Introduction to Organic Chemistry - 3.1
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-definitions -functional groups -nomenclature -isomerism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is empirical formula?
the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
what is molecular formula?
the true number of atoms of each element in a compound
what is structural formula?
shows the arrangement of atoms in a simplified form, without showing all the bonds
what is displayed formula?
shows every single atom and every single bond in an organic compound
what is skeletal formula?
carbon atoms are not drawn
-carbon atoms are assumed to be where the lines meet
-hydrogen is not drawn but is assumed to be bonded to the carbon
what is a functional group?
an atom or group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of the molecule
ALKANES
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿ⁺²
C-C
ALKENES
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿ
C=C
HALOALKANES
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿ⁺¹X
-X
ALCOHOLS
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿ⁺¹OH
-OH
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿO²
C=O—OH
ALDEHYDES
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿO
H
-C=O
KETONES
-general formula
-functional group
CⁿH²ⁿO
-C=O
what are structural isomers?
what are the different type of structural isomers?
have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
three types:
-chain
-position
-functional group
ALKYL
any branch or side chain
e.g → CH3 - methyl
CH2CH3 - ethyl
CH2CH2CH3
what is chain isomerism?
have the same functional group but different arrangement of the carbon skeleton → some are straight chained others are branched
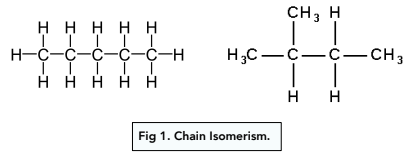
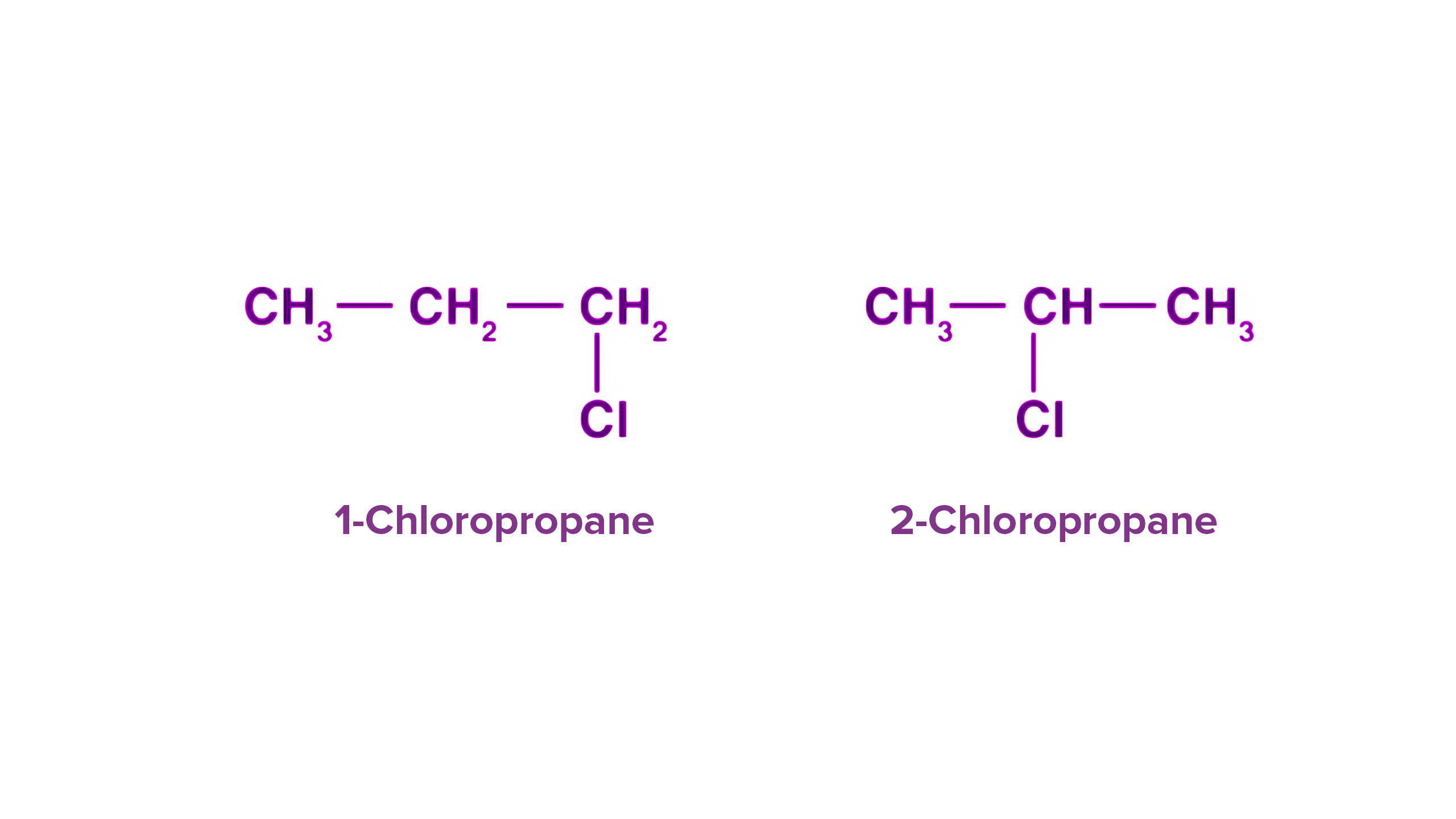
what is position isomerism?
the same functional group but it is in a different position on the carbon chain
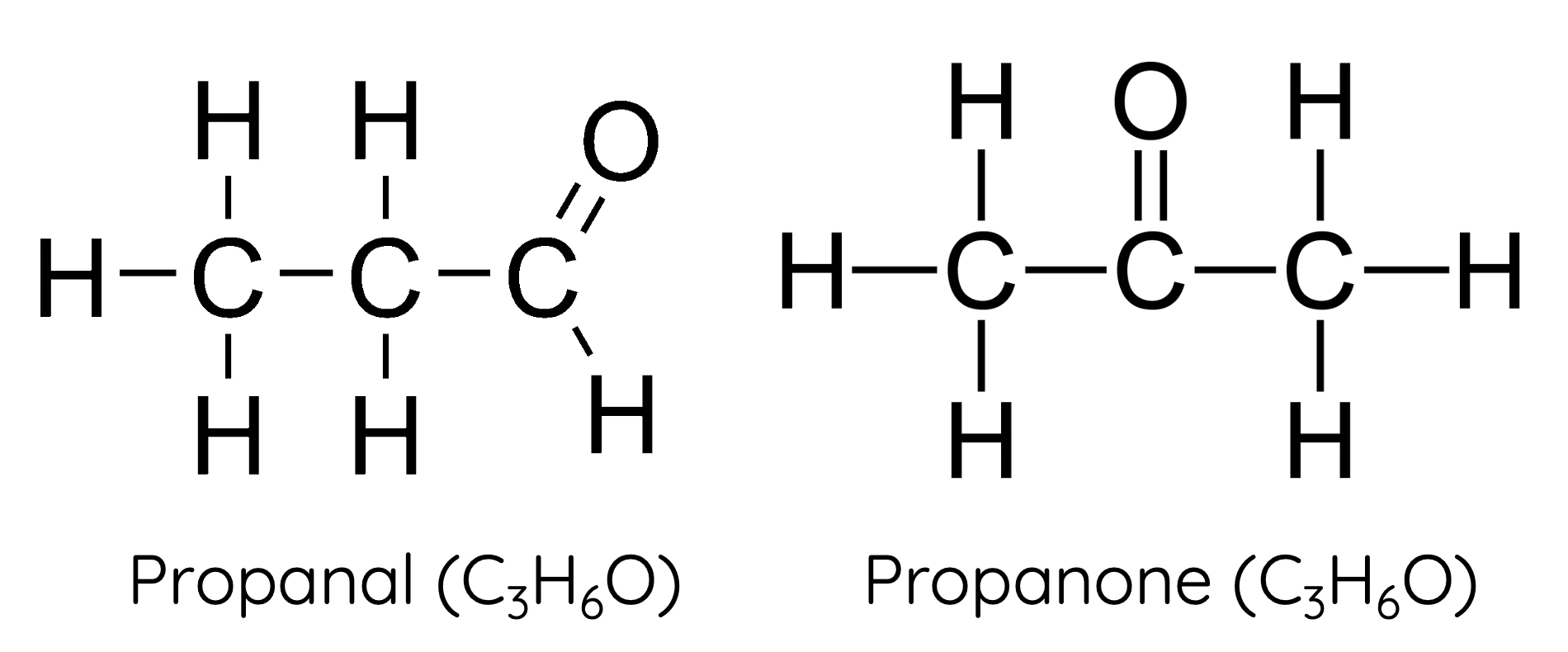
what is functional isomerism?
same atoms arranged into different functional groups
define stereoisomerism
isomers have the same structural formula but their atoms are arranged differently in space
one type of stereoisomerism is E/Z isomers in alkenes
what is the difference between e-isomers and z-isomers?
Z-isomers have the same group/atom above or below the double bond (zame side)
E-isomers have the same group/atom on different sides of the double bond (e=enemies ∴ opposite sides)
what is a homologous series?
a series of chemically similar compounds which conform to a general formula. Each member of a series differs by a CH₂ group. members of the group show a graduation in physical properties.
What is the CIP method?
briefly describe the CAHN, INGOLD, PRELOG (CIP) method
CIP priority rules are rules which determine whether a molecule is an E or a Z isomer.
compare atomic number of atoms directly attached to each side of the double bond ; atom of higher atomic number is given priority
if the atoms are both high priority and they are on the same side of the carbon bond it is the Z form.
If both priority atoms are on the opposite side of carbon bond it is the E form