of species and their relative proportions
- Habitat diversity: range of habitats in an ecosystem or biome
- Genetic diversity: range of genetic material present in a population of a species
Smaller populations have lower genetic diversity than a larger one because of the small gene pool
Scattered populations (animals) / plant-wise (humans) have high genetic diversity
Many ecological niches due to layering of forests result in habitat diversity
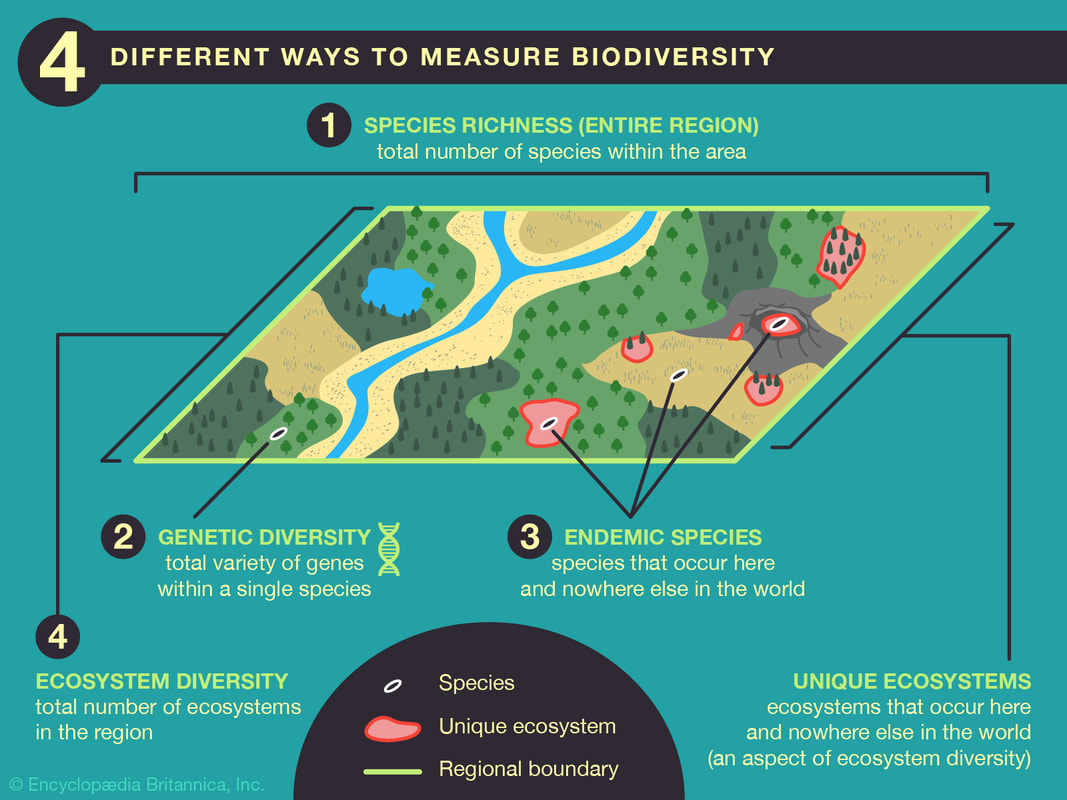
The number of species present in an area is often used to indicate general patterns of biodiversity.
Richness is a measure of the number of different species in an area; more species means a richer environment
- Abundance is the number of individual organisms in a species. We can measure abundance on a small scale as they appear in a forest, for a larger scale, environmentalists tend to measure abundance by the amount of organisms all around the world
- Richness does not take into account the rarity of a species
A biodiversity hotspot is a region with high levels of biodiversity that is under threat from human activities
- 70% of the habitat has been lost
- They cover 3.2% of the land surface
- Tend to have large densities of human habitation nearby
- contains more than 1.5k of plants which are endemic
The Diversity Index is a quantitative measure of the diversity of a species in a community, it includes calculations and information about the availability and rarity of species in a specific community.
- measuring species is important for biologists and environmentalists to comprehend the structure of the community which habitats a diverse number of species
3.2 - Origins of Biodiversity
Biodiversity arises from evolutionary processes
- variation in biological areas can be beneficial to, damaged to, or have no impact on the survival of the individual
- Environmental change gives new challenges to the species, those that are suited survive, and those that are not suited will not survive
Natural selection: those more adapted to their environment will flourish and reproduce and those less adapted do not survive for long
- survival of the fittest
- contributions to evolution of biodiversity over time
- give new challenges to the species so those better suited will survive
Speciation: gradual change of a species when populations of the same species become separated. They cannot interbreed since they inhabit the characteristics of other species
- a slow process can be sped up by humans using artificial selection
- only processes of animals and plants, also by genetic engineering
- separation may have geographically or reproductive causes
Isolation of species can be caused by:
- physical barriers: will split up gene pool, which results in species developing in different directions
- Examples: Mountain range, ocean
- land bridges: allows species to invade new areas and for species to relocate, created from lowering of sea levels
- Created from the lowering of sea levels
Isolation factors are:
- Geographical factors: island formation, loss of land bridges and mountain ranges
- Behavioural factors: reproductive displays, songs, daily activity
- Genetic factors: inability to produce fertile offspring due to genetic different
- Reproductive factors: anatomical different especially in reproductive organs
Continental drift: caused from drifting of the globe, results in new and diverse habits
- changing climate conditions force species to adapt which increases biodiversity
- distribution of continents caused climatic variations and variation in food supply, both contribute to evolution
Plate tectonics: study of the movement of the plates. When plates move and meet due to continental drift, they might:
- slide past each other, diverge
- converge: collide and both face upwards
- collide and one sinks underneath the other
The earth is 4.6 billion years old
- Current era: Cenozoic
- Current time period: quaternary tertiary
Isolation of populations → caused by environmental changes the surface is divided into curstal, tectonic plates which moved throughout geological time
Mass extinctions have been caused by a contribution of factors, some of which are tectonic movements, super volcanic eruption, climate change, and meteor impact which resulted in a new direction in evolution and increased biodiversity.
- Extinctions are caused by:
- Climate change over a period of time, as the dust incoming from volcanic eruptions led to increasing solar radiation which causes plants to die due to a lack of ability to photosynthesize. Many species are affected by this as well since food webs collapse over time.
- Volcanic eruptions and the impact of meteors which release large amounts of harmful dust and ashes into the atmosphere.
3.3 - Threats to Biodiversity
Estimates of the total number of species vary considerably
- Most are animals and most are terrestrial
- ⅔ rds are in the tropics, mostly tropical rainforests
- 50% of tropical rainforests have been cleaned by humans
When nearly all that habitat goes, extinction rates increase rapidly
- current rates of species loss = greater than the past due to increased human influence
- extinction can be caused by human activities, such as: habitat destruction, invasive species, pollution, overharvesting, haunting
Factors maintaining biodiversity:
- complexity of the ecosystem: the more complex a system is, the more resilient its species will be
- stage of succession: older, more resilient and stable ecosystems which undergo succession are less vulnerable than in young ecosystems
- limiting factors: changes to materials provided will make it harder and result in species disappearing system is more likely to manage it one of abiotic factors is reduced
- Inertia: property of an ecosystem to resist when subjected to a disruptive force
Factors which lead to loss of biodiversity:
- Natural hazards: naturally occurring events that may have a negative impact on the environment and humans
- are considered natural disasters when the impact worsens
- major cause of loss of biodiversity = loss of habitat
Fragmentation of habitat: the process where a large area is divided up into patchwork of fragments
- separated from each other by roads, towns, factories, fences
Pollution: caused by humans can degrade or destroy habitats and make them unsuitable to support the range of species
- local pollution, environmental pollution, eutrophication, climate change which alters weather patterns and shifts biomes
Overexploitation: has escalated as human populations expand
Introducing non-native species → can upset a natural ecosystem
Spread of a disease → decrease biodiversity
Modern agricultural practices: can reduce diversity with monocultures, genetic engineering and pesticides
Vulnerability of tropical rainforests:
- Tropical biomes: contain some of the most globally biodiverse areas in their unsustainable exploitation results in massive losses in biodiversity and their ability to perform globally impotent ecological services
- most tropical biomes occur in less economically developed countries and there is conflict between exploitation and sustainable development and conservation
International Union for conservation of nature (IUNC): published the red list of threatened species in several categories
- Extinct (EX): inability to record an organism, all individuals are dead
- Extinct in the wild (EW): captivity as a naturalised species outside past range
- Critically end (CE): considered to be in extremely high risk of extinction
- Vulnerable (VU): high risk of extinction
- Near threatened (NT): close to qualifying for one of the threatened once in the category
- Not evaluated (NE): not evaluated against the criteria
3.4 - Conservation to Biodiversity
Diversity of species: in the ecosystem promotes healthy and good environment
- extinction = normal
- A community thrives when species evolve and adapt to changes, every species has its own ecological importance
Why should we conserve biodiversity?
- Direct value: food species, natural products
- Indirect value: human rights, environmental services, scientific education values, human health, and ecocentrism
Conservation biology: sustainable use and management if natural resources
Preservation biology: attempts to exclude human activity in areas where humans have not yet encroached
Conservation → protect natural resources and proper use of nature
- Use water from water sources such as lakes
Preservation → protect what has been built from resources and protection of nature from use
- From water sources such as cleaning and washing
Organisations of biodiversity conservation:
- IGO (intergovernmental organisation): composed of different groups from different countries
- Governmental organisations (GO’s): composed of groups funded by a national government
- Non-governmental organisation (NGO): composed of groups run by volunteers, no relation to governments non-profit
Approaches to conservation:
- CITES (conservation pn the international trade in endangered species):
- Appendix 1: species cannot be traded internationally as they are threatened with extinction
- Appendix 2: species can be traded internationally but with strict regulations to ensure sustainably
- Appendix 3: a species included at the request of a country which needs help of other countries to prevent illegal exploitation
- Captive breeding and zoos:
- Holding and caring for species in captivity for research and maintenance of species
- Maltreatment and poor habitats of reserves and zoos
- Reintroduction of species does not guarantee survival and may cause a loss of money
- Botanical gardens and seed banks:
- Protection and cultivation of different species whether common or rare
- Some plants need extra care or technology to grow and survive
- Flagship species:
- Prioritised over other species
- Most common species and known worldwide
- If they become extinct, we failed to take care of them
- Keystone species:
- Species that are considered to have a critical role in maintaining the structure of the ecosystem
Designing protected areas: where a conservation area is within a country is a significant factor in the success of the conservation effort
- Surrounding areas including land formations and urban areas
- Location in a remote area where people don't usually live
- high biodiversity
- low population density