HS1 - Adrenal Medulla
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L42/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Adrenal medulla
Part of the autonomic nervous system
Specialized ganglia supplied by sympathetic preganglionic neurones (ACh as a transmitter)
Synthesises catecholamines
Main site for adrenaline synthesis
Not essential for life
Deepest part of adrenal gland
What do adrenal medulla cells release
Adrenaline and noradrenaline
!!! Cateocholiamine synthesis
Noradrenaline is synthesises in 3 steps from tyrosine
!!! What happens to catecholamines after synthesis
Transported into syaptic vesicles using a specialised transporter (vesicular monoamine transporter)
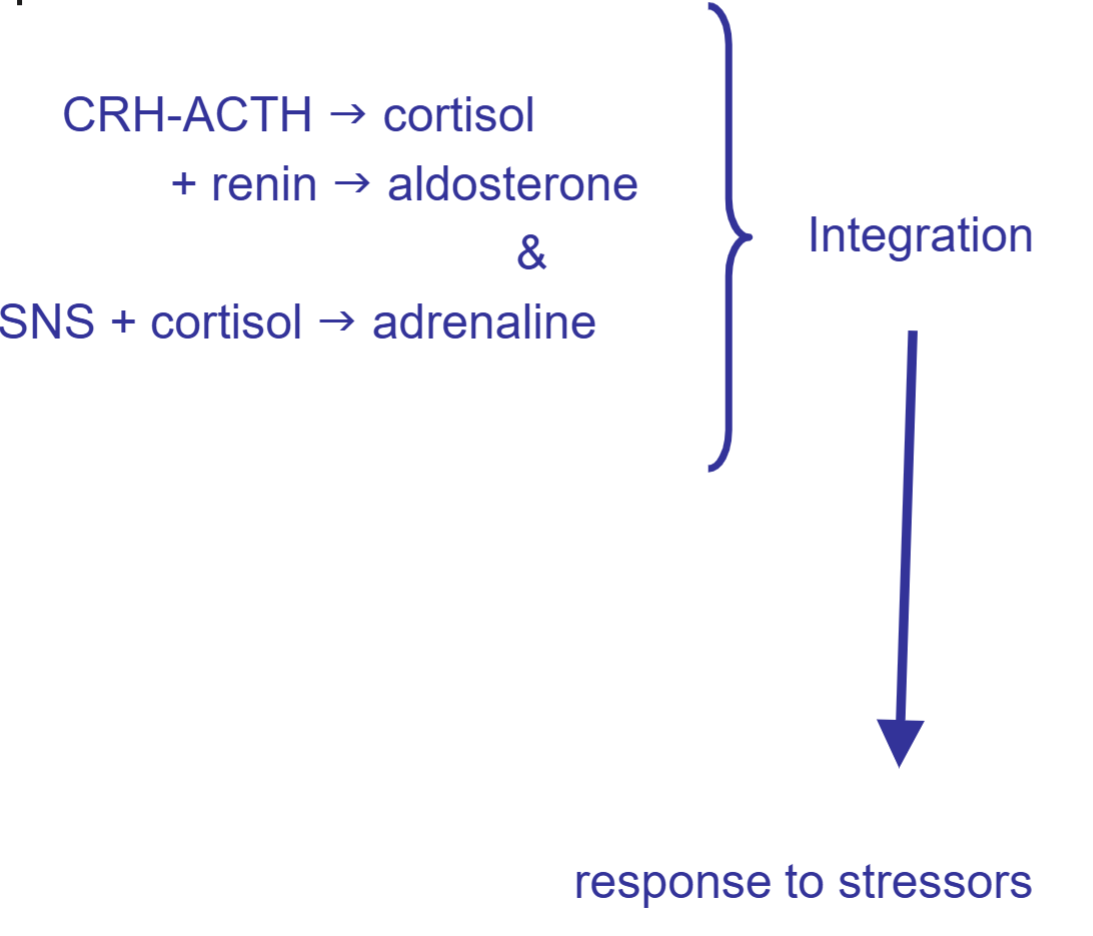
!!! Regulation of catecholamine release
Cortisol can supplement (not replace) SNS activation to help increase adrenaline secretion
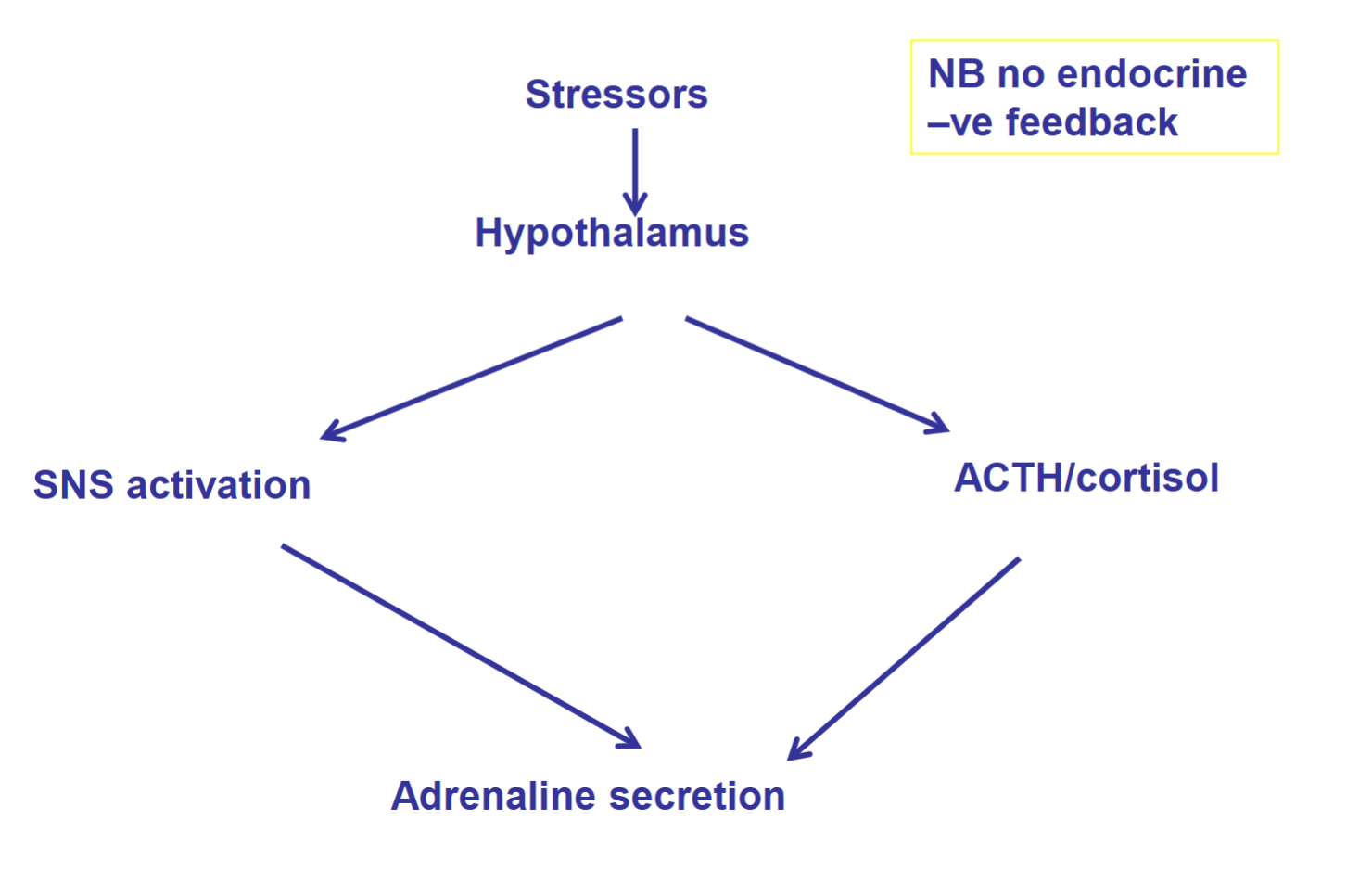
If adrenaline has no -ve feedback, how is it reduced
Breakdown of adrenaline in liver and kidneys
Uptake into nerve terminals
!!! systemic effects of adrenaline
Why do we need adrenaline in addition to SNS [check what SNS is] innervation
Phaeochromocytoma
Excess catecholamines
Tumour of chromaffin cells
Causes over secretion
OR
Dramatic episodes
Sudden stressor (exercise, rapid posture change)
How is phaeochromocytoma diagnosed
Adrealine is too short-lived to measure directly, so urine is measured for its metabolites (such as VMA)
OR
Scan adrenals using MIBG (iodinated tracer which
mimics noradrenaline and is concentrated into
adrenal medulla cells)
How is phaeochromocytoma treated
Surgery (removal of tumour)
Catecholamine crisis risk must be managed
First, alpha blocker prevents vasoconstriction
Second, beta blocker minimises cardiac stimulation
Order is important to prevent hypertensive crisis due to inhibition of beta mediated vasodilation
If surgery is not an option, then hypertensive drugs may help
Hypofunction of adrenal medulla
Medulla is no necessary, so no clinical problems who gaf
Adrenal glands summary