BIOE3100 Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Engineering Analysis of Physiological Processes: Chapters 1-6
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
1
New cards
Physiology
Study of the normal functioning of a living organism and its component parts
2
New cards
Wolfe’s Law
Form follows function. Function explains the “why” and the process or mechanism describes the “how”.
3
New cards
Homeostasis
Regulation of the body’s internal environment. “Dynamic disequilibrium”
4
New cards
Law of mass balance
Amount remains constant if input is offset by loss.
\
Total amount of substance X in body = Intake + Production - Excretion - Metabolism
\
Total amount of substance X in body = Intake + Production - Excretion - Metabolism
5
New cards
Mass flow
Mass Flow = Concentration of Z \* Volume flow
Amount Z/min = (Amount Z/vol) \* (vol/min)
Amount Z/min = (Amount Z/vol) \* (vol/min)
6
New cards
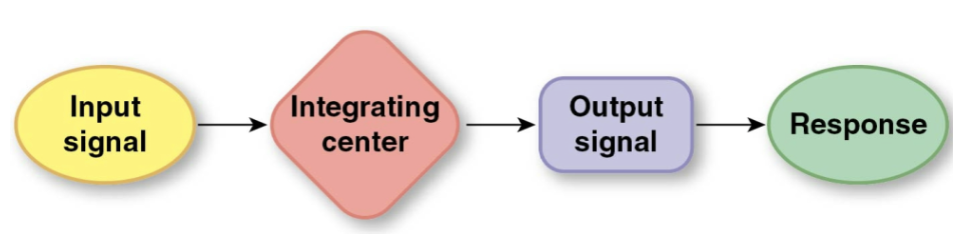
Simple control system
Regulated variables are kept within normal range by control mechanisms.
\
Two types:
* Local control restricted to a tissue
* Reflex control for long-distance pathway i.e. nervous and/or endocrine systems
\
Two types:
* Local control restricted to a tissue
* Reflex control for long-distance pathway i.e. nervous and/or endocrine systems
7
New cards
Negative feedback
Response counteracts stimulus, stopping loop. Stabilizes variable.
8
New cards
Positive feedback
Response reinforces stimulus, sending variable away from setpoint. Reinforces stimulus.
9
New cards
Feedforward control
Anticipates change.
10
New cards
Acclimatization
Naturally
11
New cards
Acclimation
In a laboratory setting.
12
New cards
Three major cavities
Cranial, thoracic (pleural sac & pericardial sac) separated by the abdominopelvic cavity (abdominal & pelvic cavity)
13
New cards
Fluid-filled compartments
Circulatory system, eyes, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
14
New cards
Hollow organs
Organs that have a small or narrow cavity or lumen inside them.
i.e. heart, lungs, blood vessels, intestines
i.e. heart, lungs, blood vessels, intestines
15
New cards
Function of cell membrane
1. Physical isolation
2. Regulation of exchange with the environment
3. Communication between the cell and its environment
4. Structural support
16
New cards
Cell membrane composition
Lipids (phospholipids, sphingolipids, cholesterol), proteins (integral i.e. transmembrane & lipid-anchored, peripheral), and carbohydrates (glycoproteins, glycolipids).
17
New cards
Cholesterol + Phospholipids
Lipid bilayers which function as a selective barrier between cytosol and external environment.
18
New cards
Sphingolipids + Carbohydrates
Glycolipids whose functions include structural stability, cell recognition, and immune system.
19
New cards
Carbohydrates + Proteins
Glycoproteins whose functions include structural stability, cell recognition, and immune system.
20
New cards
Fluid mosaic model
Scientific model that describes a cell membrane.
21
New cards
Cell composition
Nucleus, cell membrane, and cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm is composed of:
1. Cytosol
2. Membranous organelles
1. Mitochondria
2. Endoplasmic reticulum
3. Golgi apparatus
4. Lysosomes
5. Peroxisomes
3. Inclusions (NO Membranes)
1. Liquid droplets
2. Glycogen granules
3. Ribosomes (fixed & free)
4. Protein fibers
1. Cytoskeleton
2. Centrioles
3. Cilia
4. Flagella
The cytoplasm is composed of:
1. Cytosol
2. Membranous organelles
1. Mitochondria
2. Endoplasmic reticulum
3. Golgi apparatus
4. Lysosomes
5. Peroxisomes
3. Inclusions (NO Membranes)
1. Liquid droplets
2. Glycogen granules
3. Ribosomes (fixed & free)
4. Protein fibers
1. Cytoskeleton
2. Centrioles
3. Cilia
4. Flagella
22
New cards
Cytoplasmic protein fibers
* Actin (microfilaments)
* Intermediate filaments
* Keratin
* Neurofilaments
* Microtubules
* Centrioles - Direct DNA movement in cell division
* Cilia - Fluid movement across cells
* Flagella - Cell movement through fluid
* Intermediate filaments
* Keratin
* Neurofilaments
* Microtubules
* Centrioles - Direct DNA movement in cell division
* Cilia - Fluid movement across cells
* Flagella - Cell movement through fluid
23
New cards
Motor proteins
Myosins - Muscle contraction
Kinesins & Dyneins - Movement of vesicles along microtubules
Dyneins - Movement of cilia and flagella
Kinesins & Dyneins - Movement of vesicles along microtubules
Dyneins - Movement of cilia and flagella
24
New cards
Mitochondria
Two membranes create two compartments
* Mitochondrial matrix
* Unique DNA
* Intermembrane space
* Essential role in cellular ATP production
* Mitochondrial matrix
* Unique DNA
* Intermembrane space
* Essential role in cellular ATP production
25
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER
* Ribosomes attached
* Protein assembly and modification
Smooth ER
* Synthesis of fatty acid, steroids, lipids
* Modified forms in liver, kidney, muscles
* Ribosomes attached
* Protein assembly and modification
Smooth ER
* Synthesis of fatty acid, steroids, lipids
* Modified forms in liver, kidney, muscles
26
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
* Stacked sacs surrounded by vesicles
* Modifies protein made on rough ER
* Packages into vesicles
* Modifies protein made on rough ER
* Packages into vesicles
27
New cards
Cytoplasmic Vesicles
* Secretory vesicles
* Released from cell
* Storage vesicles
* Lysosomes
* Enzymes to degrade bacteria or old organelles
* Acidic interior
* Lysosomal storage diseases
* Released from cell
* Storage vesicles
* Lysosomes
* Enzymes to degrade bacteria or old organelles
* Acidic interior
* Lysosomal storage diseases
28
New cards
Cytoplasmic Vesicles
* Peroxisomes
* Enzymes to degrade long-chain fatty acids and toxic foreign molecules
* Generate and breakdown hydrogen peroxide
* Enzymes to degrade long-chain fatty acids and toxic foreign molecules
* Generate and breakdown hydrogen peroxide
29
New cards
Nucleus
* Nuclear envelope: two membranes
* Nuclear pore complex
* Chromatin: DNA and associated proteins
* Nucleoli
* Control synthesis of ribosomal RNA
* Nuclear pore complex
* Chromatin: DNA and associated proteins
* Nucleoli
* Control synthesis of ribosomal RNA
30
New cards
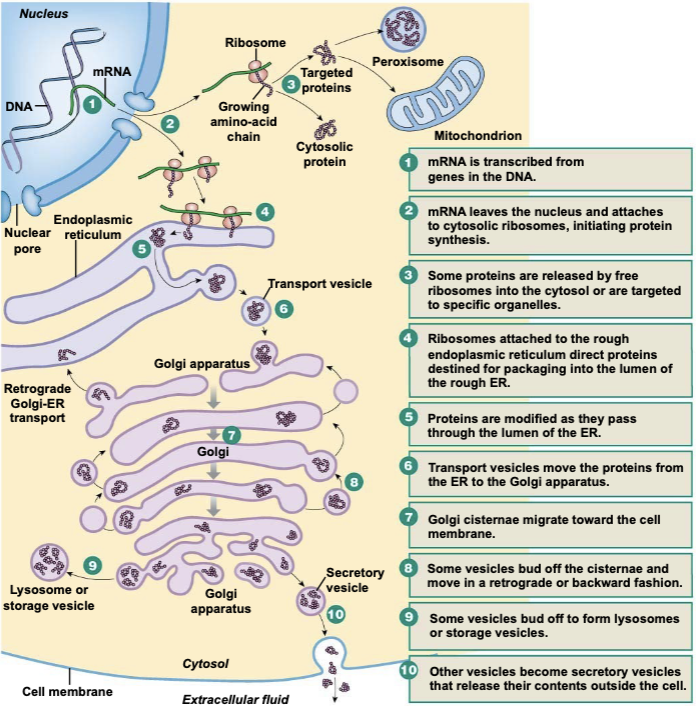
Protein synthesis
1. mRNA is transcribed from genes in the DNA
2. mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to cytosolic ribosomes, initiating protein synthesis
3. Some proteins are released by free ribosomes into the cytosol or are targeted to specific organelles
4. Ribosomes attached to the rough ER direct proteins destined for packaging into the lumen of the rough ER
5. Proteins are modified as they pass through the lumen of the ER
6. Transport vesicles move the proteins from the ER to the golgi apparatus
7. Golgi cisternae migrate toward the cell membrane
8. Some vesicles bud off the cisternae and move in a retrograde or backward direction
9. Some vesicles bud off to form lysosomes or storage vesicles
10. Other vesicles become secretory vesicles that release their contents outside the cell
31
New cards
Primary tissue types
Epithelial, connective, muscle, neural/nerve
32
New cards
Extracellular matrix
* Synthesized and secreted by cells
* Proteoglycans
* Glycoproteins covalently bound to polysaccharides
* Insoluble protein fibers
* Examples: collagen, fibronectin, laminin
* Strength
* Anchor cells to matrix for communication
* Proteoglycans
* Glycoproteins covalently bound to polysaccharides
* Insoluble protein fibers
* Examples: collagen, fibronectin, laminin
* Strength
* Anchor cells to matrix for communication
33
New cards
Cell Junctions and Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
* Cell-cell junctions
* Gap junction (communicating junction)
* Tight junction (occluding junction)
* Anchoring junction
* Gap junction (communicating junction)
* Tight junction (occluding junction)
* Anchoring junction
34
New cards
Five functional categories of epithelia
Exchange, transporting, ciliated, protective, secretory.
35
New cards
Exchange epithelia
Thin, flat cells of exchange epithelium allow movement through and between the cells.
36
New cards
Transporting epithelia
Selectively move substances between a lumen and the ECF.
37
New cards
Ciliated epithelia
Beating cilia create fluid currents that sweep across the epithelial surface.
38
New cards
Protective epithelia
Have many stacked layers of cells that are constantly being replaced.
39
New cards
Secretory epithelia
Make and release a product.
Exocrine secretions such as the mucus shown here, are secreted outside the body.
The secretions of endocrine cells (hormones) are released into the blood.
Exocrine secretions such as the mucus shown here, are secreted outside the body.
The secretions of endocrine cells (hormones) are released into the blood.
40
New cards
Connective tissue cells
Extensive matrix with varied matrix and cartilage has no blood supply.
Mobile cells
* Blood cells (red & white)
Fixed
* Macrophages
* Adipocytes
* Fibroblasts
Mobile cells
* Blood cells (red & white)
Fixed
* Macrophages
* Adipocytes
* Fibroblasts
41
New cards
Connective tissue matrix
Ground substance
* Mineralized (bone)
* Gelatinous/Syrupy
* Loose connective tissue
* Dense connective tissue
* Cartilage
* Adipose tissue
* Watery (blood plasma)
* Protein Fibers
* Fibronectin (connects cells to matrix)
* Fibrillin (forms filaments and sheets)
* Elastin (stretch and recoil)
* Collagen (stiff but flexible)
* Mineralized (bone)
* Gelatinous/Syrupy
* Loose connective tissue
* Dense connective tissue
* Cartilage
* Adipose tissue
* Watery (blood plasma)
* Protein Fibers
* Fibronectin (connects cells to matrix)
* Fibrillin (forms filaments and sheets)
* Elastin (stretch and recoil)
* Collagen (stiff but flexible)
42
New cards
Loose connective tissues
Elastic tissues under skin.
Ground substance is the ECM.
Tissue that is very flexible with multiple cell types and fibers.
Ground substance is the ECM.
Tissue that is very flexible with multiple cell types and fibers.
43
New cards
Dense connective tissues
Tendons (connect skeletal muscles to bone)
Ligaments (connect bones to bones)
Collagen fibers of tendon are densely packed into parallel bundles.
Ligaments (connect bones to bones)
Collagen fibers of tendon are densely packed into parallel bundles.
44
New cards
Supporting connective tissues
* Cartilage
* Solid & flexible
* Lacks blood supply
* Nose, ears, knee, windpipe/trachea
* Bone
* Calcified
* Strong & rigid
Hard bone forms when osteoblasts deposit calcium phosphate crystals in the matrix. Cartilage has firm but flexible matrix secreted by cells called chondrocytes.
* Solid & flexible
* Lacks blood supply
* Nose, ears, knee, windpipe/trachea
* Bone
* Calcified
* Strong & rigid
Hard bone forms when osteoblasts deposit calcium phosphate crystals in the matrix. Cartilage has firm but flexible matrix secreted by cells called chondrocytes.
45
New cards
Additional connective tissues
* Adipocytes
* Adipose connective tissue
* White (single liquid droplet)
* Brown (white liquid droplets)
* Blood
* Plasma matrix
* Free blood cells
In white fat, the cell cytoplasm is almost entirely filled with liquid droplets.
Blood consists of liquid matrix plus red and white blood cells and the cell fragments called platelets.
* Adipose connective tissue
* White (single liquid droplet)
* Brown (white liquid droplets)
* Blood
* Plasma matrix
* Free blood cells
In white fat, the cell cytoplasm is almost entirely filled with liquid droplets.
Blood consists of liquid matrix plus red and white blood cells and the cell fragments called platelets.
46
New cards
Muscle tissues
Excitable and contractile (force and movement)
Minimal matrix with external lamina that can generate electrical signals, force, and movement.
There are three types:
* Cardiac
* Smooth
* Skeletal
Minimal matrix with external lamina that can generate electrical signals, force, and movement.
There are three types:
* Cardiac
* Smooth
* Skeletal
47
New cards
Nervous tissues
Neurons (nerve cells) that send signals & are excitable.
Glial cells (neuroglia) support.
Minimal matrix with external lamina that can generate electrical signals.
Glial cells (neuroglia) support.
Minimal matrix with external lamina that can generate electrical signals.
48
New cards
Tissue remodeling includes
* Cell death
* Necrosis (death from injury)
* Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
* Stem cells
* Totipotent
* Pluripotent
* Multipotent
* Necrosis (death from injury)
* Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
* Stem cells
* Totipotent
* Pluripotent
* Multipotent
49
New cards
Organs
Groups of tissues with related function i.e. skin
50
New cards
Properties of living organisms
1. Have a complex structure whose basic unit of organization is the cell
2. Acquire, transform, store, and use energy
3. Sense and respond to internal and external environments
4. Maintain homeostasis through internal control systems with feedback
5. Store, use, and transmit information
6. Reproduce, develop, grow, and die
7. Have emergent properties that cannot be predicted from the simple sum of the parts
8. Individuals adapt and species evolve
51
New cards
Work
Chemical work - the making and breaking of chemical bonds
Transport work - moving ions, molecules, and larger particles.
* Useful for creating concentration gradients
Mechanical work - moving organelles, changing cell shape, beating flagella and cilia
* Contracting muscles
Transport work - moving ions, molecules, and larger particles.
* Useful for creating concentration gradients
Mechanical work - moving organelles, changing cell shape, beating flagella and cilia
* Contracting muscles
52
New cards
Energy
Kinetic energy
* Energy of motion
* Work involves movement
Potential energy
* Stored energy
* In concentration gradients and chemical bonds
* Must be converted to kinetic energy to perform work
* Transformation efficiency
* Energy of motion
* Work involves movement
Potential energy
* Stored energy
* In concentration gradients and chemical bonds
* Must be converted to kinetic energy to perform work
* Transformation efficiency
53
New cards
1st law of thermo
Total amount of energy in the universe is constant.
54
New cards
2nd law of thermo
Processes move from state of order to randomness or disorder (entropy).
55
New cards
Reactants and products of combination reactions
A+B → C
56
New cards
Reactants and products of decombination reactions
C → A+B
57
New cards
Reactants and products of single displacement reactions
L + MX → LX + M where X represents atoms, ions, or chemical groups.
58
New cards
Reactants and products of double displacement reactions
LX + MY → LY + MX where X and Y represents atoms, ions, or chemical groups.
59
New cards
Activation energy
The “push” needed to start a reaction
60
New cards
Exergonic reaction
Release energy because the products have less energy than the reactants.
61
New cards
Endergonic reaction
Trap some activation energy in the products, which then have more free energy than the reactants.
62
New cards
Enzymes
Speed up the rate of chemical reactions
* Catalysts
* Reactants (substrates)
Can be activated, inactivated, or modulated
* Catalysts
* Reactants (substrates)
Can be activated, inactivated, or modulated
63
New cards
Isozymes
Catalyze same reaction, but under different conditions. Diagnostic enzymes
64
New cards
Oxidation-reduction reaction
Add or subtract electrons.
* Transfer electrons from donor to oxygen
* Remove electrons and H+
* Gain electrons
* Transfer electrons from donor to oxygen
* Remove electrons and H+
* Gain electrons
65
New cards
Hydrolysis-dehydration reaction
Add or subtract a water molecule
* Split large molecules by adding water
* Remove water to make one large molecule from several smaller ones
* Split large molecules by adding water
* Remove water to make one large molecule from several smaller ones
66
New cards
Addition-subtraction-exchange reaction
Exchange groups between molecules
Add or subtract groups
Add or subtract groups
67
New cards
Ligation reaction
Join two substrates using energy from ATP
68
New cards
Metabolism
All chemical reactions that take place in an organism.
69
New cards
Metabolism regulation
1. Controlling enzyme concentrations
2. Producing modulators that change reaction rates
1. Feedback inhibition
3. Using different enzymes to catalyze reversible reactions
4. Compartmentalizing enzymes within organelles
5. Maintaining optimum ratio of ATP to ADP
70
New cards
Reversible reactions
Reversible reactions are chemical reactions that can proceed in both forward and reverse directions. They involve the conversion of reactants into products and the conversion of products back into reactants. The reaction can reach a state of equilibrium where the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. This allows for the possibility of the reaction to be reversed under certain conditions.
71
New cards
Irreversible reactions
Lack the enzyme for reverse direction.
72
New cards
Catabolic pathways that produce ATP
1. Glycolysis
2. Citric acid cycle
3. Electron transport chain
73
New cards
Anaerobic metabolism
0 NADPH and 2 ATP
74
New cards
Aerobic metabolism
6 H2O, 30-32 ATP, and 6 CO2
75
New cards
Codons in genetic code
64
76
New cards
Protein synthesis
Converts genetic code of DNA into a functional protein.
1. Gene activation
2. Transcription
3. mRNA processing
4. Translation
5. Post-translational modification
1. Gene activation
2. Transcription
3. mRNA processing
4. Translation
5. Post-translational modification
77
New cards
Transcription
1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA
2. The section of DNA that contains the gene unwinds
3. RNA bases bind to DNA, creating a single strand of mRNA
4. mRNA and the RNA polymerase detach from DNA, and the mRNA goes to the cytosol after processing.
78
New cards
Translation
1. Transcription
2. mRNA processing - processed mRNA leaves nucleus and associates with ribosomes
3. Attachment of ribosomal subunits
4. Translation - Each tRNA molecule attaches at one end to a specific amino acid. Anticodon of tRNA molecule pairs with appropriate codon on the mRNA, allowing amino acids to be linked in the order specified by mRNA code.
5. Termination
79
New cards
Translation components
* mRNA, rRNAs, and tRNAs
* Ribosomes and amino acids
* Ribosomes and amino acids
80
New cards
What are the post-translation modifications that proteins may undergo?
1. Protein folding
2. Cross-linkage
3. Cleavage
4. Addition of other molecules or groups
5. Assembly into polymeric proteins
81
New cards
Intracellular fluid
2/3 of the total body water volume
82
New cards
Extracellular fluid
is 1/3 of the total body water volume and consists of the interstitial fluid and blood plasma.
83
New cards
Osmosis
Movement of water across a membrane in response to a solute concentration gradient
84
New cards
Aquaporins
Transport water across cell membranes in response to osmotic gradients.
85
New cards
Osmolarity
Expresses number of particles
86
New cards
Molarity
Expresses concentration
87
New cards
Hypotonic
Higher concentration of non-penetrating molecules than net movement of water into cell
88
New cards
Hypertonic
Lower concentration of non-penetrating molecules than net movement of water into cell
89
New cards
Isotonic
Equal concentration of non-penetrating molecules and net movement of water into cell
90
New cards
Tonicity
Refers to the relative concentration of solutes in two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane
91
New cards
Rules for osmolarity and tonicity
1. Assume all intracellular solutes are non-penetrating
2. Compare osmolarities before cell is exposed to the solution
3. Tonicity of a solution describes the volume change of a cell at equilibrium
4. Determine tonicity by comparing non-penetrating solute concentrations in the cell and the solution. Net water movement is into the compartment with the higher concentration of non-penetrating solutes.
5. Hyposmotic solutions are always hypotonic
92
New cards
Bulk flow
Fluids are gases and liquids
* pressure gradients
* pressure gradients
93
New cards
Methods of passive transport
* Simple diffusion (concentration gradient)
* Protein-mediated
* Facilitated diffusion (concentration gradient)
* Ion channel (electrochemical gradient)
* Aquaporin channel (osmosis)
* Protein-mediated
* Facilitated diffusion (concentration gradient)
* Ion channel (electrochemical gradient)
* Aquaporin channel (osmosis)
94
New cards
Methods of active transport
* Vesicular transport (ATP)
* Exocytosis
* Endocytosis
* Phagocytosis
* Protein-mediated
* Direct or primary active transport (ATPases)
* Indirect or secondary active transport (concentration gradient created by ATP)
* Exocytosis
* Endocytosis
* Phagocytosis
* Protein-mediated
* Direct or primary active transport (ATPases)
* Indirect or secondary active transport (concentration gradient created by ATP)
95
New cards
Rules for Diffusion
General Properties of Diffusion
1. Diffusion uses kinetic energy of molecular movement -- does not require external source
2. Molecules diffuse from areas of high concentration to low concentration
3. Diffusion continues until concentrations reach equilibrium
4. Diffusion is faster if:
1. higher concentration gradients
2. over shorter distances
3. at higher temperatures
4. for smaller molecules
5. Can take place in an open system or across a partition that separates to systems
Simple Diffusion across a membrane
6. Rate of diffusion faster if:
1. Membrane’s SA is longer
2. Membrane is thinner
3. Concentration gradient is larger
4. Membrane is more permeable to molecule
7. Membrane permeability to a molecule depends on
1. Molecule’s lipid solubility
2. Molecule’s size
3. Lipid composition of membrane
1. Diffusion uses kinetic energy of molecular movement -- does not require external source
2. Molecules diffuse from areas of high concentration to low concentration
3. Diffusion continues until concentrations reach equilibrium
4. Diffusion is faster if:
1. higher concentration gradients
2. over shorter distances
3. at higher temperatures
4. for smaller molecules
5. Can take place in an open system or across a partition that separates to systems
Simple Diffusion across a membrane
6. Rate of diffusion faster if:
1. Membrane’s SA is longer
2. Membrane is thinner
3. Concentration gradient is larger
4. Membrane is more permeable to molecule
7. Membrane permeability to a molecule depends on
1. Molecule’s lipid solubility
2. Molecule’s size
3. Lipid composition of membrane
96
New cards
Functions of membrane proteins
Structural proteins
* Create & maintain cell-junctions
* Maintain cell shape
* Attach cells to ECM
Enzymes
* Catalyze reactions outside of membrane
* Membrane receptor proteins
Transporters
* Channel proteins - water-filled tubes
* Form open & gated channels
* Carrier proteins - bind substrate. NO tubes.
* Change confirmation
* Create & maintain cell-junctions
* Maintain cell shape
* Attach cells to ECM
Enzymes
* Catalyze reactions outside of membrane
* Membrane receptor proteins
Transporters
* Channel proteins - water-filled tubes
* Form open & gated channels
* Carrier proteins - bind substrate. NO tubes.
* Change confirmation
97
New cards
What are the types of channels
1. Water channels
2. Ion channels
3. Open channels
4. Gated channels
1. Chemically gated chemicals
2. Voltage-gated channels
3. Mechanically gated channels
98
New cards
What are the types of carrier-mediated transport & how many molecules do they transport?
Uniport - 1 kind of substrate
Symport - 2 or more substrates in **same** direction across membrane
Antiport - move substrates in opposite directions
Symport - 2 or more substrates in **same** direction across membrane
Antiport - move substrates in opposite directions
99
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Uses carrier proteins
* No energy input
* Down concentration gradient
* Conformational change
\
* No energy input
* Down concentration gradient
* Conformational change
\
100
New cards
Active transport
Uses carrier proteins
* Energy input, against concentration gradient
* Competition vs saturation
* Energy input, against concentration gradient
* Competition vs saturation