Zoology Exam IV
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Arthropoda + Animal Behavior + Echinodermata + Chordata
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Phylum Chordata: 3 Living Subphyla
Urochordata, Cephalochordata, Vertebrata
Phylum Chordata: Major Groupings
“Agnatha”, Gnathostomata,Tetrapoda, Amniota
Supraclass “Agnatha”
jawless fish
class myxini - hagfishes
class petromyzontiformes - lampreys
Group Amniota
Class “Reptilia” - reptiles
subclass anapsida
order testudines - turtles & tortoises
subclass diapsida
order sphenodonta - tuatara
order squamata - lizards & snakes
order crocodylotarsi - alligators & crocodiles
order ornithischia - bird hipped dinosaurs
order saurischia - lizard hipped dinosaurs
Class Aves - birds
Class Synapsida
order pelycosauria - early mammal like reptiles
order therapsida - late mammal like reptiles
subclass mammalia - mammals
infraclass prototheria - platypus & echidnas
infraclass metatheria - marsupials
infraclass eutheria - placental mammals
Supraclass Gnathostomata
jawed vertebrates
class placodermi - placoderms
class chondichthyes - sharks, skates, rays, & chimeras
class acanthodii - acanthodians
class “actinopterygii” - ray finned fishes
class “sarcopterygii” - fleshy finned fishes
Superclass Tetrapoda
Class Amphibia - amphibians
order labyrinthodontia - labyrinthodonts
order anura - frogs & toads
order urodela - salamanders & newts
order gymnophiona - caecilians
Urochordata
tunicates, sea squirts, & salps
Cephalochordata
lancets & amphioxus
Vertebrata
fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, & mammals
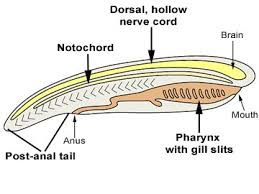
Pharyngeal Gill Slits
Phylum Chordata Synapomorphy
Effect: Allows water to flow through the body, picking up food
Innovation: More efficient food capture
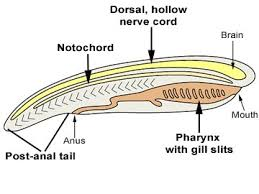
Endostyle
Phylum Chordata Synapomorphy
Effect: Produces mucus to pick up food
Innovation: More efficient food capture
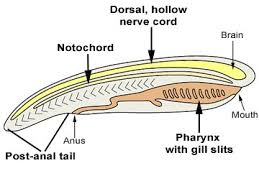
Post-Anal Tail
Phylum Chordata Synapomorphy
Effect: Further isolates muscles of locomotion of the gut
Innovation: Specialized locomotion
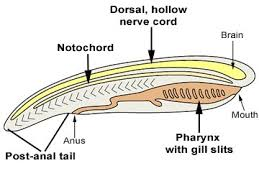
Notochord
Phylum Chordata Synapomorphy
Effect: Stiffens body so muscles bend rather than telescope
Innovation: More efficient locomotion
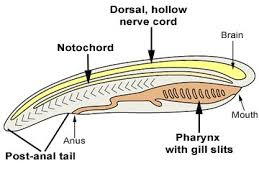
Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord
Phylum Chordata Synapomorphy
Effect: Allows cerebrospinal fluid to diffuse nutrients to larger brain & spinal cord
Innovation: Bigger body size

Caenorhabditis elegans
phototaxis: react (move due) to light
photophobia: don’t like light - move away

Horse Fly
thermotaxis: react to heat
thermophilic: like heat - move towards

Lumbricus terrestris
vibrotaxis: react to vibrations
vibrophobia: don’t like vibrations - move away

Ground Squirrel
communication
tonal: changing tone changes meaning

Dolphins
communication + cognition
invent new moves together

Crows & Jays
problem solving + intelligence
use/make tools

Rhesus Monkeys
choice + preference

Karl Von Frisch (1886-1982)
studied honey bee communication
translated meanings to the waggle dance

Niko Tinbergen (1907-1988)
“father of modern ethology”
observed birds feeding fish
Genetic vs Learned - 3 Methods
deprivation & learning experiments
isolate young
behavior exhibited = genetic, not = learned
interbreeding experiments
interbreed species w/ different behaviors
offspring display mixed behaviors = genetic, not = learned
gene knockout experiments
identify & mutate a gene possibly responsible for behavior
behavior changes = genetic control
Ultimate Questions - Why?
based on microeconomic theory
underlying assumption - particular behavior should benefit fitness (beyond costs):
increased mating (individual fitness - direct passage of genes)
increased food
increased inclusive fitness - family are more successful due to individual efforts
Types of Costs (Grouse)
energetic: use energy in displays
risk: not paying attention to predators
opportunity: not using time to feed/drink
Proximate Questions - How?
underlying mechanisms of behavior
genetic vs learned
nature vs nurture
evolutionary vs non-evolutionary

widow birds
runaway sexual selection
females prefer males w/ abnormally long tail feathers
males struggle to fly - easier prey

irish elk
runaway sexual selection
males had extremely large antlers that females preferred
antler size possibly meant males struggled to survive - likely resulted in extinction
stalk-eyed flies
runaway sexual selection
males w/ more distance between eyes is preferred by females

manakin birds
runaway sexual selection
males have increasingly long & elaborate mating dances - moonwalk
dances can involve other males
Female Behaviors
females are choosy - QUALITY over quantity
greater investment of energy
often raise young alone
maternity is guaranteed
Male Behaviors
males are more “liberal” - QUANTITY over quality
low investment of energy
often provide no parental care
paternity not guaranteed
monogamy
type of pair bond - albatrosses
1 male & 1 female
mate for life beginning at maturity (18-20 years)
will not find another mate after 1 dies
very rare
polygamy
1+ mate over a season
promiscuity
multiple males & females - bonobos
mate w/ multiple individuals during season
no specific mating pairs
males mate w/ males, females, & self
polygynous systems
lekking, female-dense polygyny, & resource-defense polygyny
polyandrous system
polyandry - extremely rare
polyandry
jacanas - 1 female & many males
female lays eggs & male cares for chicks - initially take turns but female goes off to start new nest
females fight over males - larger, compete, have 4-5 mates
female has many males protect her nests
many nests likely due to crocodile predation
lekking
grouse & pufferfish - 1 male w/ multiple females
females watch dances & choose male based off it - join their harem
female chooses a mate based on qualities
female chooses male w/ other females
female-defense polygyny
lions - 1 male defends 2+ females
females have strong bond & stay together
males are satellites & defend territory when females come into heat
male is just only available mate in area - females aren’t really attracted to them
males protect females against males
resource-defense polygyny
elephant seals - 1 male controls territory/resources/females
males arrive early to breeding grounds & claim territory/resources
females have to come to land to give birth & immediately go into heat after
females don’t really find males attractive - simply go into their territory for resources
males protect resource females need
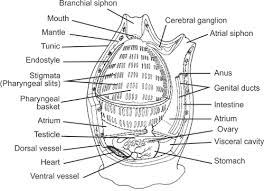
Urochordates structure
tunicates, sea squirts, ascidians, salps
synapomorphy: notochord in tail only
filter feeders
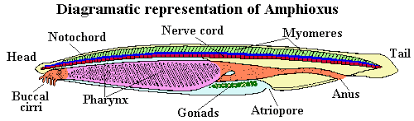
Cephalochordates structure
amphioxus & lancets
synapomorphy: notochord extends over head & w/out vertebrae
filter feeders
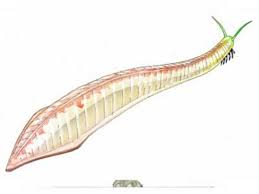
chordate fossil origin: pikaia
cambrian
best candidate for a long time
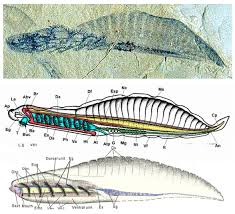
chordate fossil origin: haikouella
cambrian
preserved soft anatomy
endostyle tbd
has all features of modern cephalochordates
best modern candidate

chordate fossil origin: conodonts
cambrian → triassic
chordate features: true bone & enamel
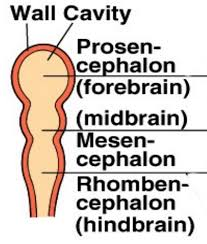
rhombencephalon
back section of tripartite brain
basic function
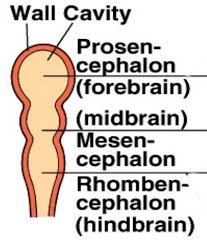
mesencephalon
midsection of tripartite brain
conduit of information between both parts
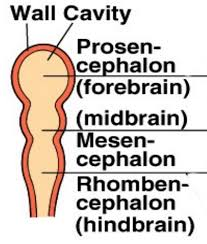
prosencephalon
front section of tripartite brain
higher thought/function
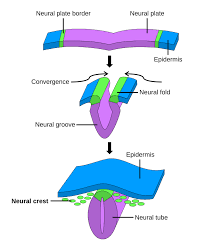
Neurulation
leads to the development of the central nervous system, starting around 21 days postfertilization in humans
involves primary neurulation for neural tube closure & secondary neurulation for spinal cord formation at lower levels
vertebrate origins
cambrian - 550 MYBP
step 1/4
evolution of jaws
silurian - 430 MYBP
step 2/4
invasion of land
devonian - 350 MYBP
step 3/4
development of amniotic egg
carboniferous - 325 MYBP
step 4/4
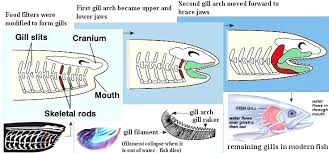
Composite Theory
evolution of jaws
gills of all fishes supported by a skeletal system called the branchial arches
initial role: pharyngeal pumping
later role: seizing prey & take bites
Invasion of land by vertebrates
predator avoidance hypothesis - out of water & away from predators
dry pond hypothesis - water ways dried up
terrestrial resource hypothesis - more food available on land
water→land FEEDING challenge
suction (-/intraoral pressure) → lingual (tongue) feeding
water→land INTEGUMENTARY challenge
scales → thick, keratinized skin
water→land CIRCULATORY/RESPIRATION challenge
gills → lungs
low → high blood pressure
water→land SKELETAL challenge
vertebrae not interlocking
could not handle gravity
fins not feet
nothing to stand on
pectoral girdle braces head
head connected to chest - no neck
pelvic girdle not connected to spine
legs not connected to spine - no locomotion under pressure from gravity
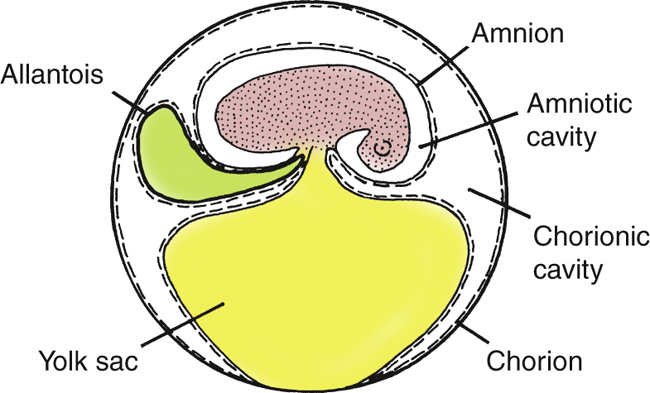
amniotes
4 double layered extra-embryonic membranes (round)
yolk sac: nutrition
chorion: separates embryo & environment - respiration
receives O2
allantois: respiration & waste storage
transfers O2 between embryo & chorion
amnion: protects embryo & prevents water loss
blue-red-red-yellow/blue
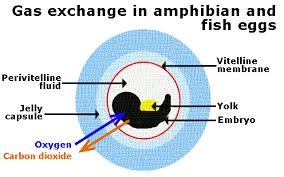
anamniotes
1 double layered extra-embryonic membrane (pear-shaped)
yolk sac: provides nutrition
blue-red-yellow
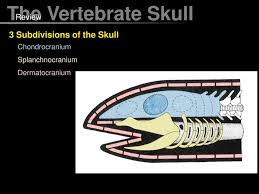
splanchnocranium
jaws & gills
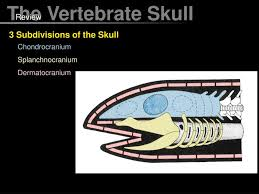
dermatocranium
outer shield + teeth/palate?
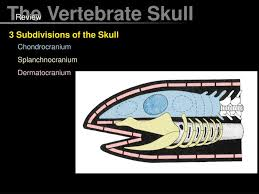
chondrocranium
brain case
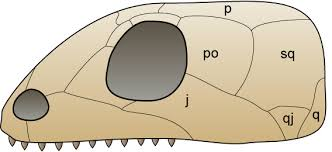
anapsid
w/out holes/arches behind orbit
testudines & basal tetrapods
small muscles → weak bite
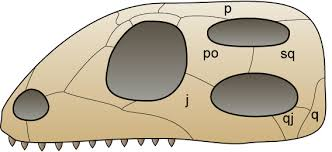
diapsid
2 holes/arches behind orbit
upper arch: postorbital + squamosal
lower arch: jugal + quadratojugal
non-testudine reptiles & birds
bigger muscles → powerful bite
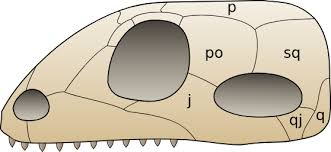
synapsid
1 hole/arch behind orbital
lower arch: jugal + quadratojugal
mammal-like reptiles & mammals
bigger muscles → powerful bite
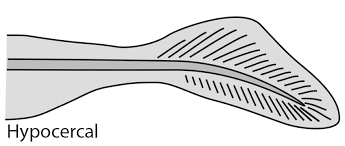
hypocercal
upper lobe smaller than lower lobe
lives in lower water column
tail morphology → pushes down
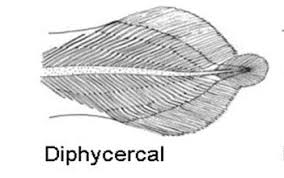
diphycercal
lobes same size & connect at end of tail
swimbladder ?
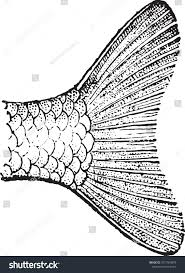
homocercal
lobes same size
swimbladders regulate vertical position
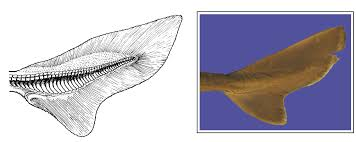
hyper/heterocercal
upper lobe larger than lower lobe
lives in upper water column
tail morphology → pushes up
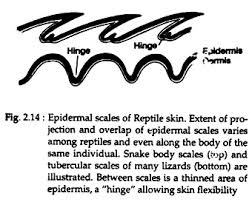
epidermal scale
reptile - thick keratinized epidermis
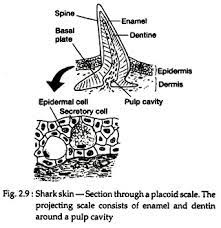
dermal denticle
teeth skin - chondrichthyans
enamel + dentine + pulp
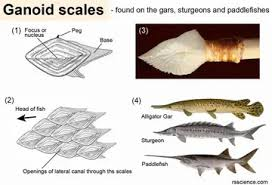
ganoid scale
gar - diamond shaped
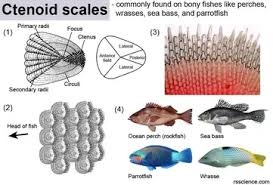
ctenoid scale
goldfish - cone shaped
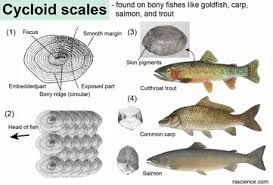
cycloid scale
herring - silvery & round
shark hunting senses
hearing: 1000-2000 m
smell: 200-500 m
lateral line: 100-200 m
senses movement using waves in cupula
vision: 10-80 m
ampullae of lorenzini: 0-5 m
jelly filled sensory pore
pitcher plant frog
raise young in pitcher plants that collect water to keep young hydrated
poison arrow dart frog
tadpoles suction to parents back as they travel to wet locations to keep hydrated
marsupial frog
tadpoles live in pouch of skin on back of parent - keeps young hydrated + safe
suriname toad
hole toad ☹
darwins frog
keep young in stomach + don’t eat - keep young hydrated & safe
midwife toad
keep young on back end & travel to wet locations to keep young hydrated
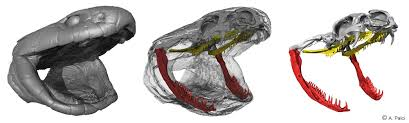
snake feeding
lower jaws: swing out laterally & jointed in the middle
left/right lower jaws joined by elastic tissue at the bottom
upper jaws: mobile & move independently
bring food into mouth/throat
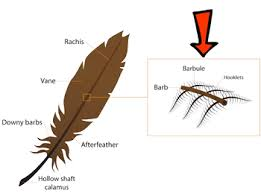
feather anatomy
calamus - sticks into skin
rachis - central tether for vanes
vane - individual extensions
barbs + barbules + hooklets
barbules & hooklets lock together like velcro
Origin of flight in birds
tree-down hypothesis
ground-up hypothesis
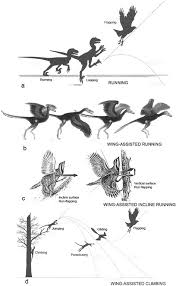
ground-up hypothesis
bournoulli’s effect helped early birds climb/speed
used wings + speed to gain altitude up trees
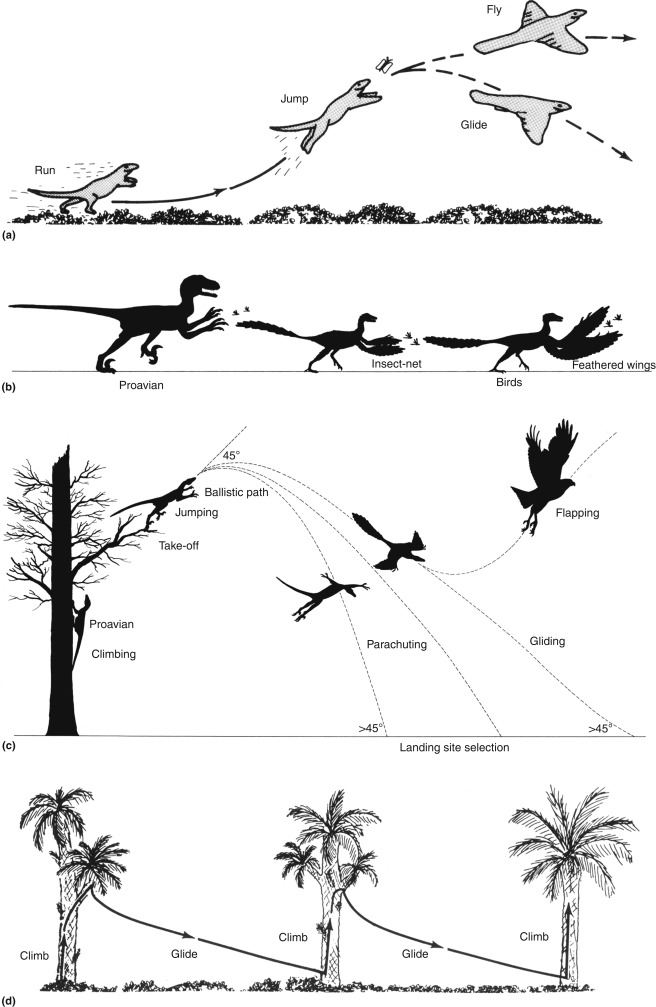
tree-down hypothesis
baby birds have clawed wings for climbing
tail + teeth + other features made early bird VERY heavy so true flight was unlikely - glided down from trees
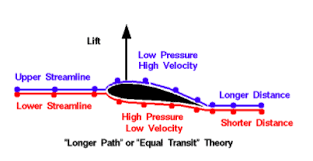
Bernoulli’s principle
wings must have camber
faster flow over wing → low pressure
slower flow under wing → high pressure
generates lift - normal force
secondary palate
2 plates of bone separate mouth from brain
advantage: breathe while eating & possibly protection from sharp prey (unlikely)
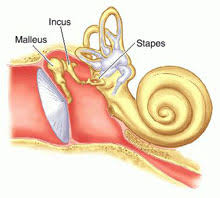
complex ear
3 middle ear bones/ossicles
malleus, incus, & stapes
advantage: low + high frequencies
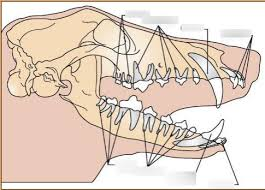
heterodonty
teeth are differently sized/shaped w/ different functions
incisors/canines - biting & premolars/molars - chewing
advantage: breaks down food
Subphylum Myriapoda
class chilopoda: centipedes
class diplopoda: millipedes
Class Pyncogonida
sea spiders
body greatly reduced
carry eggs
Class Merostomata
horseshoe crabs
walking legs act as gnathobase
carapace covers tagmata
aposematic coloration
bright colors - dangerous/warning
cryptic coloration
environmental colors - try to hide/disguise